| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2088938
![]()
A method for detecting intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections
Name of the inventor: Bukharin OV .; Valyshev AV .; Zykov LS .; Sitting is Konnova .; Sokolov VY .; Chelpachenko OE
The name of the patentee: Orenburg department persistence of microorganisms Institute of Ecology and Genetics of Microorganisms, Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1993.07.01
A method for detecting intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections. Use: in the field of medical microbiology, namely in the laboratory diagnosis of intestinal disorders microbiocenosis. The inventive in discovering grown on nutrient agar by plating colonies fecal enterobacteria ability to inactivate a commercial preparation of human leukocyte interferon in a concentration of 2 IBC for test culture Corynebacterium xerosis GISCO N 181. In this case, the lack of activity in antiinterferonovoy colonies indicates eubioz; feature detection at 1-50% of the colonies indicates intestinal dysbiosis, while the presence of a trait in 50% of the colonies - on intestinal infection. The method makes it possible to carry out early diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections by reducing the time and more informative studies by pre-orienting assessment of the state of the intestinal microflora. The method can be used to perform mass screening to identify high-risk groups, and for the differential diagnosis of various intestinal conditions microbiocenosis in complex clinical and bacteriological situations.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, in particular to medical microbiology, and can be used for diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections.
In recent years, all over the place there is a significant increase in the incidence of intestinal dysbiosis (dysbiosis), which is a source of acute endogenous infections (peritonitis, appendicitis, cholecystitis, pyelonephritis, pneumonia), it contributes to the development of allergic diseases, the formation and progression of chronic inflammation in various organs. Intestinal microflora with intestinal dysbiosis plays a role in carcinogenesis, atherosclerosis, is a source of antibiotic resistance genes that can be transferred to other bacteria.
Due to the high prevalence of intestinal dysbiosis issue of timely recognition of his becoming one of the tasks of the diagnostic service. To detect intestinal dysbiosis are known to use expanded bacteriological examination of faeces in the classical way with a certain amount, and biological properties of the anaerobic microflora (Epstein-Litvak RV and other bacteriological diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis:.. Guidelines M. 1977). Extreme diversity of the intestinal microflora (in the cecal contents are representatives of 17 families, 45 genera and more than 400 different species) requires a large set of culture media and the creation of special conditions for the cultivation of microorganisms. This leads to the fact that intestinal dysbiosis laboratory diagnostic methods to date are expensive, labor intensive, time consuming and unacceptable for mass research.
Based on the above it can be concluded about the importance of early detection of intestinal dysbiosis for the timely and effective implementation of correction of microflora and biological Immunopreparat. To solve this problem requires population screening programs for intestinal dysbiosis.
Since the violation of the intestinal ecological community all the properties of the microflora (antagonistic and vitamin-generating activity, participation in metabolic processes, and others.) Vary greatly, offered a variety of indirect diagnostic tests of intestinal dysbiosis. Thus, the state microbiocenosis judged by the level of metabolites of the intestinal microflora. To this end, define indican, p-cresol and phenol in the urine; hydrogen and methane in the exhaled air; volatile fatty acid contents in the jejunal or faeces; ammonia in the blood in the stool or in the exhaled air (AO Tamm et al. Metabolites in the diagnosis of gut intestinal dysbiosis. Antibiotics and medical biotechnology. 1987, Vol. 32, N 3, s.191-195). Methods for detection of intestinal dysbiosis, based on the detection of metabolic products, provide satisfactory results in severe imbalance of intestinal microflora and have low sensitivity and diagnostic value in the initial stage of intestinal dysbiosis (ibid, p. 192). Therefore, these methods are not sufficient for screening populations to intestinal dysbiosis. The basis of a different method to identify violations dysbiotic put the degree of antagonistic activity of the microorganisms isolated from the feces (Zavgorodnyaya EF et al. The antagonistic activity of the intestinal autoflora as an indirect method of detection of intestinal dysbiosis. Physician job. 1981, N 6, s.113-116) . The disadvantage of this method of assessing bowel microflora condition is duration study (day 5).
In connection with the above circumstances the search for new methods of screening for intestinal dysbiosis is an urgent task of Clinical Microbiology. During the mass of the population, especially the children's examinations, to identify intestinal dysbiosis of considerable importance is the differentiation of the last sporadic cases of intestinal infections. Currently, there are no clear clinical and microbiological criteria for differentiating these two diseases. Existing laboratory intestinal infections diagnostic methods, caused by opportunistic enterobacteria (PEO) Escherichia, Proteus, Klebsiella, and others. Based on the detection thereof in an amount of not less than 10 June CFU in 1 g of feces, evaluation of their biological properties, the presence of antibodies to opportunistic enterobacteria in titer 1:40 or higher with an increase in their levels in the dynamics of the disease in the study of "paired" sera (Queen LB et al. The clinic, diagnosis, treatment, epidemiology and control measures in case of acute intestinal infection caused by opportunistic bacteria in infants: guidelines, M. 1988, p.19). The high cost, labor intensity, the duration of studies precludes the use of these methods of diagnosis of intestinal infections caused by PEO, for screening. Therefore, a special activity becomes to develop a method of bacteriological screening, allowing the first stage of examination (search program) to identify and to carry out a differential diagnosis of the most common infectious intestinal diseases intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections caused by opportunistic bacteria.
The closest technical solution chosen as a prototype, is a method of determining intestinal dysbiosis deficit of bifidobacteria (seeding suspension of faeces produced in environment Blaurock; accounting by microscopy, Gram-stained smears prepared from typical colonies) and the detection of tissue protein in the feces (deposition of soluble protein by the addition of trichloroacetic acid to the emulsion of faeces, accounting degree visual check bleached supernatant), indicating possible damage to the cellular elements of the intestinal wall (Dorofeychuk VG, etc. The key tests for intestinal dysbiosis: Pristendovy leaf VDNKh Moscow. 1991. ). The disadvantage of this method is the lack of intestinal dysbiosis diagnostics at an early stage, characterized by only slight changes in the aerobic part microbiocenosis (increase or decrease in the number of E. coli in the absence of reducing the level of bifidobacteria 1 degree of dysbiosis) (Grachev, N. et al. The use of bacterial biological agents in the practice of the treatment of patients with intestinal infections Diagnosis and treatment of intestinal dysbiosis:.. Guidelines M. 1986, pp 16-17).. In addition, the visual assessment ( "complete", "large", "small" bleached liquid) does not allow to objectively evaluate and standardize the results.
The foregoing generalized description of the identified methods analogues with the reasons preventing the production of the required technical result gives grounds to conclude that the claimed invention is not known from the prior art, ie, It is new.
The big difference is that determined antiinterferonovuyu activity simultaneously in all the colonies of Enterobacteriaceae in sowing feces on nutrient agar with a preparation of human leukocyte interferon in a concentration of 2 IBC for test culture Corinebacterium xerosis GISCO N 181 and inactivation colonies interferon conclude on the state of the intestinal microbiocenosis : antiinterferonovoy lack of activity in the colonies indicates eubioz; feature detection at 1-50% of the colonies indicates intestinal dysbiosis, while the presence of a trait in 50% of the colonies on intestinal infection.
The authors suggest that significant differences are novel and provide an opportunity to implement early diagnosis of intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections by reducing the time and more informative studies by pre-orienting assessment of the state of the intestinal microflora. The inventive method can be used to perform mass screening to identify high-risk groups, and for the differential diagnosis of various intestinal conditions microbiocenosis in complex clinical and bacteriological situations.
The process is as follows.
Rectal loop seeded contents of the rectum to the Petri dish with 1.5% of meat-peptone agar containing preparation of human leukocyte interferon (NGO "Immunopreparat", Ufa) in an amount of 0.3 ml working solution of 7.5 ml of agar which corresponds to a concentration of 2 MBC test culture Corynebacterium xerosis GISCO N 181. The working solution is prepared according to the instructions of the solute vial in 2 ml of sterile 0.85% sodium chloride solution. At the same time one cup may be sowing feces sector from two or three subjects. Cultures were incubated in an incubator for 18-24 hours at 37 o C. colonies clean pairs of chloroform. For this purpose, holding the cup upside down, put it in a piece of paper Whatman cover an area of 8-10 cm 2 and impregnated with its 0.3-0.5 ml of chloroform. Keep closed cup for 20-30 minutes. Turn the cup on top of the colonies and 4.3 ml of soft laminated (0.6-0.7%), agar, mixed with 0.1 ml of suspension (in about 1 ml on September 10 indicator cells through an optical turbidity standard) daily agar test culture Corynebacterium xerosis GISCO N 181.
The results were assessed after 18-24 h incubation in a thermostat at 37 o C, i.e. after two days from the start of the study. After the incubation period to determine the activity antiinterferonovuyu plating of faeces on the growth of the test strain on the surface of and around the colonies, indicating that the troubles in the intestinal microbiocenosis. Detection antiinterferonovoy activity in 1-50% of colonies indicates intestinal dysbiosis; there is no evidence from more than 50% of the colonies indicates intestinal infection, and the absence of signs on eubioz.
Based on the results of adult and children surveys search program suspicion of intestinal dysbiosis, or intestinal infection in the number antiinterferonaktivnyh colonies can be considered confirmed. The main program used in the second stage of diagnostic search in addition to the search engine, you need to deploy bacteriological studies of feces in order to clarify the type and degree of intestinal dysbiosis, the form (ehsherihioza, klebsiellez et al.) Intestinal infection and a decision on the methods of their correction.
Theoretical background to the development of the proposed method of detection of intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections have served we found differences in the number antiinterferonaktivnyh colonies on agar crops faeces from healthy subjects and patients with intestinal dysfunction (Table. 1).
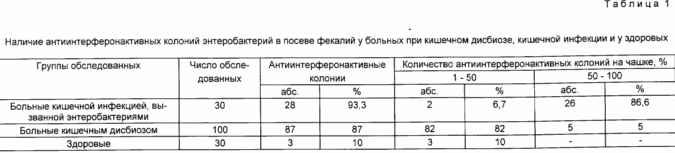
So, when sowing faeces from 30 patients with intestinal infection caused by EPKP 0.18, non-typeable Escherichia, Klebsiella, Proteus, and other enterobacteria, in 28 cases (93.3%) were found antiinterferonaktivnye colony. For this group of patients appeared antiinterferonovoy characterized by activity in the majority (80-100%) colonies.
When sowing isparazhneny from 100 patients with intestinal dysbiosis antiinterferonovogo positive results of the test have been identified with the same frequency (87% patients), as well as intestinal infections. However, antiinterferoaktivnyh accounted for from 1 to 50% of the colonies, ie less than half grown on the cup.
The examination clinically and bacteriologically 30 healthy children and adults in the 27 cases (90%) in the plating of faeces were detected colonies inactivating the interferon. Only 3 of 30 surveyed identified antiinterferonovy positive test, and the number of active colonies amounted to 3-5% of the grown.
Using the method described above, it was carried out a screening study of 140 children of children's somatic hospital CSS PO "Strela" Orenburg over prolonged intestinal dysfunction. results are shown in Table. 2.
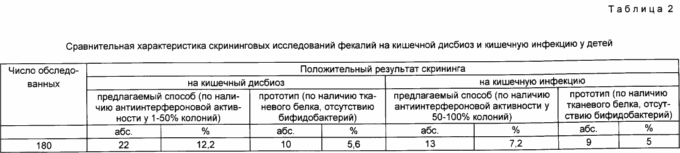
When using the claimed process criteria (antiinterferonovoy activity in the presence of 1-50% of the colonies) screening for positive intestinal dysbiosis detected in 22 cases out of 180 (12.2%), while the prototype method (Detection of tissue protein in the absence of feces bifidobacteria) in 10 cases (5,6%), P <0,05.
In the group of children with intestinal dysbiosis positive screening results were confirmed by bacteriological examination of faeces deployed as described in RV Epstein-Litvak FL Vilshanskoy (1977).
Patients with a positive screening test for intestinal infection diagnosis was confirmed by bacteriological method (detection of PEO in pure culture from breeding faeces 10 -5, which corresponds to the number of their more June 10 CFU in 1 g), and a positive immune response of host - the presence of serum SEA antibody titer of 1: 160 and higher.
The method was used to examine three groups of children: the first - patients with intestinal dysbiosis; Second, patients with intestinal infections; third control. Here are some examples.
The first group of children (patients with bowel disbizom).
Example 1. Patient C 10 years. The diagnosis on admission chronic pyelonephritis esherihioznoy etiology in acute stage. During the screening of the proposed method detected intestinal dysbiosis (the number of colonies when plated antiinterferonaktivnyh feces was 15%), while a parallel survey conducted on a prototype stool dysbiotic phenomena not found. In further conventional manner validated violation intestinal microbiocenosis as increasing the total number of E. coli (4.6 × 10 September CFU / g) c hemolytic appearance and lactose-forms (8 and 20%) and a reduction bifidoflora (October 7 cfu / g). Spend a targeted intestinal microflora correction biologics. Consequently, the proposed method in a patient diagnosed intestinal dysbiosis in the early stage of the survey, which allowed to conduct the correction of violations and to reduce the number of relapses of pyelonephritis.
Example 2. Patient R. 8 years. He suffers from eczema since the age of three. Bacteriological examination of feces proposed method detected 30% of the colonies, inactivating the interferon. Character detected violations dysbiotic set further detailed analysis by a deficiency of bifidobacteria (10 5 cfu / g), and Escherichia (Oct. 6 CFU / g), increasing the content of PEO Klebsiella (July 10 CFU / g).
The second group of patients (patients with intestinal infections).
Example 1. Patient M. 2 month. From history we know that the child is attached to his chest on the third day after birth (post-partum haemorrhage in the mother). After discharge from the hospital chair speeded up to 8-10 times with mucus. Feeding natural. Behind the mass (increase of 1 850 g per month, for the second 300 g). On examination revealed signs of malnutrition 1 degree. Stool 2-3 times a day, the liquid without pathological impurities. Antibiotics are not treated. In the study of the proposed method faeces conducted on admission revealed antiinterferonovaya activity at 100% inoculation fecal colonies on nutrient agar leukocyte interferon, indicating that intestinal infections. Further clinical and bacteriological examination confirmed the presence of intestinal infection esherihioznoy: enterpatogennaya revealed E. coli serogroup 018 in an amount of 6.3 h 10 9 cfu / g with weakly expressed enzymatic properties. Targeted antibiotic therapy in combination with pathogenic agents has led to a positive effect.
Example 2. Patient G. 7 years. Complaints of low-grade fever, diarrhea for two days after eating dried fruit. In the course of the clinical and laboratory examination of the proposed method in two days after the receipt of set intestinal infection, which is justified by the presence of fecal matter in the crop at 80% of the colonies ability to inactivate interferon. Subsequent examination revealed non-typable Escherichia in an amount of 2.1 parts September 10 cfu / g, hemolytic inactive, and a four-fold rise in antibody titer to autostrains E. coli in the second week of illness.
A third group of children (control).
Example 1. A child 5 years. The diagnosis on admission enuresis. During the screening for intestinal trouble in microbiocenosis a negative result antiinterferonaktivnyh colonies were found in the crop of feces. Eubioz deployed confirmed by bacteriological analysis.
Example 2. Boy O. 6 years. At the age of 5 years, he operated on for stenosis prilohanochnogo ureter. The postoperative period was complicated by Pseudomonas infection of the urinary tract. Finding the source of infection of the urinary tract examined with feces on the proposed method. A negative result. Bacteriological examination of feces confirmed eubioz. Urinary tract infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa was the result of nosocomial infection. Application of Pseudomonas phage resulted in the reorganization of the urinary tract.
Thus, conducted microbiological research and clinical trials have shown that the proposed method has the following advantages: easy to test, affordable, non-invasive, does not require special facilities and equipment, as compared to the prior art improves the accuracy of diagnosis in half, reduces the duration of the study for one day. The possibility of repeated, even daily analyzes and an advantage of the method.
CLAIM
A method for detecting intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal infections by inoculating the test material on a medium, wherein determining antiinterferonovuyu activity simultaneously in all Enterobacteriaceae colonies plating of faeces on nutrient agar with a preparation of human leukocyte interferon at a concentration of 2 MBC for test culture Corynebacterium xerosis GISCO N 181 and in the inactivation of colonies interferon conclude on the state of the intestinal microbiocenosis: antiinterferonovoy lack of activity in colonies testify eubioz; feature detection from 1 to 50% of the colonies indicates intestinal dysbiosis, while the presence of a trait in 50% of the colonies on intestinal infection.
print version
Publication date 30.03.2007gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.