| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2112763
![]()
Method of producing liquid biostimulant plant growth and development
GUMUSOSODERZHASCHIH OF SUBSTANCES
Name of the inventor: Titov I.N .; Shishova TI .; Denisov AA .; Feoktistov VI .; Damirov II
The name of the patentee: Igor Titov; Shishova Tatiana
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1996.10.01
The invention: the method relates to agriculture and for the production of liquid bio-stimulating drugs from gumusosoderzhaschih substances, namely compost. The inventive subject matter gumusosoderzhaschie alkaline extraction followed by neutralization of the hood. It is proposed as a starting gumusosoderzhaschego substance use pre-prepared manure from livestock waste composts enterprises from which further isolated the bacterial water suspension which is separated from the solids compost. The solid fraction is subjected to alkaline extraction 0.1 - 1.0N. alkaline solution at a temperature of 20 - 50 o C followed by the separation of the liquid extract which is mixed with the bacterial suspension and advocate for manufacturing molten desired product. The proposed method provides higher quality and an increase in the target yield, lower material costs and energy on its production, increased industrial efficiency.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to agriculture and can be used in the preparation of liquid preparations gumusosoderzhaschih substrates, namely compost.
A method of obtaining a preparation liquid humic vermicompost by soaking in water and then separating the liquid fraction [1]. The method provides a liquid formulation comprising a water-soluble substance (micro and macro nutrients and some physiologically active substances) and soil bacteria and spores, which, when applied to the soil and promote the breeding soil enrichment necessary for the growth and development of plant substances.
The disadvantage of this method is the low quality of the product because of its low growth activity. Furthermore, in this method, there is low product yield, because concentration of nutrients and substances required for plant growth enhancing substances in the resulting liquid suspension rather insignificant.
The closest to the proposed method is a known method of producing liquid biostimulant plant growth and development of gumusosoderzhaschih substances by extraction with alkali followed by neutralization extract [2]. The process is carried out at high temperature (100 o C), as a raw material used fossil fuel (lignite).
The disadvantage of this method is that derived from brown coal, humic substances undergo chemical resistance rather rigid, resulting in modification and hydrolysis of the polymer molecules, which reduces the quality of the preparation. Moreover, using this method there is a relatively low product yield, because it consists substantially only humic substances. A disadvantage of humic substances derived from brown coal, low-moor peat and sapropel (lake sludge) is the fact that they tend to contain in its structure a large amount of heavy metals. Furthermore, the manufacturing process has a high energy consumption and require large expenditures for equipment and heat transfer fluids. As a result, the method has a low efficiency in its implementation on an industrial scale.
The purpose of the invention - improving the quality and increasing the target yield, lower material costs and energy on its production, increased industrial efficiency.
The goal is achieved by a method of producing liquid biostimulant plant growth and development of gumusosoderzhaschih materials by alkaline extraction, followed by neutralization hoods according to the invention as starting gumusosoderzhaschego substance used manure waste livestock production, previously passed biotech processing for producing compost, further from compost aqueous bacterial suspension is isolated, for which the compost is soaked in water, it is extracted from the bacterial mass in the aqueous solution, the resultant bacterial suspension was separated from the solid compost fraction is subjected to alkaline extraction and the resulting solid fraction, and extraction is carried extracts 0.1 - 1 0 n. alkaline solution at a temperature of 20 - 50 o C followed by the separation of the liquid extract, the latter being mixed with the bacterial suspension and defend to obtain the desired product.
Thus alkaline extract was subjected to neutralization prior to mixing with the bacterial suspension; subjecting the mixture to neutralize alkaline extract of a bacterial suspension; Liquid remaining after separation of the solid fraction of the extract alkali water is poured at a temperature of 30 - 50 o C in a volume equal to the volume used for the extraction of the alkaline solution. The resulting mixture is stirred, settled and the washing liquid is mixed with the suspension previously isolated alkaline extract and the mixture was subjected to neutralization with an alkali wash extract slurry. Rinsing operation to receive the slurry is repeated at least twice; advanced biotechnological waste treatment to obtain compost spend vermicultivation methods, solid-state fermentation or natural composting; compost is used with a humidity of 45 - 65%. For compost the aqueous mixture using water at a temperature of 30 - 35 o C; Compost prepared aqueous mixture at a volume ratio of the compost - the water of from 1: 3 to 1: 5; separation of the bacterial mass produced by settling, filtration, separation, or centrifugation; settling the aqueous mixture to produce compost bacterial suspension was carried out for 30 minutes; as used alkali caustic lithium, caustic potash, caustic soda or aqueous ammonia; the volume ratio of the precipitate fraction and the alkaline solution is from 1:10 to 1: 20 depending on the humidity of the first; settling the mixture with an alkaline solution to obtain a precipitate compost extract liquid is carried out for 30 minutes; neutralization is carried out to a value of pH of the medium equal to 7 - 8; produce neutralizing with inorganic acids, preferably nitric acid; produced via neutralization of organic acids such as oxalic, malic, citric or succinic. To neutralize used preferably citric or succinic acid; settling the mixture neutralized extract with a bacterial suspension is carried out for 10 - 12 hours; resulting bacterial suspension prior to mixing it with the extract stored at 30 - 35 o C.
Comparative analysis with the prototype shows that the proposed method is characterized by a new combination of features, consisting in the fact as a starting gumusosoderzhaschego substance use manure waste of livestock enterprises, previously passed biotech processing for compost addition of compost recovered aqueous bacterial suspension, for which the compost is soaked in water, it is extracted from the bacterial mass in the aqueous solution. The resulting bacterial suspension was separated from the solid compost fraction is subjected to alkaline extraction and the resulting solid fraction, and extraction is carried extracts 0.1 - 1.0N. alkaline solution at a temperature of 20 - 50 o C followed by the separation of the liquid extract, the latter being mixed with the bacterial suspension and defend to obtain the desired product. Thus alkaline extract was subjected to neutralization prior to mixing with the bacterial suspension; subjecting the mixture to neutralize alkaline extract of a bacterial suspension; Liquid remaining after separation of the solid fraction of the extract alkali water is poured at a temperature of 30 - 50 o C in a volume equal to the volume used for the extraction of the alkaline solution. The resulting mixture is stirred, settled and the washing liquid is mixed with the suspension previously isolated alkaline extract and the mixture was subjected to neutralization with an alkali wash extract slurry. Rinsing operation to receive the slurry is repeated at least twice; advanced biotechnological waste treatment to obtain compost spend vermicultivation methods, solid-state fermentation or natural composting; compost is used with a humidity of 45 - 65%; to obtain an aqueous mixture of compost use water with a temperature of 30 - 35 o C. The aqueous mixture is prepared by composting the compost-volume ratio of water of from 1: 3 to 1: 5; separation of the bacterial mass produced by settling, filtration, separation, or centrifugation. Settling of the aqueous mixture to produce compost bacterial suspension for 30 minutes; as used alkali caustic lithium, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or aqueous ammonia. The volume ratio of the precipitate fraction and the alkaline solution is from 1:10 to 1:20, depending on the humidity of the first; settling the mixture with an alkaline solution to obtain a precipitate compost extract liquid is carried out for 30 minutes; neutralization is carried out to a value of pH of the medium equal to 7 - 8; produce neutralizing with inorganic acids, preferably nitric acid; produced via neutralization of organic acids such as oxalic, malic, citric or succinic acid; for neutralization are preferably used, citric or succinic acid; settling the mixture neutralized extract with a bacterial suspension is carried out for 10 -. 12 hours resulting bacterial suspension prior to mixing it with the extract stored at 30 - 35 o C.
These circumstances indicate conformity of the claimed technical solution to the criterion "novelty".
Comparison with known proposed device indicates that it is for the specialist should not explicitly in the art, that testifies the conformity of the claimed technical solution to the criterion "Inventive Level".
The proposed technical solution is industrially applicable and used on an industrial scale in a number of agricultural enterprises (livestock complexes) of the Russian Federation and the Republic of Belarus.
Production of liquid bio-stimulator of plant growth and development of gumusosoderzhaschih substances as follows.
Initial gumusosoderzhaschee matter (manure waste of livestock enterprises) are subjected to pre-processing methods vermicultivation biotechnology, solid state fermentation or natural composting to produce compost.
Isolated from compost obtained aqueous bacterial suspension. For this purpose compost loaded into a container, soaked with water and the resulting aqueous mixture was stirred well. Optimum moisture compost - 45 - 65%, which corresponds to a standardized moisture commercial compost: the humidity below 45% denaturation occurs humic substances, humidity greater than 65% when stored in compost piles does not occur practically. Soak compost should preferably be made with water at a temperature of 30 - 35 o C, because it promotes optimal conditions for the growth of microbial biomass, fungal community in aqueous suspension and contributes to the preservation and nativity some labile physiologically active substances. The volume ratio of the compost - the water is desirably maintained in the range from 1: 3 to 1: 5, as while providing the maximum "efficiency" process producing bacterial suspension. While stirring the compost aqueous mixture is extracted (extraction) from his bacterial mass, and water-soluble substances that contain macro- and micronutrients, plant hormones and other biologically active substances, a positive influence on physiological processes in plants. Extracted biomass growth of microorganisms in the aqueous medium further proceeds during storage (infusion) of the bacterial suspension in a separate vessel before the end of the process. Enrichment of an aqueous suspension by soil microorganisms contributes to the quality of the desired final product.
After stirring the aqueous bacterial suspension is separated from the solid compost fraction by sedimentation, filtration, centrifugation or separation. Thus optimum settling time of the mixture is 30 minutes. During this time there is sufficient quality separating into a liquid fraction and a precipitate greater settling time does not affect the physico-chemical composition, and the bacterial suspension, but increases the technological cycle. The resulting aqueous fraction - bacterial suspension was poured into a separate container and stored until the end of the process.
The solid fraction is subjected to alkaline extraction compost. For this purpose, a vessel containing a solid fraction, making a dry sample of alkali and pour water to give a final concentration of alkali in the reaction mixture of 0.1 - 1.0N. and the temperature of the mixture to achieve 20 - 50 o C. These temperatures and the concentration of the alkaline solution is necessary from the point of view of efficiency of the process, their values were obtained experimentally. The required amount of alkali to obtain the indicated final concentration is determined by calculation.
The resulting mixture was stirred well and advocate for the separation of alkali extract. The supernatant (alkaline extract) is decanted into a separate container. It is possible to extract the resulting alkaline solution to neutralize the acid and then mix it with the previously prepared bacterial suspension. To increase the stability of the preparation when stored in conditions of high ambient temperature environment (more than 20 - 25 o C) the mixture may be subjected to neutralization with an alkali extract of bacterial suspension. When this happens mostly lysing microflora, which prevents further fermentation of the finished liquid formulation. Furthermore, in the process of lysing bacteria of selection occurs other nutrients which are useful for improving plant growth characteristics.
Or otherwise obtained by the mixture of extract and alkali bacterial suspension was stirred and decanted. Insufficient fluid is a liquid, the desired product, which was emptied and filled into containers.
To improve the quality of the target product remaining after separation of the liquid extract of the precipitate of alkaline water is poured at a temperature of 30 - 50 o C in a volume equal to the volume used for the extraction of the alkaline solution. The temperature of 30 - 50 o C is optimal in this case and set experimentally. The resulting mixture is well stirred and decanted. The supernatant liquid (slurry wash) was combined with the previously isolated alkaline extract. This operation is repeated at least twice. Subjecting the mixture to neutralize alkaline extract with flushing suspensions (before mixing with the bacterial suspension), or the final mixture of the alkaline extract of the bacterial suspensions and washing the slurry.
For alkaline caustic extraction can be used lithium, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or aqueous ammonia solution. Processing sludge compost these alkaline solutions is most effective, because this is accompanied by the formation of water-soluble salts, humates. Sludge treatment, such as calcium hydroxide solution gives a smaller effect because calcium humate poorly soluble in water. The optimum volume ratio of the precipitate fraction and the alkaline solution is from 1:10 to 1:20, depending on the moisture content of sludge. Defending liquor mixed with sludge compost produced within 30 minutes. This time is sufficient to separate the mixture, more settling time increases the technological cycle.
The neutralization of alkaline extract its mixture with flushing suspensions or the final mixture of the extract, washing suspensions and bacterial suspension produced to a pH environment of 7 - 8. These values are the optimal pH of the medium in terms of maintaining nativity biologically active substances and the viability of spores in the soil microflora finished product. Thus the neutralization can be carried out using inorganic acids. Nitric acid is preferred, because formed in its application nitrate which are useful as plant nutrients. Uses for neutralization, for example, hydrochloric acid is less effective as chlorides thus formed and the use of sulfuric acid results in the formation of sulfates. The presence of both of those, and other salts in the finished product is undesirable for soil treatment and plant. Using, for example, phosphoric acid leads to deterioration of the organoleptic properties of the product - the appearance of unpleasant odors.
To neutralize can be used and organic acids such as oxalic, malic, citric, succinic. The most preferred is the use of citric acid or succinic acid. Citric acid imparts a higher quality of the drug, as in neutralizing the formed chelate compounds with nutrient macro- and microelements. The use of succinic acid enhances the growth properties of the drug, since it in itself is a stimulant plant growth.
Settling mixture neutralized extract (extract mixture neutralized with suspensions flushing) is performed with the bacterial suspension for 10-12 hours: this time is sufficient for effective separation of the mixture and isolating the desired product. In this bacterial suspension prior to mixing it with the extract in a separate vessel kept at a temperature of 30-35 o C.
As gummusosoderzhaschego raw materials can be used zookompost or BioPeregnoy obtained biotechnological utilization of organic waste (manure) invertebrates, especially larvae of synanthropic flies. Zookompost is an excellent organic fertilizer, which has pesticidal activity. Therefore zookomposta extracts obtained via the present invention will possess biopesticidal properties.
gumusosoderzhaschih and as substrates for preparation of extracts of the proposed method can be used composts.
EXAMPLES OF METHOD
Example 1. The flask was placed 250 L of a sample of 10 kg of compost with 45% humidity. Then, it is soaked 3-5 volumes of water (30-50 L) at a temperature of 30-35 o C, the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes and bring to obtain a water-soluble bacterial extract containing the substance of the slurry vermicompost and soil microorganisms - microbiocenosis compost. This aqueous extract is poured into a separate container and the drive 1 is left at a temperature of 30-35 o C. To the residue was soaked compost is added 20 volumes (200 L), 0.2N. potassium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 40-50 o C, the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes and bring to give an alkaline extract of brown color which is drained (pumped) into a drive 2. The remaining residue is poured in the same volume (200 l) of water at 40 50 o C, stirred again and defend for 30 minutes to obtain a first aqueous wash hood, and that drained (pumped) into the drive 2. Then compost the remaining sediment is poured again in the same volume (200 liters) of water at a temperature of 40-50 o C and procedure repeat to obtain a second wash hood, and which is poured into the hopper 2.
The alkaline extract was combined in the storage vessel 2 by wash with aqueous suspensions of nitric acid solution was neutralized to pH values of the medium 7 - 8, to give the neutralized aqueous extract. Next to the neutralized extract was added from the drive 1, the bacterial suspension. The thus obtained total aqueous extract was stirred and allowed to stand overnight and the resulting liquid formulation is dispensed from the container in a compost.
The remaining residue on non-waste technology is used in the future to obtain drugs humic acid, fulvic acid and humic compounds in the form of liquid, paste or dry products.
Example 2. Same as in Example 1, but instead of potassium hydroxide soaked compost to the residue was added 200 l of 0.2N. sodium hydroxide solution and the temperature is 40-50 o C, and the mixture was stirred for 30 min defend give alkaline extract. The neutralization is conducted and a nitric acid solution until pH value of the medium 7 - 8.
Example 3. Same as in Example 1, except that instead of potassium hydroxide soaked compost to the residue was added 200 l of 0.2N. ammonia solution.
Similarly, other tests were conducted to implement the inventive method using both the boundary values (concentration of 0.1-1.0 N alkali. And the temperature of the reaction mixture of 20-50 o C), average values (concentration 0.15 N alkaline solution. And reaction temperature 30-50 o C), and go beyond the boundary values (concentration of the alkali solution and 0.01-0.05 1.05-1.10 n., and the temperature of the reaction medium 10-15 o C and 55- 90 o C).
For the industrial production of a liquid formulation can be applied line, based on the use of industrial washing machines of the type KP-019. and may for this purpose the use of standard vessels reactors capacity 630 liters or more.
As a result of experiments it was established that:
- in the preparation of water extract of the compost at a temperature of 20-35 o C in the aqueous phase is extracted only 2-3% of soluble substances of compost;
- alkali solution at a concentration of less than 0.1N. humic substances reduced extractability of the compost pellets in a concentration above 1.0 N alkali. extractability humates and fulvic acids increases, but there are losses of some labile biologically active compost materials;
- at a reaction temperature below 20 o C extraction of the humic substances it is much slower, thereby reducing the quality of liquid drug and increases the time of its production, and at a temperature above 60 o C in a basic medium hydrolysis of humic substances, but also inactivation of certain biologically active substances and lysing cells of representatives of soil microflora.
The proposed method is now widely used on an industrial scale to produce valuable high performance stimulator of plant growth and development. Production of the drug by the inventive process is carried out on a number of agricultural enterprises (livestock complexes) in the Russian Federation (Vladimir, Rostov, Leningrad and Moscow regions, the Udmurt Republic) and in the Republic of Belarus (Minsk, Vitebsk region).
Feedstock - compost is not only a valuable organic and environmentally friendly fertilizer. It can be regarded as not only natural ingredients humic substances, but also a number of biologically active substances which are absent in the peat, and lignite. The proposed method makes it possible to extract almost all compost ingredients in water-soluble state: humic acid, fulvic acid, vitamins, growth regulators, and plant development, bacteriological and fungicides, as well and micro- and macronutrients and spores of soil microorganisms.
The liquid preparation of the compost produced by the proposed method is a dark brown, odorless liquid. Its use in agricultural practice, environmentally safe for humans and for animals and soil microflora.
It has the following important properties:
- enhances seed germination and vigor;
- It stimulates root formation, growth and development of plants;
- increases crop yields;
- reduces the amount of nitrates in the plants;
- inhibits certain bacterial and fungal pathogens of plant diseases.
These studies confirm the above properties of the liquid preparation of compost are shown in Table. 1-5.
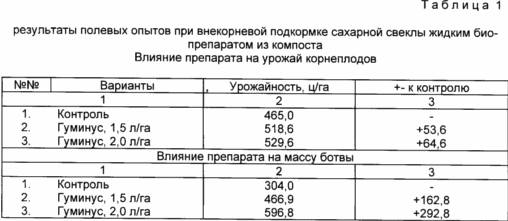
The biological activity of a liquid preparation, obtained by the claimed method was tested in a leached chernozem on sugar beet varieties "Ramonskaya odnosemennaya 47" in the Institute of rape (Lipetsk). Crop processing performed in the period of intensive growth of the roots via foliar application (spraying on leaf surface) at a dose of 1.2 l / ha. Results from field tests are shown in Table. 1. From the Table. 1 data show that the liquid preparation of compost for example sugar beet stimulates root formation, growth and development of plants.
Assessment of the liquid preparation of the compost on the fungicidal activity in vitro was carried out at the Research Institute of Phytopathology (n. Odintsovo, Moscow Region.). Were evaluated in vitro the effect of this drug on the pathogens causing root rot and wilt: Fusarium graminearum, Rhizoctonia solani; on the pathogen gray mold Botrytis cinerea; to the pathogen Septoria Septoria nodorum; at the blast pathogen Pyricularia oryzae. In parallel, we assessed the sensitivity to the drug causative agent of bacterial blight of cotton Xanthomnas malvacearum. The drug is introduced into the molten potato-glucose agar at different concentrations. The effectiveness of the drug was determined by the degree of inhibition of growth of colonies of pathogens cutting culture placed on the environment with the drug. As widely known standards used fungicides TMTD, and benlat folikur. The results are shown in Table. 2, which show that the tested liquid formulation of the compost at certain concentrations in vitro has provided significant fungicidal effect on F. nivale, R. solani, B. cinerea, S. nodorum, R. oryzae and less pronounced on F. graminearum. Detected bactericidal activity against X. malvacearum. Thus, the liquid preparation of the compost can be used in seed dressing to remove seminal infections.
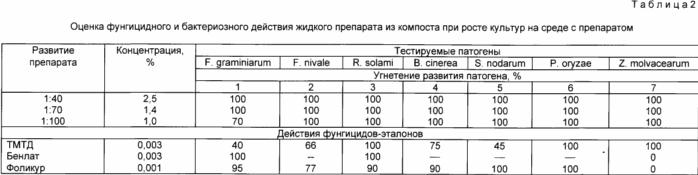
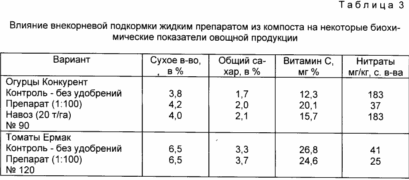
Table. 3 presents data on the effect of processing liquid preparation of compost on some biochemical indices of vegetables grown under irrigation. A single processing liquid formulation at a dose of 3.5 l / h, diluted with water 100 times resulted in increased yields of up to 20% of vegetables. This was accompanied by an increase in dry matter accumulation, increasing the percentage of sugars and vitamin C at the same time substantially reducing the content of nitrate and vegetable products (2.0-4.5 times).
Conducted field tests of a liquid formulation for the treatment of seeds and plants in the phase of earing crops in the conditions of northern and central agro-climatic zones of the Tambov region (tab. 4). It has been found that soaking the seeds in a liquid formulation dose of 1 l / m foliar application and seed plants in a dose of 0.8 l / ha on the cereal crop raised 3,9-16,5%.
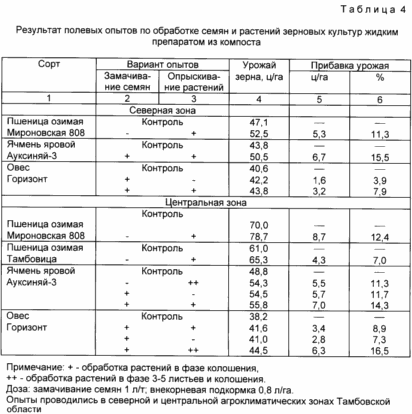
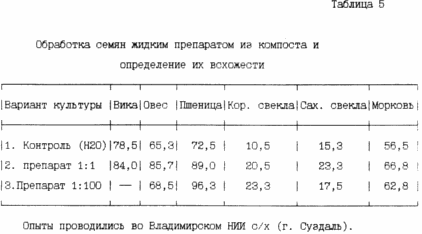
Table. 5 presents data on the effect of treating seeds with a liquid formulation of the compost on germination, which show that the liquid preparation is diluted with water, increased seed germination wiki, oats, sugar beet and carrots, fodder beet and wheat.
Implementation of the proposed method for producing a liquid preparation of gumusosoderzhaschih substances does not require special equipment (autoclaves, centrifuges) and catalysts. Alkaline extraction is conducted at a temperature of 20-50 o C, which greatly reduces energy consumption, material costs and of metal, thereby increasing the efficiency process for producing a liquid preparation. At the same time, as the results of these experiments, obtained a liquid preparation with high activity, which stimulates root formation, plant growth and development, increases seed germination and crop yields, reduces the amount of nitrates in agricultural products. In addition, it contains fungicidal and bacteriological pronounced activity in seed dressing to allow some seed eliminate infection.
Upon receipt of the proposed method for a liquid preparation from the remaining residue by composting waste technology used for further humates, humin and fulvic acids in the form of concentrated aqueous solutions, pastes, powders or dry fertilizing pastes.
CLAIM
1. A process for producing liquid biostimulant plant growth and development of gumusosoderzhaschih substances by extraction with alkaline extraction followed by neutralization, characterized in that as starting material a gumusosoderzhaschego livestock manure waste companies, biotechnology previously passed for processing compost from the compost further separated aqueous bacterial slurry to produce compost which is soaked in water, it is extracted from the bacterial mass in the aqueous solution, the resultant bacterial suspension was separated from the solid compost fraction is subjected to alkaline extraction and the resulting solid fraction, and extraction is carried extracts 0.1 - 1.0N. alkaline solution at 20 - 50 o C followed by the separation of the liquid extract, the latter being mixed with the bacterial suspension and defend to obtain the desired product.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the alkaline extract was subjected to neutralization prior to mixing with the bacterial suspension.
3. The method of claim 1, wherein the mixture is subjected to an alkali neutralization of the extract with a bacterial suspension.
. 4. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the liquid remaining after separation of the solid fraction of the extract alkali water is poured at a temperature of 30 - 50 o C in a volume equal to the volume used for the extraction of the alkaline solution, the resulting mixture is stirred, settled and the washing liquid are mixed slurry with the previously isolated alkaline extract and the mixture was subjected to neutralization with an alkali wash extract slurry.
5. The method of claim 4, wherein the operation of obtaining the wash suspension is repeated at least twice.
6. The method according to claim 1, characterized in that the pre-biotech recycling for compost spend vermicultivation methods, solid-state fermentation or natural composting.
7. The method of claim 1 or claim 6, characterized in that said composts with a humidity of 45 - 65%.
8. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the compost to obtain an aqueous mixture using water at a temperature of 30 - 35 o C.
9. The method of claim 1, wherein the aqueous mixture is prepared by composting the compost volume ratio: water of from 1: 3 to 1: 5.
10. The method according to claim 1, characterized in that the bacterial mass produce separation by settling, filtration, centrifugation or by separation.
11. The method according to claim 10, characterized in that the sedimentation of the aqueous mixture to produce compost is carried out in the bacterial suspension for 30 minutes.
12. The method according to claim 1, characterized in that as alkali caustic used lithium, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide or aqueous ammonia.
13. The method of claim 1, wherein the volume ratio of the precipitate fraction and the alkaline solution is from 1: 10 to 1: 20 depending on the humidity of the first.
14. The method of claim. 1, characterized in that the sedimentation liquor sludge compost mixture to obtain a liquid extract is carried out for 30 minutes.
15. The method according to any one of claims 1 - 3, characterized in that the neutralization is carried out to a value of pH of the medium, of 7 - 8.
16. The method according to any one of claims 1 - 3, characterized in that the neutralization is carried out with mineral acids, preferably nitric acid.
17. The method according to any one of claims 1 - 3, characterized in that produce neutralizing with organic acids such as oxalic, malic, citric or succinic.
18. The method according to claim 13, characterized in that the neutralization is preferably used, citric or succinic acid.
19. The method according to any one of claims 1 - 3, characterized in that the sedimentation mixture neutralized extract with a bacterial suspension is carried out for 10 - 12 hours.
20. The method of claim 1, wherein the resulting bacterial suspension prior to mixing it with the extract stored at 30 - 35 o C.
print version
Publication date 04.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.