| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2290140
![]()
LEG OF ENDOPROSTHESIS OF THE THAZATIC JOINT
The name of the inventor: Gafarov Haydar Zaynullovich (RU); Gimmelfarb Arkady Leizerovich (RU); Bizyaeva Lyudmila Nikolaevna (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Research Center of Tatarstan "Restorative Traumatology and Orthopedics" (RU)
Address for correspondence: 420015, g.Kazan, st. Gorky, 3, SIC "WTO", the patent department
Date of commencement of the patent: 2005.04.19
The device belongs to the field of medicine, namely traumatology and orthopedics. The invention provides improved treatment outcomes due to a significant increase in the stability of the position of the endoprosthesis leg in the medullary canal of the thigh. The endoprosthesis is made in the form of a tube and fastening elements. The tube is made with a muffled lower end, holes on the side surface and a rod, mounted with the possibility of axial movements. The holes in the tube are round, located obliquely along the surface of the tube, and in each tier their axes are separated at an angle of 120 ° relative to each other. Elements of fastening are mushroom-shaped, the legs of these elements are made cylindrical with tapering at the ends and installed, with the possibility of axial movements and fixation, in the holes of the tube. The heads of the fastening elements with spherical surfaces are placed in the cavity of the tube, they come into contact with the pushers in the form of conical annular projections located on the rod and opposite the holes on the tube. The bases of the conical projections face upward. The lower end of the rod is installed in the guide channel of the blind end of the tube. The upper part of the rod is threaded to interact with the thread of the tide on the inner surface of the tube and ends with a key-cut. The upper part of the tube is equipped with an external thread, on which the cap closing the tube will be screwed.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The device belongs to the field of traumatology-orthopedics, it is used as a leg of the endoprosthesis of the hip joint.
Loosening of the endoprosthesis leg is observed in 50% of patients undergoing hip replacement surgery. Usually this happens 8-12 years after endoprosthetics and does not depend on whether the fixation of the foot was cement or cement-free. Therefore, researchers conduct research in the direction of creating a reliable contact in the "metal-bone" system, trying to achieve replenished compression in cases where the bone is caged under the pressure of metal elements.
Known devices, for example, the hip joint endoprosthesis [1], the leg of which is equipped with prestressed, deflected from its axis rods embedded in the bone tissue of the hip diaphysis. But this is not sufficient for the stable fixation of the stem in the given position. The long free ends of the rods can not sufficiently prevent the occurrence of instability, including rotational instability. They can not prevent the axial displacement of the leg upwards.
Another analogue is the stem of the endoprosthesis [2], which is a rod with a head, installed in the holes of the spacer sections, the large bases of the skirts are notched. However, this design does not provide sufficient fixation rigidity.
The closest to the claimed by its technical solution is the hip joint endoprosthesis [3] adopted for the prototype, whose pedicle has the greatest number of essential features common to the claimed one. The prototype leg, like the axial channel made in it, has a variable cross section, which requires the use of a special reamer, which repeats the stepped shape of the prosthetic leg, when it is inserted into the medullary canal of the thigh. The same circumstance does not provide an opportunity to correct the change in the degree of immersion of the leg into the medullary canal of the thigh. In addition, the petals fixing the leg in the medullary canal are directed at their ends to one (distal) side of the thigh, which does not ensure a reliable preservation of the position of the stem at a given depth.
The essence of the invention consists in a set of essential features that ensure the achievement of the desired technical result, namely, improvement of the treatment outcomes due to a significant increase in the stability of the position of the endoprosthesis leg in the medullary canal of the thigh.
This essence lies in the fact that the leg of the hip joint endoprosthesis is made in the form of a tube with a muffled lower end and openings along the lateral surface, a shaft installed with the possibility of axial movements, and fastening elements. The holes in the tube are round, located obliquely along the surface of the tube, and in each tier their axes are separated at an angle of 120 ° relative to each other. Elements of fastening are mushroom-shaped, the legs of these elements are made cylindrical with tapering at the ends and installed, with the possibility of axial movements and fixation, in the holes of the tube. The heads of the fastening elements with spherical surfaces are placed in the cavity of the tube, they come into contact with the pushers in the form of conical annular projections located on the rod and opposite the holes on the tube. In this case, the bases of the conical projections face upward, the lower end of the rod is installed in the guide channel of the blind end of the tube, the upper part of the stem is threaded to interact with the thread of the tide on the inner surface of the tube and ends with a key-cut. The upper part of the tube is equipped with an external thread, on which the cap closing the tube will be screwed.
On the legs of the fastening elements, between the bases of the heads and the inner surface of the tube, cylindrical compression springs are installed.
The location of the holes along the surface of the tube, and hence the legs of the fastening elements, at an angle of 120 ° relative to each other excludes the possibility of deviations of the axis of the endoprosthesis from the thigh axis and ensures the attainment of the maximum possible stable position in the medullary canal on each tier at three points corresponding to the vertices of hard Geometric figures - equilateral triangles.
The execution of the legs of the fastening elements with the tapering at the ends ensures their reliable contact with the tissue of the medullary canal due to the insertion of acuminate into it.
The execution of the heads of the spherical attachment elements ensures their contact with the conical surface of the pushers at any level of their location.
Simultaneous extension of the legs of all fastening elements, when they interact with the pushers, outside the outer surface of the tube and inserting them into the tissue of the medullary canal, provides accurate insertion of the stem along the center of this channel.
The location of the pointed ends of the legs of the fastening elements flush with the outer surface of the tube at the initial position ensures free insertion of the endoprosthesis leg into the prepared bone marrow channel of the thigh.
The spring-loaded fastening elements ensure the constant contact of the heads with the pusher at any level of their location.
 |
 |
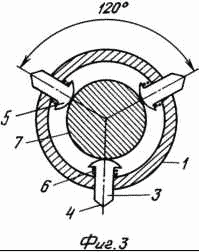 |
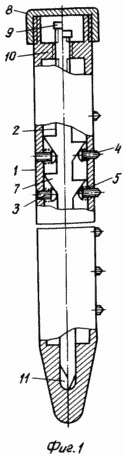
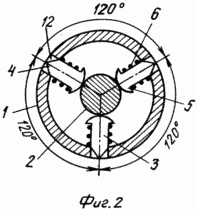
The device is depicted in the attached drawings. Fig. 1 shows a general view with breaks: to the left of the axis the arrangement of the fastening elements at the initial position, to the right - at the working position. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of the endoprosthesis foot at the level of the attachment elements; FIG. 3 shows the same in the operative position. FIG.
The leg of the endoprosthesis of the hip joint is made in the form of a tube 1 in which the rod 2 and the fastening elements 3 are placed. The latter have a mushroom shape, the cylindrical legs 4 with sharp points at the ends, facing outward, and the heads 5 with spherical surfaces - into the cavity of the tube 1. At the initial The position of the sharpening of the legs 4 is flush with the outer surface of the tube 1, and with the working - protrude from the holes to the outside. The heads 5 at the initial position are pressed by the springs 6 to the rod 2 at the places of its transition into the narrow part of the conically shaped annular ridges that are uniformly placed on it. 7. In the working position, the heads 5 are pressed to the surface of the cones at their bases - to the largest diameters of the rod 1. In the upper section The tube 1 is equipped with an external thread on which the cap 8 closes the tube 1. The upper end 9 of the rod 2 has a cut-through section for the key. Below the faceted portion 9, a part of the rod 2 is provided with threads cooperating with the thread of the circular tide 10 enclosing the upper end of the rod 2 in the cavity of the tube 1. The lower part of the rod 2 is axially displaceable in the guide channel 11 formed in the monolithic plugged lower end of the tube 1.
DEVICE WORKS AS FOLLOWING
In the operation of hip arthroplasty, at the stage of setting its legs in the medullary canal of the thigh, the latter is processed by sweeping up to dimensions permitting free movement of the endoprosthesis legs. The leg, with the initial position of its parts, with the cap removed, is immersed in the medullary canal to the required level and the given deviation of the neck is established by turning it around its own axis. Then, rotating the key rod, move it in the distal direction. In this case, the movement of the contact point between the heads of the fastening elements and the surfaces of the pushers is shifted towards the bases of the cones by large diameters. The pressure on the heads of the fastening elements is strengthened, the spiral springs are compressed, the pointed ends of the fastening elements protrude out of the tube outwards and are introduced into the bone tissue of the medullary canal. The end of the endoprosthesis is closed by the cap, after which the remaining stages of the hip joint endoprosthesis are completed.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2089136, A 61 F 2/32, BI 1997, No. 25.
2. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2066153, A 61 F 2/32, BI 1996, No. 25.
3. The patent of the Russian Federation №2045247, A61F2 / 36, BI 1995, №28.
CLAIM
1. The leg of the hip endoprosthesis made in the form of a tube with a muffled lower end and holes along the lateral surface, a rod axially movable and fastening elements, characterized in that the holes in the tube are circular, In each tier their axes are separated at an angle of 120 ° relative to each other, the fastening elements are mushroom-shaped, the legs of these elements are cylindrical with tapering ends and are installed with the possibility of axial movements and fixation in the holes of the tube, heads with spherical surfaces are placed in the cavity of the tube, Contact with the pushers in the form of conical annular projections located on the rod and opposing the openings on the tube, the bases of the conical protrusions facing upward, the lower end of the rod being installed in the guide channel of the blind end of the tube, the upper part of the stem being threaded to interact with the tide thread on the inner Surface of the tube and ends with a key cut, the upper section of the tube is equipped with an external thread on which the cap closing the tube will be screwed.
2. The leg of the hip arthroplasty according to claim 1, characterized in that on the legs of the fastening elements, between the base of the heads and the inner surface of the tube, are cylindrical compression springs.
print version
Date of publication 06.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.