| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2279859
![]()
METHOD OF SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONSEQUENCES OF FRACTURES OF SPINS
The name of the inventor: Shevtsov Vladimir Ivanovich (RU); Khudyaev Alexander Timofeevich (RU); Balaev Ivan Ivanovich (RU); Balaev Pavel Ivanovich (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Federal State Institution of Science "Russian Research Center" Restorative Traumatology and Orthopedics "named after GA Ilizarov of the Federal Agency for Public Health and Social Development (FGUN" RSC "WTO" named after GA Ilizarov Roszdrav) "(RU)
Address for correspondence: 640014, Kurgan, ul. M.Ulyanova, 6, RNC "Restorative Traumatology and Orthopedics" im.ad.ad.G.A.Ilizarov, scientific patent and licensing group, Patr.T.N.Kovalenko
The effective date of the patent: 2002.01.08
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to traumatology and orthopedics, namely to neuroorthopedics and is intended for the treatment of patients with consequences of complicated vertebral fractures in the thoracolumbar and lumbar regions. The method of surgical treatment of patients with consequences of complicated vertebral fractures in the thoracolumbar and lumbar spinal cord decomposes, dosage correction of the spine axis, anterior spondylodesis with a metal implant after resection of the Urban wedge from the anterior approach, front sections of the injured vertebra are resected in front of the anterior spondylode - the rear size, the metal implant being installed from the rear access in a single step, which prevents the recurrence of kyphosis.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to traumatology and orthopedics, namely to neuroorthopedics and is intended for the treatment of patients with consequences of complicated vertebral fractures in the thoracolumbar and lumbar regions.
A method for surgical treatment of patients with consequences of complicated vertebral fractures in the lumbar region is known, the first stage of which is transpedicular osteosynthesis of the spine with the introduction of transpedicular reduction rods into the injured vertebra and adjacent devices with external supports and closed decompression of the dural sac by correcting the deformation of the spine, Was performed before the appearance of a minimal increase in neurological disorders in the repositioning process, the second stage was an open anterior decompression of the dural sac and anterior spondylodesis with an auto-graft transplant under conditions of continuing transpedicular osteosynthesis of the spine, and the third stage transosseous osteosynthesis with external support was transferred to submersible transpedicular osteosynthesis (Kornilov N. V., Usikov VD Spine injuries Tactics of surgical treatment - SPb .: MORSAR AV, 2000. - p.136-145).
However, the known method does not allow one to achieve complete reduction of the spinal deformity, since the appearance of signs of an increase in neurological disorders, due to ischemia of the spinal cord during distraction, is a contraindication to further correction. In addition, it is not possible to fully audit the spinal cord from the ventral access because of the large depth of the wound and the angle of the operation, the small area of the auditory area of the brain tissue, the bleeding from the vertebral bodies treated during decompression, and the third stage of osteosynthesis by submersible transpedicular The device is an additional traumatic intervention, accompanied by a large blood loss due to skeletonization of the arches of the vertebrae throughout the 4-5 segments of the spine.
There is a known method for treating spine injuries complicated by spinal disorders, including spinal cord decompression with restoration of the spinal canal form by eliminating the Urban's wedge and stabilizing the spine (Application No. 96116105/14, "A method for treating vertebral injuries complicated by spinal disorders", published on October 11, 1998) .
However, the known method involves carrying out an anterior spinal fusion with a bone autograft. When using this method of anterior spondylodease under the influence of the axial load, fractures are possible, the flushing of the reconstructing grafts with the appearance of a recurrence of kyphosis and pseudoarthrosis in the operated segment. Another disadvantage of anterior spondylodesis with an osseous graft is the resorption of the graft in the distant period, which leads to the development of a recurrence of kyphosis.
The object of the present invention is to prevent the recurrence of kyphosis and to shorten the duration of treatment of patients with sequelae of complicated fractures in the thoracolumbar and lumbar spine.
The goal is achieved in that in the method of surgical treatment of the consequences of complicated vertebral fractures, including spinal cord decompression, dosed spinal axis reconstruction, anterior spondylodesis and fixation of the spine in the achieved position, perform spinal cord decompression by resection of the Urban wedge from the posterior access, after decompression of the spinal cord Restore the axis of the spine, then resect the 1/2 part of the body of the damaged vertebra with adjacent discs, after which the anterior supporting spondylodesis with a metal implant is performed, the spine is fixed in the achieved position by an external transpedicular fixation device.
It is advisable for chronic clavicular fractures in the lumbar region after resection of the Urban wedge, the formation of the bed and the installation of the metal implant should be done from the rear access in a single step.
The patent invention is explained with a detailed description, diagrams, clinical example, radiographs and computer tomograms, in which:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
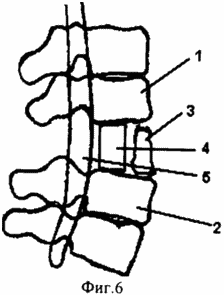 |
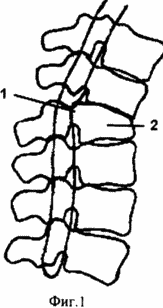
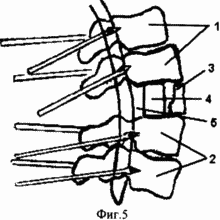
FIG. 1 illustrates a chronic, complicated compression fracture in the thoracolumbar region with compression of the spinal cord and kyphotic deformation of the spine;
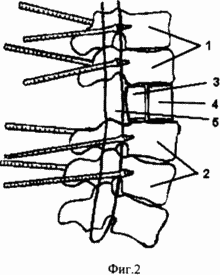
2 illustrates the state after the implementation of an enlarged laminectomy of the damaged vertebra, spinal cord decompression, superimposition of the apparatus of the external transpedicular fixation of the spine, correction of the kyphotic deformation, anterior spondylodesis with an implant of porous nickelide of titanium and fixation in the apparatus:
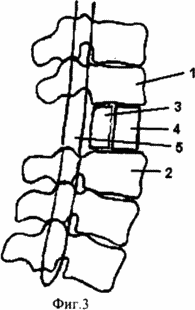
3 illustrates the condition after treatment;
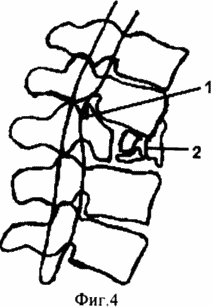
FIG. 4 illustrates a chronic complication of a comminuted fracture in the lumbar spine with compression of the spinal cord and kyphotic deformation of the spine;
5 illustrates the state after the implementation of an enlarged laminectomy of the damaged vertebra, spinal cord decompression, spondylodesis with an implant of porous titanium nickelide, application of an external transpedicular fixation of the spine, correction of the kyphotic deformation, and fixation in the apparatus;
6 illustrates a condition after treatment;

Fig. 7 - X-ray pictures of the patient T. - 25 years. Before treatment, a - a straight line, b - lateral projection of Kyphosis in the lumbar spine 50 °;
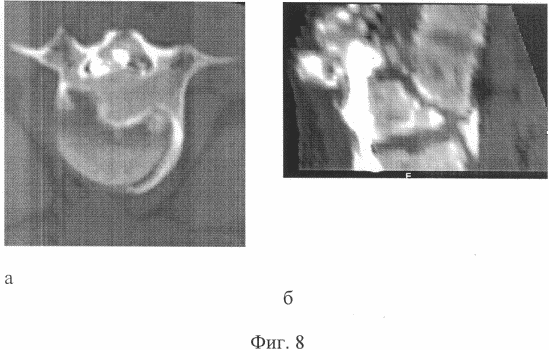
FIG. 8 shows computer tomographs of a patient T., 25 years old. Before treatment, a - axial section - b - sagittal reconstruction. Anterior compression of the cone of the spinal cord;
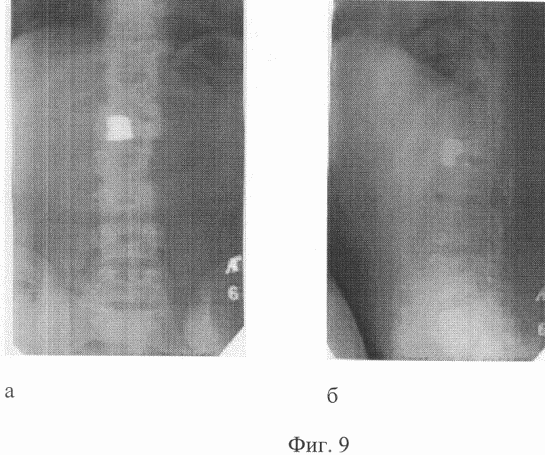
FIG. 9 shows X-ray photographs of a patient T., 25 years old. After treatment, a - a straight line, b - lateral projection. Kyphosis in the lumbar spine 30 °;
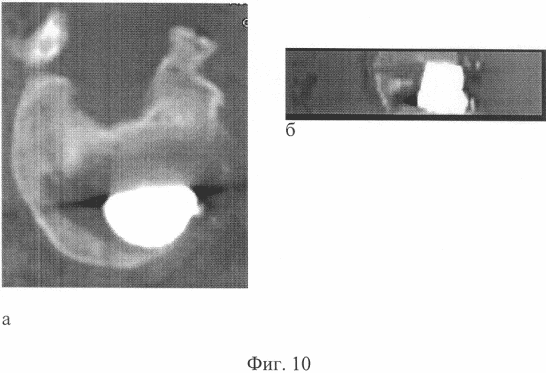
Fig. 10 - computer tomographs of the patient T., 25 years old. After treatment, a - axial section, b - sagittal reconstruction. The condition after an expanded laminectomy, anterior decompression of the spinal cord, anterior spondylodesis with metal.
THE METHOD IS PROVIDED AS FOLLOWS:
To implement the proposed method under endotracheal anesthesia, a wide laminectomy is performed at the level of compression of the spinal cord. A wide laminectomy involves the removal of the vertebral arch to the articular processes of the vertebra on both sides. If the length of the compressing substrate is long in order to expand operative access to the spinal cord, the laminectomy of one vertebra is supplemented by partial resection of adjacent arches. Laminectomy is performed by conventional narrow neurosurgical nippers and a narrow chisel (0.5 cm). The vertebral canal is opened at the back, right and left strictly along its side walls. Meningoradiculolysis is performed, during which a dural sac and the roots of the horse tail from the adhesions are excreted. Decompression of the spinal cord and the roots of the "horse tail" is performed. The mobilized dural sac is moved away, the compressing factor is removed alternately from one and the opposite side. Klin Urban 1 (Fig. 1) and other compressing factors are removed step by step, by the "lump" method, which reduces the degree of spinal cord trauma. If there is a chronic fracture and a rough axial deformation of the spine, the spinal canal is reconstructed by the type of formation of a new canal in the surfaces of the vertebral bodies projecting into the canal, where the spinal cord 5 is laid (Fig. 2). Spopdilotomy (discotomy) is performed at the apex of kyphoscoliotic deformation of the spine for its subsequent gradual correction. Myelolysis is the last stage. The dural sack is opened with a linear cut, the cyst is emptied. The permeability of cerebrospinal fluid on all subarachnoid chambers is restored. The dural sack is closed tightly. When the fibrosis of the wall of the dural sac is expressed, its plastic expansion is carried out using a hemostatic fibrin sponge.
An open application of the apparatus of external transpedicular fixation is performed.
In the legs of the arches of two above and two lower relative to the damaged vertebrae, rod-screws are introduced in pairs under the control of the electron-optical converter (Fig. 2.1, Fig. 5.1.2). The submaponeurotic space is drained by a polyvinylchloride tube. The surgical wound is sutured. In the future, the installation of an external fixation device is performed.
The rod-screws are connected in pairs with the plates by means of L-shaped brackets. The device is assembled from two support blocks, each of which has two pairs of rod-screws. Taking into account the kyphotic deformation of the spine, the support blocks are joined together by means of rods-distractors. On the operating table, for partial elimination of kyphotic deformation, a compression between blocks of 2.0-3.0 cm is performed simultaneously.
From 5-7 days after the operation, the correction of the spinal column deformity is continued by creating a compression between the units of the device at a rate of 1 mm per day until the correct axis of the spine is fully restored. In the future, the device is transferred to the fixation mode and the second stage of treatment is performed.
From the crespural access, anterior supporting spondylodesis is performed at the thoracolumbar level.
Under endotracheal anesthesia thoracotomy is performed in the VIII intercostal space on the right side by side access. The lung moves upward, the dome of the diaphragm is down. The anterolateral surface of the bodies of the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae is mobilized. With the help of an electron-optical converter, the level of spinal fusion is controlled. They produce discotomies, while the cranial disc is cut off from the caudal closure plate of the vertebra above, and the caudal disk from the vertebral cranial plate located below the damaged vertebra. Resection of the anterior parts of the damaged vertebra by 1/2 of its anterior-posterior size is performed (Fig. 2.3). Intervertebral discs together with hyaline plates are removed from the end plates of the adjacent vertebral bodies with a sharp bone spoon.
In the formed bed, a correspondingly sized implant of porous nickel titanium is installed. Its height should correspond to the normal height of the body of the damaged vertebra and adjacent intervertebral disks 4 (Fig. 2).
The integrity of the anterior longitudinal ligament is restored. The pleural cavity is drained, the wound is sutured layer by layer.
In old lobular fractures in the lumbar region (Fig. 4.2) after resection of the Urban wedge (Fig. 4.1), the formation of the bed and the installation of the metal implant are made from the rear access in a single step, by removing fragments of the damaged vertebra and adjacent discs by lapping to 1/2 part of the body of the damaged vertebra (Fig.5.5.). In the lumbar region at level LII-LV vertebrae in the dural sac are only the roots of the horse's tail. Therefore, a significant mobilization of the dural sac and the realization of interbody fusion from the rear access are permissible here. A prerequisite for the installation of an implant made of porous nickel titanium in a bed is the creation of a reserve space of 0.5-0.7 cm from the back surface of the implant to the anterior wall of the spinal canal due to the intensive process of osteogenesis around the implant in the postoperative period.
Clinical observation.
Patient T., 25 years old, in 1998, as a result of a road injury, he received a compression fractured fracture of the LI-LII vertebrae with a bruise and compression of the spinal cord. In the acute period of the trauma in the place of residence, an operation was performed in the volume of LI laminectomy and partial resection of the LII arc of the vertebra. Has arrived in clinic instiuta in 3 years after a trauma with the diagnosis: Traumatic illness of a spinal cord, the late period. Consequences of compression fractured fracture of LI, LII vertebrae with bruise and continuing compression of the spinal cord. Lower flaccid lung paraparesis. Violation of the function of the pelvic organs. The condition after laminectomy is LI and partial resection of the arc of LII vertebrae.
I entered the institute clinic 3 years after the trauma with the diagnosis: Traumatic spinal cord disease, late period. Consequences of compression fractured fracture of LI, LII vertebrae with bruise and continuing compression of the spinal cord. Lower flaccid mild paraparesis, dysfunction of pelvic organs. The condition after laminectomy is LI and partial resection of the arc of LII vertebrae. On the overview spondylograms, a chronic compression fracture of the body of the LI vertebra, bone block of the ThXII-LI-LII segments is determined. Angular kyphosis 50 ° at the level of LI. The condition after laminectomy LI, partial resection of LII arc (Fig. 7a, b). On computer tomograms it is noted: compression of the dural sac by the posterior and posterior margin of the LI body by 1/2 of the width of the spinal canal (Fig. 8a, b). The patient was operated on. The first stage was carried out by the extended laminectomy ThXII - LII vertebrae, anterior decompression of the spinal cord, meningoradiculolysis, open application of the device of external fixation of the spine. In the postoperative period, correction of the kyphotic deformation of the spine with a device at a rate of 1 mm per day was carried out. 40% of kyphosis correction was achieved. In 1 month after the first stage, the second stage of operative treatment was performed. From the right-sided Corso-pleural access through the VIII intercostal space, anterior spondylodesis ThXII-LI was made with an implant of porous titanium nickelide, which was mounted with support for the LX plate of the ThXII and LII bodies of the vertebrae that were retained after removal of the discs and body remains. The postoperative period proceeded without complications. For 2 months, a stable fixation of the spine was maintained. In the zone of spondylodesis, a bone block was attained, confirmed by densitometry data. After removal of the device, the achieved correction of the kyphotic deformation is retained (Fig. 9a, b). According to computed tomography, there is no compression of the spinal cord (Fig. 10a, b).
The proposed method allows to restore the supporting function of the spine, to shorten the terms of fixing the damaged spine. It is used in the Russian Research Center "Restorative Traumatology and Orthopedics" in the Department of Neurosurgery.
CLAIM
1. A method for surgical treatment of consequences of complicated vertebral fractures, including spinal cord decompression, dosed spinal axis reconstruction, anterior spondylodesis and spine fixation in the achieved position by an external transpedicular fixation device, characterized by resection of the Urban wedge from the posterior approach, The anterior parts of the damaged vertebra are resected at 1/2 the antero-posterior size of the damaged vertebral body with adjacent discs, followed by the anterior supporting spondylodesis with a metal implant.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that the formation of the bed and the installation of the metal implant are made from the rear access in a single step.
print version
Date of publication 06.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.