| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2280824
![]()
HEAT GENERATOR FOR LIQUID HEATING
The name of the inventor: Vadim Alekseevich Rukavishnikov (RU); Rukavishnikov Alexey Vadimovich (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Vadim Alekseevich Rukavishnikov (RU); Rukavishnikov Alexey Vadimovich (RU)
Address for correspondence: 140186, Moscow Region, Zhukovsky, ul. Embankment Tsiolkovsky, 24, ap.170, V.A. Rukavishnikov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2005.03.03
The invention relates to the field of heat power engineering and can be used for heating and hot water supply of buildings, structures, vehicles, in particular for the elimination of emergency situations caused by failures in the operation of central heating and hot water supply systems. The proposed design of the heat generator allows reproducing the loading of the motor with a nominal torque, which ensures a stable heat output corresponding to the rated power of the electric motor, with the maximum efficiency. The heat generator for heating the fluids includes at least one fluid generating means arranged in the form of finned wheels arranged coaxially to form a gap between their end surfaces with ribs. The first finned wheel is rotatably mounted under the action of the drive, and the second is stationary. Between the ribs at equal distance from them are established small ribs of thickness equal to the thickness of the main rib. In the cross section, the small ribs have a rectangle profile that, on the side of the edge facing the axis of rotation of the wheel, ends in a semicircle with a radius equal to half the width of the main rib, the rib length is not more than one third of the length of the main rib. On the surface of the movable wheel, at least one opening is formed at least in the circumference of the minimum distance from the free end of the small rib. The center of each hole lies on the extension of the axis of symmetry of the small rib in the direction of the axis of rotation of the wheel at a distance of the diameter of the hole from the small edge. On the underside of the un-brushed surface of the wheel around these holes are chamfers. At the end of the finned surface of the fixed wheel is a removable disk, fixed flush with the end surface of the ribs.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of heat power engineering and can be used for heating and hot water supply of buildings, structures, vehicles, in particular for the liquidation of emergency situations caused by failures in the operation of devices of central heating systems and hot water supply, the invention and can be used for heating viscous liquids at Their pumping through pipelines and to ensure other household needs associated with the supply of hot liquids.
A heat generator for heating liquids is provided, comprising means for supplying liquid, a body and at least one means for accelerating the movement of the liquid in the housing, in the form of an impeller rotatably mounted under the action of a drive, and at least one Means for inhibiting the movement of the fluid in the form of a vane element and located near the impeller to form a gap between the blades which are formed by radial grooves formed on the end surface of the impeller and blade element, respectively ( GB 2239704 A, cl. F 24 J 3/00 , Published on 10.07.1991 ).
The main drawback of the described analogue is the instability of heat output.
The closest analogue (prototype) is a heat generator including a means for supplying liquid, a housing and located in the housing, at least one means for accelerating the movement of the liquid, made in the form of a paddle wheel mounted rotatably under the action of the drive, and at least At least one means for inhibiting the movement of the fluid, in the form of a stationary blade element and located near the impeller to form a gap between the blades. These blades are formed by radial grooves formed on the end surface of the impeller and blade member, respectively, and positioned at an angle to the radius of the circumference defining the outer ends of the grooves and passed through the point of intersection of the outer end of the corresponding groove and the circumference. In a particular embodiment, the impeller can be mounted with the possibility of adjusting the clearance between the end surfaces of the impeller and the blade member, and the means for supplying the liquid can be a screw member ( RU 2197688 C1, class F 24 J 3/00, published 27.01. 2003 ).
The disadvantages of the prototype are as follows. The heat output of the generator depends significantly on the viscosity and heat capacity of the liquid used. The presence of a braking effect reduces the efficiency of the installation. The resulting pressure drop between the volume of liquid in the housing and the volume of fluid between the impeller and the blade element creates considerable axial forces on the drive shaft, which tend to reduce the working gap of the heat generator, which in the case of using the motor exceeds the permissible loads on the motor shaft. There is no possibility to regulate the heat output without a complete disassembly of the heat generator.
The object of the invention is to increase the efficiency, stability and controllability of the liquid heating process, as well as the power factor of the drive. The technical result is to ensure a stable and predictable fluid flow in the device.
This object is achieved in that in a heat generator for heating liquids, comprising at least one means for creating a fluid motion, in the form of finned wheels arranged coaxially with a gap between their end surfaces with ribs, the first finned wheel Is mounted with the possibility of rotation under the action of the drive, and the second is fixed, between the ribs at an equal distance from them are installed small ribs with a thickness equal to the thickness of the main rib having a rectangular profile in the cross section, on the side of the rib facing the axis of rotation ending in a semicircle with a radius , Equal to half the width of the rib, the length of the rib is not more than one third of the length of the main rib; moreover, on the surface of the movable wheel, at least as far as possible from the free end of the small edge, at least one hole is formed on the surface of the movable wheel, the center of which lies on the continuation Axis of symmetry of the small rib in the direction of the axis of rotation of the wheel at a distance of the diameter of the hole from the small rib; on the underside of the undoped surface of the wheel, chamfers are made around these holes; in addition, a removable disk fixed flush with the end surface of the ribs is mounted on the end face of the fixed surface of the fixed wheel.
The possibility of implementing the invention characterized by the above set of features, and the possibility of implementing the assignments of the invention can be confirmed by a description of the construction of a heat generator for heating a liquid made in accordance with the claimed invention. The description of the construction is explained by graphic materials, in which the following is depicted.
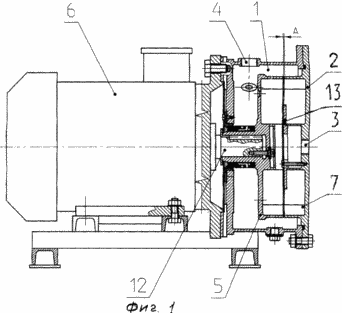 FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a heat generator |
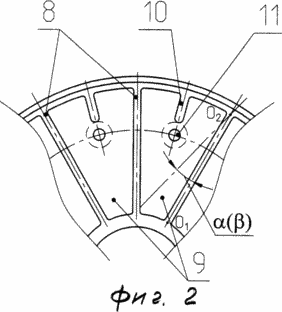 2 is a diagram of the formation of blades and ribs |
The heat generator for heating liquids contains a pressure vessel 1, which is a heat-insulated tank with a lid 2, which is both a lobe element. The inlet has an inlet 3 in the lid, and an outlet 4 is located in the pressure housing 1, which are connected by means of a drain and discharge nozzles, respectively, with at least one heat exchanger (not shown). A means for accelerating the flow of fluid from the center to the periphery and developing the turbulent flow at the periphery is provided in the housing 1, which is designed as a paddle wheel 5 rotatably mounted under the action of the drive mechanism 6 and means for twisting the liquid relative to the axis of the fluid acceleration vector. The latter is made in the form of a brake lobe element 7 and is located near the impeller 5 with the formation of a gap A between them. The blade wheel 5 and the blade member 7 are hydrodynamic transmission wheels with radial blades 8. The blades 8 are the ribs formed by the grooves 9 at the respective ends of the impeller 5 (the hydrodynamic transmission pump wheel) and the blade member 7 (the hydrodynamic transmission reaction wheel).
In order to increase the speed of twisting of the fluid in the radial grooves of the impeller 5 and the blade element 7, additional small ribs 10 are provided between the ribs 8 equally spaced from them, with a thickness equal to the thickness of the main rib 8. In cross-section, they have a rectangle profile that is on the side of the rib 10, Facing the axis of rotation of the wheels, ends in a semicircle with a radius equal to half the width of the rib 8. The length of the rib 10 is not more than one third of the length of the main rib 8. The longitudinal axes O 1 O 2 of the radial grooves 9 formed on the end surface of the impeller 5 and the blade Element 7 are located at an angle ![]() To the radius of the circumference bounding the outer ends of the grooves 9 and passing through the point of intersection of the outer end of the corresponding groove and the circumference. The longitudinal axes of the grooves may be located at an angle other than 0 °, including the grooves 9 and the small ribs 10 may be formed in such a way that the (ribs) of the blade 8 of the blade wheel 5 and the blade member 7 face each other. In addition, on the impeller 5, at each free end of the small rib 10, the holes 11c are chamfered from the side of the pressure vessel of the heat generator. The openings on the surface of the movable wheel 5 are uniformly circumferentially at the minimum possible from the free end of the fin 10. The center of each of the holes 11 lies on the extension of the axis of symmetry of the small rib 10 towards the axis of rotation of the wheel 5 at a diameter of the hole 11 from the end of the small rib 10. In this case, on the extension of the axis of symmetry of each small edge 10, not one hole can be made but several. The optimum hole diameter is 8 mm. The blade member 7 is fixedly fixed to the body 1 and the blade wheel 5 is mounted coaxially to it on the shaft 12 of the drive mechanism 6 with the possibility of adjusting the gap A between the ends of the impeller 5 and the blade member 7 by moving the impeller 5 along the shaft 12. In addition Moreover, on the face finned surface of the blade element (fixed wheel) 7, a replaceable disc 13 is installed so that it does not violate the established working gap between the blades. The disk is fixed flush with the end surface of the ribs and has 130-170 mm.
To the radius of the circumference bounding the outer ends of the grooves 9 and passing through the point of intersection of the outer end of the corresponding groove and the circumference. The longitudinal axes of the grooves may be located at an angle other than 0 °, including the grooves 9 and the small ribs 10 may be formed in such a way that the (ribs) of the blade 8 of the blade wheel 5 and the blade member 7 face each other. In addition, on the impeller 5, at each free end of the small rib 10, the holes 11c are chamfered from the side of the pressure vessel of the heat generator. The openings on the surface of the movable wheel 5 are uniformly circumferentially at the minimum possible from the free end of the fin 10. The center of each of the holes 11 lies on the extension of the axis of symmetry of the small rib 10 towards the axis of rotation of the wheel 5 at a diameter of the hole 11 from the end of the small rib 10. In this case, on the extension of the axis of symmetry of each small edge 10, not one hole can be made but several. The optimum hole diameter is 8 mm. The blade member 7 is fixedly fixed to the body 1 and the blade wheel 5 is mounted coaxially to it on the shaft 12 of the drive mechanism 6 with the possibility of adjusting the gap A between the ends of the impeller 5 and the blade member 7 by moving the impeller 5 along the shaft 12. In addition Moreover, on the face finned surface of the blade element (fixed wheel) 7, a replaceable disc 13 is installed so that it does not violate the established working gap between the blades. The disk is fixed flush with the end surface of the ribs and has 130-170 mm.
The device works as follows. When the drive (motor) is turned on, the liquid, being in the working zone formed by the grooves of the impeller 5 and the blade element 7, starts to accelerate under the action of centrifugal forces, moving from the center to the periphery, twisting in the grooves of the blade member 7. Then, reaching the small ribs 10 , Is maximally turbulized, as a result of dissipation of energy, the liquid is heated and through the gap A under pressure enters the body 1, then through the hole 4 and the discharge branch to the heat exchangers. Due to the resulting pressure drop between the housing 1 and the working zone, the heated liquid through the holes 11 enters the working zone even more turbulized. When the heat generator is in operation, the useful mechanical energy expended on the rotation of the impeller 5 almost completely passes into the thermal energy of the heated liquid. Therefore, the heating capacity of the device can be determined by the product of the loading torque of the impeller 5 on the shaft rotation frequency. In this case, the magnitude of the loading torque is stable, because Depends mainly on the active diameter of the wheels and can be calculated from the known formulas for hydrodynamic gears. In addition, the actual value of the load torque in small limits can be adjusted by changing the amount of gap A and changing the diameter d of the disk 13 of the blade element 7 in order to approach the nominal torque of the drive (motor). Thus, the proposed design of the heat generator allows reproducing the loading of the motor with a nominal torque, which ensures a stable heat output corresponding to the rated power of the electric motor, with the maximum efficiency.
The above-described heat source construction for heating a liquid made in accordance with the claimed invention proves the possibility of realizing the purpose of the invention and achieving the above technical result, but does not exhaust all the possibilities of implementing the invention characterized by the combination of features given in the claims.
CLAIM
A heat generator for heating liquids, including at least one fluid generating means, in the form of finned wheels arranged coaxially with a gap between their end surfaces with ribs, wherein the first finned wheel is rotatably mounted under the action of a drive , And the second is fixed, characterized in that between the ribs at equal distance from them there are small ribs of a thickness equal to the thickness of the main rib having a rectangular profile in the cross section, from the side of the rib facing the axis of rotation ending in a semicircle with a radius equal to half Of the width of the rib, the length of the rib is not more than one third of the length of the main rib; moreover, on the surface of the movable wheel, uniformly along the circumference, at least as far as possible from the free end of the small edge, at least one hole is located, the center of which lies on the extension of the axis Symmetry of the small rib in the direction of the axis of rotation of the wheel at a distance of the diameter of the hole from the small rib, chamfers are made from the underside of the wheel surface around these holes, and a removable disk fastened flush with the end surface of the ribs is mounted on the end face of the fixed wheel.
print version
Date of publication 08.12.2006гг




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.