| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2201675
![]()
EXPRESS METHOD OF COLONING COCONES OF EARTHWALDS
The name of the inventor: Stom DI; Antonova E.V.
The name of the patent holder: Irkutsk State University
Address for correspondence: 664003, Irkutsk, ul. Karl Marx, 1, ISU, Patent Department
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.01.09
The invention relates to biotechnology, in particular to methods for collecting egg cocoons of oligochaetes. The method involves breeding worms in the habitat, removing worms from the habitat with the aid of an extract of water pepper. As a habitat, sand with a particle size of not more than 1 mm is used, into which are added decoctions of vegetables, cereals or plant extracts. Collection of cocoons of worms is carried out by sifting the substrate through a sieve with a cell diameter of not more than 2 mm. The method allows to increase efficiency of collection of cocoons, to reduce their mechanical damage during collection.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to methods for collecting egg cocoons of oligochaetes.
A method is known for collecting the cocoons of earthworms manually [1]. To do this, take a small amount of substrate after vermicultivation and use tweezers to select cocoons of worms.
The closest analogue is a method involving the cultivation of worms in a substrate, and for extracting worms from the substrate a water pepper extract (Polygonum hydropiper) is used [2]. Water pepper, irritating the skin, causes the worms to crawl out, without harming them.
The disadvantages of the known method of collecting the cocoons of earthworms are: the duration and considerable laboriousness of the process, incomplete sampling, the possibility of mechanical damage to cocoons.
Earthworms, and in particular the red Californian hybrid, are one of the most important biodestructors of polluted, including oil products, soils. To populate contaminated sites with vermiculture, it is more convenient to use not the worms themselves, but their egg cocoons. The latter take considerably less space during transportation. So, for example, the size of cocoons of red Californian worms varies from 2 to 6 mm, and the adult worm is from 6 to 10 cm. At the same time, up to 20 worms can hatch from one cocoon. In addition, when using cocoons, there is no need for additional fertilizing and, possibly, such a bulk substrate as moist soil. When mass collection of worm cocoons is carried out by manual sampling, a large amount of time is required and this is an extremely laborious process, in addition, there is a danger of mechanical damage to worms and cocoons.
The object of the present invention is to provide a method for harvesting cocoons of earthworms, which makes it possible to increase the efficiency of the method.
The task is achieved by the fact that in a known method involving the breeding of worms in the habitat, the removal of worms from the habitat by means of an extract of water pepper, sand is used as the habitat with a particle size of not more than 1 mm, into which are added decoctions of vegetables, cereals or Extracts of plants, and the collection of cocoons of worms is carried out by sifting the substrate through a sieve with a cell diameter of not more than 2 mm.
THIS METHOD IS CONDUCTED AS FOLLOWS:
Sand is used as a substrate, sieved through a sieve with a 1 mm cell diameter. Start sexually mature worms, maintaining optimal conditions for their life (temperature 20-25 o C, humidity 80%, pH = 7). Food additives can be water broths or extracts from various vegetables, plants, etc. After about 10 days, cocoons can be collected by first removing worms from the substrate using an extract of water pepper. Using a sieve with a 2 mm cell diameter, the substrate is sifted, while the cocoons remain in the sieve, since their diameter is 3-5 mm. Worms can be used again in work, because water pepper, irritating the skin, causes the worms to crawl outward without harming them.
Example. Pour about 200 grams of sand (with a particle diameter of not more than 1 mm) into the cup (15 × 10 × 5 cm) and launch 20 mature worms.
After 10 days in the substrate add 20 ml of extract of water pepper. To prepare the extract, take 50 g fresh mass of water pepper in 1 liter of standing water, filter. After 20-30 minutes after the addition of this extract, about 90% of worms crawl to the surface of the substrate, of which 60% - completely, the rest - in part. After this, the worms are collected, and the substrates are allowed to dry for 48 hours. Then the substrates are sieved through a sieve with a 2 mm cell diameter and cocoons are collected (80.7 ± 2.6 cocoons were collected in 30 days). After a day, the substrates are used again.
To determine food additives that positively affect the reproductive capacity of worms, a square-shaped cage with 9 compartments is used [3]. In 7 compartments are placed sod-podzolic soil with various food additives, in 8 - soil without additives (control) and in the central compartment - dry sand. In the cage, sexually mature worms are started at the rate of 5 individuals per compartment. The preference for worms of a certain substrate is judged by the number of worms and the cocoons they set aside for 10 days.
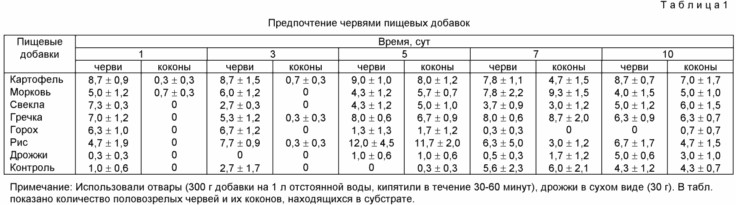
As can be seen from Table 1, worms preferred buckwheat broths (13.3-20% worms, 22 cocoons), carrots (10-19.5% worms, 20.7 cocoons), rice (11.8-30% worms , 19.7% of cocoons).
Judging by the materials in Table 2, for the worms, nettle extracts (13.3-19.3% worms, 22.9 cocoons), clover (10.8-20% worms, 20.9 cocoons), dandelion (11, 8-17.5% of worms, 18.6 cocoons).
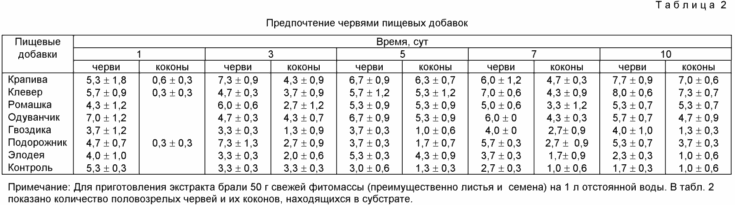
Thus, of the additives used, the most effective were buckwheat decoction (207.5% cocoons versus control) and nettle extract (347% cocoons from control).
The proposed method allows to increase the efficiency of collection of cocoons, to reduce their mechanical damage during collection.
USED BOOKS
1. Gorodnyi NM, Melnik IA, Povkhan MF Bioconversion of organic wastes in biodynamic economy. - Kiev: The harvest, 1990. - 256 p.
2. Chaudhuri PS, Nanda DK The extraction earthworms Eutyphoeus gammiei with using water extract of Polygonum hydropiper and comparison with other chemical methods of estimation of eartfiworms population // Philipp.J. Sci., 1996, 125, 3, p. 277-234.
3. Application of the Russian Federation 98117992, C 05 F 3/06, 1998.
CLAIM
Express method of collecting earthworm cocoons, including worm breeding in the habitat, removal of worms from the habitat with the help of water pepper extract, characterized in that sand is used as the habitat for particles with a particle size of no more than 1 mm, into which are added decoctions of vegetables, cereals Or extracts of plants, and the collection of cocoons of worms is carried out by sifting the substrate through a sieve with a cell diameter of not more than 2 mm.
print version
Date of publication 04.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.