| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2185724
![]()
METHOD FOR PRODUCING A natural hybrid SOI
Name of the inventor: Trembak EH .; Kochegura AV
The name of the patentee: State Scientific Institution of RAAS All-Russian Research Institute of Oil Crops im.V.S.Pustovoyta
Address for correspondence: 350038, Krasnodar, ul.Filatova, 17, VNIIMK, Patent Group
Starting date of the patent: 1999.12.21
The invention is intended for use in agriculture in the preparation of the natural soybean hybrids. The process includes the selection of maternal and paternal forms with the presence of the latter is visually defined by the dominant traits of alternative maternal, joint planting of parental forms on the plots, which is carried out for 30-45 days than optimal for the culture period, the scheme provides for separate tiers of cross-pollination, each of which it consists of several plots. In this central series of plots of each tier pollination is seeded with a mixture of seeds of paternal and maternal forms in the ratio 1: 1, and the two edge of a number of plots - seeds only paternal form, between the tiers pollination provide a protective circle, which seeded the seeds form, without supporting dominant paternal features while growing parental forms are treated during the flowering attractants, in particular beer, the selection of mother plants culled 2-3 productive upper node on the main and lateral shoots of each plant, and the seeds obtained after threshing mother plants are sorted according to size sieve and reject the small and large seeds. Sprouting seeds obtained after threshing is carried out in the field or artificial conditions, the selection of hybrid plants are by the presence of their father's dominant features by visual inspection of seedlings or mature plants. The method allows to create optimal conditions for soybean directed pollination, but also reduce the amount of analyte material used for the isolation of hybrid plants.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to agriculture, in particular to breeding soybean, namely to obtain soy natural hybrids. In determining the level of technology used publicly available information, presented in all known sources of information.
A method of obtaining natural hybrids of soybeans, including the selection of parental pairs, the joint planting of parental forms on the plots and their cultivation, harvesting plots and threshing plant, separation of smaller parent seeds with the help of soil sieves, seeding them in the field, identification of F 1 hybrids violet color hypocotyl (Ala AY Using spontaneous pollination in soybeans at interspecific hybridization. Reports of Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 6, 1988, s.10-12).
A disadvantage of the method is that it can be used only for interspecies hybrids spontaneous soybean.
It is known and the method of obtaining natural hybrids of soybeans (prototype), including a selection of maternal and paternal forms with the presence of the latter is visually defined by the dominant traits of alternative maternal, joint planting of parent components on the plots and their cultivation, selection of maternal plants and their threshing, germination obtained after threshing seeds in the field or artificial conditions, the selection of hybrid plants by visual inspection of seedlings or mature plants by the presence of their father's dominant traits (Myakushko Yu Lunin ND, Lygina LM et al. The use of cross-pollination in the soybean selection work Guidelines "Selection of hybrid soybean plants by genetic taps at artificial crosses and spontaneous pollination.." - M., 1979, s.11-15).
The disadvantages of prototype should include low process efficiency.
The present invention solves the problem of increasing the efficiency of a method for producing natural soybean hybrids.
The purpose of the invention - to create optimal conditions for soybean directed pollination, and reduction of the analyte and the material used for the isolation of hybrid plants.
The technical result is achieved in that, in a process involving the selection of maternal and paternal forms with the presence of the latter is visually defined by the dominant traits of alternative maternal, joint planting of parent components on the plots and their cultivation, selection of maternal plants and their threshing, germination obtained after threshing seeds in the field or artificial conditions, the selection of hybrid plants by the presence of their dominant paternal signs by visual inspection of seedlings or mature plants according to the invention the joint planting of parental forms is performed on stacked located plots in the timeline later than recommended for the culture, the scheme ensures optimal conditions for the pollination of the parental forms in tier-pollination and conditions that impede the transfer of pollen between tiers of cross-pollination, while growing parental forms during the period of mass flowering use tricks to attract insect pollinators, and the selection of mother plants after their thrashing cull not very prosperous undertaking material, while joint parental forms sowing is carried out for 30-45 days after the optimal culture period, according to the scheme, under which the central rows of each tier pollination plots seeded with a mixture of seeds of paternal and maternal forms at a ratio of 1: 1, in two rows on each side of each plot seeded seeds only father mold and between plots of different tiers-pollination provide protective tier which is inoculated seeds forms without carrier dominant paternal features while growing parental forms they are processed in the period of mass blossoming attractants plants, in particular beer, and discarded in the selection of mother plants two or three upper productive node on the main and lateral shoots per plant, seeds obtained after threshing are sorted by size, in particular through the sieve when sorting cull large and small seeds.
Comparative analysis of the proposed technical solutions with the prototype allows us to conclude that the proposed method differs from the known the later period of the joint planting of maternal and paternal forms, diagram of their placement, the use of techniques to attract pollinating insects in growing these forms and rejection of unpromising material in the selection and after threshing plant parent form.
Thus, the claimed method meets the criteria of patentability "novelty."
Investigating the level of technology in the process of conducting a patent search for all types of information generally available to the press, we found that the method of obtaining natural hybrids of soybeans, including the stated set of features for the expert in the field of soybean breeding does not obviously follow from the known to date in the prior art.
Our studies revealed the possibility of obtaining natural hybrids of soybeans at the joint planting of maternal and paternal forms it at a later date than that recommended for culture, while ensuring optimal conditions for the pollination of the parental forms in tier-pollination and conditions that impede the transfer of pollen between tiers of cross-pollination between adjacent plots within one tier of cross-pollination, using techniques to attract insect pollinators and reject unpromising material during the selection of mother plants and after threshing. It is this combination of features is necessary and sufficient to achieve the goal - to create optimal conditions for the directed cross-pollination in soybeans, but also reduce the amount of analyte material used for the isolation of hybrid plants. Based on this we can conclude that the claimed invention criteria of patentability "inventive step".
The claimed technical solution complies with the criteria of patentability and "industrial applicability", since it can be used in agriculture. And besides, in the description of the invention are means and methods by which the possible implementation of the technical solutions in the form as it is characterized in the independent claim.
The process is as follows. Starting with the selection of the maternal and paternal forms of soy, so that his father's form is determined by the dominant visual signs, alternate parent, such as the color of the corolla, and (or) painting plant pubescence. Carry out joint crop parental forms on plots after 30-45 days than recommended for the culture time.
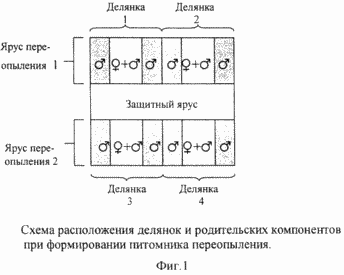
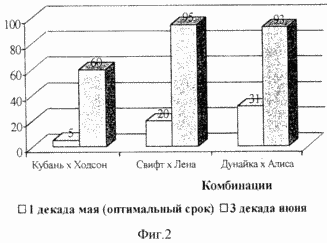
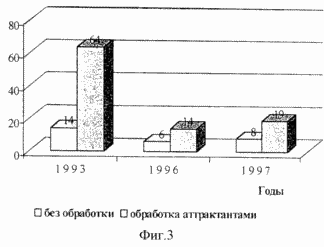
Figure 1 shows the layout of the plots and the parent component in the formation of cross-pollination nursery. Figure 2 shows the frequency of natural hybridization soybean sowing period of parental components (1993-1995). Figure 3 shows the effect of treatment attractant substances on the value of natural hybridization in soybean.
 |
 |
 |
The plots are formed on the principle that the central plot rows seeded with a mixture of maternal When growing parental forms used tricks to attract pollinators, such as processing the last attractants, in particular for bees, in the period of mass flowering plots. Selection of the mother plants is carried out based on visual evaluation and the selection of material is not very prosperous discarded, in particular two or three upper productive node on the main and lateral shoots. |
After the thrashing of mother plants and not very prosperous undertaking discarded material - small and large seeds, in particular through the sieves. Selection lattice performed so that the coarse fraction was about 5.3%, fine - 20-25%.
Sprouting obtained after threshing and rejection seed parent form is carried out in the field or under artificial climate.
Isolation of hybrid plants is carried out by visual inspection of seedlings or plants by the presence of their father's dominant features.
Example. Used as paternal form of soybean cultivar Hodson, who is visually determined by the dominant feature is the violet color of the corolla (purple hypocotyl), as well as the maternal form - Bystritsa2 soybean variety (white corolla, green hypocotyl). Sowing of parent forms was carried out in the conditions of Krasnodar in wide, row spacing - 0.45 cm to 10 seeds per 1 linear meter, series length - 5 m, the central rows of each plot were seeded with a mixture of seeds of maternal and paternal forms in the ratio 1: 1 (number of central series planned in accordance with the demand for hybrid seeds, for example to reliably produce one hybrid seed with an average of 0.13% of cross-fertilization is enough to have one central plot in the series). To the right and left of the central rows were seeded number two paternal form. In cases where the plot for natural hybrids of different combinations of crossing was necessary to place several layers between the various tiers of pollination plated form, not carrying a dominant feature of his father. Sowing was carried out on 35 days than the optimum time for this group of varieties, that is. E. In the second decade of June.
During the period of mass flowering plants (1-2 decade of August) plots were treated with 2-3 attractants for bees (honey solution, infusion linden inflorescences).
Motherboard plants was determined visually by the presence of a recessive trait (white color of the corolla), an alternative to the dominant father-ground (purple corolla flower); at the time of mass flowering in the central rows of plots etikitirovali plants bearing this sign.
The selection of mother plants was carried out in full maturity phase, while not very prosperous undertaking culled material is removed manually 2-3 upper productive unit on the main and side shoots of each plant.
After the selection and rejection of the remaining part of the mother plants threshed Snopova way to combine selective "Hege-125 C". Obtained after threshing seeds were fractionated using a sieve (coarse, medium and fine fractions). Sieve selected in such a way that the coarse fraction contained 3-5%, small - 20-25% of the seeds. Seeds of fine and coarse fractions is not very prosperous undertaking material excluded from further work.
Selected seeds middle fraction germinated in the field and among them are (to label) hybrid plants by visual search of plants with purple corolla, that is by the presence of their father's dominant trait.
Sowing at a later date provides better working conditions for the implementation of cross-pollination in soybeans. As a result, the natural frequency of the hybridization increases 3-12 times (Figure 2) compared to the optimal seeding culture period (May 1 decade). Sowing 30-45 days after the optimal period allows for a smooth transfer of the activities of insect pollinators of crops with the optimum period for the portion of cross-pollination, as in this case the end of the flowering plants of optimal planting dates coincide with the beginning of flowering experimental plots at the same time achieved a temporary isolation.
Formation of the plots so that the central rows seeded with a mixture of maternal and paternal forms in a ratio of 1: 1, and two rows on the left and right sides include plants paternal form, provides improved cross-fertilized conditions by increasing the concentration of donor pollen portion pollination and prevention pollen drift from neighboring plots.
Treatment of experimental plots at the time of mass flowering attractant substances is aimed at increasing the concentration of carriers of pollen in this area and to intensify their activities. As a result, the frequency of cross-fertilization is increased 2-5 times (Figure 3).
Rejection unpromising material reduces by 30-40% the amount of seed of the parent form, prepared for the separation of natural hybrids of soybeans, which leads to saving space, planned for carrying out tests and to reduce the time and labor performer.
Thus, the claimed invention allows to improve a method for producing soy natural hybrids.
CLAIM
1. A method for producing natural hybrids of soybeans, including selection of the maternal and paternal forms with the presence of the latter is visually defined by the dominant traits of alternative maternal, joint planting of parent components on the plots and their cultivation, selection of maternal plants and their threshing, germination of seeds obtained after threshing in the field or artificial conditions, selection of hybrid plants by the presence of their father's dominant traits by visual viewing mature plants or seedlings, wherein seeding joint parental forms on the plots carried out after 30-45 days than optimal for the culture period, the scheme provides for separate tiers of cross-pollination, each of which consists of several plots, with the central series of plots of each tier pollination is seeded with a mixture of maternal and paternal forms in the ratio 1: 1, and the two edge of a number of plots - seeds only paternal form, between the tiers pollination provide protection tier, which forms the seed is inoculated is not dominant carrier paternal features while growing parental forms are treated during the flowering attractants, in particular beer, the selection of mother plants culled 2-3 productive upper node on the main and lateral shoots per plant, after thrashing mother plants produced seeds are sorted by size and are rejected small and large seeds.
The method of claim 2. 1, characterized in that the mother plants after threshing sorted seeds obtained through the sieve.
print version
Publication date 11.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.