| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2264238
![]()
METHOD OF COMPLEX DIAGNOSTICS OF DIGESTIVE-GASTRAL FUNCTIONS
The name of the inventor: Anishchenko V.V. (RU); Pilipenko P.I. (RU); Shmakova E.A. (RU); Mordvintseva E.R.
Name of patent holder: State institution Road Clinical Hospital
Address for correspondence: 630003, Novosibirsk, Vladimirsky descent, 2-a, the state. Institution Road Clinical Hospital
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.10.01
(EN) The invention relates to medicine, in particular to gastroenterology and neurology, and can be used to diagnose diseases of the esophagus of various genesis: both primary muscle musculoskeletal disorders and those caused by a violation of the central control of the esophageal muscles. The method consists in conducting a comprehensive diagnosis of esophageal gastral dysfunction. In this case, the patient is transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortical representation of the esophagus. At the same time, the EMG of the esophagus muscles, the muscle response and latent time are recorded with the help of myography and manometry at segmental levels. The method allows to expand diagnostic possibilities of one-stage examination of the esophagus by differentiation of neuromuscular lesions of the esophagus, central and peripheral mechanisms of the regulation of esophageal gastric dysfunction
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
(EN) The invention relates to medicine, in particular to gastroenterology and neurology, and can be used to diagnose diseases of the esophagus of various genesis: both primary muscle musculoskeletal disorders and those caused by a violation of the central control of the esophageal muscles.
The wide prevalence of diseases of the esophagus and cardia facilitated the isolation of esophagology into a separate area of gastroenterology (Tamulevichyute DI, Vitenas AM "Diseases of the esophagus and cardia", Moscow, Medicine, 1986, p. 3). In the diagnosis of these diseases and the changes accompanying them, the functional methods of research, in particular, the determination of the motor function of the esophagus and cardia (Vasilenko V.Kh., Suvorova TA, Grebnev AL "Akhalasia cardia", Moscow, medicine, 1976, pp.103-109). Disorders of motor function of the esophagus themselves cause a number of painful symptoms, in addition, they are an important pathogenetic link in diseases such as hernia of the esophagus of the diaphragm, achalasia of the esophagus (Tamulevichyute DI, Vitenas AM, "Esophageal and cardiovascular diseases "Moscow, Medicine, 1986, p.58-60). Further progress in the treatment of these diseases by clinicians is associated with the improvement of diagnostic methods ("Wege zur Diagnose - Entscheidungsprozesse in der Medizin." Urban, Munchen, 1992, s.152-157).
Esophagastric dysfunction - gastroesophageal reflux disease, esophagospasm, cardiac achalasia, solitary phlegm, dysphagia - can be a manifestation of a number of diseases and are constantly being investigated by neurophysiologists, neurologists, gastroenterologists, and for almost all dysfunctions there are indications for therapeutic treatment and for performing surgical interventions on certain Stages of the development of diseases. The development of methods and methods of research allows you to more accurately determine the prognosis of the disease, choose treatment tactics and predict its effect.
The prototype is a method for studying the motor function of the esophagus, which includes a local measurement of intraluminal pressure and measurement of the electrical impedance of the entire esophageal wall at various levels (Abakumov MM et al., RF patent No. 2154540 published on August 20, 2000). The obtained information of the manometric investigation at each stage is compared with the data of the impedance registration.
The prototype method has the following disadvantages. When measuring impedance, an error is permissible, depending on the blood filling of the esophagus, there will be various data when taking hot or cold water, if there is a significant content of fatty tissue, scar tissue, etc. This study provides indirect data on the muscles of the esophagus. Measurement of impedance does not allow obtaining data on bioelectrical activity of muscles and sphincters of the esophagus both at rest and in certain phases of swallowing.
The task of the invention is to expand the diagnostic capabilities of a one-stage examination of the esophagus by differentiating neuromuscular lesions of the esophagus, central and peripheral mechanisms of regulation in esophageal gastric dysfunctions.
To solve the task in the process of complex diagnosis of esophageal gastric dysfunction by recording changes in the physical characteristics of various parts of the esophageal tract, the patient is transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortical representation of the esophagus and the surface electromyography of the esophagus muscles, muscle response and latent time from exposure to response.
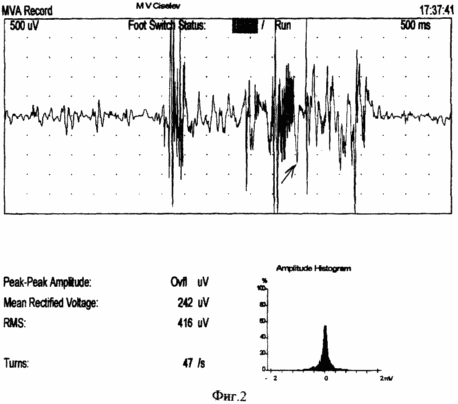
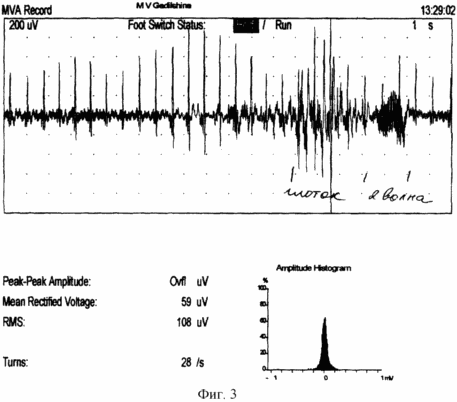
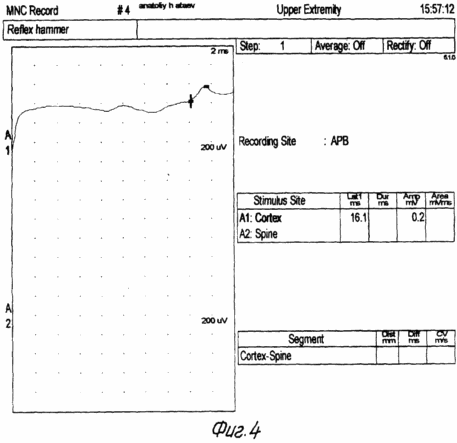
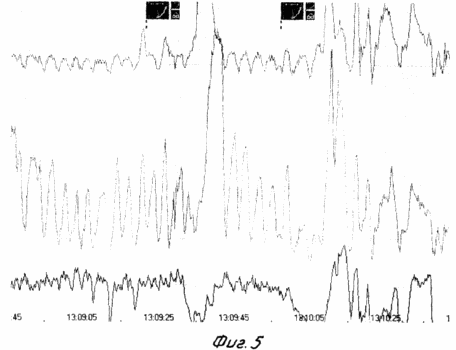
FIG. 1 shows the scheme of the implementation of the method, FIG. 2 shows the myogram of the esophagus body, FIG. 3 shows the myogram of the superior esophageal sphincter, FIG. 4 shows the registration of the response and the latent time of the impulse with the esophagus, FIG. 5 shows the body manometry Esophagus.
In the claimed method, a probe equipped with electrodes is used and connected to a Nicolet recording device (USA).
The diagnostic method is performed as follows
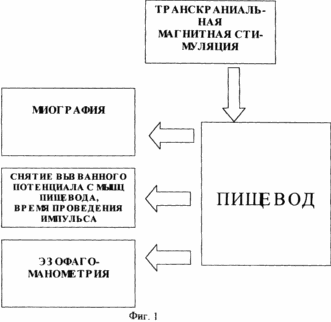 |
48 hours prior to the study, the administration of medications affecting the contractile activity of the esophagus (nitrates, H2 blockers, sedatives, analgesics, antidepressants, anticholinergics, blockers of Ca channels) is canceled. The last meal is at least 6 hours before the study to exclude vomiting or aspiration. The study is carried out in the position of the patient lying on his back. The probe is injected through the nose. The probe along the entire length has a centimeter scale, which allows one to determine the localization of its electrodes relative to the wings of the nose in centimeters (Fig. 1). On the monitor screen, the average pressure is fixed and the basal line of the stomach is fixed, that is, the zero level of the electrode position of the probe. Then the probe is moved in the opposite direction with the fixation of the sites of the lower esophageal sphincter, the body of the esophagus, the upper esophageal sphincter. Record the myography of all departments at rest, and with a "dry" and "wet" throat. While the electrode is located in the lower esophageal sphincter, transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortical esophagus is performed and the surface electromyography of the esophagus muscles, muscular response and latent time from exposure to response are recorded on the monitor (FIG. 2, FIG. 4). The verification of the location of the electrodes and the evaluation of the contractility were carried out according to manometry performed simultaneously with the claimed method. According to the ECG study of the muscles of the esophagus, various types of interference curves with smooth, mixed or striated muscle are obtained (Fig. 3). During transcranial magnetic stimulation, the change in the tone of the esophagus muscles is verified (Fig. 5). |
This method allows you to clearly differentiate the mechanism of the esophagus, assess the functional state of the muscle, determine not only the primary-muscular, but also the neurogenic origin of the disorders, determine the need for therapeutic or surgical treatment and predict its effectiveness.
CLAIM
A method for carrying out a comprehensive diagnosis of esophageal gastric dysfunction, characterized in that the patient undergoes transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex of the esophagus, during which the EMG of the esophagus muscles, muscular response and latent time are recorded with the help of myography and manometry at segmental levels.
print version
Date of publication 29.03.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.