| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2160525
![]()
METHOD FOR INCREASING THE FIELD IN PLANTS phytoimmunity Lupin
Name of the inventor: Kononov AS
The name of the patentee: All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of lupine
Address for correspondence: 242024, Bryansk, Bryansk district, pos.. Michurinsky, All-Russian Research Institute of lupine, Kononov AS
Starting date of the patent: 1999.01.29
The invention is intended for use in agriculture, plant breeding to improve phytosanitary state agrocenosis for growing lupine. The method includes the increase in the accumulation of the most vulnerable parts of lupine polymeric phenolic compounds, the penetration preventing fungal diseases in a plant, by co-seeding with yellow lupine spring barley, while the ratio of yellow lupine seeds of spring barley and corresponds to 0.8: 0.9 - 1.0 2.0 mln.vskhozhih seeds per 1 ha. The method can reduce the damage lupine fungal diseases, reduce the consumption of seeds.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to agriculture, namely to horticulture, and can be used to improve the phytosanitary status agrocenosis for growing lupine.
The plant is well known that the cultivation of crops in the single-species crops dramatically reduces the adaptive capacity agrophytocenosis. To increase the field figoimmuniteta agrocenosis technologies used in fertilizers, physiologically active substances, pesticides.
However, a significant disadvantage of the known methods of growing crops, for example, yellow lupine feeding is their low efficiency, high costs of pesticides, pollution, high loss of plant fungal diseases, with yield losses remain at the level of 30-40% [1 Zhuchenko A. A. The adaptive capacity of cultivated plants (ecological and genetic basis) / Chisinau. "Shtiintsa". 1988. C.337].
The purpose of the invention - a method for sowing of lupine, which is due to allelopathic interaction of different cultures enhances the field of biology phytoimmunity seeding is an economical, it reduces the loss of lupine fungal diseases.
To achieve this goal the yellow lupine further added, and spring barley seeds are sown in a quantitative ratio of 0.8: 0.9-1.0: 2.0 million viable seeds per 1 ha, respectively..
Comparison of the analysis of the claimed solution to the prototype shows that the claimed method differs from the known composition of complementary crop components, including the stern yellow lupine and spring barley, and seeds in the seed mixture ratio depending on the composition of the soil and weeds, is 0.8: 0, 9-1,0: 2.0 million viable seeds per 1 ha.. Thus, the claimed technical solution meets the criterion of "novelty".
New technical solution is different from the known fact that the new species composition and a new mixing ratio agroftiotsenoza a positive effect on the accumulation of polymeric phenolic compounds in the most vulnerable parts of the stem, peduncle, yellow lupine beans flaps, thus increases the field phytoimmunity lupine plants to fungal diseases.
This allows to conclude that the proposed method of sowing the criterion of "substantial differences". The proposed method for the cultivation of lupine in the practice of agriculture compares favorably known for its accessibility and high efficiency.
As the components used agrophytocenosis crops stern yellow lupine and spring barley in the appropriate proportions. As a result of allelopathic interactions lupine and barley plants Lapin in agrophytocenosis increase in the most vulnerable parts of the stem, stalk, wings bean accumulation of polymeric phenol compounds 26.5; 80.8; 137.4%, respectively, compared with the patients, such as anthracnose plants and 28.6; 52.1; 88.9%, respectively, compared with healthy yellow lupine plants that are grown in a known manner sowing single-species. Data accumulation of polymer compounds in the phenolic mixed lupine crop plants in comparison with the known method given in the Table. 1.
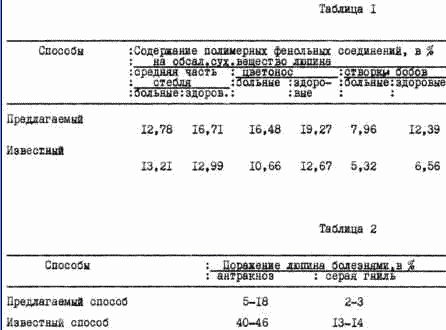
The new method allows growing plants lupine due allelopathic interaction with barley accumulate an increased amount of phenolic resin of fungicidal compounds which operate in plants as a protective barrier to mechanical, thermal and pathogenic influences. Increased concentration in the most vulnerable parts of the plant phenolic fungicidal substances reduces lupine defeat fungal diseases: anthracnose 2-4 times, botrytis 4-8 times. Data on the phytosanitary condition of lupine in a mixed sowing barley in comparison with the known method - single-species planting lupine are given in Table. 2.
Using the new method reduces crop by 60-70% at the expense of barley seeds consumption 35-75% lupine seeds. Furthermore, the new method of growing in culture lupine bean agrocenosis - barley changes the ratio of protein synthesis and starch in the grain. Protein barley grain and vegetative mass increases by 2-2.5%. The total protein yield in the grain mixture at 40-55% higher than the average amount of protein crop output with single-species cultures components. The new method of sowing reduced the cost of nitrogen fertilizer at the rate of two tons per hectare, ie 100 hectares of crop farming saves 35-40 tons of ammonium nitrate, with the yield of grain mixture at 28-32% higher than the average amount of grain yield from single-species crops lupine and barley.
CLAIM
A method for improving field phytoimmunity lupine plant, comprising sowing the seeds, characterized in that the increased accumulation in the most vulnerable parts of lupine polymeric phenolic compounds that prevent the penetration of plant fungal diseases by co-seeding of yellow lupine to spring barley, while the ratio of yellow lupine seeds barley meets ardent 0.8: 0.9 - 1.0:. 2.0 million viable seeds per 1 ha.
print version
Publication date 09.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.