| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2233577
![]()
A method of controlling environmental factors PLANTS IN GROWING
Name of the inventor: Molchanov AG
The name of the patentee: Stavropol State Agrarian University
Address for correspondence: 355017, Stavropol, trans. Zootechnical, 12, Samara State Aerospace University, patent office
Starting date of the patent: 2003.04.14
The invention can be used in agriculture, phytotron, biotechnical human life-support systems in research in the field of physiology, but also in research to explore the potential of plant capacity. The method includes an automatic change of environmental factors, depending on the photosynthetic productivity of plants and the accumulation of the main photosynthetic pigments. Upon reaching the maximum in the daily course of photosynthesis, the levels of environmental factors changed to optimal values of conditions to ensure the greatest accumulation of the major photosynthetic pigments. After that environmental factors alter the levels of the conditions to maximize photosynthetic efficiency of plants. The method allows to increase the intensity of the process of photosynthesis and energy savings.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention can be used in agriculture, phytotron, biotechnical human life-support systems in research in the field of physiology, but also in research to explore the potential of plant capacity.
There is a method of regulation of environmental factors to optimize photosynthesis of plants (AS USSR №535921, cl. A 01 G 7/00, 1975), where the control of environmental factors is performed, depending on the level of photosynthesis, measured by the gas composition of the atmosphere assimilation chamber with plants. However, this method of optimization of photosynthesis associated with significant energy costs for maintenance of environmental factors at a high level.
The closest in technical essence and attainable positive effect and adopted by the author as a prototype of a method for optimizing environmental factors when growing plants (AS USSR №456595, MKI A 01 G 7/00, 1975), including their automatic adjustment in accordance with plant needs for environmental factors which continuously change in accordance with time-varying point of maximum optimality criterion photosynthetic productivity of plants in the n-dimensional space controlled factors. This method uses information about the state of the object only on its photosynthetic productivity. However, it is known that the rate of photosynthesis and the level of concentration of photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll, carotenoids, etc.) Are directly proportional, ie with a decrease in pigment concentration decreases the rate of photosynthesis, and vice versa (Rabinovich E. Photosynthesis -. M .: IL, 1959). It is also known that to maintain the rate of photosynthesis at a relatively high level of relatively high levels required by environmental factors. For example, for most varieties of cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, wheat, sunflower, and other crop optimal levels of temperature, illumination, concentration of CO 2 are respectively in the range of 30 ... 40 º C, 20,000 ... 80,000 lux 0.3. ..1,5%. But these relatively high levels of temperature, light exposure, the concentration of CO 2 have a depressing effect on the accumulation of photosynthetic pigments, moreover, the high levels of factors of plant habitats contribute to the rapid removal of leaf chlorophyll, carotenoids and other photosynthetic pigments (1 Akimova TW and others. The effect of temperature and light on the content of pigments in the leaves of cucumber -.. Proc .: Ekologofiziologicheskie mechanisms of plant resistance to extreme temperatures -.. Petrozavodsk, 1978, p.74 ... 80 2. Problems of chlorophyll biosynthesis / Ed . Shlyk AA - Minsk: Science and Technology, 1971 252 3. Gaponenko VI The influence of external factors on chlorophyll metabolism - Minsk.. Science and Technology, 1976, 240 p 4. Kaler VL. . autoregulation of chlorophyll in higher plants - Minsk.... Science and Technology, 1976, 192 5. Rabinovich E. Photosynthesis - M .: IL, 1959, with 715 6. Lebedev SI, etc. Changes in the structure. and function of chloroplasts of various crops during germination conditions. - In the book .: chloroplasts and mitochondria. - M .: Nauka, 1969, p.164 ... 172).
Therefore, if the external environment factors are maintained at a relatively high level for the high-intensity of photosynthesis (as proposed in the known method AS №456595), then this will inevitably lead to a decrease in the concentration of photosynthetic pigments. Reducing the concentration of pigments, of course, lead to a decrease in the rate of photosynthesis at relatively high levels of external environment (Rabinovich E. Photosynthesis -. M .: IL, 1959, 715 pp.). Therefore, to increase the rate of photosynthesis to optimal values necessary to increase the light level, temperature, CO 2. This means that the photosynthesis of plants is carried out with a very low energy efficiency, which leads to unnecessarily high consumption of thermal and electrical energy.
The aim of the present invention is to intensify the process of photosynthesis and energy savings.
The purpose of the invention is achieved by the method of controlling environmental factors when growing plants involves them automatically change depending on the photosynthetic productivity of plants with the change in external environmental factors is performed additionally based on the accumulation of basic photosynthetic pigments, wherein when a maximum in the daytime during photosynthesis levels of environmental factors changed to optimal values of conditions to ensure the greatest accumulation of the main photosynthetic pigment, and then environmental factors alter the levels of the conditions to maximize photosynthetic efficiency of plants.
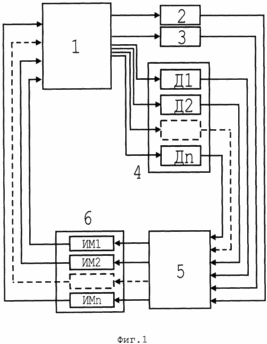 |
The essence of the method is illustrated a functional diagram shown in Figure 1 and the graphical illustration shown in Figure 2. Functional diagram (Figure 1) contains: 1 - regulatory entity (assimilation chamber with plants); 2 - the gauge of the state of the controlled system for photosynthesis; 3 - the gauge of the state of the controlled system for chlorophyll; 4 - Sensors levels of environmental factors; 5 - a multi-channel controller; 6 - actuators. |
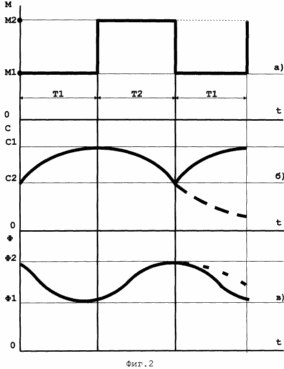 |
Figure 2 shows: a) - the change in levels of environmental factors; In this case the following notation:
|
The dashed line in Figure 2 shows a possible change in the concentration of photosynthetic pigments (b) the rate of photosynthesis and (c) if the value of M2 levels of environmental factors (a) to a value not changed after the photosynthesis M1 value F2.
The daily course of photosynthesis intensity characteristic of significant unevenness - raising periods are replaced by periods of decline. According to the proposed method for controlling environmental factors levels in the recession period of photosynthesis in the object 1 (1), the conditions for the greatest accumulation of photosynthetic pigments. The values of the levels of environmental factors in which the plant produced the largest concentration of photosynthetic pigments mistaken for M1, and the time during which the concentration of photosynthetic pigments reaches its greatest value - T1 (Figure 2, B).
By creating a plant for the time T1 is the largest concentration of photosynthetic pigments C1, ie, this technique increases the potential for the plant to increase the intensity of photosynthesis, with the help of the control unit 5 and actuators 6 varying levels of environmental factors to optimal values for maximum M2 F2 intensity of photosynthesis.
Monitoring the levels of environmental factors produced sensors 4, the rate of photosynthesis - sensor 2, the concentration of colored pigments - sensor 3. After reaching the intensity of photosynthesis maximum F2 determined by the sensor 2 and the control unit 5 changes the levels of environmental factors control unit 5 via executive M1 mechanisms 6 to values which provide the greatest accumulation of photosynthetic pigments. After the greatest accumulation of photosynthetic pigments defined sensor 3 and the control unit 5 changes the level of environmental factors by the control unit 5 by actuators 6 to M2 values that provide a maximum photosynthesis against high concentrations of pigments. Of course, these M2 levels much lower than those that would ensure the same level of intensity of photosynthesis, but against the background of a low concentration of pigments (AS №456595). This means that the rate of photosynthesis is provided in the method of lower energy costs. Then, level control process of environmental factors periodically with T1 and T2 intervals, repeated.
Unlike the prototype after the photosynthesis maximum change levels of environmental factors to create an environment in which there is the greatest accumulation of photosynthetic pigments, and after the plant was the largest accumulation of photosynthetic pigments, n environmental factors levels are changed to values that maximize the rate of photosynthesis with simultaneous saving of energy, since In this case, the maximum photosynthesis provided by lower energy costs due to the presence of well-developed plant photosynthetic system.
The proposed method was tested in laboratory conditions in a climatic chamber PMMC 1250 type produced in Germany. Laboratory tests have shown high efficiency of this method and perspective. Plants experienced option favorably compared the quality and pace of development in comparison with the plants in the control variant. This power savings of 40%.
CLAIM
A method for controlling environmental factors for growing plants, said method comprising automatically change depending on the photosynthetic productivity of plants, characterized in that the change of the environmental factors is performed additionally based on the accumulation of basic photosynthetic pigments, wherein when a maximum in the daytime during photosynthesis levels factors of medium was changed to optimal values of conditions to ensure the greatest accumulation of the main photosynthetic pigment, and then environmental factors alter the levels of the conditions to maximize photosynthetic efficiency of plants.
print version
Publication date 04.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.