| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Products Patents / In the section of the catalog / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2208786
![]()
METHOD determining spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity
Name of the inventor: Niche ES .; Galustyan A.
The name of the patentee: State educational institution of higher education St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical Academy
Address for correspondence: 194100, St. Petersburg, ul. Lithuanian, 2, St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical Academy, the patent office, O.V.Zheleznyakovoy
Starting date of the patent: 2001.12.28
The invention relates to medicine and can be used in immunology, virology, cancer, transplantation. The method is as follows: from the patient's peripheral blood mononuclear cells is isolated, the target cell is prepared, which is used as the rat mast cells, mononuclear cells were mixed and target cells at a ratio of 20-30: 1, the resulting mixture was centrifuged, incubated for 30 minutes, after it is carried out keeping cytotoxic response results by counting the number of degranulated mast cells of rats as a percentage of the total number of rat mast cells in a mixture of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats. If the value of this index is determined 25-35% normal spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity, a value of less than 25% determine the reduced spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity, and a value of said index of more than 35% determined by increased spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity. The method improves the accuracy of the forecast.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medicine, namely to immunology, virology, cancer, transplantation, and can be used to assess the immune status of patients and healthy individuals; to assess the level of antiviral and antitumor defense of the body; for predicting crises transplant rejection.
Known methods of determining the spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity (RCC) using as target cells for cytotoxic cells of mice artificially cultured tumor cells, particularly cells of P815 murine tumor, EL4, BW5147, radiolabeled. Known methods include analogs of the following operations: isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells; Preparation of target cells, including radioisotope labeling them; mixing of mononuclear cells and target cells, and records the results of cytotoxic reaction by the exit of the radionuclide used. The use of radioisotopes as 31 Cr, 3 [H] -proline, 125 [I] -dezoksiuridin, 3 [H], etc. -uridin [12].
Known methods do not provide counterparts to achieve a technical result of the claimed method in connection with the following. Tumor cell lines used for determining the SCC mice are usually not used for the determination of SCC in humans [2]. According to the inventors, this may be due to the absence of specific receptors on target cells specified, whereby the cytotoxic effect of human cells hardly manifested on the morphological and functional properties of the target cells.
Known methods for determining the SCC using as target cells for cytotoxic artificially cultured human tumor cell mouse lymphoma YAC-1 cells [3] and myeloid continuous cell line K-562 [4].
The closest to the claimed solution of the essential features is the method for determining the SCC using as target cells transplanted myeloid cell line K-562 [4]. The method adopted for the prototype was performed as follows. The patient blood was drawn from a vein in an amount of 6 ml vials with 5 ml 0.2% EDTA and were separated by density gradient Ficoll / verografin (d = 1,077). The resulting suspension of mononuclear cells (mononuclear cells) were washed once in 8 ml of phosphate buffer and twice - Hank's solution with 5% bovine serum. The final concentration of cells was adjusted to 5x10 6 / ml RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% bovine serum. Preparation of target cells was performed as follows. Cell line K-562 was grown in culture medium RPMI-1640, which is enriched "additives": 500 ml RPMI-1640 +20 mM glutamine + 20 mM Hepes (Serva) +100 Units / ml penicillin 10 U / mL streptomycin or gentamicin; a serum supplement used inactivated bovine serum. The sterile vials were placed 0.6 ml of the cell suspension transplantable (containing 3x10 5 cells), 0.6 ml of inactivated bovine serum and 1.8 ml RPMI-1640 medium; flasks were incubated for 4 days at 37 o C. At the 4th day of cultivation, when the cell density reached 5x10 5 in 1 ml cells inoculated in fresh medium. Cells of the 2nd or 3rd day of culture were pelleted by centrifugation at 150g for 5 min, resuspended in fresh RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% bovine serum. 1x10 6 cells were labeled with 250 micron Ku 51 Cr (Na 2 CrO 4) (92,5xl0 5 Bq) with a specific activity of 5.2 mCi / mM (7,4-18,5h10 7 Bq) in a volume of 0.5 ml; placed in an incubator and incubated for 1 hour at 37 o C. The cells were washed three times in Hanks medium with 5% bovine serum, centrifuging at 150g for 5 min; the final concentration of cells was adjusted to 1x10 5 in 1 ml RPMI-1640 medium with 10% bovine serum. Connecting the target cells, and mononuclear cells. In this case 0.1 ml of target cells (1x10 4 cells) were pipetted into the wells of a round bar "Cook" firm considering the required number of samples and scope of experience. Mononuclear cells with 0.1 ml (0,5h10 6 cells) were dug so that for each sample examined the blood accounted for a number of holes; both experienced and control samples were tested in triplet; to control samples instead of 0.1 ml of suspension of mononuclear cells was added 0.1 ml of culture medium, the ratio of target cells and mononuclear cells in experimental samples corresponded to 1: 50. In step pipetting 0.1 ml of target cell suspension was poured into centrifuge tubes and stored prior to end of the experiment; they were used to determine a maximum inclusion of 51 Cr (M). The panel was placed in an incubator (37 o C) with 5% CO feed 2 and a relative humidity of 100%, which was incubated for 16 hours. After incubation of the wells with 0.1 ml of the supernatant were taken, activity was measured with the experimental samples to control samples U -schetchike .
Consideration of the results of the reaction was carried out as follows. The cytotoxic activity of mononuclear cells (SCC), expressed in% based on the total inclusion of 51 Cr and its spontaneous release: ![]()
where A - twice the average output value of 51 Cr in the three test wells;
B - is the same, but in the control wells;
With - 80% of total 51 Cr in the inclusions 1x10 4 cells (M) -misheney.
Spontaneous 51 Cr yield (V) in such an experimental averaged 16% of the C (1% per hour).
If the value of this index is an average of (53,6 ± 3,7)% (the level of cytotoxic activity in healthy people), measured normal cytotoxic activity (SCC). For values of this index was significantly reduced compared with the norm, determined reduced cytotoxic activity (SCC). For values of this index was significantly higher than the average values of the cytotoxic activity in healthy people, determined the increased cytotoxic activity (SCC).
Prototype method [4] does not allow to obtain a technical result achieved when using the inventive process for the following reasons. It is known that cells of a living organism having RCC (called hereinafter "cytotoxic mononuclear cells" or "effector cell"), belong mainly to normal killers and have the ability to destroy foreign cells, cells affected by virus, but also tumor cells .
Currently, due to inability to assess cytotoxic reactions in vivo determination of SCC produced by setting laboratory reactions using target cells not normally contained in the body [2].
It is known that, as used in the prototype method [4] artificially cultured tumor cells of myeloid line have small pellets [5], which is output from the cells in the cytotoxic response is almost impossible to consider using microscopy. It is also known that due to the cytotoxic action of mononuclear processes that result in significant morphological changes in target cells, occur over a long period of time (incubation of 16 hours to 5 - 6 days) [2].
In addition, the target tumor cells, according to the authors of the claimed solution, no special highly sensitive receptors specific to perforin and cytokines produced by effector cells. In this regard, in consideration of morphological changes of tumor cells is only possible in principle by counting the dead mononuclear cells under the action of the target cells. However, the description of such a method for determining the SCC in a review of scientific and medical literature and patent, the inventors have found. This may be due to the fact that the practical implementation of such an approach using standard laboratory techniques and laboratory equipment is characterized by a relatively high subjectivity and relatively low accuracy determination (owing to the possibility of mass spontaneous killing of the target cells during long-term incubation) even when using the respective specific dyes for identification of dead target cells.
The basis of the prototype method [4] is put predominantly accounting functional changes of tumor target cells by the cytotoxic action of human cells. Evaluation of cytotoxic effect performed by labeling target cells with radioactive chromium-51. It is known [3, 2] that the cytotoxic effect is in direct contact only effector cells and target cells by effector cells, producing various cytokines, and consequent release of perforin with these mediators. In the prototype method is carried out after the contact of the spontaneous sedimentation of the cell mixture to the bottom of the test tube, which is terminated after 3-5 hours. After settling the mixture and the occurrence of contact between the target cells and cytotoxic cells and cell products begins the release of cytotoxic mediators and their impact, and on target cells, which takes 12-140 hours. Thus, the required incubation for at least 16 hours, which makes the procedure for determining the duration of symptoms of a cytotoxic effect on tumor cells. In addition, a prerequisite to ensure contact of effector cells and target cells respectively and expressed to obtain a cytotoxic effect on tumor cells according to the method-prototype is the relatively high ratio between the mononuclear cells and target cells (50: 1). The implementation in practice of this condition makes it necessary to work with a relatively large volume of blood, which in turn eliminates the possibility of obtaining blood from the patient for the study of the finger (using only the venous blood).
During incubation of mononuclear cells and tumor target cells by cytotoxic effect of changing permeability mononuclear cell membranes of the target cells, resulting in the release of 51 Cr target cells. However, even with the method provided by the prototype method and mixing conditions optimal incubation mixture in the absence of target tumor cells highly specific receptors to specific mediators of effector cells in some cases may lead to insufficient expression of functional target cells changes during cytotoxic response.
In particular, increased permeability of the cell membrane may be sufficient to release 51 Cr (according to the authors of the invention is a mixture of 40-80% of the target cells with intact membranes). In these cases, there will be a relatively low specific (i.e. due to the cytotoxic effect of mononuclear cells) in a yield of 51 Cr experiment that will produce a cytotoxic response lozhnozanizhennyh results. Furthermore, when using 51 Cr as an index of the cytotoxic effect of a number of reasons (quality target cell incubation media and quality cookware, insufficient qualified nurses, etc.) may experience increased spontaneous (non-specific) yield of the radionuclide in the control (16-50%). This makes it difficult to take account of the cytotoxic response, causing lozhnozanizhennye results of determination, and in some cases (for spontaneous release 51 Cr in the control of more than 20%) makes the accounting results of the reaction is practically impossible.
The relatively low strength characteristics of target tumor cell membranes results in a relatively high probability of damage to these cells by pipetting, centrifugation (at the stage of preparation of the target cells), making the solutions in a mixture of mononuclear cells and the target cells and the like. D. This is reflected in a relatively high spontaneous (non-specific) output of 51 Cr in the experiment, which, according to the inventors, can in some cases reach 30-40%, which leads to the determination lozhnozavyshennym results. All this leads to a relatively low accuracy of the SCC via the prototype method. Finally, the method provided by the prototype method [4] 51 Cr application involves working with the material, said radionuclide labeled, that requires a specially equipped laboratory and trained personnel.
The object of the invention is to provide a method for determining the RCC providing the opportunity supravital, early and severity of morphological manifestations of the cytotoxic effect of the exclusion of the possibility of spontaneous target cell lysis, mechanical damage to their membranes and spontaneous release of a radioactive isotope of the target cells, by the use of cells with specific, Sensitive receptors specific mediators produced by human cytotoxic cells, large cytoplasmic granules capable of exocytosis, and relatively high mechanical strength of the membranes.
The problem is solved by a method for determining the SCC, which includes isolation of mononuclear cells from the patient's peripheral blood, preparation of target cells, mixing of mononuclear cells and target cells, the incubation of mononuclear mixture and target cells followed by light of the cytotoxic response, according to the invention as a cell -misheney used mast cells of rats. Mix mast cells and mononuclear cells of rats in a ratio of 20-30: 1. Directly after mixing mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats resulting mixture was further centrifuged. The incubation mixture of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats produced within 30 minutes. To take account of the cytotoxic reaction is carried out by counting the number of degranulated mast cells of rats as a percentage of the total number of rat mast cells and mononuclear cells in a mixture of mast cells and rat at a value of said index of less than 25%, determined by SCC decreased, a value of said index 25-35% determine the normal SCC, and a value of said index of more than 35% determine the increased SCC. The most effective when the accounting results in a cytotoxic reaction immediately before counting the number of degranulated mast cells of rats in a mixture of mononuclear cells and rat mast cell pellet manufacture and stirring the mixture of the supernatant of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats.
Selecting the optimum mode and conditions of implementation of the claimed method, ensuring the greatest effectiveness of the invention in its implementation, carried out as follows.
To establish diagnostically significant range of cytotoxic activity of human blood cells in normal and pathological comparative studies of SCC in these patients have been carried out:
- In healthy children;
- Defects in children with antiviral immunity, which is known [3, 6, 7], is evidence of reduced normal functions of killers - the main cells responsible for SCC;
- In children with severe reaction "graft versus host" clinically manifested rejection of the transplanted tissue that are known [1, 6, 3], due to a significant increase in the activity of cytotoxic cells.
The distribution of patients by groups was as follows:
Group I - practically healthy children aged from 3 to 16 years - 26 people;
Group II - children (aged 3 to 16 years) with frequent acute respiratory viral diseases / SARS / (more than 8 times a year), confirmed by a virological survey methods (immunofluorescence staining smears - imprints from the mucosa of the nose and throat, the study paired sera for antibodies to the respiratory viruses) - 31 people .;
Group III - burn patients (aged 3 to 16 years) with a crisis of rejection of the transplanted skin flap - 6 people.
SCC in each of these groups were determined using the method claimed and the prototype method [4]. In the course of determining the SCC and the claimed method and the prototype method to ensure the adequacy of the conditions of the experiments blood of each patient was examined in three parallel experiments with three parallel controls (3 experimental and 3 control samples). In determining the RCCs as described in the method of the prototype activity test and control samples were measured on a radioactivity counter "Ultra-Gamma 1280" (produced by LKB, Sweden).
Statistical processing of the results produced by calculating sigmalnogo deviation (s), but also by precise calculation of shares of the significance of differences by the method j (corner of Fisher transformation) [8].
Comparative studies SCC Group I - III are shown in Table 1.
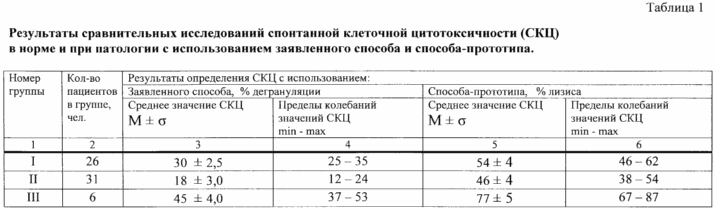
The data in Table 1 shows that in healthy patients (Group I) the number of degranulated mast cells of rats in the mixture of the total number of mononuclear cells and the target cells of rat mast cells (% degranulation), averaging (30 ± 2,5)% by varying values specified index in the range of 25-35%. This interval has been adopted as a range of values that characterize the normal RCC. In group II patients (with a confirmed reduction function of cytotoxic cells) degranulation% averaged (18 ± 3.0) with swing values specified index in the range of 12-24% (p <0.001 compared with those obtained in group I). In this regard, it was decided that the indicator is reduced SCC% degranulation of less than 25%. In Group III patients (confirmed with an increased activity of cytotoxic cells) based on the obtained average value degranulation%, equal to (45 ± 4.0)%, and the limits of its deviation 37-53% (p <0.001 compared to those obtained in group I), it was decided that the increased SCC can be diagnosed at a value of said index greater than 35%.
Table 1 and show that the SCC in the determination by the procedure prototype method [4] The inventors SCC values were obtained that are comparable with the data presented by the authors prototype method in the cited paper. For example, an author of the invention as described in the average level of the prototype method SCC in healthy patients was (54 ± 4)%; according to the prototype method the authors of the same period was (53,6 ± 3,7)%. Correlation SCC values determined by the procedure prototype method [4], the present inventors and creators prototype method, was observed for patients with higher and lower SCC, particularly for patients with a crisis of transplant rejection (see. Graph 6 in Table 1 of the specification, and table 65 on pp. 162 describing prototype method [4]).
To determine the optimum ratio of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats in the mixture we investigated the effect of different ratios on the accuracy of the SCC. For the study were pre-selected 10 healthy children (aged 3 to 16 years), in which the SCC values were in the range 28-32%. Each of the patients was determined by SCC at ratios of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats in the mixture components: 5: 1, 10: 1, 15: 1, 20: 1, 25: 1, 30: 1, 35: 1, 40: 1, 45: 1, 50: 1. Thus each of the patients blood with each test and the claimed ratio mononuclear target cells was tested in triplicate with three parallel controls (3 experimental and 3 control samples). Each of the tested relations with other fixed-optimal conditions and terms of implementation of the claimed method.
Statistical processing of the results was performed similarly to the processing of the results of experiments to establish the ranges of SCC diagnostically significant in normal and pathological conditions.
The results are shown in Table 2.
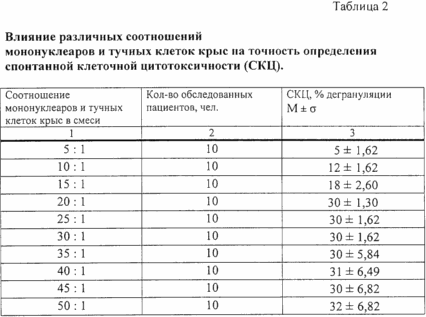
From Table 2 it follows that the optimum ratio of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats in the mixture is 20-30: 1, as It provides this ratio is highest percentage specifically damaged target cells sensitive to the cytotoxic action of mononuclear cells, with minimal scatter of the results of experiments in parallel. At lower proportions between the declared and mononuclear cells to target cells (5-15: 1) there is a lower percentage of degranulated target cells (5-18%), suggesting that not all of the target cells sensitive to the cytotoxic cells were subjected to cytolysis. At higher (compared with the optimum) and mononuclear ratio of the target cells (30-50: 1), despite the fact that all target cells that are sensitive to the cytotoxic action of mononuclear cells, subjected to cytolysis (30-32%), there is a relatively large scatter of results in parallel experiments. The latter, apparently, can be attributed to the entry into force of mechanical or other factors preventing contact cytotoxic cells and target cells, or cytotoxic mediators that adversely affects the reproducibility of reactions and thus reduces the accuracy of the SCC.
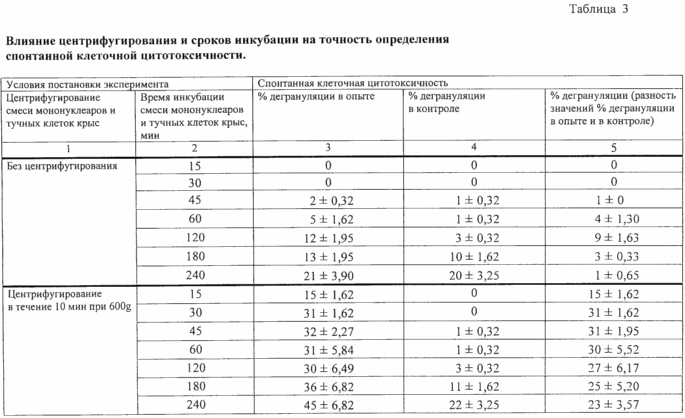
To establish the relevance centrifugation step combined action of the claimed method and the optimal time of incubation and investigated the influence of the presence or absence of a centrifugation step in combination with various incubation periods at the accuracy of the SCC. For the experiments was chosen as the standard mode centrifugation (for 10 minutes at 600g), recommended against the peripheral blood mononuclear cells [7]. For the study were pre-selected 10 healthy children (aged 3 to 16 years), in which the SCC values were in the range 28-32%. Each of the patients was determined by the SCC in the presence and in the absence of centrifugation step in the claimed method, the sequence of actions, and the incubation periods in each case ranged from 15 to 240 minutes at other fixed optimum conditions and conditions of implementation of the claimed method. Each patient's blood in each experimental formulation variants examined in three parallel tests with three parallel controls (3 experimental and 3 control samples).
Statistical processing of the results was performed similarly to the processing of the results of experiments to establish the ranges of SCC diagnostically significant in normal and pathological conditions.
The results are shown in Table 3.
Previously, the inventors suitability test was conducted in accordance with the received recommendations of [7] for the purpose of centrifugation regime claimed process. Thus as a result of experiments, it was found that, on the one hand, by centrifuging the mixture of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats in the above mode settle to the bottom 100% mononuclear tubes and 100% of the target cells, which was confirmed by the absence of said cells in the supernatant (supernatant) after centrifugation. On the other hand, during centrifugation in the specified mode is virtually no mechanical damage of target cells, in particular their membranes. It was confirmed that, firstly, the number of entries to the target cell and remains constant after centrifugation; Second, the control samples (without mononuclear cells) rat mast cell degranulation by centrifugation (at optimal incubation period) is practically not observed (the number of degranulated cells after centrifugation of the control was 0%). In this regard, said the regime was adopted as a working (hereinafter - the "working centrifugation mode").
The data in Table 3 show that in the absence of centrifugation step in the claimed method, the sequence of actions with a short term incubation (15-60 min), a cytotoxic effect on target cells claimed almost appears that excludes the possibility of determining the SCC. With increasing incubation periods over 60 min cytotoxic effect increases, but the percentage of damaged specific target cells sensitive to the cytotoxic action of mononuclear cells, is relatively low (12-21%), which prevents the accurate estimation SCC. Additionally, when timing over 60 min incubation process increases spontaneous degranulation of mast cells of rats (number of degranulated cells in 3-20% of control in function of the incubation time). Thus, these experimental results indicate that in the absence of centrifugation step results accounting cytotoxic response is virtually impossible.
From Table 3 it can be seen and that the centrifugation operation the mixture of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats in the combination, followed by incubation mixture maximum specific damage to the stated target cells sensitive to the cytotoxic cells is obtained, starting with 30 minutes incubation time. Given that this minimum variation observed in parallel experiments results indicated incubation period adopted as the optimum. By increasing the period of incubation mixture (45-120 min) Number of degranulated target cells remains essentially constant, however, results in increased scatter parallel experiments. The latter is due to begin the process of spontaneous degranulation of mast cells in rats (as an initial manifestation of non-specific lysis of the cells), as evidenced by increase of degranulation% in controls (1-3%). This reduces the reproducibility of cytotoxic reactions and accordingly accuracy of the SCC.
With further increase of the period of incubation mixture (over 120 minutes) there is a significant increase in the number of degranulated mast cells of rats in the control (11-22%), which indicates the growing non-specific cell lysis processes. This results in a significant underestimation of the results of cytotoxic responses, which consequently precludes determination of SCC. Thus, the analysis of the experimental results shown in Table 3, suggests that the mixture of mononuclear cells by centrifugation and rat mast cells is an essential feature of the claimed method, as said step (a method for its availability sequence) directly affect the achievement of the claimed effect. This mixture is a combination of centrifugation followed its incubation allows the selection of the optimal incubation time (30 min), allowing to obtain the highest accuracy of the SCC.
For comparison, the inventors have performed experiments to evaluate the possibility of introducing a centrifugation step set of actions prototype method [4]. At the same time I checked the suitability of two standard centrifugation regimes:
- Mode recommended against tumor cells of myeloid line according to the procedure prototype method [4] (for 5 min at 150g) - 1 mode;
- Mode recommended against the peripheral blood mononuclear cells [7] (for 10 min at 600g) - 2 mode (working mode centrifugation in the inventive process).
It has been found that centrifugation in mode 1 leads to insufficient settling of mononuclear cells - in the supernatant of mononuclear cells was 15-30%, which led to the final violation ratio mononuclear cells and target cells in the prototype method the mixture which in turn reduced the accuracy of the SCC. Furthermore, spontaneous 51 Cr yield increased in the control to 25-30%, indicating a significant part mechanical damage of target cells (in particular, their membranes) during centrifugation. These negative factors combine to exclude the possibility of determining the SCC. Centrifugation in the mode 2 it virtually impossible to account the results of the cytotoxic response of the high (50-60%) of the spontaneous 51 Cr release in the control, indicating that the vast majority of mechanical damage to the target cell (in particular, their membranes) during centrifugation. Thus, administration centrifugation (as in mode 1 and mode 2) to the prototype sequence process action resulted in impossibility determining SCC as described in the prototype method.
Achieving technical effect provided by the invention due to the following. It is known that under the influence of the allergens occurs degranulation serum pre-sensitized rat mast cell patient. Morphologically, it is shown exiting the cell cytoplasmic granules which are large enough to take into account the degranulation process under the microscope. This sensitization of mast cells of rat blood serum of the patient in the course of determining the cause significant allergen is a necessary step for degranulation reaction [9]. The latter is due to the fact that the initially on the surface of mast cells in rats lacking allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) person responsible for the establishment and functioning of the receptor complex necessary for the response to the allergen.
The authors declared no solution found sources of information, which would be described changing of mast cells in rats during cytotoxic reactions. The inventors have experimentally found that the implementation of the declared set of actions under optimal conditions and modes of their implementation under the influence of cytotoxic mononuclear cells of rats happens degranulation of mast cells without prior sensitization of the last patient's blood serum, which is a manifestation antitelonezavisimoy cellular cytotoxicity. According to the authors of the proposed method, this may be due to the fact that obese rats cells initially have specific receptors to specific highly sensitive perforin and cytokines produced by cytotoxic human mononuclear cells. It is also possible that the cytotoxic mononuclear cells producing specific cytokines are capable of directionally affect the receptors and / or mast cell membranes of rats. Therefore, for the establishment and functioning of the receptor complex, sensitive to the cytotoxic effects of effector cells, it does not require prior sensitization declared target cells the patient's blood serum.
The results of experimental studies by the inventors have shown that rat mast cell degranulation in cytotoxic reactions manifested morphologically exocytosis - exit to the surface of said transparent cell granules sufficiently large, clearly distinguishable under the microscope. It was found that the co-incubation of the target cells within the stated time period effector cells and declared (30 minutes) does not result in the death of the target cells. All this enables keeping supravital morphological changes rat mast cell - by the action of cytotoxic degranulation of human cells. The ability to evaluate the results of cytotoxic reactions on the morphological changes of the target cells, in turn, eliminates the need for labeling the latter radioactive isotope. This, on the one hand, avoids the need to take into account the ability of the target cells for spontaneous release in the absence of the radionuclide even effector cells and thereby enables optimal control of the reaction and thereby increases the accuracy of the SCC. On the other hand, eliminating the need to carry out the analysis in a specially equipped for operation with radioactive isotopes laboratory and with the participation of specially trained personnel.
The presence of the stated target cell specific receptors highly specific to the action of effector cells allows early manifestation pronounced cytotoxic effect even at the minimum level of perforin and cytokines produced by mononuclear cells. This allows a significant cytotoxic effect and thus to achieve relatively high accuracy in determining when a relatively low ratio of effector cells and target cells declared (20-30: 1). As a result, it becomes possible qualitative analysis using relatively small amounts of blood, which gives the possibility of obtaining the blood for the study not only of a vein, but also from the patient's finger.
Introduction to the cumulative action of the claimed method additional (by comparison with the prototype) step - centrifuging the mixture of mononuclear cells and the target cells - enables rapid deposition of cells contributing to the achievement of an earlier and more intimate contact between
effector cells and target cells, respectively, and the earlier the production and release of mediators of cytotoxic effector cells and their effect on target cells.
In this experiment, the inventors found that the mechanical damage of rat mast cell membranes by centrifugation operation is insufficient for spontaneous degranulation of these cells, which was confirmed virtually complete absence (0%) degranulated cells in the control (incubation at optimum mode). On the contrary, when the centrifugation used in the method-prototype tumor cells of myeloid line of mechanical damage significant portion of these cells (in particular their membranes) were observed even when using the (5 minutes at 150g), recommended for these cells to the procedure prototype method [4] (spontaneous yield 51 Cr in the control to 25-30%). Mode during centrifugation (10 min at 600g), recommended for peripheral blood mononuclear cells [7] (working mode of the claimed method), mechanical damage of the target cells become even more significant (spontaneous 51 Cr yield 50-60% in the control). Thus, the results of comparative experimental study of the inventors (cited above) showed that when using the claimed target cells (as opposed to the target cells prototype method) centrifuging has no significant negative impact on the accuracy of the SCC due to the relatively high mechanical strength rat mast cell membranes.
Using as target cells rat mast cell having a particular specific receptor apparatus and strength characteristics of membranes that allow artificially accelerate deposition of cells in combination with the inclusion of centrifugation (as further compared with the prototype stage) in the set of actions of the claimed method makes possible obtain expressed cytotoxic effect in relatively short time of incubation (30 min). Stated incubation periods, in turn, eliminates the possibility of non-specific lysis of mast cells in rats, whose initial manifestation in the form of spontaneous degranulation of the cells marked with the timing of incubation of 45-60 minutes and reach significant values after 2-3 hours of incubation. This makes a significant contribution to improving the accuracy of determining the SCC.
Stirring cell pellet and a supernatant mixture of mast cells and mononuclear cells of rats carried out immediately before counting the number of degranulated target cells allows destroy conglomerates formed during centrifugation of a cell mixture to facilitate the reaction morphological evaluation results - count of degranulated mast cells of rats under the microscope. This contributes to further increase the accuracy of determining the SCC.
Thus, morphological and functional features of the claimed target cells (presence of a particular specific receptor unit specific characteristics cytoplasmic granules, the strength characteristics of the membranes), the presence of additional steps (centrifugation) and declared and (optimal) modes and conditions for carrying out the method actions (mix mononuclear and target cell incubation) together account supravital allow morphological changes of the target cells (their degranulation), specifically due to the influence of human cytotoxic cells.
As a result, the claimed combination of features in their relationship achieves supravital early and severity of morphological manifestations of the cytotoxic effect of the exclusion of endogenous and exogenous significant negative factors that directly affect the accounting cytotoxic response results (spontaneous lysis of target cells, mechanical damage to their membranes, spontaneous release of the radioactive isotope of target cells). This in turn improves the accuracy of the SCC, to reduce the time of analysis, eliminating the need to work with a radioactive isotope. In this prior art is not detected, according to the applicant's invention, the influence of prescribed transformation, characterized by distinctive essential features of the prototype, the achievement of the technical result.
The process is as follows. The patient or the finger from the vein, blood is taken in an amount of 0.5 ml into the test tube, soaked heparin. From taken peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated by standard methods, such as described in [7]. When this blood is diluted twice with a solution of 0.9% NaCl, the mixture was layered over Ficoll-Pack 1,077 g / cm 3 and centrifuged for 30 min at 400g. Formed in interphase "ring" of mononuclear cells is removed with a pipette, the resulting cell suspension was washed three times with 0.9% NaCl and adjusted to a concentration of 2x10 6 cells / mL. Mast cells are prepared by the procedure rats LM Ishimova and LI Zelichenko [9]. When this white male rats weighing 140 g are sacrificed under ether anesthesia and injected into its peritoneal cavity is heated to a temperature of 37 o C Hemotsell medium in an amount of 5.3 ml. Produce rat abdominal massage for 2-3 minutes, after which the abdominal cavity is opened and the liquid layers from rat mast cells are collected into a vessel preheated to a temperature of 37 o C. The cells were washed three times with medium 199 and the cell concentration adjusted to 1x10 5 cells / ml . Thereafter pilot centrifuge tube making slurry mononuclear 25-38 .mu.l and 25 .mu.l suspension of rat mast cells (ratio of mononuclear cells and target cells in experimental samples corresponds to 20-30: 1). The control is made centrifuge tube 25 .mu.l suspension of rat mast cells and 25-38 ul of medium 199. experimental and control tubes were centrifuged for 10 min at 600g, then placed in an incubator and incubated for 30 minutes at 37 o C.
After incubation, the contents in the test and control tubes were shaken to agitate the cell pellet and the supernatant (supernatant). The cell suspensions of the test and control tubes are transferred to glass slides (from each tube - to a separate glass), previously coated with an alcoholic solution of neutral red. Drops of cell suspensions of the test and control samples, placed on glass slides, cover the top cover glasses, which are lubricated with petroleum jelly the edge (to prevent liquid evaporation). Calculate, for example under the microscope at 15h25, the number of degranulated mast cells of rats as a percentage of the total number of rat mast cells in the experimental sample and a control sample (hereinafter - respectively '% degranulation in the experiment "and"% degranulation in control "). SCC is defined as the difference in the experience of degranulation% and degranulation% in the control (hereinafter - "% degranulation"). If the value of% degranulation of less than 25, a reduced SCC determined, a value of said index 25-35% the normal SCC determined, and a value of said index of more than 35% determine the increased SCC.
The invention is illustrated by the following examples.
Example 1.
Alesha K., age 7. It was examined in the framework of a screening program to identify predisposition to common respiratory diseases in children's clinic at Children's City Hospital 1 St. Petersburg (DGB 1). In the history of the patient noted a rare SARS (1-2 times per year). At the dispensary examination of pathology of the internal organs are not revealed.
The patient was identified SCC using the claimed method. In determining the child's finger from blood taken at 0.5 ml per vial, moistened with heparin. From taken peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated by standard methods [7]. Thus the blood was diluted twice with a solution of 0.9% NaCl, the mixture was layered over Ficoll-Pack 1,077 g / cm 3 and centrifuged for 30 min at 400g. Formed in interphase "ring" mononuclear removed by pipette, the resulting cell suspension was washed three times with 0.9% NaCl solution and the concentration was adjusted to 2x10 6 cells / ml. Prepared by Procedure rat L.M.Ishimovoy LI and mast cells Zelichenko [9]. When this white male rat weighing 140 g anesthetized under ether anesthesia and was injected into its peritoneal cavity is heated to a temperature of 37 o C Hemotsell medium in an amount of 3.5 ml.
Produced rat abdominal massage for 2-3 minutes, after which the peritoneal cavity was opened and a liquid layer by layer from rat mast cells were collected in a vessel, heated to a temperature of 37 o C. The cells were washed three times with medium 199 and the cell concentration was adjusted to 1x10 5 cells / ml . the patient's blood was tested in triplicate experiments with three parallel controls (3 experimental and 3 control tubes.). In each experimental centrifuge tube was added 25 .mu.l of suspension of mononuclear cells and 25 .mu.l suspension of rat mast cells (ratio of mononuclear cells and mast cells in rat experimental samples corresponded to 20: 1). In each control centrifuge tube was added 25 .mu.l of rat mast cell suspension and 25 ul of medium 199. The test and control tubes were centrifuged for 10 min at 600g, then placed in an incubator and incubated for 30 minutes at 37 o C.
After incubation, the contents in the test and control tubes were shaken to agitate the cell pellet and the supernatant. The cell suspensions of test and control tubes transferred to glass slides (from each tube - to a separate glass), previously coated with an alcoholic solution of neutral red. Drops of cell suspensions of the test and control samples, placed on glass slides, closed the top cover glasses, the edges of which have been greased with Vaseline. With the aid of a microscope "BIMAM P-11" (produced by "LOMO", St. Petersburg) was calculated (increasing 15h25) in each of the experimental and control samples 100 rat mast cells; one of them pointed degranulated fat rat cells; the number of degranulated mast cells of the rats was expressed as 100% of the calculated rat mast cells (% respectively in the experiment and degranulation degranulation% in control) (see. Table. A).
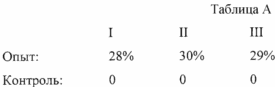
SCC determined as the difference in the experience of degranulation% and in the control of degranulation% in each of the pairs (% degranulation I,% degranulation II,% degranulation III):
Degranulation% I = 28%
% degranulation II = 30%
% degranulation III = 29%
We calculate the average (of 3 samples) SCC value (% degranulation Wed):
Degranulation% Wed. = 29%
The obtained value of the SCC (29%) falls within the range of normal values of the SCC, SCC made it possible to regard this as a normal patient. Taking the time to determine the procedure for 2 hours and 5 minutes (2.08 hours) (according to the timing of the inventors).
Parallel determination of SCC was performed using the prototype method as described in [4]. In this patient's blood was tested in triplicate experiments with three parallel controls (3 experimental and 3 control samples). The activity of the experimental and control samples were measured on a radioactivity counter "Ultra-Gamma 1280" (produced by LKB, Sweden). The average (of 3 samples) SCC value (% lysis), defined by the formula given in the procedure [4], was 55.2%, which corresponded to the level of the norm prototype method. The duration of the procedure was the definition of 89 hours and 10 minutes (89.2 hours) (according to the timing of the inventors).
Thus, the value of the SCC as prepared using the claimed method and the prototype method, fell to the corresponding intervals of values that characterize the normal RCC. This is confirmed by the results of a clinical examination of the child, but also observations of them in the dynamics within 2 years (2 year old baby 1 time ill rhinovirus infection), which indicated an absence of immunity defects in the child. Other diseases of the surveyed child is not revealed. In this case, there has been agreement between the results determining the SCC using the claimed method and the prototype method, with the results determining the SCC correlated with clinical data.
Example 2.
Natalia K., 16 years old. Addressed to the children's clinic at Children's hospital No.1 with complaints of frequent colds (SARS 1-2 times a month), which were observed during the last 6 years. Diseases in some cases (for hospitalization of patients in hospitals for severe acute respiratory viral infections, bronchitis) confirmed virological research methods (Immunofluorescence study of smears from the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, the study of paired sera for antibodies to the respiratory viruses). In the study of the immune status of the patient number of T and B lymphocytes, the level of immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, IgG) corresponded to the normal age indicators.
The patient held SCC determination using the inventive method and the prototype method described in Example 1.
In determining the SCC using the inventive process in each experimental centrifuge tube was added 31 .mu.l of suspension of mononuclear cells and 25 .mu.l suspension of rat mast cells (ratio of mononuclear cells and mast cells in rat experimental samples corresponded to 25: 1). In each control centrifuge tube was added 25 .mu.l and 31 .mu.l rat mast cell suspension medium 199. The determination results are shown in Table. B.

Degranulation% I = 12%
% Degranulation II = 13%
% Degranulation III = 12%
% Degranulation Wed = 12.3%
The resulting average value of the SCC (12.3%) made it possible to conclude that the reduced (compared to the norm) SCC at the surveyed patients. On determination procedure took 2 hours and 30 minutes (2.5 hours).
The results of the RCC using the prototype method: the average (of 3 samples) SCC value (% lysis) was 58.1%, which is indicative of a finding in a patient with SCC in the normal range. determination procedure took 88 hours 15 minutes (88.3 hours).
When monitoring a patient in dynamics for 14 months, despite treatment (IRS-19, ribomunil), the frequency of SARS remained relatively high (1 every 1-2 months), although it declined in comparison with the frequency of SARS observed before treatment .
Thus, the results of clinical examination of the patient and observing the dynamics leads to the conclusion that in this case there is a reduced antiviral resistance, which is caused by the activity of cells possessing the SCC. This confirmed the results of determination obtained by the claimed method, and provided an opportunity to interpret the results of determination by the method of the SCC-like prototype lozhnozavyshennye.
Example 3.
Sasha K., 3 years. He entered in the burn unit DGB 1 with a diagnosis of thermal burns thighs, drumsticks, S = 25%, IIA-III degree.
The patient was transplanted skin of a human embryo. Starting from 2 days after the skin graft operation, carried out daily monitoring transplant rejection using the claimed method and the prototype method described in Example 1.
In determining the SCC using the inventive process in each experimental centrifuge tube was added 38 .mu.l of suspension of mononuclear cells and 25 .mu.l suspension of rat mast cells (ratio of mononuclear cells and mast cells in rat experimental samples corresponded to 30: 1). In each control centrifuge tube was added 25 .mu.l suspension of rat mast cells and 38 .mu.l of 199 medium.
Determination results are shown in Table. AT.
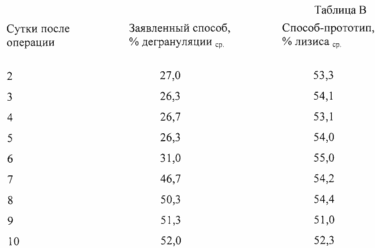
Taking the time to determine the procedure for using the claimed method and the prototype method, it amounted to, respectively, 2 hours 10 minutes (2.2 hours) and 89 hours 30 minutes (89.5 hours).
On the 10th day after the operation was registered clinically crisis of transplant rejection - transplanted embryonic skin. Thus, the claimed method will predict the probability of a crisis, because starting from the 7th day after the operation there was an increase SCC values compared with normal SCC. HPCC, determined by the prototype method, during the entire period of observation fluctuated slightly, without going beyond the range of normal SCC values, allowing to regard the results as a cytotoxic response lozhnozanizhennye. Predict the probability of a crisis of transplant rejection by the method of the prototype was not possible.
With the claimed method was examined in vitro 286 children aged 3 to 16 years. At the same time in the survey 274 children claimed method was used in the framework of a screening program to identify immunological predisposition to frequent respiratory infections (group A). In addition, the claimed method was used to survey 12 burn patients (group B) for the purpose of monitoring the reaction of graft rejection (transplanted skin graft). Investigations were carried out on the basis of the Children's City Hospital 1 St. Petersburg (Children's Clinic at Children's hospital No.1, burns unit 36 DGB 1), and on the basis of children's polyclinic 60 (St. Petersburg) and the regional children's clinic. The criteria for determining the effectiveness of the SCC using the claimed method served as the accuracy of determination (number of confirmed results of the definition), and the definition of procedures and duration (as a result of timing of the inventors). To confirm the presence or absence of abnormality SCC values conducted medical history, assessment of clinical disease, clinical and instrumental and clinical and laboratory monitoring of patients in the dynamics.
Those children were examined in parallel using the prototype method [4]. Efficiency determination of SCC was assessed using the same criteria as in the case of the claimed method.
Statistical analysis was performed by calculating the exact significance of differences share the method j (corner of Fisher transformation) [8].
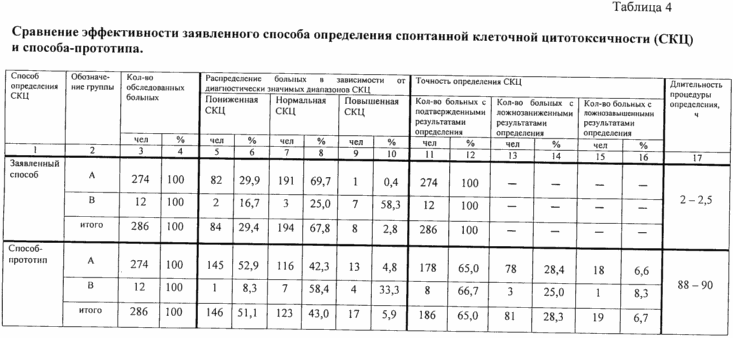
The data in Table 4 that the inventive method is provided to obtain a clinically proven results determining SCC in 100% of cases and in the absence of lozhnozanizhennyh lozhnozavyshennyh determination results. In the group A reduced SCC was registered in 82 children (29,9%). All of these children, or (usually) have a history of frequent (8-10 times a year), acute respiratory infections / ARI / (SARS, bronchitis, pneumonia), confirmed by clinical, clinical and instrumental, clinical and virological laboratory methods of examination, or when viewed in the dynamics of a sharp increase in the incidence of ARI (up to 8-10 times per year) compared to the period preceding the immunological examination. Normal SCC registered in group A at 191 child (69.7%), and was confirmed by the results of clinical examination and observation in dynamics (frequency of ARI 1-2 times a year; the absence of other diseases). The increased value of the SCC obtained in group A in 1 patient was not seen as lozhnozavyshennoe, t. To. At this patient worm infestation (ascariasis) was detected on clinical examination. It is assumed that the cells involved in SCC, and may participate in the protection from helminth, which leads to increased activity of cytotoxic cells.
In group B increased SCC was found in 7 patients (58.3%) for 7-8 days after transplantation. All of these patients (100% of the time) on day 10-14 after transplantation was clinically member crisis transplanted skin graft rejection. In 3 patients with a transplanted skin graft was observed normal SCC; in 2 patients of group B - reduced SCC. None of these patients when observing the dynamics have been recorded transplant rejection crises. At the same time in both patients with reduced SCC history, frequent acute respiratory viral infection (8 and 9 times per year), confirmed by clinical, clinical and instrumental, clinical and virological laboratory methods of examination.
From Table 4 it is clear and that obtained using the prototype method of determining the SCC were clinically confirmed in only 65.0% of the cases; in 28.3% of cases received by the SCC values were regarded as lozhnozanizhennye, and in 6.7% of cases - as a result lozhnozavyshennye definition (p <0.001 compared with corresponding values of parameters of the claimed method). In the group A reduced SCC, noted in 145 patients (52.9%) was confirmed clinically (similar to the claimed method) in only 68 patients (24.8%) (the frequency of ARI 8-10 times per year). Registered in 77 children (28.1%) decreased performance SCC were regarded as lozhnozanizhennye, that they were not confirmed by any medical history or under the supervision of the dynamics (frequency of ARI 1-2 times per year.. The absence of other diseases, such as tumors , leukemia, etc., which could determine the low SCC values).
Normal values SCC identified in 116 children (42.3%) were confirmed clinically (similar to the claimed method) only 110 children (40.1%). In 5 children (1.8%) out of 116 of these results were considered to determine the lozhnozavyshennye because have a history of frequent acute respiratory infections (8-10 times per year) and one child (0.4%) registered a normal SCC has been hailed as lozhnozanizhennaya due to the presence of helminthic invasion, which can, as mentioned above, to determine the increased activity of cytotoxic cells. In 13 children (4.8%) increased SCC was awarded, which has been hailed as lozhnozavyshennaya because 4 children (1.5%) were almost healthy, and 9 children (3.3%) had a history of frequent respiratory infections (ARI frequency of more than 8 times per year).
In group B increased SCC was determined using the prototype method only 4 of 7 patients with a clinical graft rejection crisis was recorded. In 3 patients with a crisis of rejection of the transplanted skin flap normal values were obtained SCC, regarded as lozhnozanizhennye. Of the 5 patients with transplanted skin graft without rejection last one patient observed declines in the SCC, which were correlated with clinical data (frequency of SARS - 9 diseases for the preceding burns a year) and in 4 patients received values SCC were within normal limits . At the same time in 3 patients (out of these 4 patients) had normal values of the SCC confirmed clinically, and one baby results were regarded as lozhnozavyshennye (in history - the frequency of SARS 8 times a year).
The data in Table 4 and show that the duration of the procedure for determining the SCC using the inventive process was 2-2.5 hours, whereas when using the prototype method similar figure was 88-90 hours.
Thus, the inventive method in its implementation provides increased accuracy in determining the SCC compared to the prototype method: the number of determination results correlate with those of clinical examination, increases by 35%, in the absence lozhnozanizhennyh and lozhnozavyshennyh determination results (in contrast to the prototype method, where lozhnozanizhennye lozhnozavyshennye and results are, respectively, 28.3 and 6.7%). The duration determination procedure using the claimed method is reduced by 35-45 times (in comparison with the prototype method). In addition, with the exception of course of action analysis associated with labeling materials with a radioisotope, it eliminates the need for a specially equipped laboratory and trained personnel that simplifies the way.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. Lymphocytes: The methods. Trans. from English. / Ed. J.. Claus. - M .: Mir, 1990. - S. 223-226,269.
2. Immunological methods. / Under. Ed. Frimelya G., ed. with it. AP Tarasova. - M .: Medicine, 1987. - P. 282-293.
3. Yarilin AA Fundamentals of Immunology: A Textbook. - M .: Medicine, 1999. - S. 51-54, 421-432.
4. Zaretsky YM Clinical immunogenetics. - M .: Medicine, 1983. - S. 159-162 (prototype).
5. Handbook of functional diagnostics in pediatrics. / Ed. YE Veltischeva, NS Kislyak. - M .: Medicine, 1979. - P. 455-462.
6. IS Freidlin The immune system and its defects: a guide for physicians. - St. Petersburg, 1998. - pp. 25-27.
7. Ketlinsky SA, Kalinina NM Immunology for the doctor. - SPb .: Publishing LLP "Hippocrates", 1998. - S. 9, 113-115.
8. Gubler EV Computational methods of analysis and detection of pathological processes. - L .: Medicine, 1978. - P. 84-86.
9. Zelichenko LI Mast cells of rats in the immediate type allergic reactions: Author. diss. on soisk. scientists. PhD degree. honey. Sciences. - M., 1969. - 18 p.
CLAIM
1. A method for determination of spontaneous cell cytotoxicity, comprising isolating mononuclear cells from the peripheral blood of a patient, preparation of target cells, mononuclear cells and mixing of the target cells, and incubating the mixture of mononuclear cells of target cells followed by light of the cytotoxic response, characterized in that the kletok- target using rat mast cells are mixed mast cells and mononuclear cells of rats in a ratio of 20-30: 1, immediately after mixing of mononuclear cells and rat mast cell further centrifuged resulting mixture, and incubating the mixture of mononuclear cells of rat mast cells produce within 30 minutes and records the results of cytotoxic The reaction is carried out by counting the number of degranulated mast cells of rats as a percentage of the total number of rat mast cells and mononuclear cells in a mixture of mast cells and rat at a value of said index of less than 25%, determined by decreased spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity, if said index value is determined 25-35% normal spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity, and a value of said index of more than 35% determined by increased spontaneous cellular cytotoxicity.
2. A method according to claim 1, characterized in that during the registration results cytotoxic response immediately before counting the number of degranulated mast cells of rats in a mixture of mononuclear cells and rat mast cell pellet manufacture and stirring the mixture of the supernatant of mononuclear cells and mast cells of rats.
print version
Publication date 02.04.2007gg





Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.