| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2197728
![]()
METHOD OF DIAGNOSTICS OF EXPOSURE OF CHRONIC CHOLECYSTITIS
The name of the inventor: Potekhina Yu.P .; A. Strakhov; Potekhin PP; Zubeyev PS; Shcherbak Y.P .; Buzoverya M.E.
The name of the patent holder: Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy; Sarov Physicotechnical Institute
Address for correspondence: 603005, Nizhny Novgorod, ul. Alekseevskaya, 1, Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy, Patent Information Department
Date of commencement of the patent: 2001.07.18
The method includes taking a vesicle bile by means of duodenal probing or a puncture followed by its study by the method of dehydration self-organization. With the help of a microscope, the structure of a pre-dried standard bile drop is analyzed and, in the presence of crystals in the form of dendrites, an exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis is diagnosed in the central zone, and in the case of a poorly structured or amorphous central zone, the absence of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis is diagnosed. The method allows you to choose an adequate treatment strategy for cholecystitis. It is relatively simple, cheap and affordable.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely, to gastroenterology.
Prevalence of cholelithiasis (SCI) is very high. Currently, almost one in five women and one in ten men suffer from this pathology. And in recent years, CSW has strongly "grown younger." The results of the study by domestic authors indicate that the number of patients is doubled in each subsequent ten years. The number of performed cholecystectomies is second only to the number of appendectomies [2].
The main methods of treatment of cholelithiasis are:
1. litholytic therapy (preparations of chenodeoxycholic and / or ursodeoxycholic acid);
2. extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy;
3. combination of litholytic therapy and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy;
4. Percutaneous transversal litholytic (contact) therapy;
5. laparoscopic cholecystectomy;
6. Cavity cholecystectomy.
At present, sparing endoscopic interventions [10] and organ-preserving methods of treatment of CSF are becoming increasingly widespread.
For the first time, endoscopic cholecystectomy was done in France in 1987 (Ph. Mouret). In Russia, a similar operation was performed by Yu.I. Gallinger and AD Timoshin in 1991 [2].
The merits of the method include the following:
- low traumatism;
- decrease in the length of stay of patients in the hospital;
- reduction of the period of restoration of work capacity;
- improving the quality of life of patients;
- good cosmetic effect;
- reduction of mortality in the group of elderly and senile patients with severe concomitant diseases.
In connection with the widespread use of organ-preserving methods for the treatment of SCI, it is important not only to ascertain the presence or absence of stones, but also to determine the degree of activity of inflammation in the mucous membrane of the gallbladder, as the choice of the method of treatment and the tactics of the patient depend on this. In addition, the process of stone formation in the bile ducts is closely related to inflammation, these processes strengthen each other. Inflammation in the mucous membrane of the gallbladder is one of the factors leading to the formation of gallstones, which changes the chemical composition of the bile [4]. In turn, the presence of stones in the gallbladder leads to the emergence or intensification of the inflammatory process.
Endoscopic interventions are shown, according to many authors, in chronic cholecystitis outside of exacerbation, when the degree of activity of inflammation of the gallbladder wall is less than in acute cholecystitis.
For the correct choice of the method of treatment and the choice of a favorable moment for the operation, it is necessary to know whether there is an exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis.
Diagnosis in patients with cholecystitis is based on the study of complaints, anamnesis, clinical picture of the disease. These data are not sufficiently informative. For example, in elderly people there is often a discrepancy between the clinical manifestations of cholecystitis and the severity of inflammation in the gallbladder.
The method closest to the present invention is a method for determining the active reaction of bile. The concentration of H + ions and OH hydroxide is one of the important factors determining the physico-chemical state of bile and the process of crystallization itself. Many authors noted that the inflammation of the pH of bile is shifted to the acidic side [4, 6, 7, 9, 10]. But about the normal pH of the gall bladder, the opinions of different authors differ greatly. V.A. Maksimov et al. Consider that the normal pH is 6.5-7.5 [12]. According to S.P. Chupina et al. Cystic bile is stable in the strict pH range of 4.0-8.3 [13].
The most reliable estimate of the degree of activity of inflammation in the wall of the gallbladder is possible with the help of morphological methods of examining the wall of the gallbladder. But morphological diagnostics can not be performed before surgery, as the technique of taking a biopsy of the gallbladder mucosa is not developed.
Since none of the existing methods make it possible to reliably estimate the state of the gallbladder mucosa, this makes it difficult to choose therapeutic tactics for calculous cholecystitis. Therefore, the object of the present invention is to increase the information content and accuracy of bile test results and ensure the selection of an adequate method of treatment.
New methods of diagnostics are known. The most interesting is the crystallography of bile, since bile is a specific product of hepatic cell activity, its study provides extensive information on the functioning of hepatocytes and the hepatobiliary system as a whole [5]. Since bile has a complex physico-chemical structure, inflammation in the gallbladder quickly leads to its significant changes, which can be characterized by crystallography data [11].
We used the method of dehydration self-organization of a biofluidic medium under standard conditions on a solid substrate. After the droplet dries, the amount of salts increases from the periphery to the center, and the amount of organic matter increases from the center to the periphery [14]. In addition to identifying zonal structures in diagnosis, the shape of the crystals in the central zone of the dried drop is of great importance [15]. However, from the viewpoint of assessing inflammation in the mucosa of the gallbladder, this method was not used.
The shape of the crystal is determined by the gradient between the crystal-forming elements and the elements of the environment. In pathology, in particular inflammation, there is a change in the quality and quantity of organic molecules, which leads to the appearance of new forms of crystals. This is possible with a change in the viscosity of the medium, the appearance in it of a large number of products of incomplete metabolism, elements of tissue degradation and so on. Based on the foregoing, it can be assumed that the shape of the crystal is a natural system for indicating the chemical composition of the biofluid.
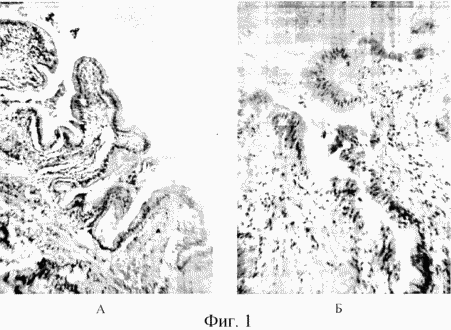
We examined 40 CHD patients aged from 33 to 76 years who underwent classical or laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Bubble bile was examined by the method of dehydration self-organization. The removed gallbladder was fixed in 10% neutral formalin, the pieces from the body, bottom, and neck of the bladder were dehydrated in alcohols of ascending concentration, they were poured into paraffin. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, alcian blue and Schiff's reagent. According to the morphological analysis, 17 patients experienced an exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis (micrograph B in Fig. 1, an increase of 7x40), in 23 there was no exacerbation (micrograph A in Fig. 1, an increase of 7x20). The majority of patients exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis was absent, they could do an organ-saving operation or prescribe conservative treatment, that is, to preserve the gallbladder.

When comparing the crystallographic picture of gall bladder and the morphological picture of the gallbladder wall, it turned out that the structure of the central zone of the dried bile drop is different for different groups of patients. In the absence of exacerbation of cholecystitis, the central zone was poorly structured, it was impossible to separate individual crystal structures or small crystals scattered on an unstructured substrate (micrograph A in Fig. 2, an increase in x40) were visible. When the cholecystitis exacerbated in the central zone, crystalline structures were present in the form of dendrites branching at an angle of 60 or 90 ° (micrograph B in Fig. 2, an increase in x40).
On the basis of this, a method for diagnosing exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis was developed, including the selection of a vesicle bile in a patient (duodenal sounding or puncture of the gallbladder) and its study by the method of dehydration self-organization. In the presence of a dried drop of crystals in the form of dendrites in the central zone, a conclusion is made about the aggravation of cholecystitis.
The method is simple, affordable and cheap.
As an illustration of the claimed diagnostic technology, we give examples that confirm the industrial application of this technique.
Example 1. Patient N., 58 years old (case history 4987), was taken to the reception room on 01.11.2000 with the first developed biliary colic attack. She complained of intense pain in the right hypochondrium with irradiation into the right scapula, dryness in the mouth, belching of the bile. An injection of antispasmodics was performed. According to the US, the wall of the gall bladder is up to 3.5 mm thick, in the lumen there is one concrement 18 mm in diameter, there is no obturation of the outlet duct. Patient with a diagnosis: acute simple calculous cholecystitis (attack removed) was hospitalized in a surgical hospital. The data of the general blood test is within the limits of the norm. In connection with the concomitant pathology: hypertensive disease IIIa, the state after ischemic stroke, dyslexia, the question arose about the choice of treatment tactics: operative or conservative. According to the control ultrasound, the contractile function of the gallbladder is good. Duodenal sounding was performed. Crystallography of the gall bladder bile by the method of dehydration self-organization showed the absence of a structured middle zone of the dried drop, that is, the absence of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis. Final diagnosis: chronic calculous cholecystitis. Conservative treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid was shown and started according to the scheme.
Example 2. Patient A., 47 years old (case history 4563), was taken to the hospital by an ambulance on 17.10.2000 with a repeated attack of biliary colic. She complained of intense pain in the right hypochondrium with irradiation to the right shoulder blade and shoulder, nausea, vomiting of bile. Injection of antispasmodics and infusion of a glucose-novocaine mixture, the attack managed to be quenched. With ultrasound, the gallbladder wall is about 3.8 mm, in the lumen the concrement is 1.8 cm in diameter, there is no obturation of the output department. The data of the general blood test is within the limits of the norm. The duodenal sounding was carried out. Crystallography of the gall bladder bile by the method of dehydration self-organization showed the presence of dendritic-like crystalline structures in the middle zone of the dried drop, that is, the presence of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis. The final diagnosis: acute calculous cholecystitis. Cholecystectomy was performed.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. Briskin BS, Kaprov IB, Fuks MA Percutaneous interventions under the supervision of ultrasound scanning. // Overview information. Series "Surgery", vol.3. M., 1989.
2. Vetshev PS, Shkrob OS, Beltsevich DG Cholelithiasis. - M., ZAO "Medical Newspaper", 1998. - 192 p.
3. Gavrilin AV, Vishnevsky VA Percutaneous interventions on the biliary tract. // Annals of surgical. Hepatology, vol.2. - 1997. Appl. Mat. V congress. Surgeons-hepatologists. - P.141-142.
4. Galkin V.A. Chololithiasis. New aspects. - Moscow: ZAO "Medical newspaper", 1996. - 192 p.
5. Ganitkevich Ya.V., Karbach Ya.I. Examination of bile. Biochemical and biophysical methods. - К .: Вища школа, Головное издательство, 1985. 136 p.
6. Dederer Yu.M., Ustinov TG, Luzgina I.B. On the occurrence of gallstones. // Clinical medicine. - 1983. - 10. - P.19-22.
7. Dzyak GV, Pererva AN, Zorin A.N., Muntyan S.A. Diagnosis of early stages of FAT. // Ross. G-l gastroenterology, hepatology, coprolactology. - 1997. - 5. - P.171.
8. Inyukina HB, Shatoxina SN, Shabalin VN. Diagnostic value of zonal structures of bile. / / Crystallographic methods of research in medicine: Sat. Sci. Tr. I All-Russia. Scientific-practical. Conf. - M., 1997. - P.127-129.
9. Kostenko A.P. Physico-chemical properties of bile in diseases of the biliary tract. / / Phys. a business. - 1990, 11. - P. 89-92.
10. Kochnev OS, Khalilov Kh.M., Biral'tsev VN, Minabutdinov PM Physical and chemical parameters of bile in the evaluation of the inflammatory process in the biliary tract. // Surgery. 1992. - 1. P.42-49.
11. Crystallographic method of research in pediatric gastroenterology (Methodological recommendations). / G.V. Plaksina, G.V. Rimarchuk, L.A. Savelieva et al. - M., 1995. - 25 p.
12. Maksimov VA, Chernyshev AL, Tarasov K.М. Duodenal examination. - M., ZAO "Medical newspaper", 1998. 192 p.
13. New Approaches to Early Diagnosis, Pathogenesis and Treatment of Cholesterol Chololithiasis. / S.P. Chupin, S.B. Nikiforov, Ya.L. Tyuryumin, G.L. Gritsky. - M., 1994. - 174 with.
14. Shabalin V.N., Shatokhina S.N. Clinical crystallography: formation, problems, prospects. / / Crystallographic methods of research in medicine: Sat. Sci. Tr. I All-Russia. Scientific-practical. Conf. - M., 1997. - P.3-9.
15. Shilkin GA, Yartseva HS, Medvedev IB at all. Results of crystallographics of lacrimal fluid in various forms of distrophic eye pathology. // Ophthalmosurgery. - 2, 1997. - P.86-92.
CLAIM
A method for diagnosing exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis based on the results of a study of a portion of gall bladder, characterized by the use of a microscope to analyze the structure of a pre-dried bile droplet in a standard manner, and in the presence of crystals in the form of dendrites in the central zone, an exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis is diagnosed, and in the case of poorly structured or amorphous The central zone is diagnosed with no exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis.
print version
Date of publication 28.01.2007gg




Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.