| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2154935
![]()
METHOD OF SELECTION OF AGRICULTURAL CROPS
The name of the inventor: Maryanovskaya MV; Tikhonova LV; A. Korshunov; Osipova EV; Masyuk Yu.A. Zeyruk VN; Konoplev GK; Chernikov VI; Yashina I.M. Tolmacheva NA; Balashevich AG; Trofimenkov V.N .; Pchelin VV; Gumanov L.L .; Vyshinsky G.V .; Dubov LI; Shumova TA; Safonov AN
The name of the patent owner: Maryanovskaya Marina Vikentevna
Address for correspondence: 103009, Moscow, Tverskoy boulevard, 14, LLC "House of Nature"
Date of commencement of the patent: 1998.11.27
The invention is intended for use in the field of agriculture, in the technology of cultivation of cucumbers and tomatoes in conditions of protected soil and food potatoes in the open field, which can be used in obtaining environmentally friendly agricultural products. The method includes preparing the soil, planting or planting the plants, periodically cultivating, and characterized in that the seeds and tubers are pre-planted with a mixture of activators, immunostimulants, antagonists and biofertilizers [Avertrop, Agat-25 or Rizoplan, Ampelomycin, Herbamin, Diprin or Nematol, Complex biological Fertilizer (CBU), Symbiont-Universal] in half doses from the recommended for this preparation (mixture 1), the same mixture in combination with biological fertilizers (Biohumus, Root mixture in recommended doses) is applied to the wells before planting, to the soil together with biological preparations Trichogram production wastes or wastes from the production of viral biopreparations (dead butterflies) with sapropel or with a chicken dropper or with powder from naturally fallen leaves or needles (mixture 2), then mixture 1 is followed by periodic land spraying or watering of vegetating plants (once in Two weeks) with preliminary spreading of Biohumus and introduction of the Root Mix into the soil (in the same norms), the soil is populated with a complex of microorganisms, microbiological antagonists contained in biological preparations [Alirin-B, Alirin-S, Batsifit, Gliokladin, Mikostop, Narcissus, Nematofagin or Nematophagin A (activated by the supernatant - a departure from the production of the Diprin biopreparation), Pentofag, Risoplan-F, various forms of Trichodermin, Trichothecin, Phytoflavin, Phytoflavin-L] (mixture 4), in half the recommended doses for this drug, Before planting, further carry out periodic (once in two weeks) spraying or watering plants; Introduced as elements of the fauna of predators and entomophages (Afidiusi, Amblyseusy, Ladybirds, Camels, Gall midges, Goldeneyes, Liselephus, Syrphids, Phytoseus) - complex 1 - by periodic release in half doses from the recommended for this drug and microorganisms, which are the effective beginning of biologics ( Avertrop, Verticilin, Cephalosporin, Entomorfin, Bicol, Bitoxibacillin, Boverin, Vertimex, Mycoafidin-T, Turicid, Entoflorin) (mixture 5), in half doses from recommended for this preparation by periodic treatments - spraying or watering; Before spraying with Diprin and / or Nematol, sodium alginate is used to prevent the nematodes from drying out and die, and when entomophages are used, at the beginning of the growing season for the cultivation of c / x crops, Compositae and / or umbellate plants are additionally planted in the aisles of the main crops, which are an additional source of nutrition For adult entomophages. The method allows increasing the yield, improving the quality of products, eliminating the use of chemical plant protection products, reducing the use of mineral fertilizers, preventing pollution of the environment and harvesting toxic substances
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of agriculture, in particular to the technology of cultivation of cucumbers and tomatoes in conditions of protected soil and food potatoes in open ground.
The aim of the invention is to increase the yield, increase the yield of vegetables or tubers from a unit of exploited area, improve the consumer qualities of agricultural products against the complete elimination of the use of chemical plant protection products, significantly reduce the use of mineral fertilizers, subject to the application of environmentally safe methods and means of suppressing weeds, diseases and pests , Ensuring the prevention of environmental pollution and crop yield of toxic substances.
The stated goal is achieved by the fact that in the cultivation of the claimed agricultural plants in open (potato) or protected (cucumber or tomato) soil conditions, we offer a set of measures to increase the yield and improve the quality of the products of agrotechnical, preventive and protective measures against weeds, diseases And pests set forth in the present application.
There is a known method of non-bred potato cultivation, including the placement of potatoes by the best predecessors, the best stubble, the application of organic fertilizers, autumn plowing of soil, harrowing or cultivation followed by non-rooting plowing, cutting the crests before planting, preplanting tubers, planting crests, interrow cultivation, combating Weeds, protection against diseases and pests with the help of biological preparations, and pre-harvesting of the tops and cleaning of tubers, organic fertilizers are applied at a dose of 60-120 g / ha, harrowing, loosening, cultivation and inter-rowing are carried out when the weeds are in the "white strand "Planting is carried out with warmed-up seed tubers with nested eyelets resistant to diseases of potato varieties, microbiological and entomopathogenic preparations are used for preplant treatment; After planting, the ridge surface is leveled by continuous loosening of the soil, and interrow cultivation begins after emergence of potato shoots with constant growth of ridges with a soil layer of 3-4 cm with simultaneous loosening of the bottom of the furrow and slopes of the ridges, and subsequent 2 - 3 interrowings are carried out at intervals of 10 - 12 days before the potato tops are closed, and microbiological and entomopathogenic preparations are used to protect plants against diseases and pests.
As microbiological and entomopathogenic preparations for the treatment of seed tubers, TRICHODERMIN or RIZOPLAN, or a mixture thereof, or a mixture of TRICHODERMIN and Pristionhus, or a mixture of TRICHODERMIN, RIZOPLANA and Pristionhaus, is used. To protect the potato from diseases, in particular from phytophthora, RIZOPLAN or TRIKHODERMIN, or a mixture thereof, which treat the tops during the growing season of potatoes from pests, in particular from the Colorado beetle, is used as microbiological biological preparations, and as an entomopathogenic biopreparation BITOXIBACILLINE or VIRIN- QL, or a mixture thereof, or a mixture of VIRINA-KZH and RIZOPLANA, or a mixture of VIRINA-KZH, BITOXIBACILLIN and TRICHODERMIN, or a mixture of VIRIN-QL, BITOXIBACILLINE and RIZOPLANA, which treats the tops during the potato growing season; Pre-harvest haulm removal is carried out mechanically, Pristionhus or its mixture with TRIHODERMIN is applied to the soil in autumn after harvesting potatoes under the plowland together with organic fertilizers (2).
Method (2) does not provide reliable protection against potato nematodes, pathogens and migrating imago Colorado potato beetles. The proposed method of cultivating agricultural crops eliminates the listed shortcomings.
There is a known method for the non-bessidic production of ecologically clean agricultural products in conditions of protected soil, including the timely release of a sufficient amount of Enclassia against whitefly and a sufficient number of aphids for aphids that ensure high yields of cucumbers that are devoid of pesticide residues (1).
However, the method (1) does not provide reliable protection against thrips and spider mite, but also from root rot and nematodes, which in recent years have become widespread and widespread.
Example 1. Cucumber cultivation in protected soil conditions.
When cultivating cucumbers in protected soil conditions, a complex of agrotechnical, preventive and protective measures is carried out.
Agrotechnical measures are aimed at obtaining healthy, high-grade and high-yielding plants; Preventive and protective measures are designed to protect cultivated plants from pests and diseases.
We have implemented a systematic approach to the solution of agrotechnical and protective measures, as these two systems of measures organically intertwine, as agrotechnical measures, contributing to the improvement of the general condition of plants, simultaneously increase the resistance of cultivated plants to pests and diseases, reducing the likelihood of their destruction.
In the process of cultivation of cucumbers under protected soil conditions, the culture is often populated by various pathogenic arthropods and microorganisms, the most harmful of which are whiteflies, aphids, thrips, spider mites, root rot and root nematodes causing a dangerous cucumber disease - meloydoginosis.
A special place among pests and diseases of cucumbers under protected soil conditions is occupied by root-knot nematodes, against which we developed a whole array of antinematode measures.
In connection with the fact that among the varieties of cucumbers there are no nematode-resistant varieties (including to the root nematodes), this circumstance makes it difficult to carry out the fight against this dangerous causative agent of the disease - meloydoginosis. However, recent experiments have shown that some new generation biochemicals can still influence the resistance and stability of cucumbers to the root-knot nematode, which we took into account when planning actions against this type of pest.
To increase the stability of cucumber seedlings to pests and diseases in the seedling department, the seeds are treated and two treatments are performed on vegetative plants with a new generation biopreparation called "SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL", which is a 60-70% alcoholic extract from mycorrhizal roots of the medicinal plant ginseng .
The drug is a combination of metabolic products of lower fungi - endophytes with a complex of useful microorganisms, contains a unique complex of hormones, 12 - 14 free amino acids, enzymes, vitamins, pigments, lipids and other valuable substances that strengthen the immune system. The drug is available in ampoules or vials. It has a high degree of stability with a shelf life of 3 years.
Advantages of the biopreparation are: low rates of consumption (operates at a dilution of 0.001%), environmental safety, high efficiency and relatively low cost. SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL is used in a mixture with copper vitriol (0.2 ml of copper sulfate per 1 ml of preparation) with the addition of trace elements - salts of copper, iron, boron, cobalt, molybdenum, zinc, which increase the efficiency of the biopreparation by stimulating the absorption of oxygen by the soil-plant system.
Preparation of the working solution: 1 ml of the preparation is dissolved in 5 liters of water, thoroughly mixed, then 0.2 g of copper sulfate and 1 tablet of microelements are added to the ampoule in 1 ml of SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL, making up a single package.
Prepared in the morning hours working solution of biopreparation in a concentration of 0.002% should be used on the day of its preparation. After soaking the seeds for 1 hour they are removed from the solution and dried, then immediately plated in pre-prepared soil, which is moistened before sowing. For the cultivation of seedlings use containers of various configurations filled with soil - vases, pots, boxes, peat.
Processing of vegetative plants. The first treatment. Treatment with the preparation "SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL" consists in spraying the grown seedlings in phase 1 - 2 of the present leaves with a working solution of the biopreparation at a weaker concentration (0.001%).
Preparation of working solution. At the rate of 1 ml of the preparation and 0.2 g of copper sulfate are dissolved in 100 liters of water to obtain 0.001% of the working solution for the seed area of seedlings per hectare, on the area of 0.5 ha, 0.25 ha and 0.1 hectare, the volume of the prepared solution Accordingly decreases.
Second treatment. Spraying of seedlings grown in the seedling compartment is carried out in the phase 4 - 5 of the present leaves. Plants are sprayed 1 - 2 days before transferring them from the nursery department and disembarking to a permanent place in the greenhouse in a pre-prepared soil. When spraying the planting material, the plant root system should be thoroughly wetted with a working solution of the biological product.
Cultivation of cucumber plants in greenhouses. In the greenhouse in the period preceding the planting of the spent seedlings, the soil is prepared in advance. The technology of soil preparation is as follows. For the first crop rotation in winter, a chlorine-free mineral fertilizer with a long action is used to increase the yield, strengthen and strengthen the root system. ROOT MIXTURE, differing from conventional fertilizers by a balanced content of nutrients with a high nutrient utilization (93 - 95%) against 35-40% in Control.
Fertilizer ROOT MIX is produced on the basis of decontaminated chicken manure with organic and structuring substances, with a full set of micro and macro elements, maintaining the required level with a balanced content of all necessary nutrients for the full growth and development of plants actually grown in soil in many cases Species of pathogens, especially widespread root nematodes and causing great economic damage in the second crop rotation. Infectivity of soil in the first crop rotation is significantly reduced due to the thermal treatment of the soil by steaming. The KORNEVAYA MIXTURE improves the structure of the soil, promotes the formation of fertile soil, is an organomineral fertilizer of long-term action, creates in the soil a favorable moisture-air regime in the basal layer.
Application of fertilizers for the main dressing of the soil: ammonium nitrate 260 kg / ha, lime or dolomite flour 350 kg / ha, in combination with the preparation ROOT MIXTURE at a rate of 760 kg / ha (that is, 1 package of the KORNEVAYA MIXTURE 70 g 1 m 2 ).
Fertilizers are applied to the soil surface in the greenhouse, evenly spreading the drug on the soil, without digging. Fertilizer contains a starting dose of nutrients and maintains the required level of macro- and microelements during the vegetative period of plants and provides an improvement in soil structure and an increase in its fertility.
When growing cucumber plants in separate places, rows and sections, where previously there was a painful condition of the previous culture and where weakened plants are found in this connection, they are fed with the BIOHUMUS preparation, which in a dose of 10 g per plant is scattered around each weakened bush. Top dressing is performed before the mass flowering of the plant. This measure prevents premature wilting and lunge of weakened plants. The degree of weakening of plants is determined by conducting appropriate phenological observations.
The proposed measures are ecologically safe for plants and humans, they provide "germination energy", the mass germination of seeds, promote their conditioning, improve the planting material (seedlings, cuttings), the accelerated development and growth of a strong root system, with an increase in its volume of one and a half - Twice in comparison with the control, the friendly approach of all phases of phenological development, with increasing their resistance and resistance to adverse environmental influences and to disease and pest damage during the growing season, which in the end ensures high survival and an increase in the yield of healthy seedlings, reduces The level of accumulation of nitrates and nitrates in fruits and vegetables in it 2 to 3 times, improves soil structure, improves the quality of the produce, makes it environmentally friendly, increases yield by 20-25% and more.
Only normal growth and development of plants can ensure the production of high and stable crop yields, which is primarily due to the formation of a well-developed powerful root system, with the volume of its biomass, which ensures a constant supply of water and all necessary nutrient components from the soil to the plant.
With a poorly developed root system, the lack of water and nutrient solutions from the soil reduces the leaf turgor and the photosynthetic process associated with it, which leads to a disruption of all physiological and biochemical functions of both underground and terrestrial organs of vegetative plants.
The weakened state of vegetating plants leads to premature wilting of the leaves, which proceeds with pronounced chlorosis, which leads to a shortage of the planned crop, a deterioration in the taste and technological qualities of the products.
The reason for the poor development of the root system and the generally painful condition of plants are many abiotic (weather) conditions - temperature, humidity, the amount of precipitation and the periods of their fallout, regimes and conditions for growing plants in sheltered soil, timing and quality of irrigation, structure, pH, fertility Soil, etc. And biotic factors - the condition of the seeds and planting material, the varietal specificity, the field endurance (tolerance) of plants to the effects of unfavorable environmental conditions and the defeat of various kinds of pests and diseases.
Anthropogenic factors (human activity) play an important role in improving the development of the root system, strict compliance with the technological regulations for the cultivation of crops with the use of new generation biologics (immunostimulants, root mixtures, root feeders), fertilization in the form of biohumus in conjunction with appropriate progressive agricultural practices and the introduction of sustainable Varieties and crop rotations contributing to the improvement of soil structure, increasing its fertility and reducing the invasive load with the preservation of a complex of beneficial soil organisms and antagonists of harmful phytopathogens, which in turn contributes to the development of a strong root system capable of actively resisting the invasion of invasive larvae of root-knot nematodes and concomitant pathogens of bacterial and Fungal diseases. A highly developed root system significantly increases the severity threshold of root-knot nematodes.
Measures to control root-knot nematodes are divided into preventive and fighter. Preventive measures include the fencing of the root system of cultivated plants from the remaining in the soil stock of invasive nematode larvae or decontamination of the soil from residual amounts of nematodes. Due to the fact that plants weakened by the nematode are much more likely to be infected with root rot and other bacterial and fungal diseases, prevention is carried out simultaneously against nematodes and concomitant microbiological pathogens (pathogenic complex), aggravating pathogenic processes in the affected plant.
Among the preventive measures against the nematodomicrobial pathogen complex are: thermal disinfection (steaming) of the soil - a common practice in greenhouses - a method of decontaminating the soil by heating it to 90-100 ° C under pressure in two atmospheres. Although this method is widely practiced, it is rather inefficient and expensive, especially in the context of economic crises, when energy prices soar. In addition, using this method, along with the destruction of galloid nematodes, pathogenic microflora and fauna, useful microorganisms and arthropods, so necessary in the root zone of vegetative plants, also perish in the soil. This circumstance negates efforts aimed at establishing biological equilibrium within the framework of cultivated monocultures.
In our development, this method was successfully replaced by biological soil heating with a plant mix of straw, fallen pine needles and autumnal fallen leaves in a ratio of 8: 1: 1. For this purpose, in a place of future planting of cucumbers, a trench 30 cm wide and 60 cm deep is pulled out, and the dug ground is taken outside the hothouse economy. The trench is filled 1/3 with the described mixture and the newly brought uncharged humus soil is covered with water. Plants are planted in freshly bred soil, in rows of formed trenches, at a normal distance from each other. In the subsequent period, the straw-coniferous leaf mixture is heated to a temperature of 70-80 ° C due to the natural biological processes that promote the rapid and powerful root formation of cucumbers, since the temperature of the soil in the basal layer reaches 22-26 ° C. Invasive larvae of the root knot nematode Can not overcome the layer of straw-coniferous-leaf mixture and die by 70 - 80%. In addition to steaming the soil, this measure partially replaces another widespread traditional preventive method for controlling root nematodes in protected soil conditions: replacing contaminated soil with a depth of 60 cm, which, like steaming the roads, is not effective enough, since most of the gallic nematode larvae descend Deeper than 60 cm.
To prevent the migration of invasive gallic nematode larvae from the interstitial space, an integral part of antinematode measures is the use of new highly effective ecologically safe biologics of a new generation that have a complex action against nematodes and concomitant diseases of cucumbers. These are biochemicals NARCISS, DIPRIN, TRIHODERMIN, various strains of fungi of the genus Trichoderma, NEMATOPHAGIN ACTIVATED (NEMATOPHAGIN-A).
NARCISS - a new generation drug, awarded with the Gold Medal of the All-Russia Exhibition Center "International Salon 1996". The active principle of NARCISSA is the natural polysaccharide HITOZAN, isolated biotechnologically from the shell of some crustaceans, the drug is safe for humans, the environment and farm animals. It is authorized by the State Chemical Commission in the form of a 40% solution for open retail sales. His high biological activity in regard to root-knot nematodes was noted. The drug NARCISS with growth regulating and immunomodulating action stimulates the production of phytoalloxines by plants, which increase the stability of cucumbers to the root nematode and to root rot and suppress the vital activity of other pathogens of concomitant diseases.
NARCISS biopreparation, suppressing the vital activity of the root knot and accompanying root rot, does not adversely affect the complex of beneficial soil-forming organisms. Spraying with NARCIS biopreparation interferes with the growth and development of powdery mildew, anthracis, fusariosis, and bacteriosis. Two-fold treatment of vegetative cucumber plants with NARCISS prevents the premature mass lunge of plants arising from the onset and development of a complex disease, when the disease caused by root-knot nematodes is combined with root rot, which is the greatest danger for hothouse combines, which is expressed in a significant shortage of cucumber yield.
The technology of application of NARCISSA. The rate of consumption of the biological preparation NARCISS at the rate of 25 liters per seed area of cucumber per hectare. The recommended concentration of the working solution for decontaminating the soil is 0.001%, which is prepared as follows: 250 ml of the drug NARCISS are dissolved in 1000 liters of water. Prepared working solution at a concentration of 0.0001% is added to pre-prepared wells (before planting them in plants) 1.5 to 2 liters per well. Before entering into the wells of the working solution of the biological preparation NARCISS, the wells are thoroughly moistened with water. Then plant cucumber plants grown in a seedling department. The period of action of the biopreparation from the moment of its introduction into the soil is 3 weeks. 20 - 25 days after the first application of NARCISS preparation in the same low dosage in a concentration of 0.0001%, spraying of the planted, planted vegetating cucumber plants is carried out in the wells. The most strongly it is necessary to moisten the biopreparation with basal soil.
DIPRIN is a new generation biopreparation created on the basis of a new strain of entomopathogenic nematodes Pristionchus uniformis var. Oz. Nematoda, Diplogasteridae. In addition to the destruction in the soil of a complex of harmful soil-dwelling arthropods, such as the Colorado beetle, wireworms, larvae of the May crickets, pupae of the scoop, etc., it also possesses phytonematodastatic action. Under the influence of living invasive larvae, nematodes and root nematodes sharply reduce fertility, as a result of which the number of parasites in the soil drops sharply. The results of a microscopic analysis of root samples and soil samples showed that when DIPRIN was applied to vegetative cucumber plants once, the number of invasive gallic nematode larvae in the root layer of the soil and in plants decreased on average by 35-40%, with repeated application of DIPRINE around the plant, a decrease in invasive The beginning of 55 - 70%, depending on the concentration of the drug. The drug also increases the endurance of plants to concomitant root rot. DIPRIN is used in a concentration of 100,000 active invasive larvae per 1 square meter (0.5 larval equivalent for the test object-winter caterpillar tracks). The biopreparation is also used in combination with trichogram production waste or with biohumus, or powder from fallen autumn leaves. The biopreparation is at the bio-testing stage and does not have a serial production.
TRIHODERMIN is a biopreparation created on the basis of microscopic fungi-antagonists from the genus Trichoderma. Various strains of this genus of fungi limit the number of root-knot nematodes (Trichoderma koningi, pc. 1/31); Against the accompanying pathogens that cause root rot, various strains of Trichoderma lignorum (81, 256, Istoksky, L-17, M-10, Omsk, pcs 119-80, pcs., TBD-93 , Pcs TK-13, etc.), against white rot using pcs. Trichoderma lignorum (Istoksky and L-17, 119-80); Against the rotting of leaves - pcs. Istoksky and pcs. SK-14-85; Against fruit rot - pcs. Istoksky, pcs. SK-14-85 and pcs. 119-80; Against gray rot - pcs. SK-14-85 and pcs. 119-80; Against powdery mildew - a microbiological biopreparation based on Ampelomyces artemisia, pcs. A (cucumber). Trichodermine in liquid or dry form is produced by domestic industry.
NEMATOFAGIN ACTIVATED (Nematophagin A) - a biopreparation whose active ingredient is the nematodophage fungus Arthrobotris oligospora Fres, is activated by the supernatant of the culture liquid Pristionchus uniformis var. Oz. (Waste production of biopreparation DIPRIN). The supernatant dramatically increases the production of nematodefagic fungus by the number of trapping rings, by which they catch and suck out the invasive larvae of the root-knot nematodes, which leads to an increase in the biological efficiency of the biopreparation to 76-80%.
Serial release of the biopreparation is not organized, it is at the stage of bio-tests.
To combat bacteria (bacteriosis of cucumbers of various origins) and fungal diseases (anthracnose, ascohitosis, rot white, root rot, rot of gray of various origins, mucous fungi, leaf burn, peronosporosis, spotted brown, spotted olive, mildew) of different origin are used and Biological preparation AGAT-25.
With a wide spreading of the Gallic Nematode, root rot, powdery mildew and other diseases, foci of complex damage (multipathogenic diseases) arise that contribute to premature wilting of plants and their death.
In this regard, the seedling department provides for the growing of a necessary set of reserve plants to replace prematurely killed plants from multi-pathogenic diseases - root-knot nematodes, together with bacterial and fungal diseases. Prematurely fading and dying plants are removed immediately, together with the root system and the radical contaminated soil. Places under the removed plants are disinfected with the biological preparation NARCISS and DIPRIN or with a mixture of TRICHODERMIN NEMATOCIDNO with TRIHODERMIN of another spectrum of action or with the activated supernatant of the entomopathogenic nematode with the biopreparation NEMATOGAGIN-A. After processing the places for the removal of dead and weakened plants, the reserve plants are planted with the biopreparations described, followed by the bioreparation BIOHUMUS, which ensures the normal growth and development of the planted plants.
After the final harvest of cucumbers, immediately remove all the plants along with the root system. The slowing down of the removal of plants from the soil and their removal from the hothouse complex will promote the disintegration of the tissues of the root system affected by root-knot nematodes and increase in the infestation of the soil with falling galls and sings from the roots, larvae emerging from fallen Gall and Sinhalla into the soil usually migrate to the deep layers Arable horizon (to a depth of 60 cm or more), as far as eggs are concerned, they are inside large galls and do not perish even under the influence of thermal steaming of the soil.
In the intertotal period - between the completed first crop rotation - in order to reduce the density of the Gallic Nematode population in the soil, it is recommended to plant unaffected lots of onions for greens, to plant peas as a "culture huntsman", and for this purpose, a vetch test is also suitable. These cultures adsorb to their root system free invasive larvae of the Gallic nematode, after which the plants are torn from the roots and taken to feed the cattle. This measure provides a significant decontamination of the soil from root-knot nematodes. Cucumber plants planted in such areas suffer from a much lesser degree of nematodes (by 30-40%).
For preventive purposes in the territories of greenhouse complexes, it is necessary to carry out the following measures: to have a separate, fixed agricultural horticultural equipment, hoses, to carry out periodic disinfection of the packaging, overalls and special footwear, to ensure the timely and accurate removal of the dead plants, to prevent their rassypki Within and outside the greenhouse, to ensure that the contaminated material (plants contaminated by the basal soil extracted from the foci of the Gallic nematode, and additionally selected from the soil, plant residues) are instilled in special waste pits.
It should be borne in mind that in scraps of roots affected by root-knot nematodes, not all the eggs of nematodes (hundreds of thousands of eggs each) in ootecs do not all perish by thermal steaming by steaming. As for the large galls, the high temperature does not reach through the thick and dense parenchyma of the tissue, and the eggs in the ootheki remain viable, which poses a great danger for subsequent cultural changes, but also creates a large additional material cost for the economy to purchase annually necessary preparations in much larger Amounts to reduce soil contamination and to increase endurance and resistance to damage by invasive nematode larvae left in the soil, which were not recovered in time when harvesting affected plants at the end of their vegetation, or when harvesting prematurely withered and dead plants.
On plants affected by root-knot nematodes, on necrotic areas develop necrosis, accompanied by blockage of the conducting system, which slows down, and sometimes completely stops the flow of water and nutrients from the soil into the plant. Biomedication SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL in combination with the biological preparation KORNEVAYA MIXTURE, carried out by feeding of weakened diseased plants with biopreparation BIOGUMUS creates favorable conditions for the plant, which promote the development of additional accessory roots and thickening of the stem, through which the supply of nutrient solutions and other substances to the aerial part of the plant and to other Developing vegetating bodies.
Thus, against the root-knot nematodes and the complex of bacterial and fungal cucumber diseases associated with meloydoginosis in our complex protective system of measures, the following agrotechnical, preventive, protective, pathogenostatic and exterminating measures are envisaged:
- prevention of importation into the hothouse complexes of invasive and other pathogenic origin (separate inventory, disinfection of containers, work clothes, special footwear, availability of disinfection sites, timely removal and burial of waste, etc.);
- timely removal and instillation of falling plants along with the basal soil;
- partial or complete change of contaminated soil in the greenhouse to sterile;
- strict observance of crop cultivation regimes (temperature, air humidity, soil moisture, length of daylight hours);
- thermal disinfection or biological soil warming replacing it;
- availability of reserve plants in the seedling department for replacing the fallen plants with newly planted ones;
- In the intertropical period, seeding with subsequent removal and exportation of cattle (together with roots and radical soil) to plants - adsorbents of invasive larvae of the Gallic nematode - onion, pea, vicovsian mixture, etc.);
- for the purpose of regulating the number of root-knot nematodes and associated putrefactive diseases, use pathogenostatic and destructive biologics of new generation - AGAT-25, AMPELOMICINE, DIPRIN, NARCISS, NEMATOPHAGIN-A, various forms of TRICHODERMIN, RIZOPLAN - in accordance with our recommendations;
- in order to improve the overall physiological condition of cucumber plants and create a powerful root system, which increases the resistance to meloydoginosis and related diseases, to use biologically new products - BIOHUMUS, ROUND MIXTURE, SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL.
The most significant advantages of the proposed complex of measures for combating root-knot nematodes and concomitant diseases in conditions of protected soil include the following:
- the use of biological warming of the soil ensures a 60-70% decrease in the invasive background, changes the quantitative and qualitative composition of the microflora of mycorrhiza of cucumber plants in a favorable direction, promotes the heating and formation of a powerful root system of the cultivated crop, contributes to the saving of energy resources and electricity;
- use of plants - adsorbents of root-knot nematodes - leads to a preventive reduction of the natural background of soil contamination by root-knot nematodes;
- use of biological preparations BIOGUMUS, ROUND MIXTURE, SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL contributes to the strengthening of the general physiological state of the cultivated plants and the formation of a more powerful root system, increased resistance to invasion of microbiological pathogens and nematodes;
- the use of biological preparations AGAT-25, AMPELOMICIN, DIPRIN, NARCIS, various forms of TRICHODERMIN and RIZOPLAN helps reduce the fertility of female gallic nematodes (DIPRIN), exterminate invasive larvae of root-knot nematodes (NEMATOPHAGIN-A), improve the overall physiological state of plants, increase their resistance and decrease Potency of root-knot nematodes (NARCISS), stopping the development of microbiological pathogens of cucumbers (root rot, etc.) - AGAT-25, various forms of TRICHODERMIN and RIZOPLAN.
A systematic approach to the implementation of our proposed new technology for combating root-knot nematodes and related diseases in protected soil conditions, where in the dominant amount the planting of grown cucumber seedlings is carried out in soil infected with root-knot nematodes, root rot and other associated pathogens - using our technology With the use of biologics of the new generation provides, throughout the growing season, starting from the soaking of seeds, the growth regulating and high immunomodulating effect, which ensures an increase in yield by 15-20% and higher and guarantees the production of environmentally friendly products.
The proposed method for combating root nematodes and concomitant diseases excludes the appearance of negative consequences inherent in traditional technology with a large-scale fascination with the use of highly toxic drugs such as chloropicrin against gallic nematodes, which pollutes the environment, produces products, destroys beneficial microflora and fauna, negatively affects the health of the attendants, Creates technical difficulties when working with pesticides, leads to large material costs.
Since microbiological control agents, in contrast to the pesticides used, are in most cases living organisms, when using them, it is necessary to create for them appropriate bioecological conditions that maximally approach the natural optimum of their natural existence, and supply them with basic or additional nutrition. In this connection, fungal microorganisms-antagonists, such as NEMATAPAGIN-A, TRIHODERMIN, as well as the nematode biopreparation DIPRIN, are introduced together with the corresponding ecological substrate and various nutritional supplements. This is sapropel or trichogram production waste (dead butterfly mills or grain moths), or wastes of biopreparation production VIRIN-ABB, VIRIN-KS, VIRIN-OS, VIRIN-NSH, VIRIN-HS (dead American white butterflies, cabbage butterflies, Winter scoops, cotton scoops, gypsy moths, etc.), or a semi-finished biohumus at the stage of processing chicken manure by the American Californian worm. Saprophytic phases of entomopathogenic nematodes develop well in these substrates. To maintain the viability of trichoderm, soil from cucumber plants grows from naturally fallen autumn leaves of the tree species or from naturally fallen pine needles or evergreen coniferous species (pine, spruce) that the fungus can feed on.
Great importance in growing cucumbers in protected soil is the organization of biological control of harmful insects and mites - a whitefly, greenhouse, thrips, spider mites.
Against the greenhouse whitefly, it is successfully used by its active endogenous parasite ENKARZIA.
Encarsia formosa Hahan. Or other similar species of this genus affects the greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporamorum W.) in protected soil conditions. The active principle of this biological control agent is the larvae of this insect, eating the whitefly larvae from the inside. Энтомофаг относится к отряду перепончатокрылых (Hymenoptera), к которому и относится целый ряд других видов паразитических наездников и множество полезных насекомых других видов - муравьи, пчелы, осы и т.д. Взрослая энкарзия - маленькое изящное насекомое с четырьмя складывающимися на спинке крыльями, осиной талией и вытянутым яйцекладом. Перелетая с места на место, окрылившиеся особи отыскивают личинок белокрылки, куда бы они не прятались, особенно на нижней стороне листьев, и откладывают в них свои яйца. Одна самка способна поразить от 100 до 500 личинок вредителя. Вышедшие в глубине тела вредителя личинки ЭНКАРЗИИ появляются через 8-10 суток после отрождения. Перед окукливанием личинки ЭНКАРЗИИ не покидают полости тела белокрылки, используя ее шкуру в качестве убежища. У пораженных личинок белокрылки сначала появляется темный ободок, а затем она окрашивается в ярко- черный цвет, чем резко отличается от своих непораженных собратьев. Шкурки пораженных личинок белокрылки с находящимися в них куколками ЭНКАРЗИИ получили название мумий. Через 10-12 дней сформировавшиеся в куколках взрослые ЭНКАРЗИИ окрыляются, проделывают дырочку в шкурке белокрылки, вылетают наружу и сразу же приступают к поражению новых личинок белокрылки.
БЕЛОКРЫЛКА - серьезный вредитель овощных культур, особенно в условиях защищенного грунта (пленочные и застекленные теплицы, оранжереи). Взрослое насекомое напоминает крохотную снежно-белую бабочку. Размножаясь в массе, своими личинками они почти сплошь покрывают нижнюю сторону листьев. Иногда количество личинок достигает 1-3 тысяч особей на один лист. Высасывая сок из жилок листьев, личинки белокрылок ослабляют растение, а размножение в больших количествах часто приводит к полному усыханию растений. Используя сладкие выделения белокрылок на пораженных листьях часто развивается так называемый сажистый грибок, который усугубляет положение.
ЭНКАРЗИЮ применяют в двух видах - в виде мумий и в виде окрыленных имаго. Мумии энкарзии внешне напоминают личинок белокрылок и отличаются от них черной окраской. Длина 1,5-2 мм. Имаго - живые летающие насекомые с крыльями, характерными для перепончатокрылых. Брюшко не вытянуто. Насекомое темного цвета, длина 2-3 мм.
ЭНКАРЗИЮ применяют путем раскладывания мумий по территории защищаемого грунта или же путем периодического массового выпуска имаго путем помещения открытых контейнеров с окрыленными насекомыми.
Применение ЭНКАРЗИИ носит как профилактический, так и истребительный характер.
 |
Prophylactic use. When carrying out preventive measures in film or glazed greenhouses, viable EMCARZIA mummies of one day of blackening in the amount of 10 individuals per 1 m 2 of useful area in the absence of cultivated plants or after planting them from the nursery every two weeks are introduced into biocenoses. For this, 100, 1000 or 10,000 mummies of ENKARZIA are placed in special cages (see Figure 1) with a solid top cover 1 in order to prevent water from entering the water during irrigation and holes 2 from the side for the flight of winged adults. Sites with mummies ENKARZIA hang around the entire area of the greenhouse independently of the presence of cultivated plants and whitefly, and the stock of mummies in the cages are renewed every two weeks. At the bottom of each tank put moistened cotton wool 3, which is poured mummies. Wadding is necessary to ensure that the mummies of the endocrine do not dry out, causing the percentage of winged individuals to decrease significantly. With this method of applying ENCARZIA, migratory and imported whiteflies will inevitably be attacked by those moving in search of the victim of Enakara and the further distribution of the whitefly will cease. Cages with mummies are hung on plants or armature. Departing adults immediately go to search for whitefly larvae - feed for future offspring. ENKARZIA - a specialized entomophage and absolutely harmless to other types of insects. In order to correctly calculate the number of hanging containers and the total number of parasite mummies required, it is recommended to use Table 1. |
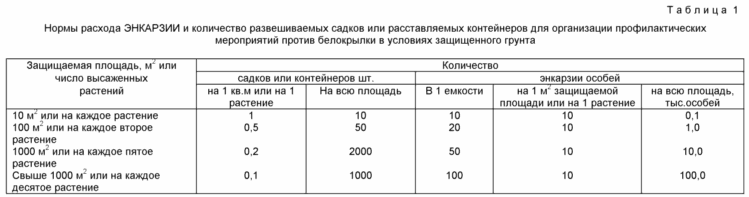
Fighter measures. Calculation of the required number of mummies or adults of the introduced ENCARZIA. In different parts of the greenhouse, 100 leaves of the cultivated crop are arbitrarily torn off and the number of whitefly larvae on each sheet is counted separately. To this number is added the number of eggs laid. The average value is then calculated and multiplied by the number of plants in the greenhouse, thereby determining the pest stock. The obtained figure is doubled (the predicted pest stock at the peak of the population before the active influence of the parasite), and the resulting number is divided by 10, thereby obtaining the number of mummies or adults of ENKARZIA necessary to suppress the whitefly foci in the protected greenhouse. Sites with mummies or containers from the imagery of ENKARZIA are hung or placed in the same quantities as in the preventive struggle (Table 1). The effectiveness of the ENKARZIA action is counted at 15, 20 and 25 days after the introduction of the entomophage, calculating the percentage reduction in whitefly abundance in the experiment for all accounting dates. Within a month, released in recommended doses, ENKARZIA completely suppresses pest activity.
Against the whitefly, the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill (the active principle of various forms of the BOVERIN biopreparation) is also effective. Active strains 80 - N 1 and V - h - 89, and other microscopic fungus Cephalosporium (Verticillium) lecanii, strain AG P82, pcs. Ch., Pcs. P-3, pcs. U-57 (active principle of the biopreparation VERTICILLIN).
Against aphids can be used a whole complex of entomophages, the main of which is the endoparasite AFIDIUS.
AFIDIUS (Aphidius matricariae Hal.) Or other similar species of this genus are active agents of biological control of aphids (the Aphididae family) of the order of the equinochid proboscis. The active principle of the biological control agent is the larvae of AFIDIUS, eating larvae and imago aphids from the inside.
The entomophage belongs to the order of the hymenoptera (Hymenoptera). Adults AFIDIUS - small slender graceful insects with four folded on the back of the wings, an aspen waist and an elongated ovipositor. Imago AFIDIUS flew well and quickly, especially active in clear sunny weather. Poorly tolerate heat above 35 o C. On such days, people prefer to stay in the shade. Flight from place to place within a radius of up to 15 m, winged individuals look for colonies or individual aphids, usually sitting on the underside of leaves or on tree trunks or flowers and lay their eggs in them. One female AFIDIUSA can infect 100 to 500 pests. Emerged in the body cavity of aphids larva AFIDIUSA, without leaving the body of the pest, begin to develop, stop the development of the host and feed on its entrails before pupation. Pupation occurs in the body cavity of the pest. The aphidiosis larvae use the hide of the aphids killed by them as a refuge. Affected thus, aphids freeze in unnatural positions and differ bloated bellies. Light-brown skins of affected aphids with the dolls AFIDIUSA in them were called mummies. After 10-12 days adult AFIDIUS (imago) formed in the dolls make a hole in the skin of aphids rather large (visible with a simple eye or with the aid of a slightly enlarging magnifier) and fly out, and immediately begin to search for and defeat new victims. Imago AFIDIUS, as well as many other Hymenoptera, need additional nectar and pollen of umbellate or composite plants (dill, carrot, sunflower, etc.), so it is highly desirable for the successful use of AFIDIUS as an agent of biological control in the greenhouse at any time of the growing season of cucumbers And flowering umbellate or composite plants.
AFIDIUSA is used in two forms - in the form of mummies and in the form of winged adults. Mummies AFIDIUSA outwardly resemble larvae or imagoes of aphids light brown with bloated bellies. The length is 2-5 mm. Imago - live flying small insects with four characteristic for hymenoptera wings. The abdomen is not strongly extended. Insects of dark color. The length is 2-3 mm. AFIDIUSA is used by laying mummies on the protected ground or periodic (bi-weekly) mass imago release by placing open containers with winged insects, and by creating conditions for the permanent reproduction of AFIDIUS in the protected area.
The use of AFIDIUSA can be both preventive and exterminating. Application of AFIDIUS for preventive purposes provides for periodic (at least once every two weeks) release of imago AFIDIUSA or the layout of his mummies in the protected area. Destructive measures include the release of imago or the layout of mummies in quantities proportional to the number of aphids.
Preventive actions. When carrying out preventive measures in film or glazed greenhouses, in greenhouses, viable mammals AFIDIUSA in the number of 10 individuals for each 1 m 2 of useful area in the absence of cultivated plants or after planting them from the nursery every two weeks is introduced into biocenoses. For this mummia AFIDIUSA 100, 1000 or 10,000 individuals are placed in special cages (see Figure 1). With this method of applying AFIDIUS, migratory and aphid infestation will inevitably be detected and destroyed by actively moving in search of the victim of imago AFIDIUS, and further distribution of aphids in this greenhouse ceases. Cages with mummies are hung on plants or armature. Departing adults immediately go to search for aphids. It is allowed to use the described cages and containers for adults for the joint release of AFIDIUS against aphids and ENKARZIA against whitefly. AFIDIUS is a specialized entomophage and is absolutely harmless for other types of insects. The insect does not bite, is aesthetically pleasing and harmless. In order to correctly calculate the number of necessary parasite mummies and the number of containers to be hung, it is recommended to use the table 1 that we offer.
Fighter measures. The calculation of the required number of mummies or imago of the introduced AFIDIUS is carried out on the same principle as for ENKARZIA, with the difference that the number of larvae and imago aphids is counted per 100 randomly torn cucumber leaves, and the resulting mean value is multiplied not by 2, as in the case of Counting whitefly, and by 5 (the multiplication factor of aphids is higher than that of whitefly). Within a month, released in the recommended doses AFIDIUS completely suppress the action of pests.
Approximately the same kind of action on aphids has another endogenous entomophage - LIZIFLEBUS.
In addition to endogenous parasites, aphids are readily eaten by many types of insects. Their wide application is largely limited by the poorly developed methods of their mass reproduction.
In addition to the different species AFIDIUS (Aphidius matricariae Hal., Aphidius difinensis Ashm.), The following species of arthropod entomophages are also used against various species of aphids (mainly melons, potato, peach): predatory larvae of the gall midges (Aphidoletes aphidimisa Rond.) - an insect from the detachment Diptera; Larvae of various species of lacewings (pearl, Chinese, beautiful, seven-spotted - Chrysopa carneal, Ch. Septempunetata, Ch. Sinica, etc.) - insects from the order of the Neuroptera family of golden-eyed (Chrysopidae); Larvae and imagoes of the Ladybirds - Coccinella septempunctata, Cycloneda limbifer Gassey, Leis dimicliata Fabr., Diaretiella rapemilutosh - insects from the Coleoptera squad of the family of cows (Coceinellidae); Larvae and imagoes of the common camel, larvae of the sirf of the venous, etc. (insects from the order of the diptera of the family of buzzers (Syrphidae), etc.
Against aphids it is possible to apply a number of pathogenic microorganisms on the basis of which microbiological entomopathogenic preparations have been created in recent years, in particular AVERTROP - the active principle of the entomopathogenic fungus Streptomyces avertimilis Aeb. , VERTICILLIN - the active principle of the entomopathogenic fungus Verticillium lecanii, pcs. AG-P82 (mainly against melons and gourds), pcs. 12, pcs. РАч89, шт. Otch89 and others, FITOVERM and CEFALOSPORIN - the active principle of the entomopathogenic fungus Cephalosporium lecanii or ENTOMOFLORINE - the active ingredient Entomophthora thaxteriana, etc.,
Aphidoderma aphidimisa Rond. Is an active entomophage of aphids. Orange fly larvae suck out aphid larvae. Each larva destroys 10-15 pests per day. Especially actively eats peach, melon and potato aphids. Pupants in the soil in fragile cocoons. Pupae are removed from the diapause and stored in the refrigerator for 6-8 months at a temperature of 2-4 ° C. In the greenhouse, pupae are introduced in containers filled with moist soil. Drying of the soil leads to the death of the pupae. Departing flies find colonies and separate aphids and lay their eggs beside them. The emerging larvae of the gall midges rush to their victims. When carrying out preventive measures, periodically (once a month) introduce viable pupae or adult flies at a rate of 10-30 individuals per 1 m 2 . When carrying out the fighter operations, the gallium is released in quantities calculated in the same way as for the release of AFIDIUS.
Larvae of gall midges, released in the required amount, completely destroy the pest in 2-3 weeks after release.
ZLATHOGLAZKI - beautiful insects with golden eyes, for which they received their name. External, they resemble miniature dragonflies with four pale green or bluish wings with pronounced net veins, for which this group of insects was called the net-winged. Flies a little, reluctantly, not far, slowly and badly and therefore often becomes the prey of insectivorous animals, often moves by wind. Female lacewings lay eggs on the underside of plant leaves, placing them on long thin legs resembling tiny stems or fruiting bodies of microscopic imperfect fungi, which is why often leaders who are ignorant in this matter try to conduct chemical warfare with them. Some naturalists compare the eggs of the zlastoplazki with protruding from the mouths of leaves with droplets of viscous frosted-white juice, which are stretched on the thread, and so freeze, not reaching the ground. After 3-4 days, larvae crawl out of the eggs, which immediately go hunting for larvae of aphids.
Larvae of lace-eyed fusiform are flat, they carry on the backs of skins of aphids, scales and spider webs. Their jaws resemble the claws of crustaceans or mandalas of narwhals. After pushing the aphids and getting to the selected larva, they suddenly pierce the mandibles in the aphid flanks. The victim begins to subside. The Predator throws a mite of skin on his back and follows the next victim. Destroy lacewings, not only aphids, but also spider mites, and adult individuals suck in sometimes small caterpillars. The larva of the lacewoman feeds for 2-3 weeks, destroying about a thousand aphid larvae, and then finds a suitable secluded place and weaves a small white cocoon, which is sometimes mistaken for a cocoon of spider eggs, in the cocoon it pupates. Before departure, the cocoon cover opens, the pupa crawls out and turns into an adult insect. Having dried and spread its wings, it goes for nectar.
Greenhouses are introduced to larvae, pupae or golden-eyed eggs. It is most effective to produce in large numbers of predatory larvae of 2 or 3 age. The rates of consumption are the same as for gall midges. The effect is the same.
GOD'S BODIES - representatives of various genera of the family of cows (Coccinellidae) from the order of beetles (Coleoptera).
Adult insects are pretty, beautifully painted and, perhaps, the most famous of all existing entomophages. Puppets of ladybirds, tied to the underside of the leaves and orange-colored with dots hanging down, are often confused with the puppies of the Colorado beetle and are destroyed by inexperience. Eggs of the entomophage also resemble the eggs of the Colorado beetle, but they are much smaller and more yellow in color than the bright orange eggs of the Colorado beetle. It should be noted that the larvae of the Colorado beetle never pupate on the leaves, but leave pupate in the soil.
Bristly, covered with warts and bright spots, the gray-brown larvae of God's Cows eat aphids on a par with imago. Ladybugs destroy various species of aphids in large quantities. Some types of entomophage are bred in biological laboratories. The adult GOD'S COW lives 30 - 40 days, during this period she lays from 100 to 1000 eggs. Usual seven-point GOD'S COW for the period of its existence eats from 400 to 800 aphids, and some individuals eat up to several thousand aphids. Larvae appear 3 to 4 days after egg laying. For a day, one larva eats about 50 aphids. The imago needs additional nectar or pollen feeding, for which the flowering plants must always grow in the greenhouse, preferably umbellate or composite (camomile, dill, coriander, carrot, sunflower, etc.). The rates of release are the same as for gall midges. The effect is the same.
VERBLYUDKA ORDINARY - small forest insects, the larvae of which penetrate under the bark of trees, where they feed mainly on bark beetles, beetroots and saplings. Its insect got its name from the external similarity of the head and the long neck of an adult insect with camels. The insect itself resembles a small dragonfly, a freckle or a scallop. The entomophage is bred in a biological laboratory and released into hothouses against aphids. The rates of release are the same as for gall midges. The effect is the same.
SIRFIDS (= HUMANS, = LADIES, = FLOWERS) are flies from the Diptera order of the family of syrphids (Surphidae). The syrphids resemble the stinging hymenoptera (bees, bees) in a manner of staining and the shape of the body, they are even often confused with each other. Obviously, this property is associated with an attempt to "deceive" insectivorous animals that prefer not to communicate with bees and wasps. MIRs in flight like to "stand" in the air for a long time in one place in the shade, or basking in the sun, issuing a melodic buzz, for which they received one more of their names "buzzers." Being scared, they instantly change location and again freeze in place.
A syrphid can often be found in natural conditions on flowers, where they eat pollen and nectar. These beautiful flies often occur on tall umbelliferous plants, herbs, in the forest, near the river, on testes of carrots, onions, dill, in vegetable gardens, on spiraea and hawthorn, in gardens, in parks, on the field visit buckwheat flowers. It is because of this craving for flowers in the babbits there is also the name of "flower girl".
Larvae SIRFID predator, eating a lot of aphids or other small insects.
The larva of a fly-murmur is a small, slightly less than a centimeter, semi-transparent "worm", similar to an elongated drop. The larva slowly crawls, pumping its body from the blunt end to the sharp one, then raises its head, swings it and, throwing it aside, pierces the body of aphids. After a few seconds, only the skin remains from the aphid, and the predator is already being selected for the next victim. For a day such a larva destroys up to 200 aphids, and for 2 - 3 weeks of its existence - up to 2000 individuals. When such a larva grows, it ceases to hunt for aphids, it is attached to some leaf of a leaf, where it is covered with a dense brown crust, turning into a pupa (in the Diptera pupa it is called a "pupary"). After one or two weeks, the puparium bursts and a fly-syrphid hatch from it. Drying and spreading its wings, she goes to the flowers for nectar and pollen. The female babbler lays 150 to 200 eggs.
The syrphidum is bred in conditions of biological laboratories and is released against aphids in conditions of protected soil. The most active in relation to aphids is the WILF SIRF. The rates of release are the same as for gall midges. The effect is the same.
Flying entomophages - aphids, lysiflebuses, gall midges, lacewings, cows, syrphids, camels - in the absence of flowering plants they starve and in the summer leave the greenhouses through transoms, rush for food and do not return to their original place. Therefore, in the conditions of greenhouses, it is always necessary to have a set of flowering composite and umbellate plants that can at least somehow compensate for the biocenosis of monocultures.
In addition to the traditional entomophages Encarsia formosa Gahan., Encarsia pantenopea Marsi, Encarsia tricolor and traditional microbiological preparations of boverin and cephalosporin against whitefly in greenhouses, the following pathogens and entomophages can be used: Entomopathogenic fungus Achersonia aleurodes W. (Asheronia biopreparation); Fungus entomopathogenic Streptomyces auranfiacus (biologic ALEITSIN); Entomophthora afidis fungus (experimental form of the preparation); Fungus entomopathogenic Entomophthora paru (experimental form of the preparation); Fungus entomopathogenic Paecilomyces fumoso-roseum (experimental form of the preparation); From entomophages - larvae of the golden-eyed Chrysopa carnea Stephens, a predatory bug of macrolofus (two species) Macrolophus costalis Fieb. (From the family Miridae and Macrolophus nubilis HS Larvae of the ladybirds of the genera Coccinella, in particular Coccinella Septempunctata L. (Ladybird of the seven-spotted) and males from the genus Exochomus, entomoacariphages Anystis bacarum L.
Against spider mites (Acarina: Tetranychidae), in particular the mite of the common arachnoid (Tetranychus urticae Koch., And natural pathogens and acariphages are used: Biologic ALEITSIN (active principle of the entomopathogenic fungus Streptomyces auranfiacus; biopreparation BIKOL (active principle is the bacterium entomopathogenic Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner var thuringiensis 98 + exotoxin, biopreparation BITXIBACILLINE (BTB) (wettable powder) - active principle of Bacillus thuringiensis var thuringiensis, piece H 1 ; biopreparation VERTIMEX (active principle of Streptomyces avermitilis Aeb; biopreparation MIKOAFIDIN-T (active principle - entomopathogenic fungus Entomophthora thaxteriana ), Biologically active drug TURICID-I active ingredient - entomopathogenic bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis var thuringiensis, H1 + exotoxin), from entomophages - predatory clopic Macrolophus nubilis HS and predaceous mites METACEISEUS (Metaseiulus occidentalis Nub.) And Phytoseiulus Persimilis Ach.), As well as the biopreparation AVERTROP (the active principle of the entomopathogenic fungus Streptomyces avermitilis Aeb.).
Phytoseiulus persimilis Ath. 11) - an entomophage and acarifagus (predatory mite), recommended for the control of a spider mite (Tetranychus urticae Koch.) (Acari: Tetranichidae) in protected soil conditions. The rate of consumption is 50 - 100 individuals per 1 m 2 of protected soil. When carrying out preventive measures - periodic (at least 1 time per month) introduction of active mite with a rate of 10-20 individuals per 1 m 2 of protected soil. Introduce the entomophagus into the open cages in the protected greenhouses (see Figure 1) - for less than 1 container per 10 m 2 of protected soil from the corresponding number of active adults of the mite.
The cages (see Figure 1) are equipped with a perforated, elastic, overlapping belt with a perforation of 5 mm in diameter with an interval of 20 mm (in accordance with the perforation of the cages themselves (see Figure 1a) .For the release of insects from the container, the perforation of the overlapping belt and perforation of the cage itself Combine, freeing the outlet for insects or ticks.
However, the above measures may not be enough to reliably protect the cucumber culture of protected soil from pests and diseases, since many diseases of cucumbers can manifest themselves in the absence of Meloydoginosis.
In such cases other biologics of the new generation should be used: against bacterial diseases - bacteriosis - biological preparation AGAT-25 (active principle - antagonistic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens); Biopreparat BACIFIT (active ingredient - bacterium antagonistic Bacillus Subtilis); Biopreparation RIZOPLAN (active principle - antagonistic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens (form F) or Pseudomonas putida (form II), biopreparation FITOLAVIN (active ingredient - bacterium antagonistic Streptomyces griseus (form D) or Streptomyces lavendulae (form A), against a complex of fungal diseases - biopreparation AGIR-B (the active ingredient is the antagonistic bacterium Bacillus Subtilis), the biopreparation RIZOPLAN-F in liquid form, the biopreparation RIZOPLAN-F in lyophilized form, the biopreparation RIZOPLAN P (liquid or lyophilized), the biologic ALIRIN-S (active principle - bacterium antagonistic Streptomyces felleus), against the rots of the root - biopreparation ALIRIN-B, biologic preparation ALIRIN-S, biopreparation BACTTOFIT (active ingredient - bacterium antagonistic Bacillus Subtilis), biological preparation GLIOCLADIN (active ingredient - antagonistic bacterium Gliocladium virens, biopreparat TRIKHODERMIN (active principle - A microscopic fungus-antagonist Trichoderma lignorum, various strains); Biopreparation FITOLAVIN-G; Biopreparation FITOLAVIN-L; Against bacterial spotting - biopreparation PENTOFAG (active ingredient bacterium-antagonist Pseudomonas pv syrigae; against angular patchiness - biopreparation PENTOPHAGUS, against dew powdery - biopreparation AMPELOMICIN (active principle - fungus antagonist Ampelomyces arremiziae Rud.), Biopreparation BACTOFIT, biopreparation BACIFIT, biopreparation PENTOFAG , The biopreparation TRICHOTECIN (active ingredient is the fungus antagonist Trichotecium roseum, against the withering of the verticillium - biopreparation BACIFIT, against the fusarium decay - biopreparation BACIFIT.
To enrich the soil with fixed nitrogen, the biological fertilizer of the CBU (complex biological fertilizer) was also applied to the soil at the rate of 10 g of fertilizers per 1 m 2 of useful area.
To ensure the flow of year-round reproduction of cucumbers under protected soil conditions, the plants were grown on four isolated plots according to the scheme of alternating short-day or long-day varieties of cucumbers and preventive measures (Scheme 1, see Table 4).
Example 2. Cultivation of tomatoes in protected soil conditions.
When cultivating tomatoes in protected soil conditions, a complex of agrotechnical, preventive and protective measures is carried out. Since the complex of pests and diseases in tomatoes and cucumbers is approximately the same, the strategies for biological control of harmful organisms for these crops are slightly different from each other.
Gall nematodes to a lesser extent damage tomato plants due to the fact that this crop has a number of varieties that are largely resistant to this type of pest. However, with a significant invasive load and the presence of aggressive races, even highly resistant varieties of tomatoes are exposed to a disease of small-legiosis, especially against the background of other bacterial or fungal infections.
To increase the stability of tomato seedlings to pests and diseases in the seedling department, the seeds are treated and two treatments are carried out on vegetating plants with the biomedication SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL. The use of the biomedical SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL is recommended for tomato culture and in 3 stages: seed soaking, spraying the bottom of the seedling, most hydrating the root system, in the concentration of the solution for seeds 0.002% and 0.001% for spraying the seedlings. The technology of application of the biomediment SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL is described in detail in Example 1 (for cucumbers).
The preparation SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL is used both for susceptible varieties and hybrids of tomatoes to the root knot nematode, and for nematode-resistant, considering that the invasive nematode larvae penetrate into the roots and nematode-resistant varieties, but do not reach the sexually mature state die. At the same time, the larvae of the nematode cause mechanical damage to the root tissue. One day prior to the removal of tomato seedlings from the seedling department and planting in a greenhouse, the plants are sprinkled with a working solution of SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL at a concentration of 0.001%.
 |
In greenhouses, prior to transplanting, preliminary soil preparation is carried out, which is carried out in the same way as described in Example 1, with respect to cucumbers. In order to promote the formation of a well-developed, powerful root system of tomato plants, a mineral fertilizer with a long action, ROOT MIXTURE and complex biological fertilizer (CBU), is applied to the soil defined for this culture, based on 10 g of biopreparation per 1 m 2 (see Fig. 3) . The rates of fertilization ROOT MIX are indicated in Example 1. Weakened tomato plants are fed with biogas BIOHUMUS in the same consumption rates as for cucumber plants. To prevent attacks on tomato plants of invasive gallic nematode larvae in greenhouses, thermal disinfection of the soil (traditional) is carried out in the regimens described in example 1 or biological soil heating (growing plants on a straw-conifer leaf cushion). The technology of using this method is set forth in Example 1. To prevent the migration of invasive larvae of root-knot nematodes in their interstitial space, new biologics are used: NARCISS, DIPRIN, TRIHODERMIN (Nematicide form), NEMATOPHAGIN-A in the norms given in Example 1. |
With a wide distribution of aggressive nematode sprouts, root rot, powdery mildew and other diseases, foci of complex (multipathogenic) lesions arise which lead to premature wilting of plants and their premature death. In this connection, in the nursery department, the necessary quantities of reserve plants are grown to replace dead or wilted plants, which are immediately taken out of the greenhouse together with the basal soil and buried deeply. The places under the removed plants are disinfected with the NARCISS biological preparation or with a mixture of TRICHODERMIN nematicide with TRICHODERMIN of a different spectrum of action, or with NEMATOPHAGIN-A, or DIPRIN biopreparation, and the planted plants are fed with BIOGUMUS biopreparation in the norms given in example 1. AGAT-25 biopreparation is also used against associated diseases.
After the final harvest, all plants are removed immediately, together with the root system. In the intertotal period - between the completed first crop rotation and the second turn - in order to reduce the density of the Gall mania nematode population in the soil, it is recommended to plant unaffected lots of onions in greens, sow the vetch mixture or peas, followed by tearing the plants with roots and yielding to livestock (detailed description in the example 1).
A set of preventive measures, set out in Example 1, is also carried out, which helps to protect greenhouses from introduction of root-knot nematodes.
In the absence of manifestation meloydoginosis and in the presence of other types of diseases should use a variety of biologics a new generation:
- against ANTRAKTOSA - AGAT-25;
- against АКОХИТОЗА - АГАТ-25;
- against bacteriosis of various origins - AGAT-25, ALIRIN-B, ALIRIN-S, MICOSTOP, RIZOPAN-F (in lyophilized or liquid form);
- against rotten white - AGAT-25;
- Against decay of root of various origin - biologic drugs ALIRIN-B, ALIRIN-S, GLIOKLADIN, TRIHODERMIN (different strains), FITOLAVIN-G, PHYTOLAWIN-L;
- against the rot of gray of various origins - AGAT-25;
- against fungi of mucous - AGAT-25;
- against a complex of fungal diseases - biological preparations AGAT-25, ALIRIN-B, ALIRIN-S, MIKOSTOP, RIZOPLAN-F (in lyophilized or liquid form);
- against peronosporosa - AGAT-25;
- against bacterial blotchiness - PENTOFAG biopreparation;
- against the spotting of brown - biological preparation AGAT-25;
- against the spot of olive - AGAT-25;
- against patchiness angular - biopreparate PENTOFAG;
- against mildew of various origins - biological preparations AGAT-25, AMPELOMICIN, BACIFIT, PENTOPHAG, TRICHOTECIN;
- against the withering of verticillosis - biopreparation BACIFIT;
- against fusarium decay - biopreparation BACIFIT;
- against late blight - biopreparation KBU.
Tomatoes in conditions of protected soil are affected approximately by the same complex of harmful arthropods as cucumbers, therefore the measures against them are similar to those described in Example 1.
Against the whiteflies of the greenhouse (= hothouse), biopreparations are used: ALEYZIN, ASHERSION, BOVERIN, VERTICILLIN or antagonist fungi Entomophthora aphidis, Entomophthora paru, Paecilomyces fumoso-roseum (Muscardine = Muscardine pink); Entomophages - larvae ZLATOGLAZKI ORDINARY, clopic predatory MACROLOFUS (two species); Ladybirds - cyclone seven-point, exohmus; Enkarsia (3 species).
Against mite spider - biopreparations: AVERTROP, ALEYTSIN, BIKOL, BITOXIBACILLIN (BTB), VERTIMEX, MIKOAFIDIN, TOURICID; Entomophages: predatory mites METASEJULUS, PHYTOSEJULUS.
Against a complex of aphids - biologics AVERTROP, VERTICILLIN, ENTOMOFLUORIN; Entomophages: various types of Afidius, Gallicus-Afidimizu, Zlatoglazki - pearl, Chinese, beautiful, ordinary, seven-point; Ladybugs - LISIS SEMITOCHECHNYU, CYCLONE, DIARETHILLA, VERBLYUDKU ORDINARY, SIRF WRENCH, etc.
Against thrips - biopreparation BOVERIN (powder wettable or granulated drug), from entomophages - predatory mite AMBLISEUS.
The norms of consumption and the methods of using biologics are set out in the corresponding instructions and leaflets attached to biologics.
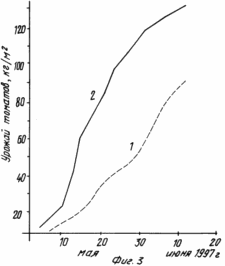
The use of the proposed method ensures year-round flow-growing of tomato plants in conditions of protected soil without the use of pesticides, with the production of ecologically clean agricultural products throughout the year and increases the yield (see graph 1 in Figures 1, 1 - control, 2 - experience).
Example 3: Bespiditsidnoe cultivation of potatoes.
Potato plants like no other culture are vulnerable to many diseases and pests, which cause great economic losses to potato growers. In this regard, the use of chemical protective equipment is a very expensive process, polluting both the external environment and the products received, and it is far from safe for people working with pesticides and processing potato plantations.
The method of potato cultivation proposed by us excludes the use of highly toxic preparations or limits their use to a minimum. Chemical preparations are necessary only in the event of the emergence of primary and isolated foci of quarantine objects or species that first appeared on the territory of our country, but also for the elimination of foci of particularly dangerous diseases and pests in limited areas. A new method of growing potatoes provides for increasing tolerance in plants, for resistance to unfavorable weather conditions and for damage by pests and diseases.
The main factor in increasing the field endurance of potato plants both to unfavorable environmental conditions, and to the defeat of various kinds of pests and diseases is the state of development of the root system. With a powerful, well-developed root system with a large volume of its mass, water and nutrient solutions are more intensively introduced into the plant, especially during arid periods of plant vegetation, with a poorly developed root system in droughty periods, this negatively affects the development of plants - the turgor of leaves, Decreases the intensity of photosynthesis, violates all the physiological and biochemical processes of developing plant vegetative organs.
With a poorly developed root system of potatoes, it is especially dangerous when the plant is affected by various pests and diseases, which in turn cause various damage to the root system, and root crops, and stems, and developing leaves, and generative organs during flowering, etc. The disease-causing processes that arise in the plant are aggravated, which adversely affects the overall growth and development of the whole plant. The succession of successive phases of development is delayed, the stems of the plant remain thin, the leaf blade is crushed, the area of the leaf surface is reduced, the plants remain short with premature appearance of chlorosis, the wilting of the aerial part and the death of the entire plant.
The new method of growing potato plants provides for the use of the above mentioned biological plant growth immunostimulator, the SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL biopreparation, an alcohol extract of microbial community producers isolated from mycorrhizal roots of WOMEN-SHENYA. The community is dominated by an endophytic fungus, a fungus, supplementing components are yeast and bacteria. The preparation of SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL activates not only the more harmonious and early appearance of the eyeballs from potatoes and more rapid development of the root system, but also increases the number of "awakened" kidneys on the tuber, from which the growth of young stems intensively begins. In order to accelerate the germination of tubers of potatoes and increase the number of ocelli and developing stems from them, reinforcing the branching of the stems of the batch of preplant material extracted from the potato storage facility is treated with an environmentally friendly biomedication SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL.
SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL accelerates the process of germination of tubers, stimulates the formation process and increases the number of "waking up" eyes, stimulates the rapid and active development of the root system both during the preliminary preplanting germination of planting material (potato tubers) and in the subsequent entire vegetative period of plants. With the application of the preparation SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL, a powerful root system is formed with an increase in its mass by 1.5-2.0 times in comparison with the control, which increases the resistance of plants to adverse weather conditions and to plant damage to pests and diseases, Soil-plant. Обработка препаратом СИМБИОНТ-УНИВЕРСАЛ в 3 этапа повышает кондиционность клубней, снижает количество во вновь развивающихся клубнях аккумулированных нитратов, нитритов и радионуклидов. В сочетании с другими используемыми биопрепаратами и корнепитателями урожайность картофеля увеличивается на 25 - 30% с улучшением их вкусовых и технологических качеств.
Препаративная форма. Биопрепарат СИМБИОНТ-УНИВЕРСАЛ выпускается в полиэтиленовых ампулах емкостью 1 мл или во флаконах емкостью по 100 мл.
Достоинством биопрепарата является простота и доступность технологии применения, низкие нормы расхода, относительно низкая стоимость и экологическая безопасность применения.
Technology of preparing a working solution for processing potato tubers. Preconditioning treatment of tubers of potatoes is carried out with 0,001% solution of the preparation in combination with 0.2 g of copper sulfate and a complex of microelements (supplied by the manufacturer in a single package) at the rate of 1 ml of biopreparation per 1 ton of potato planting stock, for which 1 ml of SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL Dissolved in 10 liters of water, 2 ml - in 20 liters of water, 3 ml - in 30 liters of water and so on, depending on the processed batch of potato tubers.
In parts, the tubers are soaked in a pre-prepared working solution at a concentration of 0.001% with an exposure of 1 hour. The tubers are soaked in a tub, vats or other suitable containers of different volumes. If there is no possibility to soak the tubers in the working solution of the drug, the tubers are evenly distributed on a polyethylene film and the tubers are sprayed carefully. After treatment, the tubers are covered with wet peat crumb for pre-germination. After the emergence of sprouts of 1.0 to 15 cm in size, tubers under the peat crumb are subject to repeated spraying, but in a weaker concentration of the working solution (0.0001%), with 1 ml of the drug dissolved in 100 liters of water. Before planting germinated tubers with developing seedlings and the root system, a third spraying of the working solution of the drug in the same weak concentration (0.001%) should be performed. When the tubers are first treated with the soak method, the prepared solution can be reused or reusable, i. E. Soaking the preplant material is carried out in parts, depending on the availability of containers of large or small size.
The preparation SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL can be used for processing of a potato of all groups of ripeness. Particular attention should be paid to a group of potato varieties belonging to the early ripening, which greatly accelerates and increases the yield and makes it possible to remove it already in the second - third decade of June (depending on the weather conditions), under the condition of introducing rotted manure, or in its absence, Introduction into the soil of the biological preparation ROOT MIXTURE. The potato harvest, received in July, is the earliest and high-calorie, tasty agricultural produce grown in open ground conditions.
Similar properties of the biomedicine SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL properties have another recommended biopreparation-biostimulator Herbamin (Herbamin), which produces the company "Herbamin industries" (Cyprus). This organic fertilizer is a bioactivator of plant growth, prepared from an extract of a specially selected assortment of medicinal herbs. The drug contains protein materials and amino acids 0.45%, fatty acids 0.15%, sodium salts, gibberellic acids 0.04%, vitamins, enzymes and phytohormones. The preparation contains a number of microelements (mg / l): nitrogen (N); Magnesium (Mg) 3.9; Copper (Cu) 70; Phosphorus (P) 2.7; Manganese (Mn) 160; Boron (B) 24; Potassium (K) 2.7; Zinc (Zn) 60; Molybdenum (Mo) 25; Iron (Fe) 17.5; Nickel (Ni) 410; Cobalt (Co) 25; Chloro (Cl) 179; Sulfur (S) 161. The most important component of this biodynamic product is the regulating activity of living cells. A carefully selected species composition of wild healing herbs makes up the raw material base for the production of Gerbamin. To extract active substances without the use of chemical agents, the developers of the biopreparation developed a unique production technology. Shelf life of the biopreparation is 2 years. In recommended doses, the biopreparation has proved itself well for flower cultures of open and protected soil, for indoor plants. Apply this drug to vegetable and fruit crops, while caring for urban and park greenery.
On potato, this biologic preparation GERBAMIN is used at a concentration of 0.001% (0.1 ml of preparation per 100 liters of water) for watering vegetative plants and at a concentration of 0.0002% for preplant tuber treatment. The method of its application on potato is similar to the method of application of the biological preparation SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL.
To increase the potato yield and to contain the spread of phytophthora, we also recommended a new biological fertilizer KBU (COMPLEX BIOLOGICAL FERTILIZER) containing living bacteria that improve the soil structure and enriching the mycorrhiza of cultivated plants with nitrogen. Bacteria, which form the basis of the biopreparation, possess phytophthorosostatic properties. The rate of consumption is 10 g per 1 m 2 of usable area. To produce a working solution, the concentrated biopreparation is diluted 10,000 times (0,01%).
To increase the yield of potatoes, strengthen and strengthen its root system, the biofeedback mentioned earlier in Example 1 is used. ROOT MIXTURE. The KORNEVAYA MIXTURE contains all the necessary elements for the full development of plants and has the following composition in terms of constituent elements (%): nitrogen (N) 4.9; Phosphorus (P) 1.0; Calcium (Ca) 3.0; Iron (Fe) 0.4; Boron (B) 0.05; Copper (Cu) 0.004; Manganese (Mn) 0.01; Zinc (Zn) 0.08; Molybdenum (Mo) 0.01; Humates up to 5%; Organic matter up to 35%.
Biopreparation ROOT MIX is added to the wells when planted along with the previously sprouted tubers of potatoes in an amount of 20 grams per each instilled hole (the drug can be scattered over the surface of the filled well).
On the depleted soils of clayey and sandy soils to improve the structure and other useful properties of soils, to increase the humus layer, to accumulate organic substances, to increase the fertility of fields, to create a reserve of nutritious organic and mineral substances, the KORNEVAYA MIXTURE preparation is introduced in the spring period before the planting of sprouted potato tubers, Perekopku, at the rate of 500 g per 10 m 2 or 5 kg per each hundred.
Considering that in the potato producing areas a dangerous disease is widespread - late blight, in which rapid spread from the primary focus arises. The above-ground part of the plant darkens, then turns black, the plant ceases its development, often dies, which affects the sharp decline in the yield of potatoes.
Against late blight, biomedicine SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL is active, which, in addition to strengthening the plant organism and increasing its resistance to late blight, contains copper vitriol, which stops the development of phytophthora, biofertilizer KBU, which possesses phytophthorostatic properties, and the biological preparation FETIL.
The drug FETHIL is an environmentally friendly remedy, which inhibits the mass development of phytophthora.
Technology of preparation of working solution. 1 tablet moistened in water diluted in water in a ratio of 1: 1 and then dissolve in 1 liter of water. 1 tablet (1 liter of working solution) is used for spraying 25 square meters of potato field. 1 pack consists of 10 tablets, which are dissolved in 10 liters of water. The volume of the working solution of 10 liters is designed to process 250 m2 of useful area. Spraying periods for planting potatoes: first spraying when the tops come together and second spraying - during the budding period.
The FETYL preparation not only has a valuable property to restrain the development of late blight, but also prevents the further progressive spread of this dangerous disease throughout the field and neighboring, bordering and nearby planting of potatoes. The drug FETYL, suppressing the vital activity of the fungus pathogen-the causative agent of late blight, promotes an increase in potato yields and accelerates the timing of the production of early products.
Along with the widespread disease of potato - late blight, a group of especially dangerous quarantine objects include potato cyst-forming nematodes that cause globberosis. These nematode species affect the root system of potatoes. Potatoes are affected by two species of cyst-forming nematodes - the golden potato cyst nematode (Globodera rostoshiensis) and the pale potato cyst nematode (Globodera palida), which are the objects of external or internal quarantine in disadvantaged countries.
On the territory of our country, the golden potato nematode is widely spread, in the fight against which a number of nematode-resistant varieties and hybrids are cultivated, the cultivation of which significantly inhibits the multiplication of this dangerous phytopathogen.
As for the second more aggressive species, the pale potato nematode, this species is currently absent in our country according to the results of systematic surveys of planting potatoes. But thanks to trade relations with states that are unsuccessful with respect to the pale potato nematode in their territories, there is always a danger of a mechanical drift into this country of this dangerous pest. Pale potato nematode is very dangerous because it lacks domestic nematode-resistant varieties of both our and foreign breeding, and varieties that are resistant to golden potato nematode, resistant to pale potato nematodes do not.
Each of these species also has a different race of aggression. We have a widely spread highly aggressive race of the golden potato nematode - Ro-1, in respect of which, basically, protective measures are being developed.
Against potato cyst-forming nematodes, we have developed a system of protective, preventive, preventive and exterminating measures that reduce the level of potato infestations by these pathogens to an economically insignificant level.
Primarily emerging and beginning to develop globodeosis foci, and small isolated foci of potato nematodes are usually subject to localization and elimination using chemical protection means by disinfecting the soil with nematicides - thiazone, DD preparation and others. Treatment of fields with nematicides is an extremely costly and environmentally hazardous process. It is possible to get rid of this kind of foci of globodeosis diseases by long-term cultivation in such areas of cultures that are not susceptible to globberosis, or globederoid-resistant varieties of potatoes.
The method of potato cultivation proposed by us envisages the use of various methods, methods and techniques in the cultivation of potato plants in combination with appropriate agrotechnics and using biologics and biofertilizers of a new generation that are environmentally safe, but which restrain the vital activity of nematodes and reduce their numbers to an economically insignificant level with Gradual complete elimination of identified globodeosis foci.
The use of biological preparations AGAT-25, GERBAMIN, DIPRIN, KBU, ROUND MIXTURE and SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL promotes the formation of a powerful root system in cultivated potatoes, which develops faster than the golden potato cyst-forming nematode, thus causing the potato bushes to "run away" from the nematode Invasion and have time to finish the vegetation, not affected to a large extent from the root parasite.
One of the most effective ways to control the foci of potato cyst-forming nematodes is to grow potatoes with the earliest possible production and immediately remove from the field after harvesting all the potato plants together with the root system and the basal soil into pre-prepared pits with the appropriate bail.
Early harvesting periods (II-III decade of June or the first decade of July), depending on the onset of early or late spring, with the immediate removal of infected roots, ensure removal from the field of the invasive (infectious) onset until the fall-off period of dead nematode females filled with mature eggs, That is, before the formation of cysts with highly viable contents. This method is bioecological (biocenotic), based entirely on the use of features of the biocenotic relations of the golden potato cyst-forming nematode with the host plant in the plant-host system-concomitant diseases-the environment-the antagonistic microflora with the emerging features of the protected field's agrobiocenosis. Getting the yield of early potato tuber production is achieved using a special technology in growing potatoes. This method is based on the cultivation of potato varieties and hybrids both from the group of resistant and from the group of susceptible early ripening varieties. Techniques are used to create conditions for the preliminary effective germination of the preplant material extracted after winter storage. Such an acceleration in the production of products is ensured by treating the tubers of seed or planting material with the newer biogeochemicals described above: AGAT-25, GERBAMIN, DIPRIN, KBU and SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL. Processing of planting biomaterial is carried out in recommended doses.
For preplant preventive treatment of tubers with biological preparation AGAT-25, 1 ml of biopreparation is dissolved in 10 liters of tap water, obtaining a working solution with a concentration of 0.001%, which is treated with 1 ton of planting material.
For preplant preventive treatment of potato tubers with DIPRIN biopreparation, 10 ml of concentrate-suspension with a titer of 1000 invasive larvae of Pristionehus uniformis in 1 ml are dissolved in 10 liters of water, obtaining a working solution at a concentration of 0.01%, which is treated with 1 ton of planting material.
For preplant preventive treatment of potatoes with GERBAMIN biological preparation, 0.1 ml of concentrate is diluted in 10 liters of water, obtaining a working solution at a concentration of 0.0001%, which is treated with 1 ton of planting material.
For preplant preventive treatment of potatoes with biopreparation KBU 10 ml of biopreparation is dissolved in 10 liters of water, obtaining a working solution at a concentration of 0.01%, which treat 1 ton of planting material.
For the preventive treatment of potatoes with the biomediment SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL, 1 ml of the biopreparation is dissolved in 10 liters of water, obtaining a working solution at a concentration of 0.001%, which is treated with 1 ton of planting material.
It is allowed to use a tank mixture of all the recommended biological agents.
The biopreparation DIPRIN can be successfully replaced by the various forms of the biological product NEMATOL that we develop, the active principle of which is the nematodes, antagonists of the golden potato cyst-forming nematode. The active principle of this biopreparation is entomopathogenic nematodes: Neoaplectana carpocapsae, pcs. DD-136 (NEMATOL-D); Neoaplectana carpocapsae, pcs. Agriotos (NEMATOL-P), Neoaplectana carpocapsae, pcs. Agrotis (NEMATOL-OS); Steinernema feltiae (NEMATOL-F) family of Steinernematidac and Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (NEMATOL-H) from the family Heterorhabditidae.
The rates of consumption and efficacy of the described biological preparations are the same as for the biological preparation DIPRIN.
Biological preparations AGAT-25, GERBAMIN and SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL accelerate and stimulate the growth and development of potato plants, increase their resistance to pathogens and nematodes. Biofertilization of KBU increases the resistance of potato tubers to late blight, enriches the potato's rhizosphere with useful microorganisms; Biopreparation DIPRIN and various forms of the biopreparation NEMATOL stimulate the growth and development of plants due to the concomitant beneficial microflora, accelerate and enhance the processes of tuber formation, increase the number of stolons formed, increase the resistance of potato plants to nematodes, and reduce the reproductive activity of the golden potato cyst-forming nematode.
Tubers treated with biopreparations are germinated in peat chips with appropriate humidification and heating by calorifiers (the temperature is maintained at least 18 ° C) or contain planting material in warm rooms. The early harvesting of potatoes is also achieved by planting the potato material in the soil at the earliest possible date (the last decade of April and the first ten days of May) in advance with the germinated and stimulated biological preparations AGAT-25, GERBAMIN, DIPRIN, NEMATOL and SIMBIONT UNIVERSAL with potato tubers in Pre-fertilized with biofertilizer KBU and ROOT MIXTURE, which ensures rapid plant growth and intense tuber formation. The powerful root system of plants has time to escape from infection by nematodes in the event of early harvesting. To quickly obtain a powerful root system and rapid tuber formation and the formation of additional stolons, as well as for prevention from attack of potato phytopathogenic nematodes and phytophthorosis, biofeedback is applied to the well before planting. ROOT MIXTURE and biologics for prevention against golden potato cyst-forming nematodes - DIPRIN, NEMATOL, NARCISS, Against late blight - KBU and FETYL and for the early formation of a powerful root system and the formation of additional stolons - biological preparations AGAT-25, GERBAMIN and SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL. Against nematodes, it is possible to use the biopreparation NEMATOFAGIN-A.
Concentrations of introduced biological products: DIPRIN in a working aqueous solution in a concentration of 0.02%; NARCISS 0.002%; Nematol 0.02%; NEMATOFAGIN-A 0.02%; КБУ 0,02%, ФЕТИЛ 0,02%; AGAT-25 0.002%; GERBAMINE 0.0002%, ROOT MIXTURE 20 g in each well and SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL 0.002%.
For the active development of saprophytic phases of entomopathogenic nematodes and bacteria - antagonists of diseases and pests of potatoes - 100 g of trichogram production waste (dead butterfly moths or grain moths) or wastes of production of viral entomopathogenic biopreparations (American white butterfly, cabbage cabbage , A winterworm, a cottonworm, a silkworm ringed, a silkworm unpaired, a silkworm monk, etc.) or a powder of naturally fallen autumn leaves, or a powder of naturally fallen pine needles, or a rotted chicken droppings, or a mixture of the listed components.
50 ml of the working solution of the biopreparation is poured into each well.
In preventive or exterminating purposes against phytophthora and golden potato cyst-forming nematodes, vegetative plants undergo treatment (spraying or watering) with biopreparations at intervals of 2 weeks. In order to accelerate the growth and development of plants, accelerate the ripening of the crop, increase the resistance of plants and enhance their resistance to pests and diseases, planting potatoes is treated with a tank mixture of biological preparations AGAT-25 or RIZOPLAN, GERBAMIN, SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL, against late blight - a tank mixture of biological preparations AGAT-25 or RIZOPLAN, KBU, SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL, FETYL, against the golden potato cyst-forming nematode - a tank mixture of biopreparations DIPRIN or NEMATOL, NARCISS, NEMATOPHAGIN-A or the listed biological preparations separately, in working solutions with the concentration used for pouring in the wells. The norms for the flow of working fluid to the protected area are the same as for the application of pesticides.
When the symptoms of late blight or globberosis appear, the concentrations of the corresponding biopreparations are doubled, and the treatments are twice as fast.
The use of the described method of biological control with late blight and cyst nematodes practically excludes spreading and development of foci of diseases. Potato plants of early varieties end vegetation for 40-50 days after planting, they escape from infection with globoidosis and late blight and give high yields (up to 2-3 kilograms of potatoes from each bush).
The main and the main important factor in combating potato globberosis with the help of the earliest maturation of potatoes is the development of a strong powerful root system, thanks to which an intensive supply of all necessary nutrients from the soil to the plant is ensured, which increases its field endurance to unfavorable environmental conditions (weather conditions ), But also increases the resistance and resistance to plant damage by potato nematode, late blight and other associated diseases and pests.
The described methods of growing potatoes are the basis for an integrated system of antinematode measures in which this biological method is combined in order to increase its efficiency with such agrotechnical methods as increasing the number of hills of vegetating plants, combining with antinematode links of rotations from nematode-infested crops, with mandatory inclusion in Crop rotation of cultivated nematode-resistant potato varieties.
To obtain a potato crop, successive hilling before the appearance of potato shoots is applied at the earliest possible time until the potential threat of morning frost disappears in order to prevent the freezing of the tops. In this way, you can speed up the harvest for 10-15 days.
Potatoes can be planted on globodeosa areas only after not less than five years of cultivation on them of unrefined crops, otherwise there is not only an accumulation of pathogen in the soil, but also the possibility of occurrence and accumulation of aggressive new races of a potato nematode.
In order to quickly form a powerful root system and obtain the earliest possible harvest of potatoes, it is possible to combine the above measures with biological soil heating. In order to do this, in the late autumn, trenches with a width of 30 cm and a depth of 60 cm are pulled out at the sites of the future rows of potatoes. In the case of settling the field with potato nematodes, the contaminated soil is taken out from the field and buried in specially prepared pits, after which unaffected soil is returned in return. Trenches in 1/3 fill with green mass from chopped or torn weeds or grass mixed with straw, naturally fallen pine needles and naturally fallen autumn leaves in a ratio of 4: 4: 1: 1. Then trenches are covered with dug or brought land.
In spring, the soil in the trenches at a depth of 10-15 cm is 10-15 ° C warmer than the surrounding ones due to the biological warming up of this green mixture to 60-70 ° C. The tubers planted in such soil quickly form a powerful root system, and on condition of a consecutive series Hills before emergence increase the underground part of the stems by 15-20 cm. In these parts of the stems, subsequently, stolons are formed in mass, from which the tubers appear, which increases the yield, sometimes 2 or more times. The biological warming of the soil creates an insurmountable barrier to attacking the potato of the invasive larvae of the golden potato nematode emerging from the cysts.
At well-to-globberose sites 10-12 days after emergence of potato shoots in the immediate vicinity of the rose bushes (10-15 cm), you can plant tubers of medium-ripened or late-ripening varieties of potatoes, which continue to develop after harvesting previously planted potatoes. In this case, two sites can be obtained from one site and, if desired, three independent crops of potatoes, even in the climatic conditions of Moscow and the region.
It has been experimentally established that, at a high density of a potato nematode population in the soil, when nematode-resistant varieties and hybrids are planted, the resistance barrier of plants is lost to some extent and the females continue to intensively feed and lay eggs. To avoid such cases, it is necessary to grow nematode-resistant varieties only after cultivating the antinematode links of crop rotation from unrefined crops. The following is also a very important factor. When cultivating susceptible varieties and potato hybrids, usually, and very often, tubers of potato varieties susceptible to potato nematodes remain in the plow horizon of the soil. Part of the remaining and overwintered tubers in the spring renew their development and the growth of plants in these cases serves as a source of conservation in the soil of the infectious onset of globberosis. Therefore, such potato plants are subject to complete removal from the fields. If the planting of nematode-resistant varieties of potatoes is carried out according to the predecessor, which was a potato-susceptible to globberosis, this inevitably leads to a mixture of varieties, especially this is dangerous in seed plots. Potato plants susceptible to the potato nematode, while on the field with plants of nematode-resistant varieties, will renew, maintain and re-accumulate in the soil the invasive principle, which will lead to a significant lengthening of the quarantine removal period from a dysfunctional farm. In this case, the focus will not be eliminated for longer periods.
The above biopreparations can be effectively used for growing nematode-resistant varieties and all varieties of potato susceptible to globoderosis for commodity production. These ecologically safe biopreparations have been successfully used both on the plant sites and on seed seed fields in order to obtain higher yields and improve their technological and taste qualities, and to obtain the output of earlier products.
The necessary preventive method, which is an integral part of growing potatoes when introducing bioecological methods to combat identified globodeosis foci, is the conduct of phenological observations of the state of growth and development of potato bushes with the purpose of their timely detection, localization and immediate elimination of the primary emerging diseased plants.
In the phase of the beginning of flowering of plants, the characteristic signs of this dangerous disease - globederoza of potatoes - are most evident. Plants lag behind in growth and development, stunted with one or two thin stems, with crushed leaves, with a wrinkled leaf plate, which prematurely acquires a light color to strongly expressed chlorosis. Detection of diseased plants, their timely removal prevents further progressive multiplication of the potato nematode, prevents further accumulation of a dangerous invasion in the soil and prevents further spread of the disease to free field locations and adjacent fields. During the period of the beginning of flowering, the introduced larvae have time to develop to mature females, which are clearly visible on the surface of the roots. In size with poppy seed, they have a milky white color in this period, then gradually the females acquire a yellow color of golden hue and darken then to a light brown color. Dying females, filled with a large number of eggs (up to several hundred in each female), turn into a resting stage - a cyst that easily falls from the root to the soil, where it tolerates even the harshest winters and survives for several years, waiting for the spring period and appearance New roots of potatoes. At this time, an intensive exit from the eggs of invasive larvae occurs, which migrate to the soil in search of a host plant and are introduced into young developing roots.
In the presence of potatoes on strongly planted plants, they are digested with the root system and root soil, removed into specially excavated pits and buried. The excavated places from under remote diseased plants are disinfected with carbamide (urea) 100 g per well. When there are diseased plants, but with a weak course of the disease, i.e. With weakly expressed signs of this dangerous disease, it is recommended that they be treated twice with new generation biologics: NARCISS, DIPRIN or NEMATOL, NEMATOFAGIN-A. In the period of hilling it is necessary to make a tank mixture of the listed biological preparations or each of them separately. Under the roots of diseased plants, one liter of a tank mixture of biologics should be added and the operation repeated every week, which prevents premature wilting and restores normal development and growth with normal tuber formation and obtaining an average yield. Otherwise, the lack of treatment of potato plants with the revealed initial signs of the manifestation of the painful symptoms of globberosis usually leads to a strong and rapid course of the pathogen process and to the practical complete loss of the crop on the affected plants.
Combination of the above biological preparations and feeding of plants with BIOGUMUS and KBU provides a significant increase in yield by 20-30%, and in some cases - by 1.5, 2, 3 or more times, with improved taste and technological qualities of the products, with an average tuber quality of 85- 90%. The use of these methods of combating potato nematodes prevents the accumulation of invasion in the soil (Tables 2 and 3).
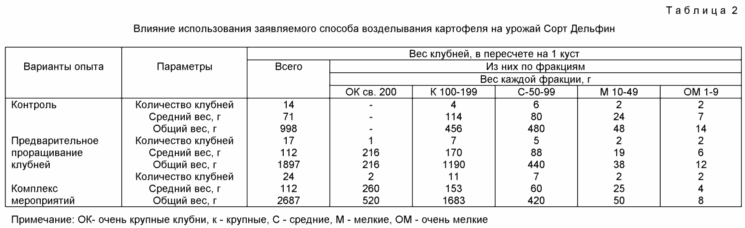 |
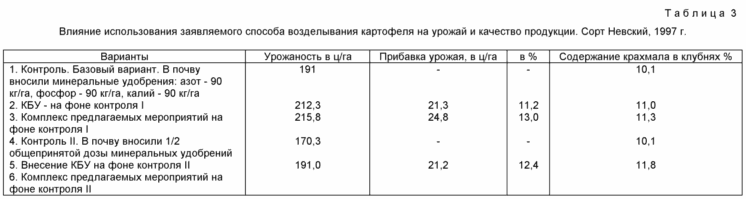 |
In the organization of biological control, an equally important problem is the control of potato pests, first of all, with the Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata Say.) And wireworms (Elateridae).
The struggle with the Colorado beetle requires a special strategy because this type of pest has a special plasticity and adapts to the conditions of the external environment. Moreover, being an alien from the American continent, the Colorado beetle does not have in Europe and Asia local specialized parasites and predators and they have to be introduced from abroad. In addition, the larva and the imago of the Colorado beetle are poisonous and not all insectivorous animals can eat them. However, our local entomophages begin to gradually adapt to the American alien and cause him more and more sensitive blows. In our strategy for combating the Colorado potato beetle, much attention has been paid to determining individual measures to control various stages of pest development.
Larvae of the 4th age (at the end of development), pronymph and imago are found in the soil and therefore inaccessible to traditional pesticides. Against these stages of the Colorado beetle, we use biopreparations based on entomopathogenic nematodes (DIPRIN, NEMATOL). The working solutions of these biopreparations are used to irrigate the vegetating potato plants during the period when they leave for pupation for larvae of the 4th age or imago for wintering. Invasive larvae of entomopathogenic nematodes enter the soil, migrate in it and find their victims. Getting into the body through the spiracle or anus, the nematode probes the intestines of the larva, pronymph or imago of the Colorado beetle, arranging the insect with a peculiar "peritonitis", while the nematode inhabits the organism of the Colorado beetle with nematophilic entomopathogenic bacteria, which also have pathogenic properties for other soil pests - Larvae of wireworms, larvae of May crunches, caterpillars of biting scoops, etc. It is enough to hit one invasive larva of an entomopathogenic nematode into the insect organism in order to ensure a fatal outcome. Entomopathogenic bacteria kill insects in the shortest time (2-3 days), causing a specific disease - septicemia - and form their colonies inside the deceased insect. These bacteria multiplying inside the insect feed on saprophytic phases of entomopathogenic nematodes that pass through several successive generations inside the affected insects. After the feeding for the nematodes inside the insect ends, they stop at the stage of invasive larvae and leave the dead insect, going to search for new victims. In the organism of one Colorado beetle, up to 200,000 invasive larvae of the entomopathogenic nematode can be reproduced. Nematodes form around the dead insects extensive (15-20 cm in diameter) zones, which, with a significant population of planting potatoes by the Colorado beetle, gradually merge, condemning the death of those who continue to enter the soil to pupate the larvae of the 4th age or adults who go to winter. The death of the Colorado beetle in the soil reaches 80-90%, which significantly reduces the risk of planting potato plantations next year in the protected area.
In spring, after the appearance of the first shoots of potatoes, immediately appear beetles that crawl out of the soil at the sites of planting potatoes or migrate from other places (the Colorado beetle can travel a few kilometers). The spring generation of the pest is the smallest, so special attention should be given to this stage of pest reproduction, so as to minimize its further reproduction and the resulting sharp increase in its number, which requires already "fire" purely chemical means of control. At this time, it is advisable to produce large batches of larvae of the predatory bug PICROMERUS, eggs of which by this time already come out of the embryonic diapause, but can be stored in the refrigerator for a long time at a temperature of 2-4 o C and can be used to obtain the entomophage by any date. Bug larvae, which by this time do not find another more suitable food, destroy 70-80% of the Colorado beetles emerging from the soil and arriving from outside. The other two kinds of carnivorous beetles devouring the Colorado potato beetle - Podzus and Peryllus - are more thermophilic and can not be successfully used during this period of the year.
Bugs emerging from the soil mate and lay eggs on the underside of potato leaves, rarely on the leaves of other plants. From the day the beetles emerge from the soil before the start of egg laying, depending on the weather conditions, from one to two weeks. At this time, the beetles undergo additional feeding of the botanical potato, without which they can not leave the highly viable offspring. The first clutches of the Colorado potato beetle are malignant, often affected by fungal diseases, which is due to the high relative humidity of air during this period of the year. At this time, it is advisable to carry out the treatment with biological preparation BOVERIN - the only biopreparation active against eggs of the Colorado potato beetle. In addition, the eggs of the Colorado beetle are massively released by the endoparasitic insect of the EDOVUMA Egg and the local egg-eaters of the Colorado beetle - larvae of golden larvae (pearl, Chinese, beautiful, ordinary, seven-spotted, etc.), larvae and imagoes of God's cows (leis, seven-spot, cycloneidae and others .), Larvae of the common camel and larvae of syrphids (sirf venous), etc. The larvae of these insects eat and the nascent larvae of the Colorado beetle and larvae of I-II age. By this time, time treatment with biological products: BITOXIBACILLINE (BTB), BIKOL, DIPRIN or NEMATOL. DIPRIN, BOVERIN and NEMATOL can be used only under condition of high relative humidity of air and high soil moisture (90-100%) and temperatures not lower than 15-18 o C. During the development of larvae of III-IV ages and further up to the end of the potato growing season An interval of two weeks is carried out treatment with biological products DIPRIN-NEMATOL and produce large quantities of predatory bugs SUBSIS, PERILLUS, PICROMERUS. These measures allow you to get rid of another 80-90% of the population of the calorie beetle, which is present during all stages of development. During this period of the year, larvae of God's cow, lacewoman, camel, syrphid eating eggs of the Colorado beetle continue to work on planting potatoes. EDOVUM continues to destroy the eggs of the Colorado beetle. The listed measures allow in 2-3 years to get rid of the local population of the Colorado beetle.
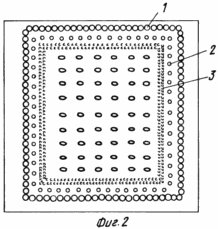 |
 |
However, the application of all these measures can not insure the planting of potatoes from migrating individuals of the Colorado beetle imago. Bug migration from other places continues throughout the growing season of potatoes and often negates the ongoing efforts to introduce biomethod. In this regard, potato planting is won, surrounded by forests, forest belts or other insurmountable obstacles for flying beetles. In order to successfully combat migratory beetles, food potato plantations (see Figure 2) should be protected by complex linear technical potato plantings located along the perimeter of the section, which can be performed in one line (see Figure 2a), in two rows (see Fig. 2b), zigzagging (see Figure 2c) or a 2-line checkerboard fit (see Figure 2d). On the inside of the solid planting of potatoes, which occupies a width of 30-50 cm, plant a row of sunflowers and sow a strip of coriander, dill, carrots, onions (20-30 cm wide) (see figure 2).
Continuous planting of technical potatoes collects 80-90% of migrating Colorado beetles, and the planting of umbellate or composite plants prevents its penetration into ware potatoes. On technical potatoes, you can apply a set of biological activities listed above, and in the extreme case, carry out treatment with pesticides (DECIS or others), which will not affect sharply the quality of technical potatoes. Potatoes for technical needs need less environmental cleanliness. Flowering plants of sunflower, coriander, dill, carrot, onion, in addition to the barrier for the spread of the Colorado beetle, serve as a source of additional nutrition for the entomophagous used and can be used for food.
As for other crops, combining the use of new high-performance biologics of a new generation in combination with the use of entomophages against pests and diseases - treatment of planting material with biological preparations AGAT-25, GERBAMIN, SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL - in order to obtain stronger and more resistant to diseases and pests Plants with a well-developed root system; Treatment with biopreparations DIPRIN or NEMATOL, NEMATOPHAGIN-A against gall, stem and cyst-forming nematodes both planting material and vegetative plants; Treatment with biological preparations AGAT-25 or RIZOPLAN, KBU, SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL, FETIL against phytophthora as a planting material, and vegetative plants; Against anthracent and ascochitosis AGAT-25, against bacteriosis of various origins AGAT-25, ALIRIN-S, MIKOSTOP, RIZOPLAN-F; AGAT-25, ALIRIN-B, ALIRIN-S, GLIOOCLADINE, TRIHODERMIN (different strains), FITOLAVIN-G, PHYTOLAWIN-L; Against fungi of mucous AGAT-25; AGAT-25, against mildew of various origins AGAT-25, AMPELOMITSIN, BACIFIT, AGAT-25, against the complex of fungal diseases AGAT-25, ALYRIN-B, ALIRIN-S, MIKOSTOP, RIZOPLAN-F, against peronosporosis - AGAT-25, against spots of various origin AGAT-25, PENTOPHAG, TRICHOTECIN; Against the withering of different origin - biopreparat BACIFIT.
The preplant treatment of plants with biological preparations of stimulating action ensures an increase in the germination of seeds and stimulates growth processes throughout the entire growing season. The introduction of biopreparations into the soil during planting or sowing, watering with working solutions of biological preparations or spraying them on vegetating plants in combination with the release of the corresponding entomophages in the ratio of the parasite-victim 1:10 or the maintenance of the necessary number of entomophages for the purpose of prevention throughout the growing season provides reliable protection From pests and diseases throughout the year, and most importantly it ensures the development of a strong and powerful root system in plants, which is the guarantor in increasing the resistance and resistance of plants to adverse environmental conditions (abiotic factors) and to disease and pest damage, allows without pesticide treatments Protect plants from pests and diseases. The use of a complex of the listed measures provides, in addition to potatoes, cucumbers and tomatoes, an increase in the yield of other agricultural crops by 15-20%, while improving the taste and technological qualities in combination with the ecological purity of the agricultural produce, among eggplants, peas, buckwheat, cabbage, onions, Carrots, oats, peppers, millet, wheat, rice, rye, sugar beet, cotton, fruit, flower and berry crops.
The biopreparations DIPRIN, NEMATOL-D, NEMATOL-P, NEMATOL-OS, NEMATOL-F and NEMATOPHAGIN-A developed in addition to potatoes, cucumbers and tomatoes can be used on peas against whites, scoops and pea grains; On cabbage against cabbage cabbage, cabbage whitewash, belly bones, moths and cabbage moths; On oats against the oat nematode; On wheat against a harmful turtle; On sugar beets against weevils; On cotton against meloydoginosis, scoops of winter and box worms (scoop); On the fruit against the gypsy moth, the American white butterfly, the apple moth and the fruiter of other species, the apple moth and the moth of other species; Against larvae of sawflies on flower and berry crops; Against caterpillar larvae on berry crops; Against the silkworm-monk, ringed silkworm, Siberian silkworm on ornamental crops, against termites and the bear.
USED BOOKS
1. Ezhov GI, Zhilyaeva IN, Makarov PP, Kostina L.Ya., Masyuk Yu.A. Preventive integrated biosecurity of the selection material. In: Technology of potato production. Scientific works of NIIKh.- M., 1991, p. 31 - 34.
2. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2041585, cl. A 01 B 79/02, A 01 G 1/00, A 01 C 1/00, A 01 M 21/04.
CLAIM
Method of cultivation of crops: potatoes in the open ground, cucumbers and tomatoes in a closed ground, including soil preparation, planting or planting of plants, periodic cultivation, use of biological products, characterized by preplanting treatment of seeds and tubers with a mixture of activators, immunostimulants, antagonists and biofertilizers (AVERTROP, AGAT-25, or RIZOPLAN, AMPELOMICIN, GERBAMIN, DIPRIN or NEMATOL, COMPLEX BIOLOGICAL FERTILIZER (KBU), SIMBIONT-UNIVERSAL) in half doses from the recommended for this preparation (mixture 1), the same mixture in combination with biological fertilizers (BIOHUMUS, ROAST MIXTURE - in recommended doses) are applied to the wells before planting, waste from trichogram production or waste from the production of viral biopreparations (dead butterflies) with sapropel or with a chicken dropper or with powder from naturally fallen leaves or needles enter the soil together with biological preparations (Mixture 2) in the following mixture 1, periodic ground spraying or watering of vegetating plants (bi-weekly) with preliminary spreading of BIOHUMUS and introduction of ROOT MIXTURE (in the same norms) is carried out in the mixture 1, the soil is populated with a complex of microorganisms, microbiological antagonists contained in biological preparations (ALYRIN-B, ALYRIN-S, BACIFIT, GLIOCLADINE, MICOSTOPS, NARCISS, NEMATOPHAGIN or NEMATOPHAGIN-A (activated by the supernatant - a waste from the production of the DIPRIN biopreparation), PENTOPHAG, RIZOPLAN-F, various forms of TRICHODERMIN, TRICHOTECIN, PHYTOFLAVIN, PHYTOFLAVIN-L ) (Mixture 4), in half doses from the recommended for this preparation, which is applied to the wells before planting, further periodic (once in two weeks) spraying or watering of the plants; Introduced as elements of the fauna of predators and entomophages (AFIDIUS, AMBLISEUS, GOD, COLOR, LAZEPHLEBLES, SILFIDES, PHYTOSEILUS) - complex 1 by periodic release in half doses from the recommended for this preparation and microorganisms, which are the current beginning of biologics (AVERTROP , VERTICILIN, CEPHALOSPORIN, ENTOMORPHIN, BIKOL, BITOXIBACILIN, BOVERIN, VERTIMEX, MIKOAFIDIN-T, TOURICIDE, ANDTFOTORIN) (mixture 5), in half doses from the recommended for this preparation by periodic treatments - spraying or watering; Before sprinkling with DIPRIN and / or NEMATOL sodium alginate is used to prevent the nematodes from drying out and death, and when using entomophages, at the beginning of the growing season, the cultivation of crops is additionally planted in the intercrops of the main cultures of the Compositae and / or Umbelliferae, which are an additional source of nutrition For adult entomophages.
print version
Date of publication 06.03.2007гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.