| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2203612
![]()
METHOD FOR DIAGNOSIS motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract
Name of the inventor: Stupin Viktor; Andrey Bogdanov; Mishulin Leonid E.; Alexander Artemev; Lavrova Nadezhda; Bel'kov Andrey Viktorovich; Narezkin Dmitry Vasilyevich; Zakirov Jalil Belguzovich; Siluyanov Sergey Viktorovich; Galina Smirnova O.
The name of the patentee: Stupin Viktor; Andrey Bogdanov; Mishulin Leonid E.; Alexander Artemev; Lavrova Nadezhda; Bel'kov Andrey Viktorovich; Narezkin Dmitry Vasilyevich; Zakirov Jalil Belguzovich; Siluyanov Sergey Viktorovich; Galina Smirnova O.
Address for correspondence: 109472, Moscow, Volgograd Ave., 171, building 1, kv.148, SV Siluyanova
Starting date of the patent: 2002.03.26
The method can be used in medicine, namely in gastroenterology. With imposed on the patient's body surface electrodes record the electrical signal and the estimate of the organ of the gastrointestinal tract. Measurement of the electrical signal is performed minutely device, in two stages 40-50 min. In the first stage it is produced on an empty stomach in 5-6 minutes after application of the electrodes. On the second - after eating a standard stimulus. Electrodes are placed on the right forearm, the left and right shin. Record the total electrical signal of five divisions GIT and an electric signal of each of the departments. On the contribution of each department in the overall electrical signal, its rhythm and magnitude of differences from the neighboring department of the electric signal is judged on the presence of gastric ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer, stenosis of the output of the stomach, dyskinesia 12 duodenal ulcer. The method improves the accuracy of the determination.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, and more particularly to methods of diagnosing the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and can be used for non-invasively identifying a patient gastrointestinal diseases and for the evaluation of the dynamics parameters after treatment.
Known X-ray method for studying motor-evacuation function of the stomach and duodenum 12, comprising a visual assessment of the tone of the stomach size, the nature and speed of the initial evacuation, the tone and the nature of the evacuation of the loop 12 duodenal ulcer, the presence duodeo-gastric reflux (see., for example, LE Kevesh "Rentgenokinematograficheskoe study esophagus" L., Medicine., 1970, p.184). [1]
A disadvantage of the known method is the necessity of introducing into the test body a contrast agent and the inability to carry out a study for a long time due to the radiation load on the patient, the inability to observe nepropulsivnye reductions, which greatly distorts the assessment of gastrointestinal function. In addition, this method does not provide information on the relationship of various motility disorders gastrointestinal tract, and to evaluate or upper gastrointestinal (stomach and duodenum 12) or lower (the colon).
Known and the method of diagnosing motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), which consists in the definition and measurement, using superimposed on the electrode the patient's body surface, an electric signal from the body of the gastrointestinal tract, its registration and evaluation (see., Eg. Collection of Scientific Papers "diagnosis and treatment of complications postvagotomicheskih", article by P. Ettinger, MD Polivada "Opportunities intraoperative electromyographic diagnosis of duodenal permeability", Moscow, 1987) [2].
This method is closest to the technical nature and the number of common features with the statement by virtue of which we adopted as the closest analogue.
The disadvantage of this method is the fact that he did not give any idea of the relationship of various motility disorders gastrointestinal tract and to evaluate either the upper sections of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach and duodenum 12) or lower (the colon). In addition, this method does not allow to detect early signs of emerging stenosis distinguish functional character evacuation disorders ulcers 12-duodenum and pyloric canal by organic.
The problem to be solved by the claimed invention is to enhance the accurate diagnosis of opportunities in the early stages of gastrointestinal diseases.
The technical result is to increase the accuracy of diagnosing disorders of motor function of gastrointestinal tract.
The above technical result is achieved due to the fact. a method for diagnosing motor-evacuation gastrointestinal tract, which consists in the definition and measurement, using superimposed on the patient's body surface electrodes. electrical signal from the body of the gastrointestinal tract, its registration and evaluation according to the invention, the electrical signal measurement is carried out in two stages at 40-50 minutes, and during the first stage of its manufacture fasting, 5-6 minutes after application of the electrodes, and the second - after a standard food stimulation, the electrodes are placed on the right forearm, the left and right lower leg, registering the total electrical signal all five GI and an electric signal of each of the departments in the relevant frequency range, 0,010-0,030 Hz colon, stomach 0,031-0,070 Hz, ileum 0,071-0,130 Hz, jejunum 0,131-0,180 Hz and 12-Hz 0,181-0,250 duodenum, followed by the contribution of each department in the overall electrical signal, its rhythm and magnitude of differences from the neighboring department of the electric signal is judged on the state of the motor-evacuation function of the digestive tract . In addition, the change in each indicator is estimated in the dynamics of constantly during the study time. Diagnosis of motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract as follows. An increase in the electrical activity of the stomach and duodenum 12 by 2-3 times. compared to the norm, and the delay of response to food stimulation, diagnosed peptic ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer with an increase in the electrical activity of 2-3 times in the frequencies of the stomach; under basal and stimulated research, reducing the electrical activity of the duodenum 12 when stimulated with respect to the normal fasting obtained, when broken phase response to stimulation with increasing rhythm of stomach contractions after stimulation with 3 or more times, with an increase in the coefficient of correlation stomach / 12 -perstnaya gut 3 or more times on an empty stomach, and when stimulated, are diagnosed with stenosis of the outlet of the stomach: with an increase in the electrical activity of 12 duodenal ulcer 4-5 times on an empty stomach, reducing it by 1.5-2 times after stimulation with increasing rhythmic contractions stomach and duodenum 12 to 10 times or more of hypertensive type psoriasis and its decrease 1.5-2 times with hypotonic type dyskinesia. fasting and when stimulated, dyskinesia diagnosed 12 duodenal ulcer.
In medicine and medical technology is known that removal of electrocardiograms (ECG), skin electrodes applied to the right forearm, the left and right shin. that is a triangle Eythovena, removing the electrical signal which can be judged on contractile activity of individual organs.
Known and registration and measurement of the electrical signal cutaneous electrodes with one stomach, on which judge about his motor activities (see., Eg, Journal "GASTROENTEROLOGY" article Marc A., MT Verhagen, Leonard J., 1999) [3] . However, by using these solutions can not achieve the above technical result, to improve the accuracy of diagnosis of functional motility disorder of gastrointestinal tract. The fact is that to get the ECG used completely different frequency, whereby the obtained records impossible to judge the state of the gastrointestinal tract. As for the method [3], then remove one common signal, attributing it entirely to the stomach, and compares only the average general statistical data, we can not get reliable accurate picture of the state of the entire gastrointestinal tract and therefore will not be able to judge when imposing a single electrode on the stomach his motor-evacuation function.
Applicants not found sources of information containing the same set of essential features specified in the claims, namely, the minute assessment during the entire time period, a sequence of actions in two stages, but also the frequency bands, which allows to conclude that the proposed technical solution criteria of invention "novelty "and" inventive step. "
The method is illustrated elektrogastroenterogrammami where: FIG. 1-5 shows the obtained per-minute using electrogastrogram graphics investigated gastrointestinal sections.
The method is implemented as follows
Electrodes are placed on the right and left leg and the right arm of the patient and, at the same place in the superposition of the skin electrodes must be rubbed and smeared alcohol conductive paste (such as PE-2). Then, using a conductive harness is connected to the device electrodes electrogastrogram EGEG-01K, which in turn is connected to a personal computer (PC) and the isolation transformer. After that include the device and begin to measure and record the electrical activity of the peripheral parts of the patient's gastrointestinal tract in two stages. In the first phase measurement of basal contractile activity produces an empty stomach, after 5-6 minutes after application of electrodes for 40-50 minutes. The results of measurements of the basal contractile activity comes in PC and fixed there. In the second stage, and producing measurements for only 40-50 minutes after receiving a standardized breakfast (200 ml warm tea, 10 g glucose, 100 g of white bread). And receives data in the PC, which compares and processed. The results of examination of the patient in the form of tables and spectrograms displayed. As it is judged on the level of the electrical activity of the stomach, intestines, and their co-ordination. When using the claimed method of diagnosis were identified electrophysiological standards gastrointestinal contractile activity in healthy subjects. These include:
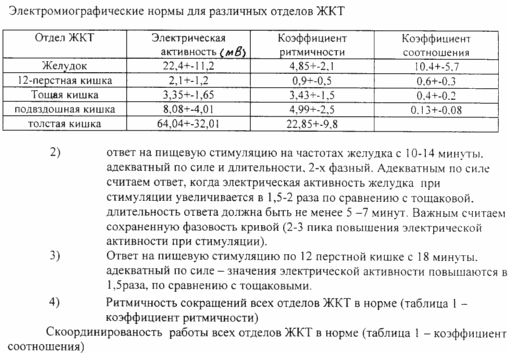
1) The percentage of basal values of the electrical activity of the gastrointestinal tract: 22.4% in the stomach and 2.1% for the 12-duodenum. 3.35% on the jejunum, 8.08% for the ileum, 64.04% on the colon.
The method is illustrated by clinical examples.
example 1
Patient A. 56 years, IB 3469/01 morning fasting superposed electrodes on the right forearm and both legs, and then after 5 minutes was performed to register the electrical signal at frequencies gastrointestinal 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes, then the patient is given a standard breakfast food, consisting of 200.0 ml of hot tea. 10 g sugar, 200 g of white bread. And again conducted registration GIT electrical signal after food stimulation at frequencies of 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves revealed an increase in the frequency of electrical activity of the stomach on an empty stomach for all 40 studies minutes 3 times in comparison with the norm, the electrical activity at frequencies of 12-, jejunum and ileum empty stomach in the normal range. Electrical activity in the colon fasting somewhat higher frequencies in the range of physiological fluctuations.
Rhythm fasting gastric contractions increased in 2 times. 12 rhythmic contractions of the duodenum is reduced by 1.5 times. Rhythm lean cuts. ileum and colon in the normal range.
Fasting was an increase in the coefficient of correlation stomach / duodenum 12 3 times, indicating that the operation of the data diskoordinirovannosti gastrointestinal disorders due to gastric emptying.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves after standard food stimulation revealed:
The slight increase in electrical activity in the stomach frequencies compared to the fasting study for all 40 minutes, the response to food stimulation to the stomach, timely, long evacuation of food from the stomach only a 32 minute study, which is 4 times after than normal. Electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer after stimulation with reduced response to food stimulation by 12 duodenal ulcer late by 34 minutes, which is 3 times after than normal. Electrical activity at frequencies of jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range, response to food stimulation - a belated.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach after food stimulation increased 3 times. rhythmic contractions of 12 duodenal ulcer in 2 times lower than normal. Rhythmic contractions jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range.
After eating a standard breakfast was an increase in the coefficient of correlation stomach / duodenum 12 4 times, indicating that the violation of evacuation from the stomach (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This picture is consistent with the output subcompensated stenosis of the stomach.
The patient holds the X-ray examination of the stomach, which is confirmed by the picture subcompensated stenosis. The patient was operated on, the diagnosis was confirmed during surgery.
example 2
Patient S. 27 years, IB 1250/00 morning fasting superposed electrodes on the right forearm and both legs, and then after 5 minutes was performed to register the electrical signal at frequencies gastrointestinal 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes, then the patient is given a standard breakfast food, consisting of 200.0 ml of hot tea. 10 g sugar, 200 g of white bread. And again conducted registration GIT electrical signal after food stimulation at frequencies of 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves of electrical activity in the frequencies of the stomach on an empty stomach within the physiological norm for all 40 minutes of the study, the electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer increased 5 times during the study time, the electrical activity in the jejunum frequencies increased to 1 5-2 times the electrical activity at frequencies of ileum and colon on an empty stomach in the normal range.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach on an empty stomach is reduced by 1.5 times, rhythmic contractions of 12 duodenal ulcer decreased by 3 times. Rhythm lean cuts. ileum and colon in the normal range.
Fasting was a reduction coefficient ratio stomach / duodenum 12 4 times, indicating that the operation of the data diskoordinirovannosti gastrointestinal disorders due to the passage of 12-duodenum.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves after standard food stimulation revealed:
increase in electrical activity in the frequencies of the stomach in 2 times in comparison with the fasting study, indicating that an adequate response to food stimulation of the stomach. Electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer after stimulation is reduced in comparison with the fasting study of 1.5 times, the response to food stimulation on the 12-duodenum timed at 12 minutes, the phase response is stored.
Electrical activity at frequencies of jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range, response to food stimulation - timely.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach after food stimulation is increased in 2 times in comparison with the fasting study, indicating that adequate motor-evacuation function of the stomach. Rhythmic contractions of 12 duodenal ulcer is increased in comparison with the fasting study by 2 times, but remains below. than normal. Rhythmic contractions jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range.
After eating a standard breakfast was an increase in the coefficient of correlation stomach / duodenum 12 by 1.5 times compared to the fasting study, but this ratio is lower than normal. This suggests a functional slowing the passage of food through the duodenum 12 (2).
Conclusion: This picture is consistent with dyskinesia duodenum 12 of hypertensive type of a functional nature, which can be regarded as a psychosomatic form of chronic duodenal obstruction.
example 3
Patient B. 47 years, IB 7895/02 morning fasting superposed electrodes on the right forearm and both legs, and then after 5 minutes was performed to register the electrical signal at frequencies gastrointestinal 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes, then the patient is given a standard breakfast food, consisting of 200.0 ml of hot tea. 10 g sugar, 200 g of white bread. And again conducted registration GIT electrical signal after food stimulation at frequencies of 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves of the electrical activity of the stomach on an empty stomach at frequencies within the physiological range for all 40 minutes of the study, the electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal, jejunal ileal and colonic fasting within the physiological norm.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach on an empty stomach in the normal range, rhythmic contractions of 12 duodenal, jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range.
The ratio of the stomach / duodenum 12, 12- / jejunum, skinny / ileum, ileum / colon fasting normal, indicating that the coordinated work of all gastrointestinal tract.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves after standard food stimulation revealed:
increase in electrical activity in the frequencies of the stomach in 2 times in comparison with the fasting study, indicating that an adequate response to food stimulation of the stomach. The answer to the stimulation of food in the stomach to 12 minutes, timely, phase response is stored. Electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer after stimulation increased 1.5 times compared to the fasting study, response to food stimulation on the 12-duodenum timed at 18 minutes, the phase response is stored. Electrical activity at frequencies of jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range, response to food stimulation - timely.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach after food stimulation is increased by 1.5 times compared to the fasting study, indicating that adequate motor-evacuation function of the stomach. Rhythmic contractions of 12 duodenal ulcer in the normal range. Rhythmic contractions jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range.
After eating a standard breakfast Coefficient stomach / duodenum 12, 12- / jejunum, skinny / ileum. ileum / colon are normal, indicating that the coordinated work of all GI food after the load (3).
Conclusion: violations of the motor-evacuation function of the digestive tract in a given patient is not revealed. The picture corresponds to the physiological norm.
example 4
Patient P. 67 years, IB 33313/00 morning fasting superposed electrodes on the right forearm and both legs, and then after 5 minutes was performed to register the electrical signal at frequencies gastrointestinal 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes, then the patient is given a standard breakfast food, consisting of 200.0 ml of hot tea, 10 grams of sugar, 200 g of white bread. And again conducted registration GIT electrical signal after food stimulation at frequencies of 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves of the electrical activity of the stomach on an empty stomach at frequencies increased by 2-3 times, for all 40 minutes of the study, the electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer is increased by 4-5 times. Fasting has been a sharp increase in the electrical activity simultaneously at the frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer and stomach for 20-22 minutes, indicating that the duodeno-gastric reflux. Electrical activity in the jejunum frequencies increased by 2 times throughout the study period, electrical activity at frequencies ileum and colon fasting within the physiological range.
Rhythm fasting gastric contractions increased, rhythmic contractions of 12 duodenal, jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range.
The ratio of the stomach / duodenum 12 on an empty stomach in the normal range, increased by 20-22 minutes in 1.5-3 times, indicating that discoordination contractions of the stomach and duodenum 12 during this time period due to duodeno-gastric reflux.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves after standard food stimulation revealed:
electrical activity in the stomach is reduced frequencies compared to toshakovym research, which indicates inadequate response to food stimulation of the stomach. The answer to the stimulation of food in the stomach with a 1-minute, early, long 16 minute. after which the electrical activity of the stomach is reduced, the second phase of response to stimulation of the stomach to 36 minutes later, indicating that the grounds of violation of the evacuation from the stomach. Electrical activity in the duodenum 12 frequencies after stimulation is reduced by 1.5 times compared to toshakovym study. Electrical activity at frequencies of jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range, response to food stimulation - a belated.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach after food stimulation is reduced by 1.5 times compared to the fasting study, indicating that the expressed violations of gastric emptying. Rhythmic contractions of 12 duodenal ulcer in the normal range. Rhythmic contractions jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range.
After eating a standard breakfast coefficient ratio stomach / duodenum 12 raised in the first 16 minutes of the study, after which - reduced, indicating that diskoordinirovannoy the stomach and duodenum 12 and signs of violation of the evacuation from the stomach (Figure 4).
Conclusion: This picture is consistent with the output subdekompensirovannomu stenosis of the stomach, fasting patient showed signs of duodeno-gastric reflux.
Subdekompensiroannogo diagnosis of stenosis of the output of the stomach is confirmed in this patient by radiographic and intraoperative.
example 5
Patient S. 26 years, IB 12341/00 morning fasting superposed electrodes on the right forearm and both legs, and then after 5 minutes was performed to register the electrical signal at frequencies gastrointestinal 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes, then the patient is given a standard breakfast food, consisting of 200.0 ml of hot tea, 10 grams of sugar, 200 g of white bread. And again conducted registration GIT electrical signal after food stimulation at frequencies of 0.01-0.25 Hz for 40 minutes.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves revealed an increase of electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer stomach in 2 times in comparison with the norm, the phase curve is stored. Electrical activity in the frequencies of the stomach, jejunum, ileum and colon on an empty stomach in the normal range.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach and duodenum 12 on an empty stomach in the normal range. The ratio of the stomach / duodenum 12 is normal.
Dynamic per-minute analysis myographic curves after standard food stimulation revealed:
increase electrical activity in the stomach as compared with the frequencies fasting study 2 times nutritional response to stimulation to the stomach 20 minutes late with adequate strength and durability. Electrical activity at frequencies of 12 duodenal ulcer after stimulation increased, the response to food stimulation on the 12-duodenum early with 1 minute, the signs of duodeno-gastric reflux recorded.
Electrical activity at frequencies of jejunum, ileum and colon in the normal range, response to food stimulation - a belated.
Rhythm contractions of the stomach, 12 duodenum, jejunum, ileum and colon after food stimulation in the normal range.
The ratio of the stomach / duodenum 12 in the normal range (5).
Conclusion: This picture is consistent with the aggravation of peptic ulcer disease 12 duodenal ulcer.
The patient performed endoscopic examination, which confirmed the presence of ulcers in the duodenum 12.
The proposed method examined 1144 patients.
The use of offers method will increase the accuracy of diagnosis of motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract as a preventive, and at any stage of the disease.
CLAIM
1. A method of diagnosing motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), which consists in the definition and measurement using electrodes imposed on the patient's body surface, an electric signal from the body of the digestive tract, registration and evaluation, characterized in that the measurement of the electrical signal is performed device per minute, in two stages for 40-50 minutes, during which the first stage of its manufacture fasting, 5-6 minutes after application of the electrodes, and the second - after eating a standard stimulus, with electrodes placed on the right forearm, the right and left tibia recorded total of five electrical signal GI and the electric signal of each of the departments in the relevant frequency range, 0,010-0,030 Hz colon, stomach Hz 0,031-0,070, 0,071-0,130 Hz ileum, jejunum 0,131-0,180 Hz and 12 duodenal ulcer 0.181 -0.250 Hz, followed by the contribution of each department in the overall electrical signal, its rhythm and magnitude of differences from the neighboring department of the electric signal is judged on the state of the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract.
2. The method of claim. 1, characterized in that an increase in the electrical activity of the stomach and duodenum 12 by 2-3 times compared with the norm, and the delay of the response to the stimulation of food, diagnose peptic ulcer and duodenum 12 .
3. The method of claim. 1, characterized in that an increase in the electrical activity of 2-3 times the stomach at frequencies under basal and stimulated research, decrease the electrical activity of the duodenum 12 with respect to stimulation of normal fasting obtained, in violation phasic response to stimulation with increasing rhythm of stomach contractions after stimulation with 3 or more times, with an increase in the coefficient of correlation stomach / duodenum 12 to 3 or more times on an empty stomach, and when stimulated, are diagnosed with stenosis of the outlet of the stomach.
4. The method of claim. 1, characterized in that an increase in the electrical activity of duodenum 12 is 4-5 times fasting reducing its 1.5-2 times after stimulation with increasing rhythmic contractions of the stomach and duodenum 12 in 10 times or more of hypertensive type of dyskinesia, and reduced it to 1.5-2 with hypotonic dyskinesia type fasting and stimulation, dyskinesia diagnosed 12 duodenal ulcer.
print version
Publication date 29.03.2007gg





Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.