| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2129766
![]()
METHOD FOR GROWING CORN GRAIN IN IRRIGATION melkodispersnaja
Name of the inventor: Borodychev VV .; KOLGANOV AV .; Saldana AM .; A. Mayer
The name of the patentee: Borodychev Viktor; KOLGANOV Alexander; Saldana Alexander Kravchuk; Meyer Alexander
Address for correspondence: 400059, Volgograd, GSP, ul.Izolyatornaya, 2, kv.89 Saldaevu AM
Starting date of the patent:
The method for growing corn in irrigated areas and can be used in agriculture. The method includes tillage and sowing seeds shirokorjadnyj by forming in the soil compacted bed and soil compaction rollers, interrow care and irrigation. Soil treatment is carried out in two periods: in the autumn with a turnover of formation, and in the spring before planting - deep loosening volume turnover without seam. Levelling and compacting topsoil combined with sowing. Irrigation alternate with large and small irrigation rates. Small particulate performed irrigation rates irrigation rate of 200 - 250 l / h / m for 0.5 - 2.0 hours at a temperature above 25 o C and a wind speed greater than 5 m / s. The use of the invention to be sure that stable yields of corn cobs with good filling.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to agriculture and can be used in growing corn on irrigated lands.
There is a method of cultivation of corn, comprising one-two-fold shallow plowing predecessor, the application of organic and mineral fertilizers, moldboard plowing to a depth of 25-27 cm, seedbed moisture-tillage, seeding rate of 30 - 35 thousand plants for early maturing hybrids and 25 - 30 thousands of plants for Middle-hybrids, but also inter-row treatments and ridging rows (method of cultivation of corn Compiled G.P.Dikanev / Factsheet N 242-94 Volgograd CNTI -.. - Volgograd. 1994).
The proposed technology of cultivation of corn on irrigated land dry steppe zone of chestnut soils of the Volgograd area can provide a grain of culture to 2.5 - 3.5 t / ha, subject to availability of stocks of moisture in the layer 0 - 70 cm and precipitation during the growing season. However, in the Lower Volga region every third year is unfavorable due to drought.
Some of these drawbacks is eliminated in the known method of cultivation of corn rainfed dry steppe zone of chestnut soils on the author's certificate N 1761014, providing for sowing maize seeds with aisles 2 · 70 + 140 centimeters (cm. The method of cultivation of corn rainfed dry steppe brown zone . soil Compiled GP Dikan / Factsheet N 166-95 Voglogradskogo CNTI -. - Volgograd. 1995).
This process due to lack of moisture reserves in the root horizon ensures efficient use of the area occupied by corn. Progal width of 1.4 m between the rows of corn are a place of intensive growing annual and perennial weeds. "Edge effect" of the two rows of corn does not provide a yield increase of grain.
There is a method of cultivation of corn for grain, including irrigation in compliance with the specified mode of soil moisture, in which, in order to obtain high stability of grain crops in regions with frequent air droughts attributable to the flowering period with a decrease in water consumption in the period from planting to phase appearance 7 - 8 leaves, soil moisture is maintained at critical, then produce four irrigations per phase by the beginning of the emergence of 7 - 8 leaves, 11 - 12 leaves before flowering with the appearance of panicle and before flowering cobs with the appearance filaments, standards-settled according to the formula ![]()
where P in - the desired irrigation rate of the i-th regular watering, m 3 / ha;
i - the number of watering, i = 1, 2, 3, 4;
HB i - the lowest average moisture content of the soil layer occupied by the roots to the end of the inter-irrigation interval, m3 / t;
V - volume weight of soil, t / (ha · m 3);
W i - moisture reserves in the root zone at the start of watering, m 3 / ha; ![]() W i + 1 - - increment of moisture content at the expense of root growth in the inter-irrigation period, m 3 / ha;
W i + 1 - - increment of moisture content at the expense of root growth in the inter-irrigation period, m 3 / ha;
h i + 1 - kornezanimaemogo depth of soil at the end of irrigation interval, m;
W k i + 1 - critical soil moisture at the time of the next (i + 1) -th watering% of HB;
VP i, i + 1 - culture water consumption in the period from the i-th watering to (i + 1) -th watering m3 / ha; ![]() i - the value threshold defined by pre-irrigation moisture relative critical humidity,% of HB, the values of
i - the value threshold defined by pre-irrigation moisture relative critical humidity,% of HB, the values of ![]() i set in the ranges:
i set in the ranges:
-10 ![]()
![]() 1
1 ![]() -5; -10
-5; -10 ![]()
![]() 2
2 ![]() -5; 5
-5; 5 ![]()
![]() 3
3 ![]() 10,
10, ![]() > 0,
> 0,
and the fourth (i = 4) and subsequent irrigations carried erosion permissible do not exceed the excess of superficial and deep discharge, the standards provide maximum transpiration ( ![]() > O) and consistent with the traditional modes of irrigation; while strongly drought weather in the early periods of the development of culture, but not before phase 3 leaves allow a brief rise of the critical humidity of the humidity level is 10 - 15%, and only when this difference is exceeded sustainable irrigation norm carried, calculated using the formula with the value
> O) and consistent with the traditional modes of irrigation; while strongly drought weather in the early periods of the development of culture, but not before phase 3 leaves allow a brief rise of the critical humidity of the humidity level is 10 - 15%, and only when this difference is exceeded sustainable irrigation norm carried, calculated using the formula with the value ![]() i =
i = ![]() 1 (SU, Inventor's Certificate, N 1554818, cl 5 M. A 01 G 1/00, 25/00;.. A 01 B 79/02 method of cultivation of corn // Dobrachev YP, Demchenko NP ., Holovaty VG and Chekhov A. Stated 14.09.1987, published on 04.07.1990).
1 (SU, Inventor's Certificate, N 1554818, cl 5 M. A 01 G 1/00, 25/00;.. A 01 B 79/02 method of cultivation of corn // Dobrachev YP, Demchenko NP ., Holovaty VG and Chekhov A. Stated 14.09.1987, published on 04.07.1990).
The described method of cultivation of corn in the conditions of irrigated agriculture requires large amounts of irrigation water and provides for at least seven irrigations with the water application rate of 400 - 700 m 3 / ha.
Known and the method of fine sprinkling of annual crops by introducing irrigation irrigation norm one-time irrigation rates determined based on climate indicators, which, for the purpose of ecological irrigation water, as climate indicators using statistical data on the number of days and number of hours in a day with temperatures above optimal for a given culture at the heart of its development phase, and the irrigation rate is determined by the following relationship:
M = m ![]() ·
· ![]() ·
· ![]()
![]() .
.
where M - irrigation rate, m 3 / ha;
m ![]() - A one-time, irrigation rate, m 3 / ha;
- A one-time, irrigation rate, m 3 / ha; ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() - Respectively, the number of days and number of hours in a day with a temperature above the optimum for this crop in the main phase of its development (SU, Inventor's Certificate, N 1732864. M.kl. 5 A 01 G 25/02 Ivantsova TI, Khrabrov M. .YU. // method fine sprinkling of annual crops. Stated 24.04.1989, published on 15.05.1992).
- Respectively, the number of days and number of hours in a day with a temperature above the optimum for this crop in the main phase of its development (SU, Inventor's Certificate, N 1732864. M.kl. 5 A 01 G 25/02 Ivantsova TI, Khrabrov M. .YU. // method fine sprinkling of annual crops. Stated 24.04.1989, published on 15.05.1992).
The method described in the cultivation of the fine sprinkling corn in the conditions of climate ostrozasushlivogo Russia Lower Volga region can be effective only if the fall were performed recharge irrigation and in the layer 0 - 70 cm soil moisture is sufficient for the entire growing season.
Known and the method of fine sprinkling of corn for grain, which includes, along with irrigation - nine irrigation irrigation rate of 4300 m 3 / ha dual console sprinkling machines DDA-100MA family when the air temperature above 25 o C, finely dispersed moisture 800 L / ha per hour with a share these deposits of 14-17% (see sprinkling of finely divided corn Compilers VV Borodychev, A. Mayer, TM Lytkova // Factsheet N 91-93 Volgograd CNTI -... - Volgograd. 1993) .
The described method requires significant improvements dual console design sprinklers DDA-100MA type of machine that could perform simultaneously or alternately two types of irrigation - irrigation and drip dispersion.
Known and the method of combined irrigation of corn in the conditions of the Trans-Volga Volgograd region, where upon reaching 70 - 80% HB drip irrigation, irrigation is carried out finely divided every 0.5 hours (see Irrigation of corn in the conditions of the Trans-Volga Compilers V.V.Borodychev, A.. .In Meyer // Factsheet N 131-94 Volgograd CNTI -.. - Volgograd. 1994).
This method is effective when the soil moisture reserves at least 70% HB.
Known and the method of cultivation of corn, which, along with well-known cultural practices, carried out finely dispersed irrigation during the growing season at intervals of half an hour of irrigation, an hour and two hours (see. The productivity of maize under mist sprinkling. Compilers A.V.Kolganov V. V.Borodychev // Information sheets N 54-95 Volgograd CNTI -. - Volgograd. 1995).
The described process, in spite of the overall decline in water consumption, does not provide sustainable produce maize harvests of grain due to soil moisture deficit during flowering and ripening molochnovoskovoy.
The closest way for the same purpose to the claimed subject on the set of attributes is a method of sowing, including soil treatment and shirokorjadnyj sowing seeds by forming in the soil compacted bed, seed placement, closing the bed soil and soil compaction rollers with a simultaneous shift towards the top layer of soil and Education soil ridges in which after laying the seed in the compacted bed is carried offset from the sides of the soil bed and its indentation together with the seeds in the bottom of the bed, and the soil ridges formed by shifting to push aside the topsoil on a bed of seeds and then combs seal (RU patent N 2086087. IPC 6 A 01 C 7/00. method and seeding device for its implementation //I.P.Kruzhilin, AM Saldana, J. B. Kruzhilina VI Pyndak. Stated 17.01. 1995 published 08.10.1997).
By the obstacles to achieve the desired technical result, when using the known method adopted for the closest analogue is the lack of guarantees of obtaining crop corn iz-za deficit of soil moisture and wilting plants at temperatures above 25 o C and wind speed of more than 5 m / s ostrozasushlivye periods of the season.
The invention consists in the following.
The problem to be solved by the claimed invention - more efficient use of soil moisture reserves and reducing irrigation water consumption.
The technical result - guaranteed to obtain stable yields of corn cobs with good filling.
Said technical result in the implementation of the invention is achieved by the fact that in the known method of cultivation of maize under mist irrigation, which includes tillage and shirokorjadnyj sowing seeds by forming in the soil compacted bed and soil compaction rollers, inter-row treatments and irrigation, soil treatment is carried out in two periods - autumn with a turnover of formation, and before planting in the spring - deep volumetric loosening without the formation of turnover, while leveling and compacting topsoil combined with sowing and irrigation are alternated with big and small irrigation rates, while small irrigation rates carry particulate irrigation 200 norm - 250 l / h / m for 0.5 - 2.0 hours at a temperature above +25 o C and a wind speed greater than 5 m / s.
Due to the fact that in the early spring before planting is carried surround deep soil loosening without the formation of turnover for aeration and reducing the top layer of warm-up time up to +10 - +12 o C and rational combination of irrigation and sprinkling melkodispernogo achieved above technical result.
The above analysis of the prior art by the applicant, including a search of patent and scientific and technical information sources and identify sources that contain information about the analog of the claimed invention, let it becomes that the applicants have not found an analogue, characterized by features identical to all the essential features of the claimed invention.
Therefore, the claimed invention meets the requirement of "novelty" under the current legislation.
To check the compliance of the claimed invention, the request "inventive step" applicants conducted an additional search for known solutions in order to detect signs that coincide with the hallmarks of the closest analogue of the claimed invention, the results of which show that the claimed invention should not be for the expert explicitly from the prior art, as in the art, certain applicants contemplated effect is not revealed significant changes of the claimed invention to achieve a technical result.
Therefore, the claimed invention meets the requirement of "inventive step" by the current legislation.
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
| ||||
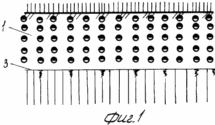
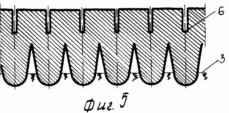
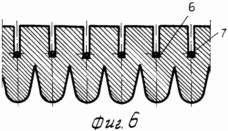
FIG. 1 hard-wired cross-sectional view of irrigated fields after the harvest of the predecessor.
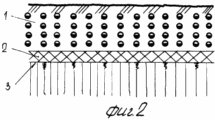
FIG. 2 - the same, after the main processing of the soil formation with a turnover of 180 o and full incorporation of plant and root residues.
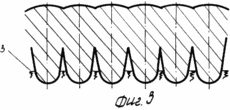
FIG. 3 - the same, after loosening the bulk of the arable layer and subsoil horizon in early spring for aerating the root zone and increase the depth of processing.
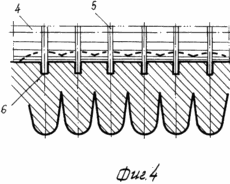
FIG. 4 - the same, compacting topsoil and seed boxes hack.
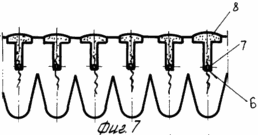
5 and 6 - the deepening of the seed boxes and stacking them in the seeds.
FIG. 7 - sealing of corn seeds and seal nadsemennogo upper soil layer.
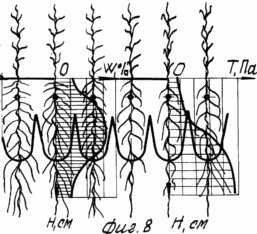
8 - distribution of roots in the soil horizon and above-ground stems with leaves reaching 8-10 in the initial period of the fine irrigation.
Detailed Description of the invention are as follows.
After harvesting the precursor is usually cereal, shallow plowing is carried out in two tracks plows LDG-10 to a depth of 0.06-0.08 m. Depending on the type of soil and nutrient content (on light-brown and medium and heavy loam soils ) introduced in late August to early September 50-60 tons of organic fertilizer, 40% of the calculated dose of nitrogen and all noma of potassium and phosphorus. After the regrowth of weeds spend plowing arable layer 1 to a depth of 0.25 -. 0.27 m plowing carried out with a complete turnover of the reservoir, and the vegetable and root remnants, together with organic fertilizers with a thin layer 2 laid on the plow sole 3 (Figures 1 and 2 ). In this state, topsoil leaves in the winter. Under the conditions of the Bottom Volga region the greatest amount of rainfall in the autumn and winter months of the calendar year. In the arable layer of the accumulation of soil moisture reserves. In the early spring spend harrowing one-two teeth marks in the aggregate harrows coupler C-IIV and crawler tractor DT-75M. Upon reaching the soil temperature above 5 o C is carried out loosening the soil volume without the formation of turnover at a depth of 0.35-0.40 m. To this end, the frame mounted or semi-mounted plows general purpose set the U-rippers that provide profile plow furrows 3 as . curvilinear arcs increments therebetween equal to 0.7 m Thus the soil treatment is performed in two periods - to fall circulation reservoir and the spring before sowing - deep layer volumetric turnover without loosening. Sowing seeds of maize hybrids spend Dnipro I47MV rate of 40-45 thousand units per hectare combined unit, which combines two-piece roller 4 to 5 on the surface of disks and seeding sections mounted pneumatic seeder SUPN-6A. Row spacing -. 0.7 m smooth surface roller 4 aligns irrigated fields, and drives each section of the roller 5 4 6 formed on the soil bed depth of 8.6 centimeters (4 and 5). Passages sowing unit via the milestones of the first passage is applied to the axis of the ditches surround preplant tillage arable layer and subsoil horizon 1 (see. Fig. 3-7). When moving combined sowing unit 7 seed grain corn stacked coulters on the seed bed 6, earthing devices drills backfilled soil 8 and musculoskeletal seeders press wheels make contact with the ground seeds 7 8 (7). Levelling and compacting topsoil combined with sowing. Thus, prior to irrigation of the spring was held three passes tractor units: 1) the cover harrowing to level the field of relief and disturbance of soil cover for retaining moisture reserves in the root horizon; 2) volume loosening plowing and subsurface soil horizon for decompression, aeration and warming of the soil, destroying both weeds early; 3) compacting and leveling topsoil, creating compacted soil bed, seeding and sealing of corn seeds. Irrigated crops are alternated with big and small irrigation rates. Small particulate performed irrigation rates irrigation rate of 200 - 250 l / h / m for 0.5 - 2.0 hours at ambient temperature +25 o C and a wind speed greater than 5 m / s.
In the period 1993 - 1997 gg. in the fields OPH "Irrigated" Gorodishchenskoye district of the Volgograd region were worked out the basic elements of the stated technology of cultivation Medium early, mid-season and srednepozdnih corn hybrids under irrigation in combination drip irrigation and particulate. fertilizer norms determined by compensation coefficients to take away the batteries. soil moisture regimes at different depths were appointed under the scheme 70 - 80 - 70% HB (during the phase of 13 leaves and flowering until the end of the cob - 80% HB, and the rest of the growing season periods - 70% HB). Field experiments were conducted with zoned grain corn hybrids Medium early (FAO = 200-300), mid (FAO = 300-400) and of medium (FAO = 400-500) maturing group. Mineral fertilizer N 180 P 95 K 50 carried by the planned corn harvest of 100 t / ha. Corn seeds were sown in the sustainable soil warming up to +10 o - +12 o C at seeding depth 0.06 - 0.08 m at the end of the first or beginning of the second decade of May the norm (70-75) × 10 3 units / ha, was the period of mid-harvest hybrid (65-70) × 10 3 / ha, and for middle-and of medium - (55-60) × 10 3 / ha. During the growing season to fulfill three inter-row treatments: the first - to a depth of 0.08 - 0.10 m after feeding nitrogen fertilizer (50 kg / ha LW) in phase 4 - 5 leaves of corn, the second - in phase 8 - 9 leaves after re-feeding to a depth of 0.06 - 0.08 m (50 kg / ha ET). Ends the processing plant hilling during the formation of 11 leaves. Watering is carried sprinkler unit DDA-100MA with equipment for fine sprinkling. Indicators fine sprinkling presented in Table. 1 and 2. The temperature conditions affect both the duration of the growing season, and the duration of the period of growth and development of plants. In the period from 1993 to 1997. the amount of biological temperatures from germination to the phase of full ripeness of corn varied from 2129 to 2470 o C. During the period of the growing season in different years conducted from 2 to 3 irrigations, and in more arid respectively 4 - 5 and 6 - 8 irrigations. Irrigation rate varied from 350 to 650 m 3 / ha. Finely dispersed irrigation norm of 200-250 l / h / ha was carried out when the air temperature above 25 o C and wind speed of more than 5 m / s.
Finely dispersed sprinkler irrigation is the main way to create an optimal climate on crops of corn. Technology fine sprinkling is to periodically moistened sheet of plant cover - small drops of water, and is characterized by three main indicators: the size of the liquid droplets deposited on vegetation, a single rate of hydration and the interval between wetting.
The lower limit of the average diameter of the droplets when mist sprinkling can assume 100-150 microns, the optimum droplet diameter - 500-600 microns. The rate of single moisturizing effect on the extent and duration of changes phytoclimate crop parameters. Average rate of single moisture depending on the plant species and their age is 0.6 - 1.2 m 3 / ha. The minimum rate that provides humidity increase by 15-17%, should be at least 0.15 - 0.20 m 3 / ha.
The interval between the humidification set depending on the droplet evaporation time. When the air temperature above +25 o C for maize is equal to the interval 1.00 - 1.05 h Number of days with higher temperatures during the growing season ranges from 30 to 60 depending on the region and weather conditions.. Carrying melkodispernogo irrigation on maize lowers the air temperature by 2 - 4 o C, increases its moisture content 15-20%. The transpiration rate is reduced by 1.3 - 2.0 times, the moisture deficit in sheets - by 10,3-11,5%, the concentration of the cell sap - to 7.7 - 8.0%, the productivity of photosynthesis reaches 19.8 g / m 2 · day.
Application of increasing standards of mineral fertilizers promoted increase in soil digestible forms of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, especially in the initial period of vegetation. Thus, in the forming phase 9 - 10 leaf content of readily available nitrogen in the soil layer of 0 - 35 cm when N fertilizer rate of 120 K 40 P 50 (the planned productivity 10 t / hectare) increased by 11-15% compared with the control ( cm. Table. 5) without fertilizer.
Consumption of nutrients by plants consists of two biological processes: Battery removal of above-ground mass of soil fertility and the cost of construction of the root mass. Battery content in tissues of corn grain is reduced by the end of the growing season, and their presence is noted in the early growing season. The rate of accumulation of nutrients by corn plants in the initial period of vegetation, in the phase formation of 9-10 leaves, were in the range of 9-16% of the maximum content of NPK. nitrogen consumption in corn buttonhole phase was already 30% phosphorus - 26% potassium - 52% in the formation of 17% of the maximum dry matter. During the intensive formation of plant dry matter attributable to the second period of the growing season of maize, at the same time there is an active accumulation of nitrogen and phosphorus. Mass of 1000 seeds of corn with mineral nutrition is higher than the cultivation without fertilizers. Optimal conditions for the formation of high yields of maize are formed in the implementation of irrigation regime in the root zone to 0.7 m. Humidity W and T hardness of the soil in this layer in the cultivation claimed method combined graphs are shown in FIG. 8.
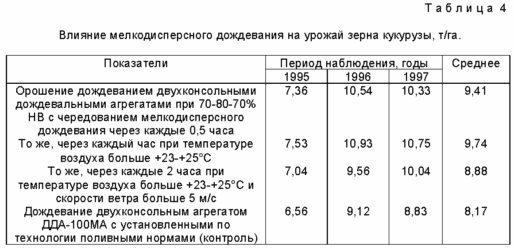
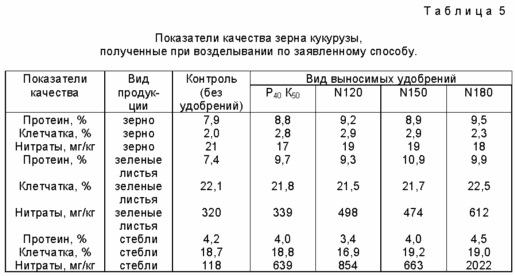
In dry conditions, the Volgograd region a major deterrent implementing productivity potential of this culture is the high daytime temperatures and low precipitation during the growing season. Under the influence of high temperatures observed maize fertilization reduction, t. To. Pollen has a low water-holding capacity, dries quickly and loses its vitality. If the air drought combined with a lack of moisture in the soil, the corn harvest is greatly reduced. Control of environmental factors - humidity increase and decrease in air temperature and soil - produce particulate irrigation. The effectiveness of technology of cultivation of corn with mist sprinkling found in the following process variants: without irrigation (control); drip irrigation sprinkler dual console unit MFD-100MA at 70-80-70% NV; DDF-100MA irrigation pri70-80-80% NV and fine sprinkling at intervals of 0.5; 1.0; 2.0 hours. In all cases were seeded hybrid corn Krasnodar 440MV. Finely dispersed irrigation was performed with the use of additional equipment, mounted on a sprinkler DDA-100MA in the hot and dry days of the growing season to 25 o C. air temperature set out above to maintain the pre-irrigation moisture of soil at 70-80-70% HB level when watering irrigation was carried out by four irrigations with a total irrigation norm, respectively 2100 and 2000 m 3 / ha. When watering, and sprinkling irrigation particulate 5-6 irrigation was conducted in drought years. Irrigating rules made in 2900, 3600 and 2700 m 3 / ha. In the structure of total water share of irrigation water is an average of over 5 years (see table 3.) In normal irrigation - 55.9%, during the sprinkling of fine, depending on the adopted irrigation regime - 48.9 - 53.7%. It is possible to reduce the air temperature at 2 - 5 o C, and the temperature of the leaves - at 2-7 o C. Humidity of the surface air has increased by 12 - 19% water deficit of leaves on the rain-fed area (control) reached 20.9%, with sprinkler irrigation - 11.2 - 13.7%, with mist sprinkling - 8.9 - 9.7%. green mass yield is shown in Table. 3, and the grains - in the Table. 4. grain quality indicators, green leaves and stems of corn are shown in Table 5. In the studies varied widely depending on the mode supported by the soil water, absolute values of the maximum surface area of the sheet in maize data (1993-1997) - from 48,9 to 74.0 thousand m 2 / ha. In the context of natural moisture total leaf surface is not exceeded in hybrid crops Krasnodar 440 MW 23.9 thousand m 2 / ha, VIR 42 - 24,3 thousand m 2 / ha, Dnepropetrovsk 147MV -. 27.7 thousand m 2 / ha ; in irrigated areas the maximum leaf area is formed, respectively, 48.9; 67.7; 53.4 thousand m 2 / ha. In areas with hourly intervals of fine sprinkling area leaves Krasnodar 440 MW hybrid is formed at the level of 51.4 thousand m 2 / ha, which is 15% more compared to conventional indicators in the area of sprinkling. Humidification crops intervals of 0.5 hours and 2.0 determines the formation of leaf area, respectively, in the range of 55.0 - 51.1 and 46,9-53,0 thousand m 2 / m and a longer productivity during the growing period. When particulate irrigation sprinkler in the early stages of growing maize hybrid Krasnodar 440MV correlation coefficient between daily photosynthesis and yield of green mass of 0,936 ± 0,03, and between daily photosynthesis and grain yield - 0,875 ± 0,04. For subsequent growing seasons correlation coefficient between daily photosynthesis and yield of green mass was 0,878 ± 0,02, and between sewage photosynthesis and grain yield - 0,869 ± 0,05. Net photosynthesis of maize productivity increases rapidly in the young plant reaches its maximum in the period of maximum development of the leaf surface.
Conduct a fine sprinkling allowed the plants during the growing season to form the photosynthetic potential (PP) in the amount of 3.03 -. 3.54 million m 3 / day / ha for plant moisture to the time interval, 3.11 - 3.61 and 2.90 - 3.36 million m 2 / day / ha, corresponding to, when wet seeding at 0.5 and 2.0 h This 1.03 -.. 1.30 times more than in the embodiment of a conventional irrigation and 1.7 - 2.1 times more compared to the portion of natural moisture.
With the improvement of the water regime of the soil and plant the corn productivity increases when mist sprinkling, output of crude fat, crude fiber, crude ash, BEV and potassium. Increase of green mass of corn hybrid VIR 42 with mist sprinkling was: on the background of 50% of the HB - 4.6 t / ha, 60% of the HB - 8.6 t / ha, 70% of the HB - 9.0 t / ha compared to the usual irrigation.
On average for 1993 - 1997 years. the maximum yield of green mass amounted to 7.49 t / ha in combination with particulate sprinkling irrigation at 0.5 hours (Table. 3).
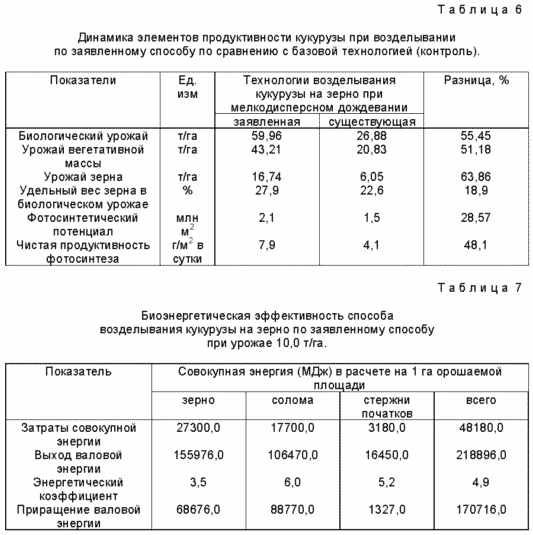
When moisture crops at 1 and 2 hours yield increase compared to conventional irrigation and amounted to 4.6 and 2.8 t / ha and was statistically significant (HCP 0,5 = 1,4 t / ha). The yield of hybrid corn grain Dnipro 147 MW was the largest during the inter-irrigation with a fine sprinkling interval 1:00 (HCP 0,5 = 0,48 t / ha). The dynamics of maize productivity elements in the cultivation of grain according to the claimed method and control is shown in Table. 6. Bioenergy efficiency of the method of cultivation of maize is shown in Table. 7.
Before cleaning all areas were examined: biological productivity is defined and determined on the basis of this method of harvesting corn cobs and justified technological complex machines for cleaning grain and corn post-harvest cycle of undermining and drying grain.
The use of the method of cultivation of corn, combined drip and fine sprinkling makes it possible to obtain a stable grain yield of maize in areas with frequent air droughts, increasing the yield of corn grain in ostrozasushlivye years, resistance to lodging, water use efficiency per unit of production, but also an opportunity high yields with a deficit of water resources. irrigation water savings increased by 18-27%.
Thus, the above data confirm that the performance of the claimed invention using the following set of conditions:
means embodying the invention as claimed in its implementation, is intended for use in agriculture;
for the claimed invention in the form as it is characterized in the independent claim set out below claims, confirmed the possibility of using it in the above application or known before the priority date of the means and methods;
means embodying the invention as claimed in its implementation, is able to achieve a technical result sees the applicants.
Therefore, the claimed invention meets the requirement of "industrial applicability" under the current legislation.
CLAIM
The method of cultivation of corn with mist irrigation, including soil treatment and shirokorjadnyj sowing seeds by forming in the soil compacted bed and soil compaction rollers, inter-row treatments and irrigation, characterized in that the soil treatment is carried out in two periods in the fall with a turnover of formation, and in the spring before seeding - deep bulk loosening without the formation of turnover, while leveling and compacting topsoil combined with sowing and irrigation are alternated with big and small irrigation rates, while small irrigation rates carry particulate irrigation rate of 200 - 250 l / h / ha for 0.5 - 2.0 hours at a temperature above 25 o C and a wind speed greater than 5 m / s.
print version
Publication date 06.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.