| section Home Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining | Stealth master Electronics Physics Technologies invention | space Mystery Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map | |
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => | Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2127849
![]()
RADIATION BURNER
Name of the inventor: Barybin NF .; Krasil'nikov E.YU .; Mjagkov K.G .; Jakushin MI
The name of the patentee: Soft Cyril G.
Address for correspondence: 117218, Moscow, ul.Krasikova, 19-37 Myagkova KG
Starting date of the patent: 1997.10.06
The invention relates to the field of teploenegretiki, namely the radiation emitting burners, and can be used for domestic and industrial needs in various thermal power plants, such as domestic and household gas stoves, heaters, dryers, furnaces. Radiation burner housing comprises a radiating nozzle installed in the body to form a distribution chamber connected to the injection mixer, and is provided with a reflector installed on the outlet side of the heat radiation emitting nozzle and combustion products, and a heat transformer, mounted over the emitting nozzle. The technical result obtained by the proposed technical solution - increasing the economic, ecological and operational characteristics of radiation burners by increasing fuel efficiency, eliminate the possibility of contamination and flooding of the emitting nozzles, reduce the level of carbon monoxide in the flue gas.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of power engineering, namely to the radiation emitting burners and can be used for domestic and industrial needs in various thermal power plants, for example, in the household and household gas stoves, heaters, dryers, furnaces.
Currently, a large number of designs known gas burners, which are used in the process of heat transfer from the heating element to the heated object due to radiation.
Known radiant burner (US, Patent N 2775294, 1956. NKI 431-328), working mainly on gaseous fuels, comprising a combustion element, mixing chamber supply fuel and air, in which the surface of the burning element that emits heat, contains a combination of heat-resistant materials, having a plurality of fine channels.
Known radiation burner (EWP, application N 0433208 A1 1990 MKI 5 F 24 C 3/06), having two independent one from another radiation unit, the first of which is provided with a circular perforated ceramic tiles and the other -ring ceramic tiles. The first block is located inside the cavity defined by the second annular ceramic tiled block.
Known porous ceramic heater with a flame stabilizer (PCT application N WO 9500803 A1, IPC 6 F 23 D 14/16, 05.01.95), has high emissivity. It contains the flame stabilizer with randomly arranged pores and ceramic particles in an amount of not less than 50% emissivity which is approximately 0.7; means for passing the fuel mixture to the flame stabilizer, a device for ignition of the mixture near the stabilizer device for transferring heat from the flame to a heat transfer medium and a device for discharging gaseous products of combustion from the heater. The air-fuel mixture is passed through a stabilizer for the formation near the flame when burning the mixture. This heater design ensures reduction in nitrogen oxide emissions.
Known radiation burner (PCT application N WO 9429646 A1 MPK 6 F 23 D 14/12, 22.12.94), which is made by mixing the ceramic fiber, and metallic bonding of the mixture to form a porous layer attached to a perforated base. Due to the composite structure of the burner has a high radiation efficiency and durability, and lower and release NOx.
Known radiation burner (PCT application N WO 9503511 A1, IPC 6 F 23 D 14/16, 02.02.95), in which combustion supporting member is made of a porous ceramic material with a large number of holes that do not contain fine particles. As such a ceramic material is proposed to use a material consisting of two, three or more layers formed particles in the form of hollow spheres.
Known radiation burner (US, patent N 5326257, MPK 6 F 23 D 14/14, 05.07.94), comprising a receiving chamber that receives the air and fuel mixture. From the receiving chamber and the air fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber open at the top, which is made in a block of insulating material. On receiving chamber combustion chamber communicates through a large number of channels formed in the block. The combustion chamber of the fuel mixture is set flammable device. Zone formed in the combustion flame is limited on the output side with the radiating chamber wall outer surface over which the object to be heated is placed.
Known radiation burner comprising a housing with a perforated cover fitted in the output portion of the emitting nozzle mounted therein to form the distribution chamber and connected to the latter on a part of its cross section injection mixer (RU, patent N 2066023, F 23 D 14/12, 1996 ).
The combustion of fuel-air mixture in the burner occurs primarily in the surface area within the channels and on the surface of the emitting nozzle and post-combustion of unburnt components in the space between the nozzle and an apertured lid and near the surface of red-hot apertured cover.
The thermal energy resulting from combustion in the radiant nozzle is distributed mainly by thermal radiation between the nozzle and the surface of the heated combustion gases.
In the conventional design during the heated heat transfer object are significant losses of thermal energy are associated with the features of construction and arrangement of the burner and burner heating object.
By using this burner is required to install the support elements of the heated object, such as a water tank, which inevitably increases the gap between the nozzle and the radiating object to be heated.
Major losses of energy in said structure associated with output through this gap and high heat radiation of the combustion gases, leading in particular to parasitic heating elements of the gas stove structure.
A purely thermodynamic reasons for losses in the construction associated with a high temperature difference between the object and the radiant heat of the burner nozzle, that is, substantially non-equilibrium heat transfer conditions.
It should be noted that this uneven heating characteristic burner nozzle emitting a low temperature at the edges, which leads to an increase in the concentration of carbon monoxide in the combustion products.
In addition, heat radiation characteristics of the burner - the radiation wavelength and indicatrix create uncomfortable conditions for the people while working on the plates, equipped with these burners.
The closest to the claimed invention is an infrared gas heater (the radiation burner), comprising a housing with a mixer at the input, the emitter adjacent to the body of the reflector with windows to remove the products of combustion, and the screen (SU, Inventor's Certificate N 315875, cl. F 23 D 14 / 12, 1971).
The main objective of the proposed technical solution is to increase the economic, operational and environmental characteristics of the burner due to increase fuel efficiency, by providing protection against wind load, excluding the possibility of contamination and flooding of the emitting nozzles, reduce the level of carbon monoxide in the flue gas.
This object is achieved in that the radiation burner, comprising a housing with a mixer at the input transducer adjacent the reflector housing with openings for removal of flue products and the screen, the latter is made of an opaque or partially transparent to infrared radiation material.
Above the perforated cap mounted transformer heat (heat transformer), to more efficiently provide radiation burners must minimize heat loss resulting from combustion of the fuel mixture.
The main problem has been solved by installing the outlet side reflector and thermal radiation of the combustion products and heat transformer of a plate attached to the reflector.
Transformer heat reflector and the emitting nozzle form a cavity in which is converted to thermal energy generated by the combustion of the fuel mixture in the nozzle structure emitting thermal radiation in the heat transformer.
The thermal energy resulting from combustion in the radiant nozzle is distributed primarily between the heat radiation and the heated combustion gases.
In the proposed design the thermal energy associated with electromagnetic radiation, with minimal loss of heat is transferred to the transformer, either directly or by reflection from the surface of the reflector.
Another part of the thermal energy associated with hot gases, and more effectively gives up energy in the process of convective heat transfer in contact with the inner surface of the transformer. This cooled gases exit through the windows in the reflector or in the lid - the radiator. The cooled gases may be selected from the cavity formed by the emitting nozzle, reflector and heat converter in a purification system and released into the atmosphere.
The proposed design of the burner and the reduction of energy losses associated with a heat transfer equilibrium conditions by emitting nozzles to the heated object at the expense of smaller temperature gradients between the participating heat transfer materials, gases and radiation.
Thermal radiation from the inner surface of the heat radiating side of the inverter allows the nozzle to maintain the required temperature of the emitting nozzle with less fuel consumption and equalize the temperature on the surface of the emitting nozzles, which leads to a reduction in carbon monoxide emissions into the atmosphere.
In the proposed design of the burner function source of heat and a heater heating the object performed by different structural elements, allowing for more efficient organization of the heat transfer process.
Reflector in this construction performs the following functions.
Firstly, it is one of the design elements that make up the closed cavity or chamber in which the afterburning of unburned fuel component and the hot gases trapped, creating the necessary conditions for a more efficient convective heat transfer from the heat transformer.
Secondly, it provides a reflection of thermal radiation, preventing its exit from the burner and directing it to a heat transformer into a closed cavity.
The third reflector is a structural element that provides heat removal gave the exhaust gases to the atmosphere through the through hole in the reflector wall or through slit clearances between the upper edge of the reflector and the heat transformer.
Fourthly, the reflector support member is heat transformer and accordingly the object of heating, installed on the heat transformer. On the wall of the reflector and it is advisable to install elements of the ignition system and combustion control.
Transformer heat in this design is a plate or screen for axisymmetric burners made of a material providing sufficient rigidity and heat resistance at operating temperatures. heat transformer carries out the following functions in the burner structure.
Firstly, it is the collector of all kinds of heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel mixture in a ceramic nozzle structure.
Second, it distributes the heat obtained in scope, and accumulates heat in accordance with the received field level and temperature, properties and surface configuration facing toward the object being heated, heat energy radiates heat toward the object. In this function it is the meaning and scope of the concept of "heat transformer", as this element receives heat while some parameters, distributes it over a larger area and pays for other parameters, more comfortable for the person and easy to use. It is possible to use the concept of "heat converter", but it has traditionally been used to determine the heat energy conversion devices.
It should be noted that heat is transferred from the transformer heat conductivity and the object at the points of direct contact.
Third, the heat transformer is the source of thermal radiation toward the ceramic nozzle, which provides a higher level of the burner heat transfer with the same fuel consumption, i.e. efficiency, and a more uniform radial heating ceramic nozzle, which increases efficiency and reduces the emission of oxides carbon in the atmosphere.
Fourth, by installing the transformer heat is eliminated and the possibility of contamination of the radiating pouring nozzle becomes an absolute wind resistance.
Fifth, the transformer heat is the supporting member for heating an object, which eliminates the need for additional devices and enhances the aesthetic quality of the gas stove.
The drawing shows a structural diagram of the radiation burner.
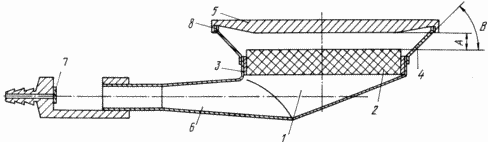
Radiation burner comprises a hollow body with a fuel mixture distribution chamber 1, at the outlet portion of which has successively emitting nozzle 2 mounted on a heat-insulating member 3, a reflector 4 and 5 the heat transformer, while the outlet section which is an injection mixer 6 with a fuel injector 7. this in the reflector 4 has through channels for the exit of combustion products 8.
Radiating head 2 is a gas-permeable plate with a regular or irregular cross-cutting porosity that provides flameless combustion mode fuel mixtures.
The reflector 4 is a thin-walled annular element having the shape of a truncated cone. Forming element may be a circular arc, a parabola and the like. D. The inner surface of the reflector is made of a polished material, well reflecting infrared radiation, such as aluminum or copper alloys. The outer surface may be insulated, for example, ceramic layer. The reflector made holes that provide for the effective cross-section of the exhaust. The most expedient to carry out venting through the annular gap 8 formed at the connection of the reflector with the heat transformer 5 by the protrusions on the upper edge of the reflector. This design provides the best conditions for convective heat transfer, minimal heat extraction from the heat transformer at the reflector and the absence of thermal stresses at the joints.
Heat transformer 5 is made of heat-resistant materials, and thermal resistance, resistant to thermal shocks. For the desired temperature level (600 - 900 K) meet these requirements, many modern metal, ceramic and composite materials such as stainless steel, glass ceramics, glassy carbon, quartz, and others.
The optical characteristics of the heat transformer internal surface advisable due to processing and coating to approximate the characteristics of the black body, for example, the creation of micro-roughness, blackening.
For axially symmetric burner heat transformer simplest form is the drive, but the heat of the transformer form should be more difficult for the more efficient operation of the burner.
In particular, the inner surface of the heat transforamatora can be developed through the fins with different shape, height and depth of the protrusions and depressions arranged radially or concentrically.
It is advisable to make the transformer and heat radially variable thickness, for example, in the form of a truncated cone so that the minimum thickness of the heat transformer has at the point of connection to the reflector and the apex of the cone facing towards the emitting nozzles, as shown in FIG.
For burners without ignition system, heat transformer can be made greater than the critical diameter of the hole to ignite the fuel mixture from an external source of ignition.
For different constructions of this type burners distance A may range from 5 to 50 mm, and the angle B of 90 to 30 o.
WORKS AS FOLLOWS THE BURNER
The air-fuel mixture from the injection of the mixer 6 enters the fuel mixture distribution chamber 1 in which there is a uniform distribution of this through the nozzle 2. radiating Burning in a ceramic nozzle channels, the air-fuel mixture heats the surface layers of the nozzle to a high temperature (900 - 1300 K). Unburned portion of the mixture burns between the nozzle and the radiating heat transformer 5. The resulting mixture of combustion energy is electromagnetic radiation, mainly infrared region of the spectrum, the source of which is a red-hot surface of the nozzle, and radiant heated gases and the heat and hot gases. All electromagnetic radiation is focused by the direct emission and reflection from the reflector 4 to heat energy converter 5. hot gases transmitted lid - the radiator due to heat transfer processes at the gas-solid.
This radiation burner design enhances the performance and environmental characteristics by increasing fuel efficiency, by providing protection against wind load and radiating from the pouring nozzle, reduces the amount of carbon monoxide in the flue gas.
The inventive radiation burner design has been made in several versions and sizes and capacities have been thoroughly tested in accordance with the standards in force in the territory of Russia. Tests have shown high efficiency burners in the emission of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides to the background level.
CLAIM
1. Radiation burner comprising a housing with a mixer at the input transducer adjacent the reflector with the housing openings for the flue and the screen, wherein the screen is made of an opaque or partially transparent to infrared radiation material.
2. Radiation burner according to claim 1, characterized in that the window for the flue gas formed in an annular gap formed in the place of connection to the reflector screen.
3. Radiation burner according to claim 1, characterized in that the screen has a hole diameter larger than the critical control for the ignition and combustion of the fuel mixture from an external source.
4. Radiation burner according to claim 1, characterized in that the screen has a radially variable thickness, for example in the form of a truncated cone, so that the minimum thickness of the screen is at its junction with the reflector.
print version
Publication date 21.03.2007gg






Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.