| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2034900
![]()
METHOD FOR DEVELOPMENT OF DEPOSITED MEDIUM-SULFUR LAND
The name of the inventor: Grammatikati O.G.
The name of the patent holder: All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Hydraulic Engineering and Melioration named after AN Kostyakov
Address for correspondence:
The effective date of the patent: 1992.12.09
Use: in melioration with the development of saline lands with the use of reclamation crop rotations. Essence: removal of salts is carried out by sowing halophytes with subsequent cleaning. At the beginning of the development of the lands, the halophytes are sown in their pure form, and in subsequent years they perform mixed planting of halophytes and forage crops, changing their ratio for several years, and then completely replacing the halophytes with fodder crops.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to land reclamation and can be used in the development of saline lands with the use of reclamation crop rotations.
The main way to develop saline lands is a method of washing the soil with subsequent removal of wash water using a drainage-collector network. This method of desalinization, depending on the region and degree of soil salinity, requires 5 to 20 thousand m 3 / ha (Combating Salinization of Lands, edited by VA Kovdy, International Series "Conservation of Nature." M. Kolos, 1981). Authors, N 1606023, 1428297, class A 01 G 25/00, 1988).
Disadvantages of these methods: large norms of washing water, which is consumed not only unproductively, but also is a source of a large number of saline drainage waters, which are discharged into natural water receivers, which leads to contamination of the latter and deterioration of the ecological situation in irrigated areas.
The closest technical solution is a method of soil desalinization, which includes supplying water to the root zone and removing salts from the upper soil layer, which is carried out with the help of halophyte plants sown in the irrigated area, followed by their mowing and removal outside the site (author's St. N 1611242, class A 01 G 25/00, A 01 B 79/00, 1988).
However, this method was developed for sandy soils under irrigation with mineralized waters and does not touch upon issues of desalinization of saline medium loamy soils under irrigation with fresh water under conditions of reclamative crop rotation.
The aim of the invention is to create an environmentally friendly method for the development of medium-clay saline soils that will allow the removal of salt from the site, rather than moving them from one place (from the soil) to another (into reservoirs using collector-drainage water).
In order to achieve this goal, it is proposed that in the known method of development with the use of halophytes the latter be sown first in the development of the field, after which it should be mixed with halophyte and forage crops, changing their ratio for several years, and then completely replacing the halophytes with fodder crops.
At the same time, on medium saline soils, halophytes are sown in the first two years of cultivation, mixed sowing is carried out for the next three years, and then the fodder crops are cleaned.
For strongly saline soils, halophytes are sown in the first three years of cultivation, mixed sowing is carried out in the next three years, and pure sowing of fodder crops for the seventh year of cultivation.
The essence of the proposed method is the desalinization of medium- and heavily saline loamy soils with the help of meliorative crop rotations. The latter are proposed as an alternative to drainage and irrigation irrigation.
When developing melioration rotations on saline soils in the first years, the most salt tolerant fodder crops are planted: Sudan grass, barley, sorghum, sweet clover, alfalfa. On average, 8-9 tons per hectare of salts can be removed during meliorative rotation in a year, and from 4 to 5 years for complete desalinization (at an average degree of salinity).
At the same time, the use of halophytes will make it possible to remove from 3 to 7 tons per hectare of salts from the soil in their aboveground part (depending on the biological features). In addition, a "mulch effect" appears in the field occupied by a continuous halophyte sowing (halophytes prevent the salts from rising from deeper layers into the upper layers), which reduces the salt content by 2-2.5 t / ha of salts.
These data indicate that the content of salts in the soil will decrease every year, which will allow gradually (before the full development of the crop rotation) to introduce into sowing cultivated plants. In this case, irrigation water is supplied to the field in accordance with the plants' need for water, which minimizes the unproductive loss of water for filtration.
Depending on the characteristics of the soils (in terms of salt content), different crop rotations are offered with different alternation of cultures in time.
An example . According to the classification of soils (NI Bazilevich and EI Pankova) in medium saline medium loamy soils under chloride salinization, the amount of toxic salts is 0.1-0.3%. In medium loamy soils, a meter layer of soil contains up to 36 tons per hectare of salts. With a high degree of salinity (0.3%), the salt content in the meter layer can reach 49 tons / ha.
With an overhead crop of 10 tons per hectare, halophytes carry about 4.5 tons per hectare of salt. Natural precipitation during the cold period of the year (in the main irrigated regions of the country) removes up to 2 tons of salt per hectare of soil from a meter layer of soil. "The effect of mulch" is about 2.5 tons per hectare of salt.
In total, 9 tons / ha of salt per year are removed annually in the area occupied by halophytes.
In Table. 1 and 2 show the process of desalinization of soil in the area with reclamative crop rotation.
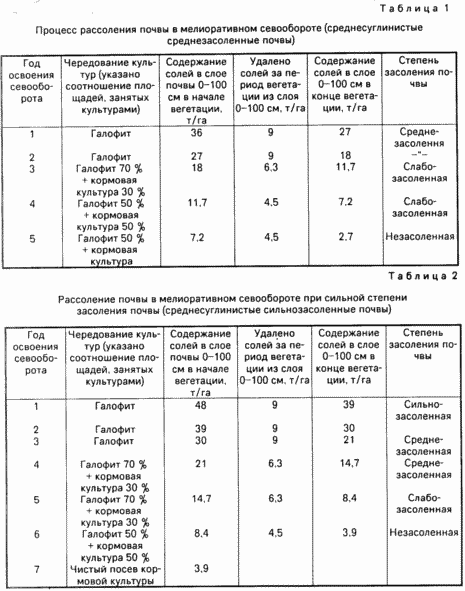
As the data of these tables show, during the development of medium- and heavily-saline lands in conditions of reclamative crop rotation, it is possible to desalinize the soil for 5-6 years; In addition to saving water for washing and washing irrigation regime (5-10 thousand m 3 / ha), in addition to obtain saline oil (halophytes) for livestock feed (on medium saline lands in the first year of development).
CLAIM
1. METHOD FOR DEVELOPMENT OF SALTED MIDDLE-COULD LAND, in which the removal of salts is carried out by sowing halophytes with subsequent harvesting, characterized by the fact that in the beginning of the development of the lands the halophytes are sown in pure form, and in subsequent years the mixed planting of halophytes and fodder crops is performed, For several years, and then carry out a complete replacement of halophytes with fodder crops.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that halophytes are sown in the first two years of development of the medium saline soils, mixed sowing is carried out for the next three years, and then the crop is sown in pure form.
3. Method according to claim 1, characterized in that on highly saline soils halophytes are sown in the first three years of development, mixed sowing is carried out in the next three years, and sowing of fodder crops in pure form is carried out for the seventh year of development of the site.
print version
Date of publication 09.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.