| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current models of the invention and / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2283669
MEDICAL POLYMER ADHESIVE
![]()
The applicant's name: Limited Liability Company "Medical Polymers Technology" (OOO "TMP") (RU)
Name of the inventor: Sirotinkin Nikolai (RU); Levecheva Nina F. (RU); Savina Yulana A. (RU); Popov Vladislav (RU); Pyshkov Evgeny (RU)
The name of the patentee: Limited Liability Company "Medical Polymers Technology" (OOO "TMP") (RU)
Address for correspondence: 191036, St. Petersburg, and / I 29, US Pat. pov.T.A. Repkina, Identification No 243
Starting date of the patent: 2005.02.21
The invention relates to the field of pharmaceuticals, namely adhesive is used, in particular for surgery. The invention consists in that the proposed composition is a polymeric adhesive latex based on a new generation, and tissue adhesives comprising acrylonitrile butylacrylate latex, an aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as a viscosity regulator, and aqueous ammonia as a pH regulator. The invention provides adhesive properties such as high adhesiveness to living tissue, biocompatibility and biodegradability, hydrophilicity, bactericidal and hemostatic properties, high tightness of anastomoses and surgical sutures for abdominal operations, pneumonia, cholera and hemostasis, raising the possibility of the organ operations, non-toxic and the absence of carcinogenic effects, preservation of properties during sterilization and storage, ease of manufacturing the composition, ease of use, not scarce raw materials.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to biocompatible adhesive materials used in the field of medicine, namely to the adhesive is used, in particular for intracavitary surgery. Proposed is an adhesive polymer composition on the basis of latex and represents a new generation of tissue adhesives.
It is known to use polymeric materials in medicine. Today, adhesive sealants are widely used in surgery, which have a significant advantage over other, more recently, traditional materials for closing wounds, sutures.
The main technical requirements for medical adhesives include: the ability to firmly hold the connection surfaces of the fabric to be sufficiently porous and elastic, autosterilnym or easily sterilized without losing properties, not to cause severe tissue reaction, not toxic, does not have allergic and carcinogenic action to disperse and excreted from the body as a natural fusion of tissue and prevent it from healing.
Currently there is a great need for polymers for medical adhesives. The most common medical adhesives applied, in particular for abdominal surgery, are adhesive compositions containing fibrinogen derived from blood plasma of cattle, and a cyanoacrylate adhesives.
It is known from the prior art fibrin tissue adhesive prepared from bovine serum. This adhesive has a good hemostatic effect, compatible with biological tissue, non-toxic, promotes rapid healing and tissue growth. However, the adhesive has disadvantages: a relatively low adhesion, cohesive strength, the complexity of the application, as It consists of several components, which are sequentially applied by means of special devices, and the complexity of preparing the composition and its high cost, and making it difficult to limit the use.
In 1999, the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation allowed commercial production and application in medical practice, "Sulfacrylate" medical adhesive, which includes plasticizing, anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial components. This adhesive is cyanoacrylate basis.
Cyanoacrylate compositions are difficult to manufacture, and are expensive. Besides these named adhesives have serious drawbacks for medical materials, namely polymerisation after application on the wound surface to form a glassy coating, leading to delamination, and tearing away the adhesive film from the surface of the operated organ. The disadvantages of these adhesives concerns their hydrophobicity, which is needed to use them in surgery additional thorough drying with tissue surfaces aggressive dryers - alcohol, ether. Polymerization adhesive is accompanied by an exothermic effect, which violates the local heat balance.
Known medical adhesive, protected by RF patent №2156140, A 61 L 24/00, publish. 20.09.2000, in which the composition contains adhesive base - ethyl 2-tsiankrilovoy acid, anti-inflammatory supplement - 1,1-dioksotetragidro-1 ![]() thiophene-3-yl ester 2-methyl acrylic acid as plasticizer - butyl or hexyl ester of acrylic acid. The adhesive is designed to perform operations on parenchymatous and hollow organs. The patent pending adhesive films increased elasticity.
thiophene-3-yl ester 2-methyl acrylic acid as plasticizer - butyl or hexyl ester of acrylic acid. The adhesive is designed to perform operations on parenchymatous and hollow organs. The patent pending adhesive films increased elasticity.
This glue should be inherent disadvantages mentioned above for all cyanoacrylate adhesives.
There is a need to create a new high-performance medical glue, which does not have the disadvantages of cyanoacrylate adhesives and is able to meet the broad needs of medicine, particularly in the field of surgery. For the foundation of a new adhesive is advisable to use latex.
The prior art medical compositions containing latex used for the treatment of superficial burns (see. Russian patent №2091082, A 61 L 15/28, publ. 09.27.97), and a means of rapid diagnosis for immunoreagents in immunoassays (see. the Russian Federation №2231366 patent, A 61 K 51/08, publ. 27.06.2004).
For the prototype of a new invention, the medical adhesive adopted by RF patent №2156140.
The object of the invention to provide a novel adhesive resin composition for medical use, namely, biologically inert, durable latex tissue glue (LTG) which is suitable for a wide application, including surgery. The technical result is to obtain the following adhesive properties:
- High adhesiveness to living tissue,
- Biocompatibility and biodegradability,
- Hydrophilicity,
- Bactericidal and hemostatic properties,
- High tightness of anastomoses and surgical sutures for abdominal operations,
- Pneumonia, cholera and hemostasis,
- Increasing the possibility of the organ operations.
- Non-toxicity and the absence of carcinogenic effects,
- Preserving properties during sterilization and storage.
- Ease of manufacturing the composition, ease of use, not scarce raw materials.
The problem is solved in the new composition of medical polymer adhesive manufactured Latex, which comprises an aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as a viscosity regulator, and aqueous ammonia as a pH adjuster with the following content of components in grams: for every 100 g of the main component - latex - the content of the PVA aqueous solution is from 40 to 60 g, and the aqueous ammonia solution - 0.6-1.0 g
This adhesive composition has a viscosity of from 7000 to 13000 mPa / s by pH from 7.1 to 7.4 and temperatures from 15 to 50 ° C.
The base is made of butyl acrylate adhesive acrylic nitrile latex. Only such a latex is suitable for creating a surgical glue, since do not contain toxic radicals has high adhesiveness and hydrophilicity, provides the necessary adhesive properties of biocompatibility. This latex on their chemical nature, biologically inert, consists of an aqueous polymer dispersion, stabilized by surfactants, used in cosmetology and medicine, and other necessary additives, which allows forming under normal conditions well filled composition. latex polymer particles and small size is 40-100 nm, which allows small polymer particles penetrate deep into tissues, providing a strong bond with their polymerizing a film of larger particles and formation of a good adhesive impregnated layer. Provides optimal curing time and an adhesive, which is particularly important in a wet environment, which is always present in the surgery.
Latex form used in its construction include high molecular substrate (WMO) consisting of butyl acrylate units, nitrile acrylic acid and methacrylic acid, and a surfactant (surfactant), which is part of the formulation needed to create stability of the polymer system in an amount of 5.2 % of WMO.
Specific formulation LTK determined elasticity or capability of increasing the strength, regulation of drying time, viscosity and coating method which can be performed by brush, swab or spray, etc., Depending on the objectives of a particular application.
Polyvinyl alcohol as a thickener - viscosity regulator is used as a 20% aqueous solution, which allows to achieve optimum drying time of adhesive for 3-5 minutes and provide optimum flowability and film strength. Provides a viscosity of from 7,000 to 13,000 mPas / s, which is good enough for basic functions of the medical glue, because viscosity of less than 7000 mPas / s is not enough, and more than 13,000 mPas / s is the technological difficulty in packaging adhesives.
PH regulator to the extent necessary - is 7.1-7.4% ammonia solution 25, which performs the role of an additional viscosity control. When dry film NH 4 OH is released from the system to the atmosphere to decompose into water and ammonia. The claimed pH limit is optimal, because pH values below 7.1 for the treated fabric can burn acidic and higher pH 7.4 - alkali burn.
The proposed structure of the new adhesive is obtained experimentally.
Unlike cyanoacrylate glues LTK prepared simply by mixing the components under normal conditions. For dosing, transportation and storage of the adhesive does not require special packaging, in addition to compliance with the usual conditions for easy storage of medicines.
The table shows the specific tissue adhesive latex formulations with viscosity values indicating pH, strength, degree of swelling.
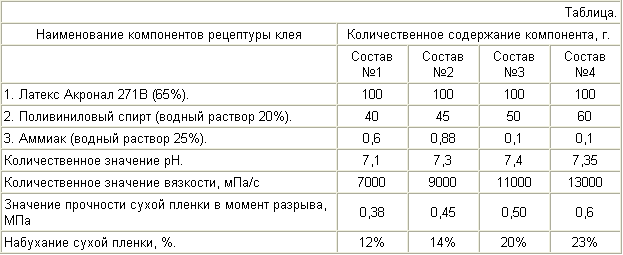
As the high-molecular bases of a plurality of these polymers was chosen butylacrylate-acrylic nitrile latex production «BASF» or «Nordsintez" which is biocompatible and is suitable for the creation of surgical glues. As the viscosity regulator used aqueous PVA 16/1 grade in accordance with GOST 10779-78.
As shown in the table, the adhesive composition provides the proposed optimal adhesive properties for surface tension strength, elasticity on by swelling. Studies have shown that the strength of the film decreases with increasing amounts of polymer. When the swelling study dry adhesive films in saline solution for a long time, it was shown that the intense weight set is only observed in the first hour and then terminated. Permanence film weight within a few days without evidence of polymer degradation processes on the main chain.
Physical and mechanical properties of the films of latex compositions are defined in the temperature range 20 ° C-42 ° C. It is known that protein folding temperature - 42 ° C. Strength and elasticity of the films does not change at different temperatures. The composition is made at room temperature, a simple mixing method.
According to the complex set new adhesive properties suitable in medicine, in particular for use in abdominal surgery.
The experimental data were processed with the assistance of mathematical statistics. The studies were conducted by biological methods, testing in experiments "in vivo" in the laboratory of the Military Medical Academy. Kirov (WMA) in St. Petersburg. Experimental studies on the comparative evaluation of topical cyanoacrylate and latex adhesives conducted at the department of operative surgery VMA, special investigations: histological - at the Department of Microbiology, Military Medical Academy, biochemical - in the Research Department of clinical and biochemical studies of the All-Russian Center of Emergency and Radiation Medicine of EMERCOM of Russia, in the Institute of Nutrition Physiology Laboratory academician Pavlov physiology, Academy of Sciences of the Russian Federation.
Experiments were carried out on dogs and rats for types of surgery: 1 - plastic defects of the visceral and parietal pleura and peritoneum, 2 - sealed seams anastomoses in elective surgery on the stomach and intestines, and against the background of progressive peritonitis, 3 - plastic wound defects (saving procedure) parenchymal organs (lungs, liver, kidney, spleen).
Of the total number of surgical interventions performed - 95 dogs and 140 rats results of comprehensive studies have reported the effectiveness of latex tissue glue, its biological inertness, lack of postoperative complications and disorders of the functional activity of the operated organs. Comparative evaluation showed significant advantages topical latex tissue glue in front of cyanoacrylate glue and the prospect of the introduction of the new adhesive in clinical practice routine and emergency, including military surgery. Designed latex fabric glue recommended for wide application in medical practice.
CLAIM
1. Medical polymer adhesives, comprising the latex polymer substrate as acrylonitrile butylacrylate latex viscosity regulator in an aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and a pH regulator in an aqueous ammonia solution at the following component ratio, g:
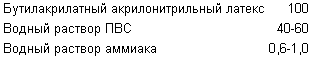
2. The adhesive of claim 1, wherein the viscosity regulator used in the form of a 20% aqueous PVA solution and the pH regulator used in the form of 25% aqueous ammonia solution.
print version
Publication date 18.12.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.