| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current models of the invention and / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2168748
METHOD FOR DETECTION GEOENERGOAKTIVNYH ZONES AND DEVICE FOR ITS IMPLEMENTATION
![]()
Name of applicant: JSC "Tomskgazprom"; Tomsk Polytechnic University
Name of the inventor: Lunev VI .; Pokholkov YP .; Parovinchak MS
The name of the patentee: JSC "Tomskgazprom"; Tomsk Polytechnic University
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1999.08.16
Usage: to identify hidden in the bowels of the earth geological, technological and other objects by detecting Geoelectromagnetic waves emitted by those objects, and to search for and exploration of mineral deposits, intrusion, tectonic dislocations, etc. The essence:. Conduct registration of photon radiation parameters occurring during relaxation atoms and molecules of an inert gas such as helium, Geoelectromagnetic excited under influence of waves in the infrared, optical and ultraviolet spectrum geoenergoaktivnoy zone in the study area. Devices that detect photon radiation, such as photodiodes, are placed in the airship hull filled with an inert gas having a density less than the density of air, in particular helium. The shell is made of soft materials transmissive electromagnetic wave but reflecting photons through opaque layer which is covered by its inner surface. The airship gondola is equipped with a propulsion system, control mechanisms, and is equipped with a cockpit electrophysical apparatus for recording and determining the photon radiation parameters. The airship has a length which is a multiple lithospheric characteristic transverse dimension of the waveguide, and its volume is in the range 2-200 thousand. M3. On the airship on a certain route is carried circled the study area at a height of several tens to hundreds of meters and record the photon radiation. The technical result: provision of continuous operation geophysical survey and eliminating the need for complex, cumbersome and expensive equipment for recording directly geoelectromagnetic radiation.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to methods and means for detecting hidden in the bowels of the earth geological, technological and other objects by detecting geoenergoaktivnyh zones using electromagnetic waves emitted by those objects, and can be applied for prospecting and exploration of mineral deposits, intrusion, tectonic dislocations, etc. .
It is generally known that the thermal effect on some minerals and rocks accompanied by electromagnetic radiation, the parameters of which depend on the magnitude of the heat flux, the material composition of minerals and rocks, and other factors. So when heated quartz samples of cassiterite, topaz, fluorite, magnetite and other minerals of different origins in a vacuum to a temperature of 720 o C value of the specific energy of the electromagnetic radiation in the range of 50 ... 20 x 10 -8 J · g -1 [1] . Given the weight of the investigated geological objects in the bowels of the earth, the integral value of the average power generated by the electromagnetic energy can reach the value of 10 5 - July 10 watts. Radiation of such power is enough to electromagnetic pulses from the geological object came through the upper layers of the Earth's crust in the surface layer of the atmosphere.
Known environmental stress indication method in an environment comprising: visual observation of surface emission gas layer in the earth's surface energy active areas during physical fluctuations fields [1]. This method provides objective information about what the earth's surface at this portion of the flow of energy occurs between the lithosphere and the atmosphere [2, 3]. However, the practical use of this method in order to find geological objects, in particular of mineral deposits, it is difficult for the following reasons:
- The phenomenon of gas emission is random for observation;
- Needed abnormal natural phenomena that can cause fluctuations in the physical fields;
- The sensitivity of the method depends on the weather conditions in the study area and the chemical composition of the atmosphere directly above the surface;
- Anomalies of geo-energy information is the identity and fragmented and does not allow the scan data within the study area.
And zvesten method of gas excitation by exposure to electromagnetic radiation, such as radio waves [1, 4]. The atmosphere was launched a weather balloon filled with helium and equipped with exhaust receiving antenna - 30-meter copper wire. This probe is irradiated with radio waves from amateur transmitter operating in the HF band. It has been found that when operating as a station on the key, and a microphone probe violet luminescence is observed, a pulsating clock transmission signals.
This method can not be used directly for detection geoenergoaktivnyh zones in the study area because the radiation power geoelectromagnetic considerably inferior power of the electromagnetic radiation generated by the radio and the volume of gas in the probe is very small.
The task - to develop methods and technical means for registration of electromagnetic radiation in geoenergoaktivnyh areas in the study of the geological area. These solutions must possess sufficient sensitivity, precision and efficiency and allow measurements of electromagnetic radiation parameters in a continuous manner throughout the territory of the study area.
The task is solved as follows. Produce registration photon radiation parameters occurring during relaxation of the atoms and molecules of the inert gas, under the influence of excited Geoelectromagnetic waves in the infrared, optical and ultraviolet spectrum geoenergoaktivnoy area of the study area.
To this end, devices that detect photon radiation, such as photodiodes, are placed in the airship hull filled with an inert gas having a density less than the density of air, in particular helium. The shell is made of soft materials transmissive electromagnetic wave but reflecting photons through opaque layer which is covered by its inner surface. The airship gondola is equipped with a propulsion system, control mechanisms, and is equipped with a cockpit electrophysical apparatus for recording and determining the photon radiation parameters. The airship has a length which is a multiple lithospheric characteristic transverse dimension of the waveguide, and its volume is in the range 2-200 thousand. M3.
On the airship on a certain route is carried circled the study area at a height of several tens to hundreds of meters (depending on the power of geo-electromagnetic radiation) and record the photon radiation produced in a gaseous medium membrane under the influence of electromagnetic waves on geoenergoaktivnymi zones.
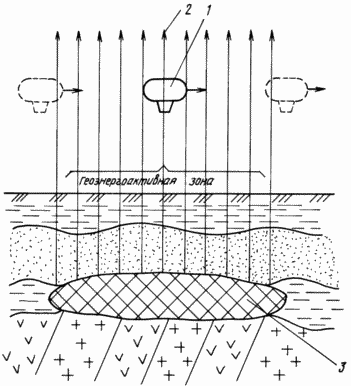 |
Next Brief Description of the drawing, which shows a diagram of the geophysical survey over the area geoenergoaktivnoy the earth's surface. On the airship 1 is carried out on a given route circled over the study area in order to identify her geoenergoaktivnyh zones created underground geological (mineral deposits, crumple zone, dike, etc..), Man-made or other objects. The airship consists of a shell and gondolas. The shell is made of soft materials transmissive electromagnetic wave, and is filled with an inert gas having a density less than the density of air, in particular helium. The inner surface of the shell is covered with an opaque layer to reflect photons. Inside the shell placed light-sensitive electronic devices, such as LEDs, catching photon radiation. The shell has linear dimensions in the range of 20-60 m, multiple characteristic transverse size of lithospheric waveguide defined by the relation: L = nx |
The airship gondola is equipped with a propulsion plant, machinery handling and a cabin for the pilot and the operator, and is equipped with electrophysical apparatus for recording and determining the photon radiation parameters.
When crossing the airship 1 border geoenergoaktivnoy area at a height of several tens to hundreds of meters (depending on the power of geo-electromagnetic radiation) electromagnetic wave 2 in the infrared, optical and ultraviolet spectral ranges emitted by underground geological object 3 (eg, mineral deposits), freely penetrate inside the envelope of the airship and causes excitation of the atoms and molecules of the gas medium, such as helium. After a certain time of the excited atoms and molecules of the gas relaxes by emitting photons. The emitted photons are captured by the light-sensitive electronic devices, such as photodiodes, which are in the form of electrical signals received on the electrical measuring equipment placed in the gondola of the airship. airship flight itinerary is chosen such that the set boundaries geoenergoaktivnyh geoenergoaktivnye zones and anomalies throughout the study area. Geophysical survey data is applied to the geological map of the study area and identify areas for long-term exploration, such as drilling.
Technical feasibility and efficiency of the proposed technical solutions for geological research facilities located in the bowels of the earth and create geoenergoaktivnye zones are illustrated in the following parameter. In the summer of 1993 on the Mid-Ob oil and gas area below-described experiment was performed. As the capacity of the gas used by ordinary weather balloon filled with helium and covered with an opaque layer. semiconductor light receivers have been installed inside the probe, and the outside - an electronic unit recording electrical signals from the light detectors. The probe extends a vehicle on a route length of 47 km at an altitude of 30 meters above the tectonic faults. It was found that the photon radiation is recorded at all times during the flight of the probe over the tectonic fault, clearly fixing its boundaries. And noted that the maximum amplitude of the signal was observed Geoelectromagnetic at night with 2 to 5 pm local standard time, ie, between highs generation of natural pulsed electromagnetic field of the Earth.
The proposed method and apparatus for detecting geoenergoaktivnyh zones have the following technical and economic advantages:
- Have sufficient sensitivity and accuracy of measurements;
- Provide continuous measurement mode geoenergoaktivnoy zone, which makes it possible to identify the boundaries of the zone Geoelectromagnetic anomalies within this zone;
- Eliminates the use of complex, cumbersome and expensive geophysical equipment for recording directly geoelectromagnetic radiation.
INFORMATION SOURCES
1. VI Lunev. Glowing balls in Siberia and the Far East: phenomenology, experiment, hypothesis. Math. universities. Physics. G. 1992, N 3, v. 35, p. 65-86.
2. The plasma formation in the energy active zones. AN Dmitriev, Yu Pokholkov, ET Protasiewicz, VP Skavinsky. Novosibirsk, UIGGM and M, Russian Academy of Sciences. Sibotdel, 1992, p. 212.
3. AN Dmitriev. Natural glowing formations. Novosibirsk, Acad. Institute of Mathematics SB RAS, 1998, p. 243 (Series "Problems of non-homogeneous physical vacuum").
4. Vatamanyuk P. Soviet Russia. M., 01/01/1987, p. 4
CLAIM
1. A method for detecting geoenergoaktivnyh zones, based on detection of electromagnetic pulses of the Earth's interior, characterized in that the measured photon radiation produced by relaxation of the atoms and molecules of the inert gas, such as helium, excited by electromagnetic waves in the infrared, optical and ultraviolet ranges of the spectrum, geophysical survey data is applied to the geological map of the study area and identify areas for long-term exploration, such as drilling.
2. The apparatus for detecting geoenergoaktivnyh zones, comprising a vessel for inert gas, characterized in that the container for the inert gas is formed as a shell covered with an opaque layer airship having linear sizes that are multiples of the characteristic transverse dimension of the waveguide lithosphere, inside which are installed electronic light receivers connected to electrophysical measuring equipment placed in the gondola of the airship, equipped with a propulsion system, control mechanisms and a cabin for the pilot and the operator.
print version
Publication date 16.12.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.