| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2267721
![]()
ENERGY CONVERSION METHOD
Name of the inventor: Henry Siebert Karlovic (RU); Zaporozhets, Eugene P.
The name of the patentee: Subsidiary Open Joint-Stock Company "Central Design Bureau of oil equipment"
Address for correspondence: 142110, Moscow region, Podolsk, st.. Komsomolskaya, 28, DOAO CKBN
Starting date of the patent: 2003.04.25
energy conversion method relates to energy conversion methods by changing parameters of the liquid into the thermal energy and can be used in all industries, including for energy specific heat collection, preparation and processing of hydrocarbon raw materials, and manufacturing chemical and petrochemical industries, particularly in heated hydrogen-containing liquids contaminated with mechanical impurities, salts, gels. Method of converting pressure energy hydrogenous fluids involves creating a vortex cavitating fluid flow through the use of its pressure, followed by imparting linear motion to the liquid. Organize rotation speed cavitating liquid flow in which of positively and negatively charged ions dissociated molecules cavitation fluid and form a central peripheral region. Under the influence of centrifugal force is concentrated in the peripheral region massive negative ions, and in the central region - positively charged ions at mass, thereby providing an electric potential difference between the regions. Use of the invention will improve the efficiency of pressure energy conversion into heat energy and ensure receipt of electrical energy.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to processes for energy conversion by varying fluid parameters, such as pressure, volume, density, etc., To thermal energy and can be used in all industries. The preferential field of application of the specific heat energy supply systems for collection, treatment and processing of hydrocarbon raw materials and production and chemical and petrochemical industries, in particular by heating hydrogen-containing liquids (water, hydrocarbons, etc.) Contaminated with mechanical impurities, salts, gels, etc.
Known way to convert potential energy - hydrogenous fluid flow pressure energy into another form of energy - heat, cavitation (RF patent №2131094, MPK 6 F 25 B 29/00) comprising heating fluid cavitation by changing its parameters in cocurrent flow such as pressure, volume, density, etc., the heat energy supply to the consumer.
The disadvantage of this method is its low efficiency. It is caused by a low concentration in a liquid cocurrent flow cavitation bubbles, through which the pressure energy is converted into thermal energy. Another disadvantage of the method is the inability to convert fluid pressure energy into another type of energy other than heat.
There is a method of energy conversion pressure hydrogen-containing fluid, which partially remedied the above drawbacks (RF patent №2153131, IPC 7 F 24 H 1/00, F 24 D 3/00, prototype). The method involves creating a vortex flow of fluid through the handshaking its use pressure, followed by imparting linear motion to the liquid. Said technique allows to increase the concentration of cavitation bubbles in the flow, which leads to increased heat output.
However, the increase achievable heat slightly and, in addition, this method can not receive another form of energy - electricity.
The proposed invention solves the problem of more efficient conversion of fluid pressure energy into thermal energy and the expansion of functionality by taking apart the thermal electric power.
To achieve said technical result in the method hydrogenous fluid pressure energy conversion into heat energy, which includes the creation of the vortex flow handshaking liquid by utilizing its pressure, followed by imparting fluid linear motion, organizes the rotational flow velocity of the cavitating liquid, which of positively and negatively charged ions dissociated molecules fluid cavitation, form a central and a peripheral region where the centrifugal force is concentrated in the peripheral region massive negatively charged ions dissociated from molecules of the liquid when cavitation and in the central region - positively charged ions at mass, thereby providing an electric potential difference between areas.
The resulting electric field provide additional dissociation of molecules in a liquid stream, since it weakens the intermolecular fluid communication. When weak intermolecular bonds decreased fluid viscosity and surface tension. This reduces the energy expended to break the cavitation fluid, and increase the amount of cavitation bubbles arise that, as a result, increased thermal energy output, i.e. the task set is solved better fluid pressure energy conversion into thermal energy.
Increase the potential difference between the ionized peripheral and central areas of the cavitating liquid flow by imposing on them an electromagnetic field.
The ions are produced from hydrogen-containing dielectric fluids.
flow cavitation fluid rotation speed is set at the maximum value of the voltage and (or) electric current.
Retraction of electrical energy in the form of electric current allowing the liquid to expand the functionality of this method, by further application of this energy.
Application of a magnetic field to the ionized region increases the electrical potential difference and electric current, as a consequence, increases the yield of thermal and electrical energy.
Production of hydrogen-ions from a liquid which is an insulator, and allows to increase the magnitude of an electrical potential difference and, consequently, increase the amount of thermal and electric energy.
Establishing optimum liquid flow cavitation rotational speed by the maximum value of voltage and (or) the electric current is achieved by obtaining the highest potential difference and, consequently, allows to increase the amount of thermal and electric energy.
The authors and the applicant of the prior art not known to the ways in which the problem is solved to a similar manner.
 |
 |
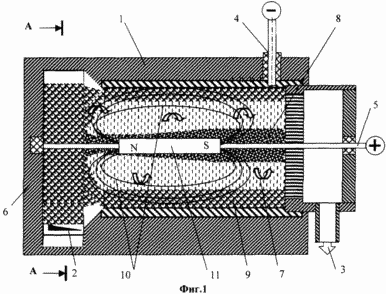
1 schematically shows a device for implementing the proposed method.
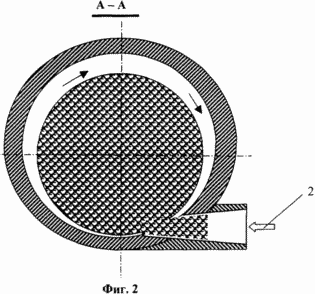
Figure 2. - A-A sectional view in Figure 1.
Device (1) for the implementation of the energy conversion process comprises a housing 1 with two tangential inlet for supplying fluid outlet 3 and the electrodes 4 and 5.
The method is as follows.
The liquid stream is fed into the housing 1 of the device (1, 2) through the tangential inlet 2 in a housing to create a vortex flow of the liquid stream in a volume which cavitation occurs in the form of vapor bubbles 6 (Figure 1).
Vortex flow cavitating liquid attached rotationally forward movement 7 (1), in which an order of magnitude of the tangential velocity exceeds the axial velocity. Moreover, the tangential velocity is a value at which the centrifugal force due to ions created from the molecules of liquid, cavitation dissociated, ionized at the electrode central 5 8 (1) and the inner wall of the housing 1 ionised peripheral region 9. Under the effect of centrifugal force in the peripheral concentrated region 9 massive ions having a charge, such as negative. In the central region 8 of concentrated ions at masses of opposite charge. Thus obtained between these areas electrical potential difference. Using this potential difference is removed from the electrodes 4 and 5 are energy in the form of electric current from the liquid stream. Then liquid impart linear motion and is withdrawn through the outlet 3.
Electrical energy in a vortex fluid further dissociate into ions liquid molecules.
On the ionized region 8 and 9, the magnetic field 10 is applied by a permanent magnet 11. The action of this field due to electromagnetic induction is increased electrical potential difference and electric current.
Ions can be generated from a hydrogen-containing fluid which is a dielectric, such as kerosene, glycol, etc.
The proposed method allows to increase efficiency of conversion of pressure fluid energy into thermal energy to 90% and increase the functionality of addition by obtaining thermal and electric energy of about 6%.
Example
The flow of pressurized water 5.10 5 Pa is fed tangentially (input 2 in Figure 1, 2) at the optimum speed of about 30 m / s, and create a vortex flow from it to the extent that cavitation occurs in the form of vapor bubbles 6.
Flow vortex cavitating liquid impart rotational-translational movement 7, wherein the magnitude of the tangential velocity (30 m / s) on the order exceeds the axial speed (2 m / s). Moreover, the tangential velocity is a value at which due to the centrifugal force created from H + ions and OH - water molecules dissociated during cavitation, ionized at the central region 8 and the electrode 5 from a peripheral region of the inner wall 9 of the housing 1. Under the influence of centrifugal force in the peripheral concentrated region 9 massive ions OH - having a negative charge. In the central region 8 concentrated H + ions at masses of opposite charge. Obtained thereby between these areas an electric potential difference of 0.5 V. With the potential difference obtained is removed from the fluid flow through the electrodes 4 and 5 are energy in the form of an electric current value of 0.25 mA. After that, the liquid attached to a linear motion and discharged through the liquid discharge pipe 3.
In a twist of electrical energy flow is further increased dissociation of liquid molecules into ions H + and OH -.
On the ionized region 8 and 9, the magnetic field 10 is applied, for example, a permanent magnet 11, in which the electromagnetic induction due to the electrical potential difference increases to 0.8 V and an electric current of 0.7 mA.
cavitating fluid flow rotational speed set by the maximum voltage value and (or) the electrical current measured at the electrodes 4 and 5.
Ions can be generated from a hydrogen-containing fluid which is a dielectric, such as kerosene, glycol, etc.
The proposed method allows to increase efficiency of conversion of pressure fluid energy into thermal energy to 90% and increase the functionality of addition by obtaining thermal and electric energy of about 6%.
CLAIM
1. A process for converting pressure energy of a hydrogen-containing fluid comprising the vortex flow creating cavitating fluid pressure by utilizing its liquid followed by imparting linear movement, characterized in that the rotational speed organize cavitating liquid stream in which of positively and negatively charged ions dissociated molecules fluid cavitation form a central and a peripheral region where the centrifugal force is concentrated in the peripheral region massive negative ions, and in the central region - positively charged ions at mass, thereby providing an electric potential difference between the regions.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the increased voltage difference between the ionised peripheral and central regions of the cavitating liquid flow by applying the magnetic field on them.
3. The method of claim 1 or 2, characterized in that the ions are produced from a hydrogen-containing dielectric fluid.
4. A method according to claim 1 or 2, characterized in that the rotational speed of a liquid flow cavitation set by the maximum voltage value and (or) of the electric current.
print version
Publication date 29.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.