|
section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2218874
![]()
HOW RADICAL duodenoplasty
AT duodenal ulcer, complicated by penetration
The pancreas foci
WITHIN THE BACK WALL BODY BULBS
Name of the inventor: Onopriev VI .; Henry SR .; Sharapova EG .; Popandopulo KI .; Bodrov LE
The name of the patentee: Russian Center of Functional Surgical Gastroenterology; Onopriev Vladimir; Henry Stanislaw R.; Sharapova Elena G.; Konstantin Papadopoulos; Bodrov Lada Emilevna
Address for correspondence: 350063, Krasnodar, ul. Sedin, 4, Kuban Medical Academy, Head. Patent Department TA Doroninoj
Starting date of the patent: 2002.05.13
The invention relates to medicine, surgical gastroenterology can be used in surgery complicated by a duodenal ulcer. In duodenal ulcer, complicated by penetration into the pancreas and foci within the posterior wall of the bulb body performing radical duodenoplasty. While retaining the continuity of the front and side walls of the duodenum. Access to the rear wall by providing greater omentum through piloropankreaticheskuyu bundle. Disconnect duodenopankreatichesky infiltrate. After excision margins ulcers and scar tissue adapting edge of duodenal injury. At the same time impose a sero-submucosal stitches on the back of the semicircle of the duodenum. The method allows to radically remove complicated penetrating duodenal ulcer and maintain the continuity of the front and side walls.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely to surgical gastroenterology and may be used in surgery complicated by a duodenal ulcer.
Surgical interventions with penetrating duodenal ulcers are one of the most difficult sections of abdominal surgery, due to the anatomical complexity of the area.
As an analogue is known a method of treatment of duodenal ulcer by excision of the ulcer and stitching the edges of the defect (VI Onopriev. Segmental duodenoplasty with SPV. Author's Certificate 971286, 1980). The method includes cross-cutting the front wall of the KDP, the mobilization of the rear wall, excision of abnormal tissue, the release nadbulbarnogo and pyloric parts of the back wall, smoothing walls pseudodiverticulum from mucosal recovery vials duodenum, followed by stitching the edges of the excised defect.
The disadvantage of this method include the full cross intersection of the duodenum and interrupt intraduodenal vascular and neural connections, followed by violation of the motor-evacuation function of the duodenum.
As a prototype method described conserving surgery in complicated duodenal ulcer (Zaitsev VT, Veligotskaya NN-sparing surgery with a bleeding duodenal ulcer // Clinical Surgery, 1982. 4. - pp. 9-13.
When the localization of ulcers on the back wall of the duodenum and its penetration into the pancreas, VT Zaitsev and NN Veligodsky developed a method of "circular excision of the ulceration area." To this effect a limited mobilization of the duodenal bulb on the lesser curvature of the intersection of the right gastric artery and the greater curvature preserving the right gastric artery. Thus duodenum intersects the bottom edge of the ulcer. Produced treatment of duodenal stump "open method" with the imposition of the first row of stitches into knots, and then - the second series of U-shaped seams, tight plugging ulcer crater. Thus, the lumen output of the digestive system and plague closes tightly. In the future, made a circular excision of the duodenal bulb ulcer in the affected area, often with the involvement in the process of scar-ulcerative pyloric zhomom. The line of intersection extends in most cases at the upper edge of the pulp. Superimposed terminolateralny pyloroduodenal anastomosis Billroth-1.
Assessing the operation Zaitsev-Veligodskogo, it should be noted that holds only limited mobilization of the duodenal bulb. Due to the extensive removal of the bulb, often together with the gatekeeper, violated not only ekstrapiloricheskie nerve relationship, but also direct pyloric nerve pathways that violates the coordination function of the pyloric sphincter. Thus operation shortcomings can be identified: the complete elimination of the bulb, creating a blind duodenal stump with tamponade crater last ulcer, pyloric denervation in violation of direct piloroduodenalnoy continuity. Furthermore, the ulcer crater plugging the proximal end of the rear wall rough duodenum leads to postoperative scarring zone duodenal anastomoses.
Tasks:
1 - increase the efficiency of surgical treatment of complicated ulcers penetration of the posterior wall of the duodenal bulb.
2 - radical removal of complicated ulcers penetration of the rear wall of the duodenal bulb while maintaining the continuity of the front and side walls.
The invention consists in that preserve the continuity of the front and side walls of the duodenum, access to the back wall provide from greater omentum through pylori-pancreatic bundle disconnect duodeno-pancreatic infiltration and after excision of ulcer edges, and scar tissue is formed anastomosis for rear semicircle duodenum.
The process is as follows. After verhnesredinnoy laparotomy carried intraoperative gastroduodenal transition zone. Identify the prevalence of scar-ulcer layers by a serous membrane duodenum and their fixation to the surrounding organs and tissues. After removing the scar-inflammatory mantle to determine the nature of the serous membrane scar-ulcer strain PDK.
Typically, an isolated ulcer damage the rear wall of the bulb is accompanied by reactive spastic contraction of the duodenum and ulcers on the level - from the front and side walls of the bulb - shaped secondary spur, by doubling the spasm of the walls of the duodenum. Infiltrative-ulcerative circular stenosis causes a reversible deformation of the front wall in the form of bulbs pseudodiverticulum. When you remove the mantle from spastic-level bulbs determine the structural safety of the front wall and the bulbous vessels. In the gastro-colic ligament at the edge of the transverse colon at the level of the antrum is opened the packing bag (size of the "window" at least 10 cm). If necessary, cross pathological gastro-pancreatic seam. Under visual control isolated piloropankreaticheskuyu bundle and cross it in the avascular portion closer to the rear wall of the pylorus. After that, it becomes possible to study the back wall of duodenum bulb. Determine the boundaries and extent of scar-adhesions layers in ulcer area, penetration depth.
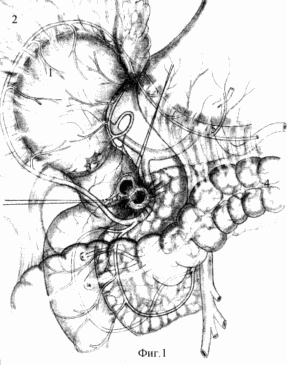 |
Figure 1 (Figure 1). Step radical duodenoplasty in peptic ulcer disease complicated by penetration into the pancreas. 1 - stomach; 2 - greater omentum taken aside the stomach ( "window" in the greater omentum); 3 - porter; 4 - transverse colon; 5 - pancreas; 6 - the plague of the rear wall of the duodenal bulb body. In retroduodenalnom cellular spaces outside the pathological focus by tonnelizatsii separated from the rear wall of the bulb of the pancreas. The edges of the ulcer penetration cut off from the pancreas. Crater ulcer penetration remains on the pancreas. The entire bulb bulbous mobilized to the level of the sphincter, ie, to the level of intimacy of a vascular seam with pancreatic head. At the same time exposing the gastroduodenal artery. Major vascular branches, reaching to the rear wall of the bulb bulbous sphincter remain. Excised posterior wall ulcer edge of the bulb and creates a wide duodenotomiya through which investigated the gatekeeper and a large duodenal soschek. After duodenotomii crushes secondary spur of the front and side walls. Crater sores on the pancreas can be located above the level of the gastroduodenal artery, at her level or below. If duodenal injury is limited only by the back wall, made of duodenoplasty rear access (through a "window" into the greater omentum). |
Go periultseroznoy infiltration into the side wall of the duodenum (large or small curvature) requires combined approach. Under the control of bidaktilnym infiltrated through the mesentery follicles without damaging the bulbous vessels carried a rubber taped. Perform radical excision of ulcer edges and scar-transformed periultseroznoy zone.
Ulcer Crater necrosis layer was purified by using a spoon Volkmann, treated with an alcohol, hemostasis is performed if necessary. For the purpose of distinguishing duodenal ulcer crater wall from performing his omentizatsiyu greater omentum flap on the "pedicle", which involves in-line joints back wall of the bulb. The edges of the duodenal injury previously adapted sero-submucosal stitches. All seams are applied across the line and then tie in stages. This okolopilorichesky mobile edge is lowered and pulled up to the lower edge seams, fixed on the pancreas.
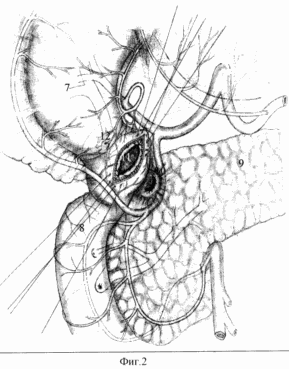 |
Figure 2 (Figure 2). Step radical duodenoplasty in peptic ulcer disease complicated by penetration into the pancreas. 7 - stomach; 8 - distal duodenum; 9 - pancreas; 10 - area of penetration in the pancreas; 11 - duodenotomicheskoe hole on the rear wall of the duodenum, scar tissue excised, duodenum edge ready for suturing; 12 - porter. Use 1-line hub outer sero-submucosal suture monofilament 4-5 / 0. |
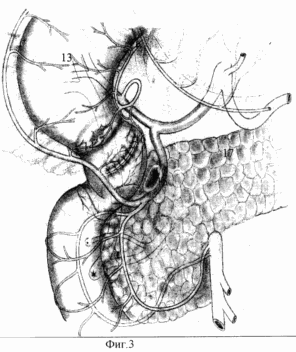 |
Figure 3 (FIG. 3). Step radical duodenoplasty in peptic ulcer disease complicated by penetration into the pancreas. 13 - stomach; 14 - porter; 15 - pancreas; 16 - the line formed by the rear wall of the anastomosis duodenal bulb; 17 - penetration zone pancreas. The proposed method we operated on 16 patients with duodenal ulcer complicated by penetration into the pancreas and localized on the back wall of the duodenum. In 2 patients penetration arrosive accompanied by bleeding. The postoperative period in all patients was uneventful, the wound healed by first intention. In 7-10 days all patients were discharged at a sanatorium or ambulatory rehabilitation, during the examination of patients one month after the radical duodenoplasty ulcer recurrence was not detected in any of the patient's motor-evacuation function of the KDP - not broken. |
example 1
Patient C., 38 years old, ulcer history - 7 years. Hospitalized in a clinic with a duodenal ulcer, accompanied by severe pain. On EGD -. Posterior wall ulcer sizes 0,5-0,6-0,2 cm Due to the inefficiency of conservative therapy the patient is proposed transaction in the amount of the radical duodenoplasty. When intraoperative study of the gastroduodenal zone in transition stenotic deformation, scar retractions in the projection of ulcer as is the case with "front" and "lateral" ulcers were found. A "window" in the greater omentum studied rear wall KDP found "back" penetrating into the pancreas ulcers. Achieved separation wall duodenal ulcer from the crater through a "window" into the greater omentum. Produced intraduodenal study: gatekeeper and BDS in scar-inflammatory process is not involved. The edges of the ulcer, scar excised field, through a "window" into the greater omentum, on the rear wall of the imposed precision monolithic sero-podlizistye seams. Thus, when the localization of ulcers on the back wall of duodenum complicated penetration in the intact pancreas, and duodenum front semicircle, succeeded by the bridge to keep the front wall.
The postoperative period was uneventful, the patient was discharged from hospital on the 7th day after the operation. At follow-up examination at 1 month after surgery motor-evacuation function of the PDK is not broken, FGDS- data for recurrent ulcers received, signs of inflammation were found in the area of the anastomosis.
example 2
Patient M, 32, at ulcer history - 9 years. Hospitalized in a clinic with a diagnosis of duodenal ulcer complicated subcompensated stenosis. If EGD - in the bulb region of the body on the back wall of the duodenum diagnosed ulcerative defect sizes 0,3-0,2-0,1 see, just behind the ulcerative defect - Stenosis bulbs Article II-III. Patients after preoperative preparation was operated. When intraoperative study in KDP bulb body from the serous membrane area revealed segmental spasm. The front wall of the KDP in scarry process is not involved. A study by the rear wall of the "window" in the greater omentum. In the study revealed the penetration zone in the pancreas "back" ulcers. The ulcer was located on the back wall near the lesser curvature of the bulb body. In periultseroznoy zone field expressed scar ulcers extending to the small curvature of the duodenum, pancreas. The wall of the duodenum bluntly separated from the ulcer crater was discovered at the same lumen WPC. After separation of the rear wall of the ulcer crater penetration KDP has become more mobile. The edges of the ulcer, scar field posterior wall and greater curvature of the bulb were cut through the "window" in the greater omentum, on the rear wall of the imposed precision monolithic sero-submucosal stitches. Thus, when the localization of ulcers on the back wall of duodenum complicated penetration in the intact pancreas, and duodenum front semicircle, succeeded by the bridge to keep the front wall.
The postoperative period was uneventful. Postoperative wound healed by first intention. Sutures are removed. The patient was discharged from hospital to outpatient treatment in a satisfactory condition for 8 days after surgery. At follow-up examination at 1 month after surgery: condition is satisfactory, no complaints. On EGD - signs of recurrence of ulcers are not found in the study of motor-evacuation function of the KDP-pathology is not revealed.
The method of surgical treatment of complicated ulcers of the posterior wall duodenal bulb, allowing to keep the front and side of its wall, creates optimal conditions for the early and full restoration of the functional activity of the gastroduodenal junction. Using the proposed access to the rear of the bulb reduces the risk of complications due to adhesions distinguishing intestinal sutures in the packing bag from the free abdominal cavity. All these advantages of the method will ensure a decrease in the number of complications in the postoperative period and improve the quality of life of patients with duodenal ulcer disease, maintaining neuromuscular connections in the gastroduodenal junction, reduce motor-evacuation disorders and improve the quality of life of patients.
REFERENCES
1. Onopriev VI Segmental duodenopdastika with SPV .// Author's Certificate 971286, 1980.
2. Zaitsev VT, Veligodsky NN Organ-operation with a bleeding duodenal ulcer. // Clinical Surgery. 1982. - 4 - pp 9-13.
CLAIM
Method radical duodenoplasty with duodenal ulcer complicated penetration into the pancreas with foci within the rear wall of the body duodenal bulb, characterized in that preserve the continuity of the front and side walls of the duodenum, access to the back wall provide from greater omentum through piloropankreaticheskuyu bunch disconnect duodenopankreatichesky infiltration and after excision of the ulcer edges and scar tissue edge duodenal wounds adapt sero-submucosal stitches on the back of the semicircle of the duodenum.
print version
Publication date 29.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.