| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2125783
![]()
METHOD OF GROWING POTATOES AND DEVICE FOR ITS IMPLEMENTATION
Name of the inventor: Vladimir Klimenko (BY)
The name of the patentee: Vladimir Klimenko (BY)
Address for correspondence: 246001 Gomel, Plekhanova 41-51, Klimenko VI
Starting date of the patent: 1997.08.05
The invention allows for at hilling sprinkling soil on tubers of the same height in the adjacent ridges, improve soil structure, increase the yield of potatoes with the number of tubers and the improvement of their quality and reduce the debris field of weeds. During hilling in pre-emergence period of the underground part of the plant is oriented on the crest of the center with respect to its vertical axis of symmetry from the sidewalls of the ridge of equal value, oppositely directed and dynamic effects on plants in an arcuate path from the bottom of the plant to the top of the forces created by the rotating clutch with the ground and arranged symmetrically with respect to the vertical axis of symmetry of the ridge dumps Hillers, countertops past in the form of discs - with earthing devices ryhlyaschimi elements and the angle of attack adjustment mechanism drives - earthing devices installed within 2 o 85 depending on the distance between the horizontal axes of the adjacent ridges. When exposed to the roots and shoots of plants stems forces last create a stressful situation. Immediately after surgery ridging soil produce separation at the top of the ridge. At the same time rotating by engagement with the soil separation element drums act on moving forward with the slowing soil and change the direction of the projection onto the horizontal symmetry of the ridge axis vectors of the linear soil particles speed, moving at the top of the ridge on the opposite of the controlled reduction of soil elevation above the tuber to 0, 01-0,5 m for each unit passage. During ridging prior separation of soil on top of the ridge 2, in each pass is provided Hillers increasing height above the soil in the ridge tubers at least 0,02-0,51 m depending on the width of the aisles.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to agriculture, namely, to methods and apparatus for growing crops including potatoes.
There is a method of growing potatoes [1], which consists of planting tubers care by planting row cultivation carried out by layering loosening each aisle three-tiered Hillers first in the middle at a depth of 8-9 cm, and then -. With 2 sides from the first hiller trace to a depth of 17-18 cm. to form a protective zone of planted with tubers of a number equal to 15-16 cm, and again at the middle 8-9 cm depth, with at Hillers cultivator arranged in three rows with the distance between the first and second rows 40-45 cm.
The disadvantage of this method of growing potatoes is its complexity due to the presence of the four operations to implement it and hoeing between rows on the middle, hoeing between rows on both sides of the first track hiller, re-loosening in the middle aisle, the alignment of the soil ridge tops. The disadvantage of this method is the fact that for its implementation uses the device with passive working bodies (Hillers with blade and harrow), which does not allow high quality milled and ground vspushivat when moving it from the aisle to the ridge.
A device [2] relating to the working organs for soil and consists of a disc with teeth. Each tooth has a plate spring. The front edge of the tooth is formed as a wedge, and the back has a groove, and the spring, its end is rigidly secured to the upper portion of the rear edge of the tooth, and the other - housed freely in a slot.
The disadvantage of the working body of the rotary tillage tools is the complexity of its construction and fragility due to the presence of additional springs, installed in front of the ryhlyaschimi tooth.
The closest to the proposed invention is a method of care for planting potatoes and device for its implementation, as described in [3]. The method includes the steps of: loosening the ridge peaks, ridges ridging, loosening the sides and top of the ridge forming the profile of the ridge. An apparatus for carrying out this method consists of Hillers and arranged for each of them on the horizontal axis conical drums of tooth and on the longitudinal axis of symmetry of the device located between adjacent Hillers Toothed additional drums, one drum placed in front Hillers and another - for the conical drums.
The disadvantages of this method and device for its implementation are as follows. When hilling using progressively moving Hillers with dumps, the soil of the aisles of the ridge moves in the form of large lumps during grinding that by putting pressure on them, conical and special form rollers with teeth (drums) there is soil compaction on the side of the ridge and its summit, which contributes rapid formation on them compacted soil crust that prevents aeration of the soil in the ridge and therefore the livelihoods of plants. In fact, the destruction of lumps and soil crust on the sidewalls of the ridge and its top is made by rolling the soil with the help of cylindrical, conical and special form rollers with teeth.
Due to the pressure surface of the cylindrical elements and specially shaped rollers to the top of the ridge, they damage the vegetative potato plants.
The presence of four to four and a method apparatus for functional elements of this method complicates the process and apparatus in deterioration of soil aeration and, as a result, reduction of potato yield and quality.
The aim of the invention is to provide at hilling sprinkling soil on tubers of the same height in the adjacent ridges, improve soil structure, increase potato yields with the number of tubers and the improvement of their quality, but also a decrease in the debris field of weeds.
The goal is achieved by a method of growing potatoes, which includes planting tubers care of plantings by row cultivation with ripping, hilling and the formation of ridges in the pre-emergence and post-emergence in the course of operation hilling in pre-emergence period, the underground parts of plants create a stressful situation, focusing its on the crest of the center, by exposing the roots and shoots of stems of the plant, from the ridge sidewalls, equal in magnitude, oppositely directed and dynamic effects on plants in an arcuate path from their bottom to top, the forces created by the rotating clutch with soil and placed symmetrically relative to the vertical axis of the ridge dumps Hillers, work surfaces which are designed as disc-earthing devices, with a special adjusting the angle of attack drives, earthing devices, directly after surgery hilling with the spraying of ground soil to the top of the ridges rotating dumps Hillers, during which the projection on the horizontal symmetry of the ridge axis the linear velocity vector of each particle sprinkles soil directed forward, produce soil separation at the top of the ridge to the impact of the separation elements rotating by engagement with the soil drums on moving forward with the slowing soil and as a result of a change in the direction of projections of linear soil particles speed, moving at the top of the ridge on the contrary, a controlled reduction in the height of the soil layer to tubers 0.01-0.5 m for each passage device for growing potatoes and separating the weeds from the soil, and during operation ridging prior separation of soil on top of the ridge, for each Hillers passage provide increased soil height on potato tubers in the crest of at least 0.02 - 0.51 m depending on the width of the aisles.
The target device for the cultivation of potatoes containing Hillers with bow and dumps, is achieved by the nose of the Hillers made as scheleobrazovateley, installed on the front bar unit, the rear tool bar device rigidly fixed blades, made in the form of rotating from the engagement with soil discs earthing devices and the ability to adjust the angle of attack of the latter, the front timber device connected to the back bar with the spring-hinge joints and flexible stabilizers, each of the spring-hinge joints is in the form of a spring mechanism mounted pivotally between the lower two-hinged frame and the upper screw mechanism , the front part of the spring mechanism pivotally connected with a removable bracket front bar, the back part is connected to the bracket, which is fixed rear removable device timber, each of the flexible stabilizers installed under the spring-hinge joint and connects the detachable bracket of the front beam and the lower part of the rear beam, and the beam back to the device through the upper and lower rigid flexible rods are pivotally connected to the separation device at the top of the soil ridge formed as a ribbed drums arranged on a horizontal axis defined on the edges of the drums of the separation elements. The angle of attack of rotating disks installed earthing devices, ranging from 2 to 85 o depending on the distance between the horizontal axes of adjacent crests. Ribs drums ryhlyaschimi elements of devices for separating the soil are arranged parallel to the axes of the reels and the separating elements on the edges of the ribbed drums can be in the form of teeth of a circular, rectangular or other cross-section with the angle of installation in relation to the perpendicular of the drum ribs at its upper point of from 0 to 180 o.
 |
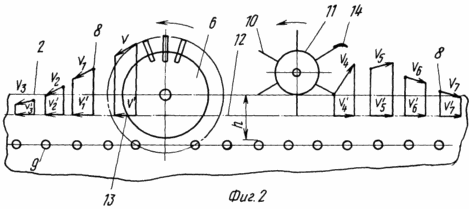 |
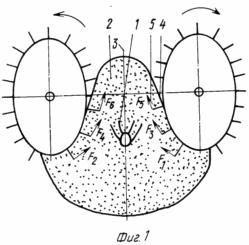
FIG. 1 shows a diagram of the impact in the pre-emergence period of the underground part of the plant forces generated by rotating disks; FIG. 2 - scheme of changing the direction of the projections on the horizontal axis of symmetry of the ridge vectors of linear velocities of the particles of the soil at the top of the ridge.
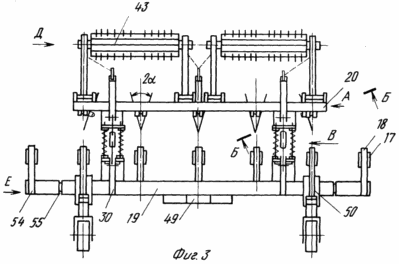
FIG. 3 - horizontal projection of the device for implementing the method.
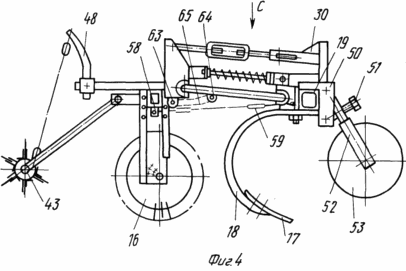
FIG. 4 - front view of the device.
 |
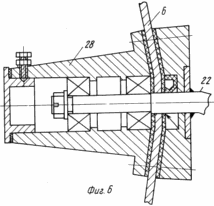 |
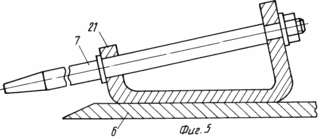
FIG. 5 - option ryhlyaschimi removable disk element-earthing devices; FIG. 6 - section B-B in FIG. 3, with the image-bearing assembly earthing devices disk.
 |
 |
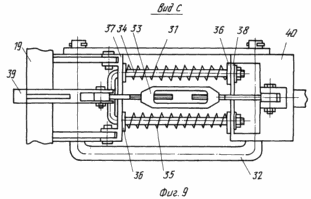 |
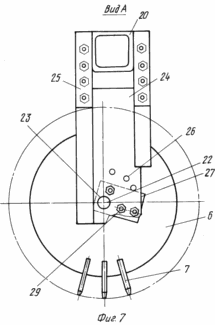
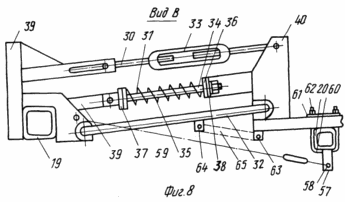
FIG. 7 - view A in FIG. 3, with the rear beam with an image fixed on it a disk-node earthing devices; FIG. 8 - view B in FIG. 3 depicting the spring-hinged assembly of flexible stabilizer; FIG. 9 - form C in Fig. 4, depicting the spring-joint assembly.
 |
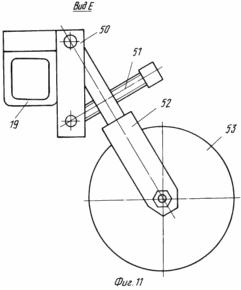 |
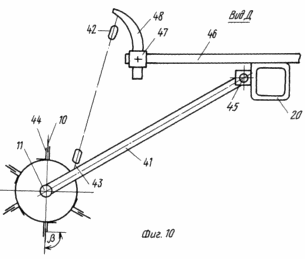
FIG. 10 - view D in Fig. 3 depicting the separation device for the soil in the upper part of the ridge; FIG. 11 - form E in FIG. 3 depicting wheel assembly support device.
Potato cultivation method includes known operations - planting the tubers and care by planting row cultivation with loosening, ridging and hilling. The distinctive steps of the method are as follows. During hilling in pre-emergence period of the underground part of the plant 1 potato (Fig. 1) is oriented on the crest of the center 2 about its vertical axis of symmetry 3 from the sidewalls 4 comb 2 equal in value, oppositely directed and dynamic effects on plants 1 in an arcuate path from the bottom parts of the plants 1 and the upper force 5 created by rotating by engagement with the soil and arranged symmetrically relative to the vertical axis of symmetry 3 crest two piles 16 Hillers working surfaces which are designed as disc-earthing devices 6 ryhlyaschimi elements 7 on their terminals, with a special adjustment of the angle attack ![]() Disc-earthing devices 6, which is set in the range of 2 to 85 o depending on the distance between the horizontal axes of the adjacent ridges. When this force 5 generated by rotating by engagement with the soil disc-zagortochami 6 act on the soil on the sidewalls 4 crest 2, shift it to the top of the ridge 2 at a tangent to the trajectory of rotation ryhlyaschimi elements 7 and, in the process of soil displacement orient the underground part of the plant 1 on the crest of the center 2 about its vertical axis of symmetry 3. When exposed to the roots and shoots of the plant stalks 1 5 forces, the latter creates a stressful situation. Immediately after surgery hilling with the spraying particles 8 (FIG. 2) of ground soil to the top of the ridges 2 rotating dumps 16 Hillers produce separation of soil on top of the ridge between the summit ridge 2 and the upper surface of the mother tuber potatoes 9. This rotating clutch with the soil separation element 10 of drums 11 act on moving forward with the slowing soil and change the direction of the projection onto the horizontal axis of symmetry of the ridge 12 2 vectors of the linear velocity of the particles of soil 8, moving the top of the ridge 2, - on the contrary. Slow movement of soil, sprinkles on top of the ridge 2 rotating dumps Hillers 16, is carried out by gravity forces acting on each particle of soil 8, and the friction between the soil particles in the layer 8, 2 sprinkles on top of the ridge. This slow movement of soil is due to the fact that each particle 8 has its mass, kinetic energy and velocity. The projection 13 of vector linear velocity slow motion of each particle 8 soil after exposure to dumps 16 directed forward, due to exposure to the particles 8 soil separation elements 10 of rotating drum 11, they alter their direction of movement is reversed and thus change the projection 13 vector of linear velocity of a particle of soil, the soil is moving back and sides, vspushivaetsya, ridge height decreases. Controlled reduction of the height of soil above the tuber 19 with the separation in the process of separating the weeds from the soil 14 produce from the soil layer above the height of tubers 9 within the 0.51 - 0.002 m and a height of 0.5 - 0.001 m depending on the width of the aisles. For example, if the width of the aisles in the 0.7 meter height h of the layer of soil over the tubers can be reduced from 0.3 meters to 0.05 meters. Soil Separation with fluffing latter and separating the weed 14 from particles 8 soil becomes possible due to the fact that the separating elements 10 on each edge of the rotating drum 11 are arranged on one line in the form of a comb, enter the soil and sieved its separating from the particles 8 soil weeds 14 having large linear dimensions in comparison with the soil particles 6.
Disc-earthing devices 6, which is set in the range of 2 to 85 o depending on the distance between the horizontal axes of the adjacent ridges. When this force 5 generated by rotating by engagement with the soil disc-zagortochami 6 act on the soil on the sidewalls 4 crest 2, shift it to the top of the ridge 2 at a tangent to the trajectory of rotation ryhlyaschimi elements 7 and, in the process of soil displacement orient the underground part of the plant 1 on the crest of the center 2 about its vertical axis of symmetry 3. When exposed to the roots and shoots of the plant stalks 1 5 forces, the latter creates a stressful situation. Immediately after surgery hilling with the spraying particles 8 (FIG. 2) of ground soil to the top of the ridges 2 rotating dumps 16 Hillers produce separation of soil on top of the ridge between the summit ridge 2 and the upper surface of the mother tuber potatoes 9. This rotating clutch with the soil separation element 10 of drums 11 act on moving forward with the slowing soil and change the direction of the projection onto the horizontal axis of symmetry of the ridge 12 2 vectors of the linear velocity of the particles of soil 8, moving the top of the ridge 2, - on the contrary. Slow movement of soil, sprinkles on top of the ridge 2 rotating dumps Hillers 16, is carried out by gravity forces acting on each particle of soil 8, and the friction between the soil particles in the layer 8, 2 sprinkles on top of the ridge. This slow movement of soil is due to the fact that each particle 8 has its mass, kinetic energy and velocity. The projection 13 of vector linear velocity slow motion of each particle 8 soil after exposure to dumps 16 directed forward, due to exposure to the particles 8 soil separation elements 10 of rotating drum 11, they alter their direction of movement is reversed and thus change the projection 13 vector of linear velocity of a particle of soil, the soil is moving back and sides, vspushivaetsya, ridge height decreases. Controlled reduction of the height of soil above the tuber 19 with the separation in the process of separating the weeds from the soil 14 produce from the soil layer above the height of tubers 9 within the 0.51 - 0.002 m and a height of 0.5 - 0.001 m depending on the width of the aisles. For example, if the width of the aisles in the 0.7 meter height h of the layer of soil over the tubers can be reduced from 0.3 meters to 0.05 meters. Soil Separation with fluffing latter and separating the weed 14 from particles 8 soil becomes possible due to the fact that the separating elements 10 on each edge of the rotating drum 11 are arranged on one line in the form of a comb, enter the soil and sieved its separating from the particles 8 soil weeds 14 having large linear dimensions in comparison with the soil particles 6.
At the orientation of the underground parts of plants 1 potatoes with soil displacement on the side of 4 comb 2 up to the top of the ridge 2 ryhlyaschimi elements 7 disk-earthing devices 6 and the displacement of soil on top of the ridge 2 back and sides under the effect of the separation elements 10 drum 11 in the process soil separation alternating oscillations transmitted soil underground parts of plants, including roots and developing. Those. plant creates a stressful situation. Tests have shown that plants, including their protective biological mechanisms that react to a stressful situation increases the number of stolons to form tubers on them and more powerful the rapid development of the root system, and further leaves and tubers.
A device for growing potatoes consists of Hillers with noses 15 (FIG. 3, 4), rotating dumps 16, representing the assembly. Nasal part 15 in the form of Hillers scheleobrazovateley. The working body is arcuate scheleobrazovatelya bezotvalnoj sock 17 (FIG. 4) fixed by means of bolting on a rigid arcuate rack 18. The arcuate rack 18 is fixed by means of detachable connections, for example, on the front threaded tool bar 19. On the rear tool bar 20 fitted with device using a rigid attachment blades 16, the working surfaces of which are wheels-earthing devices 6 to 7 ryhlyaschimi elements on their periphery. Ryhlyaschimi elements 7 can be executed and installed in a detachable special holders 21 (FIG. 5) rigidly fixed on the perimeter of disc-earthing devices 6. The right and left wheels, earthing devices 6 mounted rotatably on a curved axis 22. In this case, the horizontal axis of symmetry of each of Hillers It passes through the horizontal axis of symmetry scheleobrazovatelya, but also the right and left disk-earthing devices. Curved axle 22 rotatably mounted in the hole 23 in the adjustments of the plate 24. The plate 24 is mounted on uprights 25, in turn, mounted on the rear tool bar 20 of the device. Plate 24 has an adjusting hole 26 arranged in an arc relative to the opening 23. With the adjustment holes 26, and bolting the plate 24 fastens bracket 27 rigidly mounted on a curved axis 22. In each of the endings of the bent axis 22 is mounted a bearing assembly 28 (FIG. 6), the bearing housing assembly 28 is secured by means of detachable screw connections to the wheel plates 6. earthing devices 24 installed at the rear bar 20 of the device terminals, one set-earthing devices disk 6. from the above it can be seen that each blade 16 is the assembly consisting of disc-earthing devices 6, and the bent axis 22 of the bearing assembly 28. Due to the bending axis in the central portion 22, and the last turning its locking position adjustment holes 26 of the plate 24, via bolt connections 29 (FIG. 7) set attack angle ![]() .
. ![]() - Is the angle between the plane passing through the end of each disc-zagortocha 6 and horizontal axis of symmetry 2. It ridge 12 is chosen between 2 and 85, depending on the distance between the horizontal axes of symmetry 12, two adjacent ridges.
- Is the angle between the plane passing through the end of each disc-zagortocha 6 and horizontal axis of symmetry 2. It ridge 12 is chosen between 2 and 85, depending on the distance between the horizontal axes of symmetry 12, two adjacent ridges.
The front bar 19 is connected with the rear unit 20 via timbers spring-hinge assemblies 30 (Figs. 8, 9) .Each of the spring-hinge assemblies 30 is a spring mechanism 31 mounted between the lower hinge frame 32 (FIG. 8) and the upper screw mechanism 33. The spring mechanism 31 is an arcuate bar 34 (FIG. 9) with two threaded ends in its right part. Each of two arcuate rods 34 of the rod set by a spring 35. The springs 35 are limited from both sides by special washers 36 and the plates 37, 38. Compression springs 35 by means of nuts mounted on the threaded rod 34. The plate terminals 37 mounted on the left part of the rod 34 is pivotally connected to brackets 39 of the front bar 19 of the device. Plate 38 mounted on the right side of the arcuate shaft 34 is rigidly secured to the bracket 40. Two rear brackets 40 secured timber 20 of the device. With the help of the upper screw mechanism 33 provides fine adjustment of the angle of attack ![]() Disc 6-earthing devices.
Disc 6-earthing devices.
By the beam back device 20 via the lower rigid 41 and upper flexible rods 42 connected device 43 (FIG. 10) for the separation of soil on top of the ridge. Each device 43 consists of a drum 11 fixed on it and arranged parallel axes drums ribs 44. On the ribs 44 attached or formed directly in the body ribs 44 separating elements 10. The separating elements 10 can be in the form of teeth of round, rectangular or other cross section with angle ![]() attitudes perpendicular to the edges of the drum in the upper point of 0 to 180 o. Each rib 44 separating elements 10 is a separating comb. Milled drum 11 is mounted on the lower two terminals 41 of the lower rigid rods 43 fit rotatably. The upper end of the lower rigid rods 41 by means of hinges 45 connected to the rear device 20 timbers. At the top of the rear beam 20 fixed longitudinal rigid rod 46 with sockets 47 at their endings. The longitudinal rods 46 can be an extension of the bracket 40. In this case, the rods 46 set the back bar 20 of the device. The outlets 47 are installed arcuate rack 48 fixed to the top of their flexible rods 42, the lower end of which is fixed at the lower end of the lower rigid rods 41.
attitudes perpendicular to the edges of the drum in the upper point of 0 to 180 o. Each rib 44 separating elements 10 is a separating comb. Milled drum 11 is mounted on the lower two terminals 41 of the lower rigid rods 43 fit rotatably. The upper end of the lower rigid rods 41 by means of hinges 45 connected to the rear device 20 timbers. At the top of the rear beam 20 fixed longitudinal rigid rod 46 with sockets 47 at their endings. The longitudinal rods 46 can be an extension of the bracket 40. In this case, the rods 46 set the back bar 20 of the device. The outlets 47 are installed arcuate rack 48 fixed to the top of their flexible rods 42, the lower end of which is fixed at the lower end of the lower rigid rods 41.
In the central part of the front beam 19 mounted frame 49 connecting the device to the back of the tractor.
By means of brackets 50 (FIG. 11) is pivotally-screw mechanisms 51 and arcuate struts 52, 19 on the front bar unit support wheels 53 are installed.
On the front bar terminals 19 are removable markers 54. Markers 54 are arcuate with subsurface scheleobrazovatel toe 17 and the rack 18 mounted to the front beam 19, for example, via the guide 55 and threaded connections 56.
To prevent the large amplitude oscillations of spring-swivel assembly 30 rear bar 20 of the device 57 via the bracket 58 and the retainer 59 is connected to a flexible stabilizer with bracket 39 of the front bar 19 of the device.
To create by the end of the ridge treatments to form a smooth sine wave in cross section accommodate the height adjustment disk-earthing devices 6 with respect to the bows 15 Hillers. To this end, the clamps 60, washers 61 and nuts 62 are removed, the rear beam 20, mounted under the arm 40, and is removed and installed on the upper part of the bracket 40, attached to the latter by means of clamps 60, washers 61 and nuts 62.
In case of breakage of the rod 34 of the arcuate spring-swivel assembly 31 is provided with a fixing bracket of the last 40, 64 latch the latch 63 two-hinged lower frame 32 and the rigid rods 65, connecting the latches 63 and 64.
The device operates as follows. Each hiller device installed in the center aisle, and the unit (the device and the tractor) is attached to the speed of translation. This sock scheleobrazovatelya 17, which is part of the bow 15 each hiller, loosens the soil in the center aisle, and forms a single pass slit in the soil depth of 0.1 - 0.3 meters. This slot is cut with the help of the right and left stockpiles 16 hiller, work surfaces which are designed as disc-earthing devices 6 ryhlyaschimi elements 7 at their endings. The process of cutting a slit is made in the following way. During the translational movement of the device for potato earthing devices, each disc 6, as a result of coupling with the ground ryhlyaschimi elements 7 mounted on its endings rotates. This ryhlyaschimi elements 7 are included in the soil in the gap area in the center of the aisles formed by progressively moving scheleobrazovatelyami located on the front bar 19 the device for the cultivation of potatoes. During rotation of the right and left disc-earthing devices 6 mounted on the rear tool bar 20 of the device, ryhlyaschimi elements 7 are crushed soil in the zone of the slots across the aisle width and sidewalls 4 ridge 2 and communicating with mikrokomkam crushed soil speed towards the crest 2 and course of movement of the device, throw crushed soil on top of the ridge 2. in inter-row cultivation (hilling) in the pre-emergence period and ryhlyaschimi contacting elements 7 discs earthing devices 6 with the soil on the side of the ridges 4 2 1 underground plant parts, especially roots and shoots, creating a stressful situation by acting on them by the sidewalls 4 ridge 2 are equal in magnitude, opposite in direction, and dynamically acting on the roots and shoots of the stems in an arcuate path from its bottom to top, the forces 5, created by rotating by engagement with the soil and arranged symmetrically relative to the vertical symmetry axis 1 2 3 dumps ridge 16 with the working surface in the form of discs, earthing devices ryhlyaschimi elements 6 and 7 on their periphery. Simultaneously with the creation of a stressful situation when subjected to the underground part of the plant 1 external forces 5 1 plant oriented on the center ridge using the same equal and opposing forces 5. got on the working surface of the rotating disk-earthing devices 6 the soil under the influence of centrifugal force is applied to the ryhlyaschimi elements 7, which is crushed and placed on the comb 2.
The grinding process is intensified due to soil compounds front 19 and rear beam 20 of the device for growing potatoes in a spring-hinge assemblies 30. This spring-hinge joints 30 provide oscillatory rear beam 20 with respect to the front bar 19. At the rear oscillatory transmitted timbers 20 through the rack 25, plate 24, bracket 27, axis 22 and 28 housing units on wheels, earthing devices 6 ryhlyaschimi elements 7. Additional oscillatory ryhlyaschimi elements 7 and the whole disk-earthing devices 6, which are the working surfaces 16 dumps hiller, intensify soil grinding process . Oscillatory through the rear beam 20, lower 41 rigid rod and flexible rod 42 is transmitted to the drum 11 and separating elements 10. Devices 43 for the separation of soil on top of the ridge 2 intensify soil separation process can improve its fluff, ie reduce specific weight of the soil after the separation process, improve soil structure and increase the quality compartment 14 weeds from the soil in the separation process. Directly soil separation process is carried out as follows: in the process of translation devices for potato cultivation, each ribbed drum 11 rotates as a result of its engagement with the soil separation elements 10. In this case, the separation elements 10 made in the form of the separation of the teeth, and representing in aggregate comb comb at entry into the soil and it is slid repeatedly during rotational movement of the toothed edges 44 of the drum 11 is crushed soil at the top of the ridge 2, it is sieved, i.e. soil separated is separated and weeds from the soil 14 in the separation process because soil mikrokomki 8 having significantly smaller dimensions than the weeds 14 freely pass through the separating drum 10, the teeth 44 of ribs 11. Weeds 14 separated from the soil and brought to the surface of the latter. In the upper part of the separation process crest 2 is destroyed to provide height above the soil tubers, for example, first pass device from 0.01 to 0.12 m. After sprouting stems of potato plants above the surface of ridges (height ranging from 0.01 to to 0.1 m, depending on the presence of the soil cover in the top part of the ridge 2, a device 43 for separating the soil in the upper ridge portion 2 is removed from the rear rod 20 and the inter-row potato device processing performed only Hillers, which include rotating blades 16 and nasal portion 15 formed as scheleobrazovateley.
An important advantage of the process of growing potatoes is to provide for the underground part of the plant stress by exposing the roots and shoots of stems outside forces. This forces the plant to fight for survival include their protective biological mechanisms, increasing the number of stolons to form tubers on them, rapidly developing root system, increasing the tops and eventually yield of tubers. Sprinkling with hilling soil on tubers 9 in adjacent crests 2 of the same height to be performed due to fixed to the rear tool bar 20 rotating dumps 16, allows for optimal and equal conditions for the growth and development of plants in adjacent ridges 2, which ultimately improves productivity potato field.
Gradual increase in the height of the soil layer above the tubers in the ridges 9 2 0.2 to 0.51 meters, with the separation of the soil at the top of the ridge 2, improves soil aeration, improve conditions for the development of plants in general, tuber, improve the quality of the latter by stabilizing plant life-support factors, and effectively separate the weeds from the 14 separated soil.
Loose soil condition in the ridge and the bottom of the aisle separating facilitates the work of working bodies, which reduces the number of failures.
The device allows you to cut ridges before planting potatoes and produce inter-row treatments for growing other crops, using soil ridges, for example, maize, fodder beet and sugar and others.
USED BOOKS
1. Author's certificate USSR N 1584781, cl. A 01 B 79/02, 1990.
2. Author's certificate USSR N 1286124, cl. A 01 B 21/08, 1987.
3. Author's certificate USSR N 1500177, cl. A 01 B 79/00.
CLAIM
1. A method of potato production, including planting tubers care by planting row cultivation with ripping, hilling and the formation of ridges in the pre-emergence and post-emergence periods, characterized in that during the operation in the pre-emergence period hilling underground parts of plants create a stressful situation, focusing it on Central ridge by the impact at the roots and shoots of plants stems from the sidewalls of the ridge equal in magnitude, opposite in direction, and dynamically acting on the plants in an arcuate path from its bottom to top of forces generated by rotating by engagement with the soil and arranged symmetrically relative to the vertical comb axis dumps Hillers, work surfaces which are designed as disc-earthing devices, with a special adjusting the angle of attack discs earthing devices directly after surgery hilling with the spraying of ground soil to the top of the ridges rotating dumps Hillers, during which the projection on the horizontal symmetry crest vector of linear velocity of each particle axis, Spreads on the soil ridge, facing forward, make the soil separation at the top of the ridge to the impact of the separation elements rotating by engagement with the soil drums on moving forward with the slowing soil and as a result of a change in the direction of projections of linear soil particles speed, moving at the top of the ridge, on the opposite the controlled reduction of the height of soil layer tubers of 0.01 - 0.5 m for each passage device for growing potatoes and separating the weeds from the soil, and during operation ridging prior separation of soil on top of the ridge, each pass provides Hillers increase soil height on potato tubers in the crest of at least 0.02 - 0.51 m depending on the width of the aisle.
2. The apparatus for growing potatoes, comprising Hillers with noses and dumps, characterized in that the bows Hillers made as scheleobrazovateley are mounted on the front bar device rear tool bar device rigidly fixed blades carried by a rotary coupling with soil discs earthing devices, with the possibility of adjusting the angle of attack of the latter, the front timber device connected to the back bar with the spring-hinge joints and flexible stabilizers, each of the spring-hinge joints is in the form of a spring mechanism mounted between the lower hinge frame and the upper screw mechanism, the front part of the spring mechanism pivotally connected to the bracket of the front bar, the back part of it is connected to the bracket, which is fixed rear removable device timber, each of the flexible stabilizers installed under the spring-hinge joint and connects the detachable bracket of the front beam and the lower part of the rear bar to the rear the beam device using the upper and lower rigid flexible rods are pivotally connected to the separation device at the top of the soil ridge formed as a ribbed drums arranged on a horizontal axis defined on the edges of the drums of the separation elements.
3. Apparatus according to claim 2, characterized in that the angle of attack zagorachey-rotating disks installed within 2 - 85 o depending on the distance between the horizontal axes of adjacent crests.
4. Device according to claim 2, characterized in that the rib elements drums ryhlyaschimi soil separation devices arranged in parallel axes drums and the separating elements on the edges of the ribbed drums can be in the form of teeth of a circular, rectangular or other cross-section with the angle attitudes perpendicular to the edges of the drums in the upper point of the 0 - 180 o.
print version
Publication date 07.03.2007gg





Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.