| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2229204
![]()
METHOD OF GROWING POTATOES
The name of the inventor: Balabanov Petr Romanovich
The name of the patent owner: Balabanov Petr Romanovich
Address for correspondence: 140193, Moscow region., Ramenskiy rn, p / o Strokino, pos. Dubki, 7, ap. 10, PR Balabanov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.04.01
The invention relates to agriculture, in particular to methods for growing seed and food potatoes under various conditions. The method is carried out as follows. In autumn, after 140 cm, ridges are formed and, depending on the condition of the soil and the development of weeds, are cultivated with a cultivator in the aggregate with a tooth ripper. In the spring, the pre-ridges are re-formed to fit the tubers into the aisles into the arid or into the ridges in wet weather and simultaneously loosen the bases of the future ridges. Then they make a one-line landing of a converted potato-sesal with simultaneous application of various fertilizers layer by layer into the specified parts of the future crest. For care of plantings, cultivators are being converted, for example, KRN-4,2. On the frame of the cultivator, after 140 cm, its sections are extended by 40 cm. To these sections, the ripper-hiller is fixed to a depth of 8-9 cm to the end. On both sides of the main sections, additional spring-loaded, self- Second row to a depth of 18 cm with a protective zone 15-16 cm from the center row with tubers. At the end of the sections, rippers of the third row are fastened to a depth of 17-18 cm, and behind them, the soil-dredging with working grab 22 cm to a depth of 24-25 cm, between the sections on the chains, the tooth rippers, adjustable in the prescribed shape and size of the ridge, They did not extract the tubers from the soil, did not injure them, and walked at a depth of 4-6 cm with a width of up to 120 cm. When the cultivator moves, two-tier or three-tier ripper-first-rowers are crumbling the soil, dividing the furrow layer 8-9 cm thick on two tiers. The lower layer 3-4 cm thick after loosening falls to the bottom of the furrow, the upper layer 4-5 cm thick flies to the sides and falls on the wake-located three-tier hillocks of the second row, which pick up this and a new, frontal layer of soil, loosen them , Are cast aside to the center of the formed crest. Part of the soil is returned to the bottom of the furrow formed by the first-rowers in the zone of work of the third-row hillocks, which pick it up, loosen it and cast it onto the ridge into the zone of action of the tooth ripper, which further crumbles the soil, destroys the weeds and forms a crest along the agro-requirements. Subsoilers, installed in the fourth row behind the third row ripper-mowers, additionally loosen row spacing, 10-12 cm at the first pre-treatment and 6-8 cm for all subsequent. The method makes it possible to increase the yield and quality of potatoes, to save resources by creating more favorable conditions for tuber formation by layer-by-layer, four-level shredding of the soil by passive multi-tiered working organs with minimal destruction of its structure, stabilization of the life support factors of plants, 2 times the seeds and all the costs associated with their preparation, storage, unloading, transportation, loading in planters, reducing the consumption of up to 30% of fuel, reducing weed infestation with weeds without the use of herbicides, 100% harvesting by harvesters with good quality.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
(EN) The invention relates to agriculture, in particular to methods of growing seed and food potatoes in various, including. Extreme, conditions.
A method is known for growing seed potatoes with a row spacing of 140 cm - prototype AS of the USSR No. 1584781 A-1, A-0-1, B 79/02, A 01 G 1/100, BI No. 30, 15.08.90. A good way, environmentally cleaner, more economical, but there are significant disadvantages:
1. Incomplete loosening of the soil at the base of the future crest when cutting the ridges through 70 cm.
2. Uneven unaddressed in relation to the roots of potatoes, the introduction of fertilizers, which reduces their use, worsens the ecology and economics of the method.
3. Injury and re-fertilization of plants by brackets-cultivator extensions at care. The installation of operating elements on the bracket-extension, due to the rigidity of the structure and the impossibility of their autonomous adjustment, does not provide a stable normal contact of the working organs with the soil, which does not allow performing agricultural demands, reduces the technological capabilities of the method, in addition, this arrangement of second row rippers facilitates clogging of the cultivator Earth with plant residues, overloads the unit securing the section to the beam of the cultivator, leading to premature wear and breakage.
4. With a distance of 40-45 cm between the rows of looser-hillers in the course of the machine, it is not always possible to loosen the soil well and destroy the weeds.
5. The well-known method (VNIIIKh) of applying, simultaneously with the planting of one type of fertilizer with an insufficient thickness of soil interlayer between tubers and fertilizer (up to 2-3 cm), does not ensure effective assimilation of fertilizers.
As a result, a decrease in the ecological compatibility, yield, quality and profitability of potatoes.
The claimed method differs from the prototype as follows.
1. Preliminary form wide ridges through 140 cm with simultaneous additional deep loosening of the bottom. When germination of weeds, the ridges are re-formed in the aggregate with tooth rippers. The working organs are installed in four rows in four levels with gradual penetration.
2. In the spring, depending on the climatic conditions, the crests are re-formed under the planting of tubers into the furrow or into the ridges and, at the same time, additionally loosen the bottom of the future crest.
3. Instead of a bracket-broadener, additional spring-mounted leashes for mounting the working bodies are installed on both sides of the sections on the frame beam. This provides a more stable, normal contact of the working organs with the soil, improves its loosening and provides for the destruction of weeds, does not damage or overfill the plants of the potato, removes 50% of the load from the section fastening unit to the beam, prolongs the cultivator's use, significantly reduces clogging with plant residues and Soil, increases productivity, saves fuel consumption and, very significantly, significantly less destroys soil structure and, consequently, its fertility.
4. The distance along the aggregate between the rows of working organs is 30-35 cm. This improves the grinding of the soil and the destruction of weeds.
5. With all the care for planting the comb is ramped up in all directions, so that before the emergence of the shoots above the tuber there is 15-20 cm of loose, clean soil.
6. Fertilizers are applied simultaneously with the planting of a potato-replanted potato plant, for example KSM-4-U, and place phosphorus and potash at the level of tubers 5 cm from both sides with two ribbons 10-20 cm wide, and nitrogen ones below them through the soil layer 5-7 cm in the center of the crest with one ribbon, 15-20 cm wide.
As a result, these differences increase the fertilizer use factor, significantly reduce environmental pollution, save resources, increase the commodity and seed quality of tubers, increase the speed of the aggregates, improve the quality of soil preparation, increase the productivity of aggregates and the profitability of potato production.
The aim of the invention is to protect nature, increase the yield and quality of potatoes, and save resources by creating more favorable conditions for tuber formation by layer-by-level four-level soil shredding with passive multi-tiered working organs, with minimal destruction of its structure, stabilization of life support factors, , 5-2 times the seeds and all the costs associated with their preparation, storage, unloading, transportation, loading in planters, reducing the consumption of up to 30% of fuel, reducing soil contamination with weeds without the use of herbicides, 100% harvesting by harvesters with good quality.
The figure shows the layout of longline hillside-rippers and a tooth-ripper on a cultivator when processing plantings.
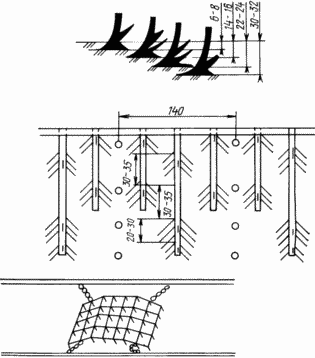 |
The method is carried out as follows. Method of growing potatoes, consisting in the fact that in the fall, loosening is carried out in 4 tiers with the formation of wide furrows and ridges with a distance of 140 cm centers, and loosening is carried out by successively cutting the soil with a distance between tiers in the longitudinally horizontal plane of 6-8 cm , And in the longitudinally vertical plane with the distance between the first. Second and third rows of 30-35 cm, and between the third and fourth 20-30 cm, depending on the condition of the soil and the development of weeds, the formed ridges are cultivated and harrowed, in the spring the ridges are re-formed to plant the tubers in the inter-row to the arid, or into the ridges - In wet weather and simultaneously loosen the bases of the future ridges, the planting of tubers in one row at the base of the ridges is carried out simultaneously with separate and layerwise application of various fertilizers, with phosphorus and potassium fertilizers placed at the level of tubers 5 cm from both sides with a tape 10 cm wide, And the nitrogen ones below them through a layer of soil of 5-7 cm in the center with one ribbon 15-20 cm wide, and the care for planting is carried out by interrow cultivation with a rise in the ridges along the height and width of the crest, similar to loosening of the soil with the formation of furrows and ridges. In autumn, after 140 cm, ridges are formed and, depending on the condition of the soil and the development of weeds, are cultivated with a cultivator in the aggregate with a tooth ripper. In the spring, the pre-ridges are re-formed to fit the tubers into the aisles into the arid or into the ridges in wet weather and simultaneously loosen the bases of the future ridges. Then they make a one-line landing of a converted potato-sesal with simultaneous application of various fertilizers layer by layer into the specified parts of the future crest. |
For care of plantings, cultivators are being converted, for example, KRN-4,2. On the frame of the cultivator, after 140 cm, its sections are extended by 40 cm. To these sections, the ripper-hiller is fixed to a depth of 8-9 cm to the end. On both sides of the main sections, additional spring-loaded, self- Second row to a depth of 18 cm with a protective zone 15-16 cm from the center row with tubers. At the end of the rear of the sections, rippers of the third row are fastened to a depth of 17-18 cm, and after them, the soil-dredging with a working grip of 22 cm to a depth of 24-25 cm, between the sections on the chains, the tooth rippers, adjustable in the shape and size of the ridge, They did not extract the tubers from the soil, did not injure them, and walked at a depth of 4-6 cm with a working width of up to 120 cm.
When moving the cultivator, two-tier or three-tier ripper-first-rowers are crumbling the soil, dividing the furrow layer 8-9 cm thick on two tiers. The lower layer 3-4 cm thick after loosening falls to the bottom of the furrow, the upper layer 4-5 cm thick, flies to the sides and falls on the wake-located three-level hillbugs of the second row, which pick up this and a new, frontal layer of soil, loosen them , Are cast aside to the center of the formed crest. Part of the soil is returned to the bottom of the furrow formed by the first-rowers in the zone of work of the third-row hillocks, which pick it up, loosen it and cast it onto the ridge into the zone of action of the tooth ripper, which further crumbles the soil, destroys the weeds and forms a crest along the agro-requirements. Subsoilers, installed in the fourth row behind the third row ripper-mowers, additionally loosen rows between 10-12 cm for the first pre-treatment and 6-8 cm for all subsequent ones.
CLAIM
Method of growing potatoes, consisting in the fact that in the fall, loosening is carried out in 4 tiers with the formation of wide furrows and ridges with a distance of 140 cm centers, and loosening is carried out by successively cutting the soil with a distance between tiers in the longitudinally horizontal plane of 6-8 cm , And in the longitudinally vertical plane with a distance between the first, second and third rows of 30-35 cm, and between the third and fourth 20-30 cm, depending on the soil state and the development of weeds, the formed ridges are cultivated and harrowed, in spring the ridges are re-formed Under the planting of tubers in the aisle to arid or combs - in wet weather and at the same time loosen the bases of future ridges, planting tubers in one row at the base of the ridges is carried out simultaneously with separate and layerwise application of various fertilizers, and phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are at the level of tubers in 5 Cm from both sides with a tape 10 cm wide, and the nitrogen ones below them through a soil layer of 5-7 cm in the center by a single 15-20 cm wide strip, and the care for planting is carried out by interrow cultivation with a rise in the ridges along the height and width of the crest, Similar to loosening of the soil in the formation of furrows and ridges.
print version
Date of publication 07.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.