| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Patent catalog / Catalog section / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2129026
![]()
METHOD FOR TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CALCULUS CHOLECYSTITIS
The name of the inventor: Shanturov VA; Tyuryumin Y.L .; Maltsev A.B.
The name of the patentee: Institute of Surgery of the East Siberian Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Address for correspondence: 664079 , Irkutsk, m. Yubileyny, 100, PO Box 23 Institute of Surgery of Patent Science
Date of commencement of the patent: 1997.04.11
The invention relates to medicine, surgery, can be used in the treatment of patients with acute cholecystitis. Percutaneous transhepatic intravesical fractional administration of methyl-tert-butyl ether is performed. Pre-sanitize the cavity of the gall bladder with antiseptics, 4% sodium bicarbonate solution. After the introduction of ether, the gallbladder is perfused with a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate. With the restoration of the permeability of the vesicle siphon, a bubble-duodenal infusion of 500-1000 ml of normovolemic solution is performed. The method allows to adequately remove degradation products of gallstones.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of medicine, namely, surgery, and can be used to treat acute calculous cholecystitis that occurs against the background of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder.
There is a known method of treatment of cholelithiasis (AS USSR, No. 1491472, M.C. A 61 B 17/00, A 61 M 25/00), intended for non-operative treatment of patients with localization of concrements in the gallbladder. Laparoscopic cholecystostomy is performed with introduction into the cavity of the bladder of double-lumen drainage with an inflatable cuff at the working end. Fractional administration of mono-octanoin is carried out via one of the drainage channels. Obturation of the cystic duct prevents the entry of mono-octanoin into the intestine, which reduces the toxic effect on the patient.
However, this method ensures the dissolution of stones for a sufficiently long time (Postolov PM, Kovalev GV, Nikishin GI, Troyansky EI, Mizintsev VV, Bykov AV, Nesterov S S., Novokschenov V.Yu., Mishin S. G. Dissolution of gallstones in patients with cholecystitis with extremely high operational risk .-- Surgery; 1988; (10): 29-32 Postolov PM, Bykov A. V., Nesterov SS, Golub VA, Mishin SG, Burchuladze N.S. Contact Contact Dissolution of Gallstones - Surgery; 1991; (9): 71-76), requires constant medical supervision Because of the known toxicity of mono-octanoin, and is technically complex and unsafe for the patient, because The drainage is established laparoscopically.
The closest to the proposed in technical essence is the method of dissolution of gallbladder stones using methyl-tert-butyl ether as solvent, which has the ability to dissolve cholesterol stones in a short period of time (Allen MJ, Borody TJ, Bugliosi TF, May JR, LaRusso NF , Thistle JL Rapid dissolution of gallstones in using methyl tert-butyl ether, N.Engl.J. Med, 1985; 312: 217-220). The known method is carried out as follows. Under fluoroscopic control, a drainage is transdermally transhepatically installed into the cavity of the gallbladder, and methyl-tert-butyl ether is introduced in portions of 2-5 ml, replacing it as it is saturated with cholesterol.
The disadvantages of the known method include the lack of recovery of the concentrated function of the gallbladder due to incomplete cleansing of the gallbladder wall and inadequate removal of degradation products of gallstones.
Moreover, the authors of the method consider acute inflammation of the gallbladder as one of the contraindications to the use of methyl-tert-butyl ether. Consequently, this method was not used to treat patients with acute calculous cholecystitis.
The aim of the proposed invention is minimally invasive, non-surgical treatment of patients with acute calculous cholecystitis.
The technical result of the proposed method is to increase the effectiveness of treatment by eliminating inflammation and cleansing of the gallbladder wall, adequate removal of the products of degradation of gallstones from its lumen, which are the main cause of recurrence of the disease and the restoration of permeability of the siphon.
The technical result is provided by percutaneous transhepatic intravesical injection of methyl-tert-butyl ether.
New in the implementation of the technical result of the method is a preliminary sanation of the gallbladder cavity with antiseptics and a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate. Then, fractional administration of methyl-tert-butyl ether is carried out followed by gall bladder perfusion with a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate. When restoring the permeability of the vesicle siphon, a duodenal infusion of 500-1000 ml of normovolemic solution is performed.
A comparative analysis of the claimed solution and the prototype shows that the proposed method differs from the known method in that methyl-tert-butyl ether is used in conditions of acute inflammation of the gallbladder. In addition, unlike the prototype, the claimed method of treatment includes the phased implementation of the following manipulations: preliminary sanation of the gallbladder; Perfusion with 4% sodium bicarbonate solution after contact chemical litholysis; Carrying out of a bubble-duodenal infusion.
Thus, the proposed solution meets the criterion of "novelty".
In the literature available to us, no information has been found on the use of methyl-tert-butyl ether for the treatment of acute cholecystitis and the use of sodium bicarbonate solution during chemical litholysis. In this connection, there is no data on the use of a vesicou duodenal infusion to "wash out" products of degradation of gallbladder stones and bile ducts into the duodenum to restore their patency and reduce the risk of recurrence of cholelithiasis.
Consequently, the proposed technical solution corresponds to the criterion of "inventive level".
This method can be used in patients with acute cholecystitis and with gallstones cholesterol stones, which corresponds to the criterion of "industrial applicability".
The essence of the proposed method is as follows.
With the confirmed diagnosis of acute calculous cholecystitis and the cholesterol nature of gallstones under the control of ultrasonography, a percutaneous transhepatic microcholecystostomy is applied. Through the microcholecystostomy, the gallbladder cavity is sanitized first with antiseptics, and then with a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate. Dissolution of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder is achieved by fractional injection of methyl-tert-butyl ether into the lumen of the gallbladder in a volume of 5 to 20 ml. Then, through a microcholecystostomy, perfusion of the gallbladder is performed with a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate, and when the permeability of the vesicle siphon is restored, a duodenal infusion of 500-1000 ml of normovolemic solution is performed. Products of degradation of gallstones, elements of inflammation are evacuated through microchildcystostomy and, in part, by antegrade infusion, are washed out into the lumen of the duodenum. The effectiveness of dissolution of gallstones and the restoration of patency of the bile ducts are controlled by conducting an X-ray examination with contrasting bile ducts through a microcholecyst. Absence of "filling defects" in cholecystography and free entry of contrast into the duodenum, restoration of the normal characteristics of the gallbladder with ultrasonography (USG) serve as an indication for the removal of microcholecystostomy.
The claimed method is illustrated by an example of a specific embodiment.
Example. Patient I., 63 years old, entered the clinic on 13.1.96 with a diagnosis of acute calculous obturation cholecystitis. The diagnosis is confirmed on the USG: the gallbladder is sharply enlarged in size (11 x 4 cm), the wall is uneven, thickened to 0.7 cm. The contents of the gallbladder are non-uniform; multiple reflective inclusions with an acoustic shadow of up to 3.2 cm 3 are determined in the lumen. Part of the stones is fixed in the neck of the gallbladder.
With computer tomography of the gallbladder, hyperdischarge inclusions are not found in its lumen.
On 15.1.96, under the control of ultrasonography, a percutaneous, transhepatic imposition of microcholecystostomy was performed. Evacuated 95 ml of turbid, viscous, dark infected bile. The cavity of the gallbladder was sanitized with 200 ml of a 0.02% solution of furacilin and then 200 ml of a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate, and then the contact chemical litholysis was started. In the gall bladder, methyl tert-butyl ether was added in portions of 10-20 ml for 2.5 hours.
After each dissolution session, the gallbladder cavity was washed from fragments of stones and inflammation products (cellular detritus, fibrin). On the 2nd day after the application of microcholecystostomy, the entry of pure hepatic bile by drainage from the gallbladder was noted. Since that time, a bubble-duodenal infusion of neutral saline solutions with a volume of up to 500 ml was carried out to restore permeability and mechanical purification of fluid from the vesicles and common bile ducts. After 5 sessions of litholysis (14 hours), the extraction of cholesterol with methyl-tert-butyl ether was stopped. With control cholecysto-cholangiography on the 4th day of defects of filling is not revealed, contrast freely enters the duodenum. 20.1.96 The catheter was removed.
With control ultrasound the next day, the size of the gall bladder is 6.7 x 2.6 cm, the wall is 0.3 cm, in the lumen - homogeneous contents without reflective inclusions.
During the sessions of litholysis and bladder-duodenal infusion, the patient did not present any complaints, the condition is satisfactory, the state of health is good. A day after the removal of microcholecystostomy, the patient was discharged from the clinic in a satisfactory condition without surgery.
The proposed method of treatment was used in 14 patients with acute calculous cholecystitis with cholesterol stones, 11 of them had a serious risk of performing a radical surgery, the remaining 3 refused surgical intervention.
The results are shown in the table.
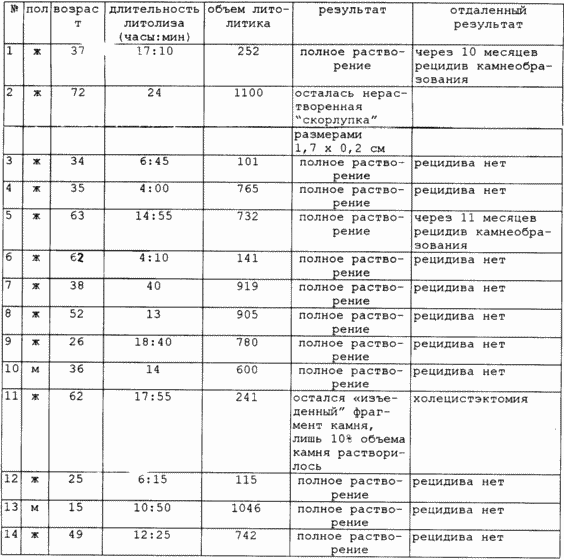
The use of the proposed method allows for 4-40 hours of litholysis to dissolve cholesterol stones in the gallbladder, normalize the choleretic and effectively affect the inflammatory process in the gall bladder without serious side effects, which makes it possible to widely introduce the method into clinical practice.
The proposed method of treatment of acute calculous cholecystitis in patients with cholesterol stones allows to eliminate stones as the cause of obturation of the vesicle siphon in conditions of acute inflammation of the gallbladder, to stop inflammation without resorting to surgical intervention, and restore the normal passage of bile through the bile ducts.
CLAIM
A method for the treatment of calculous cholecystitis, comprising percutaneous transhepatic intravesical fractional administration of methyl-tert-butyl ether, characterized in that the gallbladder cavity is sanitized with antiseptics, 4% sodium bicarbonate solution, then methyl tert-butyl ether is introduced, followed by The gallbladder is perfused with a 4% solution of sodium bicarbonate and when bubble siphon is repaired it is performed a vesicou-duodenal infusion of 500-1000 ml of normovolemic solution.
print version
Date of publication 28.01.2007gg




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.