| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2286736
![]()
METHOD FOR TREATMENT OF DEFORMING ARTHROSIS OF THE KNIFE JOINT
The name of the inventor: Vasiliev Vyacheslav Yurievich (RU); Puseva Marina Eduardovna (RU); Tkachenko Alexey Vasilyevich (RU); Zedgenidze Ivan Vladimirovich (RU)
The name of the patent holder: State Scientific Center of Reconstructive and Reconstructive Surgery of the All-Union Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (GU SSC RVH VSNTS SB RAMS) (RU)
Address for correspondence: 664003, Irkutsk, ul. Fighters of the Revolution, 1, State Scientific Center of Reconstructive and Reconstructive Surgery of the All-Union Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, patent group, RN. Kharlamova
Date of commencement of the patent: 2004.04.14
The invention relates to medicine, namely orthopedics and traumatology, and may be applicable for the treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint. A transplant is formed from the cortical plate taken in the channel forming zone. Introduce a threaded rod into the transplant. Produce a pressure along the axis of the rod, compacting the spongy bone to a depth of at least 35 mm. Fix the threaded rod in the support of Ilizarov's apparatus. Perform on the 5th day dosed traction of the threaded rod along its axis at a rate of 1 mm per day before the advance of the transplant - the fragment of the cortical plate to its original position. The method allows to reduce traumatism, shorten treatment time, prevent the emergence of contractures.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The proposed invention relates to the field of medicine, namely traumatology and orthopedics, and can be used to treat deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, especially accompanied by pain syndrome.
Known in the art is the treatment of arthrosis of the knee in the form of a scoring osteotomy of the proximal epithelium of the tibia (1). From the incision of the skin along the inner surface of the proximal epithelium of the tibia, through the hole in the cortical plate with a diameter of 8 to 18 mm, scoop out the spongy bone along the perimeter of the epiphysis. A curved rod introduced through the same aperture is simultaneously subjected to free communication of the epiphysis with the bone marrow canal.
The main disadvantage of this method is that weakening of bone in the metaepyphysis zone as a result of full scooping against the background of osteoporosis, a common satellite of arthrosis of the knee, can lead to a compression fracture of one of the tibial condyles.
The closest to the proposed method is the method of distraction stimulation of the proximal tibia in arthrosis of the knee joint (2). The essence of the method is reduced to the fact that from the tibia, on the side of the intervention, a sampling of 2 autografts with a size of 5 cm × 1 cm is made. The grafts are injected into the canals made by a drill in the thickness of the metaphase of the femur from the outside and in the proximal metaphysis of the tibia from the inside, At a distance of 2-3 cm from the level of the joint and parallel to it in the frontal plane. The outer ends of the transplants are usually inserted with some penetration (by 0.5-1.0 cm) and fixed with Kirschner knitting needles, which in turn merge with the "sliders" on the rings of the two-piece Ilizarov apparatus applied at the same level. After 2-3 weeks, slow traction begins at a rate of 0.25-0.5 mm per day for 1.5-2.5 months. With the help of the same Ilizarov apparatus, a moderate decompression of the knee joint (with a force of 5-8 kg) lasting up to 3-4 months is made. Full load on the limb was resolved after 1-2 months after removal of the apparatus.
However, the known method has significant drawbacks:
1. Taking two free bone autografts with a size of 5 cm × 1 cm leads to a significant additional trauma, an increase in the duration of the surgery and, as a consequence, increases the risk of infectious complications.
2. The need to fit the autografts after they are taken to the size of the holes made by standard drills, and lengthen the operation time.
3. The use of two mini-distraction systems in one Ilizarov apparatus makes it difficult for patients to independently perform the transplantation distraction, especially at the outpatient stage of treatment.
4. Fixation of the knee joint against the background of degenerative-dystrophic changes characteristic of osteoarthrosis, within 3-4 months, as a rule, leads to the formation of a firm extensor contracture, completely leveling the effect of unloading the knee joint. In this case, the duration of the repair period for the removal of the contracture is equal to the duration of the knee fixation in the Ilizarov apparatus, which significantly increases the overall duration of the patient's treatment.
To correct the identified shortcomings, the following task was set:
- to increase the effectiveness of treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint by reducing the traumatic nature of the method, the risk of infectious complications and the shortening of treatment.
The task is achieved as follows.
Treatment of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint involves the introduction of a graft into the canal made from the inner surface of the proximal epithetaphysis of the tibia at a distance of 2-3 cm from the joint level and parallel to it in the frontal plane, followed by fixation of the graft in the Ilizarov apparatus. New in solving the problem is that the transplant is formed from the cortical plate taken in the channel forming zone. Then a threaded rod is inserted into the transplant and pressure is applied along the axis of the rod to compact the sponge bone to a depth of at least 35 mm, followed by fixing the threaded rod in the support of the Ilizarov apparatus. Then on the 5th day, the threaded rod is dosed along its axis at a rate of 1 mm per day until the fragment of the cortical plate-transplant is advanced to its original position.
We explain the essential distinctive features of the proposed method of treatment.
The formation of a transplant from the cortical plate taken in the channel formation zone provides a rejection of the sampling of free autografts from additional incisions, and the absence of the need for precise fitting of the grafts to the formed openings. Using the cortical plate of the inner condyle of the tibia significantly reduces the time of surgery and anesthesia, minimizing the risk of anesthesia and infectious complications.
The introduction into the transplant of the threaded rod and the compaction of the spongy bone by pressure along the axis of the rod to a depth of at least 35 mm and subsequent fixation of the threaded rod in the support of the Ilizarov apparatus allow the stimulation of regeneration in the metaepiphysis of only the tibia, without affecting the femur, in combination with the preservation of the function Knee joint in the process of treatment is not inferior to the prototype on the stimulating effect. In this case, the use of a single support of the Ilizarov apparatus allows the patients to retain their motor activity at the outpatient stage of treatment, which significantly improves the quality of life during the treatment.
Carrying out the dosage traction of the threaded rod along its axis at a rate of 1 mm per day starting from 5 days from the operation to moving the fragment of the cortical plate-transplant to its original position is necessary for the formation of a distraction regenerate. This corresponds to the concept of the stimulating effect of stretching tension on the circulation of the operated limb according to Ilizarov (3), and as a whole reduces the duration of treatment of the patient in this way by 2 times.
The conducted patent information studies have shown that the proposed method is new and industrially applicable, since it does not require exceptional means for its implementation. The interconnection of essential techniques ensures the achievement of a new technological result and has an inventive level.
The essence of the proposed method is as follows.
Under general anesthesia, in aseptic conditions, in the position of the patient on the back, along the inner surface of the proximal epimetaphysis of the tibia, the skin incision is made from the joint slit 2-3 cm, followed by layered access to the cortical plate. A bit having a width of 15 mm and oriented parallel to the joint in the frontal plane forms a window in the cortical plate 15 mm × 15 mm in size with a bit deepening of at least 35 mm. A threaded rod with a diameter of 6 mm is inserted into the middle of the square graft-graft flap, the end of the rod not to stand more than 3 mm inward from the cortex plate (see the appendix to the description, Fig. 1, a).
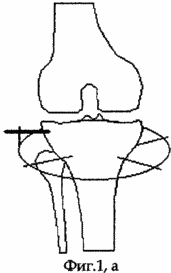 |
 |
 |
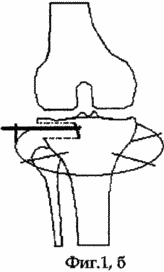
After this, pressure along the axis of the rod is made by compacting the spongy bone to a depth of at least 35 mm. At 3-4 cm distal to the threaded rod, an annular support of the Ilizarov apparatus is mounted and two mutually intersecting spokes with a diameter of 1.8 mm stretched in it are mounted. Further, the threaded rod is fixed to the base support by means of a bracket and two nuts (see the appendix to the description, FIG. 1, b), the nut that is located closer to the shin is the lock nut and the second nut is the main nut. Postoperative wound is sutured with nodular sutures.
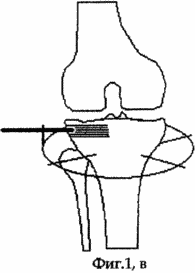
On the 2nd day after the operation, the patient is allowed to load the operated limb, which he brings to full load no later than 7 days after the operation. Simultaneously with the beginning of the load, the patient is prescribed exercise therapy for the knee joint. On the 5th day after the operation, the distraction regenerate is formed by dosing the threaded rod along the axis at a rate of 1 mm per day, which is achieved by loosening the locknut and turning the main nut 360 degrees around the longitudinal axis of the rod, and then tightening the lock nut. Distraction is continued until the fragment of the cortical plate-transplant reaches its original position (see the appendix to the description, Fig. 1, c). The duration of distraction, which the patient performs first under medical supervision, and later independently, is equal to the depth of the initial compaction of the spongy bone of the metaphysis of the tibia; Not less than 35 days. During the entire period of distraction, the patient moves with full load and preserves the static-dynamic function of the knee joint. After the transplant has been placed in the maternal lobe of the cortical part of the tibial condyle, which is periodically monitored by radiographs, the external fixation system and the threaded rod are dismantled, the wounds heal by secondary tension.
The term of the patient's treatment by the proposed method consists of separate periods: the preoperative period is 3 days, the pre-dilution period is 5 days, the distraction period is 35-40 days. Thus, the period of inpatient and outpatient treatment of the patient before returning to daily life is 45 days.
This method was used to treat 2 patients with knee arthrosis deforming with severe pain syndrome.
The result of treatment of these patients was complete relief of the pain syndrome, including nighttime, improving the static-dynamic function of the knee joint, estimated on the Leken's scoring scale (Leqens MG, 1997) (4), in the form of a painful syndrome with a pronounced (8-10 Points) to poorly expressed (1-4 points), subjective improvement of the quality of life associated with the expansion of motor activity.
The essence of the proposed method is explained by a clinical example.
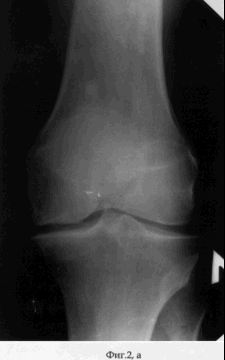
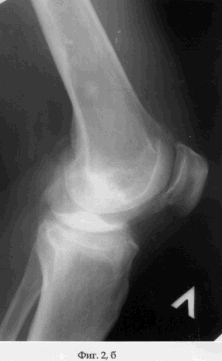
Patient M., aged 59, entered the clinic of the State Scientific Center of the RVH of the All-Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, May 13, 2003. Diagnosis: bilateral posttraumatic osteoarthritis of the knee joints, left of the third degree, on the right of the I degree; Varus deformity and extensor contracture of the left knee joint (see the appendix to the description: Fig. 2, a, b). The volume of movements in the left knee joint, measured by the "0" -passing method, was: flexion / extension = 100/5/0. The degree of severity of the pain syndrome according to the Leken scale is 10 points, which corresponds to a pronounced degree.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
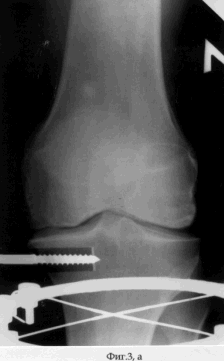
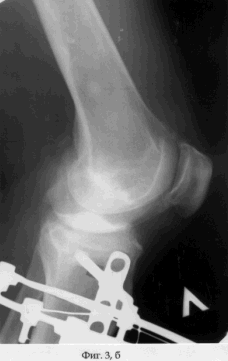
On May 15, 2003, surgical intervention was performed under spinal anesthesia. In aseptic conditions, in the position of the patient on the back, along the inner surface of the proximal epimetaphysis of the tibia, a skin incision is made from the joint slit by 2.5 cm, followed by layered access to the cortical plate of the tibia. A bit having a width of 15 mm and oriented parallel to the joint in the frontal plane was formed into a cortical plate with dimensions of 15 mm × 15 mm with a bit deepening of at least 35 mm. A threaded rod with a diameter of 6 mm is inserted into the middle of the square graft-graft flap (see the appendix to the description: Fig. 3a, b).
After this, pressure along the axis of the rod was made by compacting the spongy bone to a depth of 35 mm. At 4 cm distal to the threaded rod, an annular support of Ilizarov's apparatus was mounted and two interlocking spokes with a diameter of 1.8 mm were pulled in it. Further, the threaded rod was fixed to the base support by means of a bracket and two nuts. Postoperative wound was sutured with nodal sutures.
 |
 |
 |
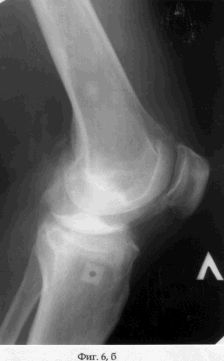 |
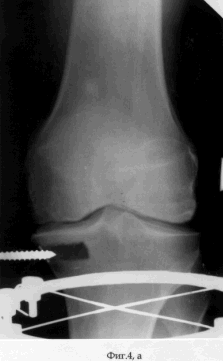
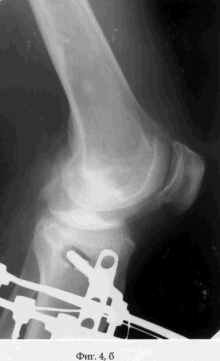
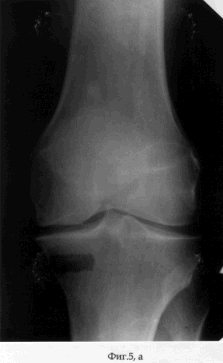
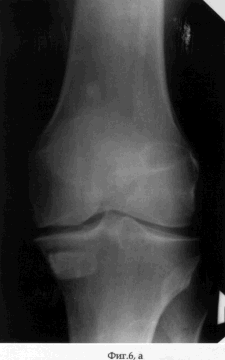
On the 2nd day after the operation, the patient was allowed to load on the operated limb, which he brought to full load on the 7th day after the operation. Simultaneously with the beginning of the load, the patient is prescribed a physiotherapy exercise for the knee joint. On the 5th day after the operation, the distraction regenerate was formed by dosing the threaded rod along the axis at a rate of 1 mm per day. Distraction was continued until the fragment of the cortical plate-graft had reached the initial position (see the appendix to the description: Fig. 4a, b). The period of distraction, which the patient performed first under medical supervision, and later independently, is 35 days. During the entire period of distraction, the patient moved with full load and maintaining the static-dynamic function of the knee joint. After the transplant was placed in the maternal bed of the cortical part of the condyle of the tibia, the external fixation device was dismantled and the wounds healed by secondary tension (see the appendix to the description: Fig. 5a, b). The term of treatment of the patient by the proposed method was 40 days. The result of treatment of the patient was the coping of the pain syndrome - the Leken index in dynamics decreased from 10 to 3 points (slightly pronounced), the increase in the volume of movements in the left knee joint was: flexion / extension = 140/0/0. When the patient was examined in the dynamics 1 month after the dismantling of the AVF, the Leken index did not decrease and the volume of movements did not change, and the filling radiograph was filled with the bone regenerate (see the appendix to the description: Fig. 6a, b). |
|
Thus, the proposed "Method of treatment of knee arthrosis deformity" in comparison with other known technologies allowed to increase the effectiveness of treatment of patients, to reduce the traumatism and risk of infectious complications, to shorten treatment terms by 2 times (3-4 months to 40-45 days) To stop the pain syndrome, and to increase the amount of motion in the knee joint.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. A.Paskachev. Bounding osteotomy in the treatment of patients with deforming arthrosis of the knee joint of 1-2 stages // Abstract of Cand. honey. Sciences. - Moscow. - 1987. - 17 with.
2. Prokhorov VP, Murugov VS Distraction biostimulation in the treatment of gonarthrosis // Orthopedics, traumatology and prosthetics. - 1991. - № 11. - P.23-25.
3. Ilizarov G.A. Some theoretical and clinical aspects of transosseous osteosynthesis from the point of view of general biological regularities discovered by us // Clinical and theoretical aspects and experimental substantiation of transosseous osteosynthesis with bone and soft tissue distraction. - Kurgan, 1986. - C.7-12.
4. Kovalenko V.N., Bortkevich OP Osteoarthritis. Practical guidance. - Kiev, 2003. - P.399.
CLAIM
A method for treating a knee arthrosis deforming arthrosis, comprising administering a graft to a conduit made internally in the proximal epithetaphysis of the tibia at a distance of 2-3 cm from the joint level and parallel to it in the frontal plane, fixation in an Ilizarov apparatus, characterized in that the graft is formed from a cortical plate Taken in the channel forming zone, a threaded rod is inserted into the transplant, the compacting of the spongy bone to a depth of at least 35 mm is made by pressure along the axis of the rod, the threaded rod is fixed in the support of the Ilizarov apparatus, on the 5th day, the threaded rod 1 mm per day before the advance of the transplant - a fragment of the cortical plate to its original position.
print version
Date of publication 06.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.