| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2142215
![]()
METHOD OF PRE-TREATMENT OF SEEDS OF SUGAR BEET
The name of the inventor: Yunusov Rauf Adgamovich
The name of the patent holder: Yunusov Rauf Adgamovich
Address for correspondence: 420078, Kazan, ul.Iskra, 31, apt.26, Yunusov R.A.
Date of commencement of the patent: 1998.10.19
(EN) The invention relates to agriculture. It can be used in seed plants for preseeding processing of seeds of sugar and fodder beet, rapeseed, maize, sunflower and other crops. The method consists in the systemic formation of biologically active nutrient and fungicidal media on the surface with a complex positive effect on growth processes in the embryo, on suppression of pathogens on the seed surface, increasing the uniformity of applying all components of the encrusting composition to the seed surface by spraying them with injectors and protecting against The inhibitory effect of toxic insecticides, included in the composition for seed encrustation. At the same time, a liquid microfertilization compound (LHSA) is introduced into the aqueous suspension of the inlaying composition at a rate of 6-8 liters per ton of seeds, and the inlaying composition is prepared in the form of two solutions that are applied to seeds with an initial moisture content of 13-14.5% in two layers alternately With drying to the initial moisture after application of each layer; The first layer is applied with an aqueous suspension consisting of a fungicide TMTD, a growth promoter, a film-forming agent Na CMC and water, a second layer is applied with insecticides with film-forming polymers. The invention makes it possible to form on the surface of seeds a biologically active nutrient and fungicidal medium effectively stimulating growth processes in the bud, to increase the uniformity of applying to the seeds all components of the composition for inlaying in each layer, and to reduce the inhibitory effect of toxic insecticides in the second layer.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
(EN) The invention relates to agriculture. It can be used in seed plants for preseeding processing of seeds of sugar and fodder beet, rapeseed, maize, sunflower and other crops.
Known methods for presowing seed treatment (see, for example, SU No. 1757497 A1, SU N 1753974 A1, SU N 1793836 A3, SU N 1809747, SU N 1655324 A1) characterize certain of its methods or preparations, do not meet the requirements of industrial production Technology and do not ensure uniform application of protective and stimulating drugs on the seeds, different in their physicochemical properties, which leads to unfriendly shoots, unequal growth of plants and shortage of crops. In addition, the lack of drying process moistened when etched seeds leads to an overestimation of their humidity, reducing flowability.
The prototype of the invention was the technology of seed treatment outlined in the "Instructions for processing seeds of sugar beet by furadan, adifur, daifuran and safety requirements" (Gosagroprom USSR, M.1988). According to the Instruction for non-invasive seeds with a moisture content of not more than 11%, preparations (eg furadan) are applied together with protective-stimulating substances in the form of a specially prepared working mixture. First of all, a suspension of protective-stimulating substances is prepared, including 1 ton of seeds; ТМТД 4кг, ЖКУ 3 l, boric acid 0,5 kg, Na КМЦ or СМААН-20 0,1 kg per 10 l of water. After thorough mixing into the suspension, the drug is applied at a rate of 0.40-0.50 mg per seed.
The disadvantages of the prototype are: the lack of a biologically active substance in the working mixture with a complex effect on the growth processes of the seed embryo, separate application of the preparations with different physicochemical properties is not provided, mixing of an aqueous suspension consisting of fungicides, fertilizers, etc., with disinfectants Carbofuran group, prepared on the basis of organic solvents, leads to the appearance in the working mixture of sediment, clots that cause technical interference in pumps and nozzles of etching equipment, which leads to uneven application of seeds in the encrusting composition, complicates the process. The direct contact of a toxic insecticide (eg, furadan) mixed with other substances with a seed coat has an inhibitory effect on them, so seed treatment with the mixture prepared in this way, as practice shows (see, for example, AV Kornienko and Etc. "Insecticides for presowing seed treatment", Journal of Sugar Beet, No. 3, 1994, p. 17) reduces their germination capacity by 5-12% (depending on the term of seed ripening after incrustation). In addition, the pericarp of seeds, which is a good substrate for pathogens of fungal diseases, is not adequately protected by a fungicide that forms a loose shell on the seed surface due to the presence of an insecticide with an organic solvent in the mixture. The requirement for a lower initial moisture content of the seeds does not exceed 11%, impairing their wettability by the working mixture during the incrustation process and, thereby, also contributes to the formation of an uneven coating, and stronger wetting of the seeds requires their additional drying, which is not provided by inlay. Thus, a lower initial humidity of not more than 11% is dictated by the maximum permissible dose of moistening of seeds during the incrustation process, which should not exceed 14.5% according to GOST, which in turn imposes a limitation on the amount of water in the working mixture to 10 liters per ton of seeds and It does not allow to reduce the concentration of the working mixture, which is necessary to increase the uniformity of the coating, in particular when treating with nozzles.
The technical problem to be solved is the systemic formation of a dense biologically active nutrient and fungicidal medium directly on the surface of the intact biologically active nutrient and fungicidal medium with a complex positive effect on growth processes in the embryo, suppression of pathogens on the seed surface, increasing the uniformity of applying all components of the encrusting composition to the seed surface by spraying them with injectors And protection from the inhibitory effect of toxic insecticides that make up the seed encrustation.
The solved technical problem in the method of presowing treatment of sugar beet seeds, consisting in applying an encrusting composition to the seed surface in the form of an aqueous suspension consisting of a fungicide of tetramethylthiuram disulfide (TMTD), sodium carboxymethylcellulose (Na CMC) film-forming substance, water, carbofuran group insecticides is achieved by the fact that In the aqueous suspension of the incrustation composition, a liquid micro-co-ordinating composition (GUSS) (TU 39-05765670-OP-201-94) was introduced at a rate of 6-8 liters per ton of seeds, and the inlaying composition was prepared in the form of two solutions that were applied to the seeds in two layers Alternately; The first layer is applied with an aqueous suspension consisting of the fungicide TMTD, the growth promoter ZHUSS, the film-forming substance Na CMC and water, the second layer is applied insecticides mixed with film-forming polymers, the water content in the aqueous emulsion is increased 1.8-2.5 times and is 18 -25 liters of water per ton of seeds, and seeds are taken with an initial moisture content of 13-14.5% after application of each layer is dried with warm air at a temperature of 38-40 o C to the initial moisture.
The proposed technical solution satisfies the criterion of "inventive level", because Proposed distinctive features: the introduction of a liquid micro-fertilizer compound (GUSS) into the encrusting composition for processing seeds of sugar beet as a growth stimulator for the new preparation, at a rate of 6-8 liters per ton of seeds, reducing the concentration of the water emulsion by 1.8-2.5 times by increasing Water up to 18-25 liters per ton of seeds (with respect to the prototype 10 liters), applying an encrusting composition to seeds with an initial moisture content of 13-14.5% in two layers followed by drying them (after applying each soda) with warm air at a temperature of 38-40 o C to the initial humidity, when the first layer is applied an aqueous emulsion containing fungicides, seed growth stimulants and a film-forming substance, and in the second layer an insecticide with an independent film-forming agent is new and essential distinctive features for inlaying sugar beet seeds. All this makes it possible to form a dense uniform shell directly on the seed surface from a biologically active nutrient and fungicidal medium with a complex effect on growth processes in the embryo, suppression of pathogens on the seed surface, increase the uniformity of applying to the seeds all components of the encrusting composition in each layer, using Nozzle spraying method of emulsion, widely used in production lines, and to reduce the inhibitory effect of toxic insecticides in the second outer layer of the seed encrusting coating. All this leads to an increase in field germination, activation of seed growth in the early stages of development, increased yield, reduces the loss of germination when storing seeds after incrustation.
Of known sources of scientific and technical information, such a technical solution for inlaying sugar beet seeds has not been found.
- The introduction into the aqueous emulsion of a new non-investigated sugar growth beet in the amount of 6-8 kg / ton ensures the activation of the hydrolysis of the reserve substances and the synthesis of new compounds in the seed germ, but also the activation of seedling growth and the initial period.
- Reducing the concentration of water emulsion improves the operation of the nozzles and allows it to be applied evenly to the seed surface, and subsequent drying to the original moisture strengthens and compacts the first layer due to the polymerization of the film-forming substance. As a result, the exact dosage of pesticides is firmly fixed on each seed.
- Separate application of aqueous emulsion and toxic insecticides with organic solvent in different layers allows to avoid formation of clots in the working mixture and clogging of injectors and pumps of etching equipment, which improves uniformity of application of each layer and incrustation of seeds as a whole.
- The spraying of insecticide with a separate layer on a dense film of Na CMC, the first layer, reduces its inhibitory effect on the seed and reliably protects against the influence of "external parasites", which increases the energy of seed growth and increases their field germination by 12% and yield (see results Tests).
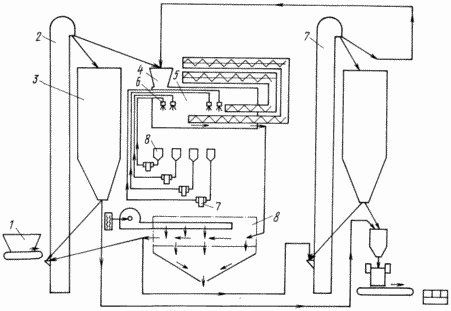
Technical realization of the method is realized on a mechanized technological line for inlaying and coating of seeds (see drawing). The line is a set of mechanisms and devices, united in a single sequential system, providing a closed technological cycle of presowing seed treatment and allowing in a continuous flow a repeated repetition of individual seed encrusting operations, in particular, layerwise application of encrusting composition and drying. In its composition, the line contains a hopper-dispenser 1; Two noria 2, 7; Storage hopper 3; Operational bin 4; Machine for inlaying 5 with injectors 6; The drying machine 8. The storage bin 3 is an intermediate storage tank for seeds located in front of the machine for inlaying 5, and serves to redistribute the flow of seeds between the units during the process change and repetition of the manufacturing operations. In particular, when the encrusting composition is layer-by-layer applied after application of the first layer in the inlaying machine, the seeds are fed to the drying machine 8, from there they are guided by the noria 7 back to the operating bin of the inlaying machine for applying the second layer, and then, after repeated drying in the machine, they are sent for packaging. For inlaying, seeds of grade 1, previously ground (in the case of sugar beet), on a special device (RF patent for invention No. 2067025) are taken, their initial moisture is 13-14.5% (the prototype is not higher than 11%). On the seeds the first layer of a separate nozzle from a separate container is applied with an aqueous emulsion consisting of 1 ton of seeds, from TMTD (4-6 kg), film-forming polymer Na CMC (0.2 kg), water (18-25 l). As a biologically active substance, 6-8 liters of a new preparation are added to the emulsion - the liquid microfertilizing compound of the ZhUSS (TU 39-05765670-OP-201-94), whose growth stimulant is copper, boron chelates obtained on the basis of ethanolamine (author's s. N 852302).
Pre-drying on the production line with warm air (38-40 o C), the furadan treated with fungicide, growth stimulant and film former seeds is applied second layer by insecticide furadan, imported as a finished paste with a film former at the rate of 0.4-0.5 mg per One seed by another nozzle from another container. Re-drying of the encrusted seeds is carried out before the free-flowing state. Being in the outer layer, a toxic insecticide separated by a film-forming polymer from the first layer penetrates more slowly into the cells of the pericarp, which reduces the inhibitory effect of the preparation.
The synergism of the action of the fungicide, which suppresses the growth of pathogens on the seed coat and the trace element of copper contained in the JUSSE, increases the resistance of seedlings, gives a positive effect against the fungal disease - beetroot corn (see Table 1).
Since the HAUS is an effective growth substance and contains nitrogen in the amine form and boron compounds, the boron microelement in the JUSS is biologically more active, the need for using HCH and boric acid disappears.
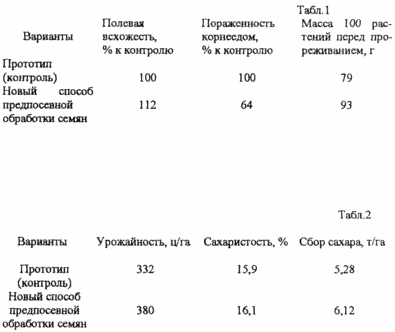 |
A new method of presowing seed treatment has been tested on sod-podzolic and leached chernozem soils. The experiments were carried out in triplicate, the registration area of the plot was 100 m 2 . Culture: sugar beet, Lgovskaya single-seed variety 52, average data for 1996-1998. The data given in Table. 1, show that a new seed treatment method increases seed field germination by 12%, reduces the affection by root-plant by 36%, and increases the weight of 100 plants before thinning (the phase of the first pair of real leaves) by 14 g. As the data from Table 1 show. 2, a new method of seed treatment raises the yield of sugar beet by 52 c / ha, sugar content - 0.2%, increases the collection of sugar from ha by 0.84 tons. Thus, the systemic layer-by-layer application to seeds of fungicides, new growth stimulants, film-forming polymers, insecticides ensures an increase in the productivity of field crops. |
CLAIM
1. A process for the presowing treatment of sugar beet seeds, comprising applying to the seed surface an encrusting composition in the form of a suspension consisting of a fungicide of tetramethylthiuram disulfide, a film-forming substance of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, water, a toxic insecticide of the carbofuran group, characterized in that a liquid microfertilizer composition is introduced into the aqueous suspension of the inlay composition 6-8 liters per ton of seeds, and the inlaying composition is prepared in the form of two solutions that are applied to the seeds in two layers alternately: the first layer is applied an aqueous suspension consisting of a fungicide of tetramethylthiuram disulphide, a growth promoter, a liquid microfertilizer, a film-forming substance, sodium carboxymethylcellulose and Water, the second layer is applied insecticides in a mixture with film-forming polymers.
2. A process according to claim 1, characterized in that the water content in the aqueous suspension is calculated per ton of seeds of 18-25 liters.
3. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the seeds are dried by warm air at a temperature of 38-40 ° C to the initial moisture after application of each layer.
4. A process according to claim 1, characterized in that the initial moisture content of the seeds is 13-14.5%.
print version
Date of publication 11.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.