| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current inventions and models / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2244762
ALLOY ON THE BASIS OF PALLADIUM OF WHITE COLOR
![]()
Applicant's name: Joint Stock Company "Ekaterinburg Non-Ferrous Metals Processing Plant" (JSC "EZ OCM") (RU)
The name of the inventor: Ermakov AV (RU); Gorskih TS (RU); Syutkina V.I. (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Open Joint-Stock Company "Ekaterinburg Non-Ferrous Metals Processing Plant" (JSC "EZ OCM") (RU)
Address for correspondence: 620014, Ekaterinburg, Lenin Avenue, 8, JSC "EZ OCM", to the Executive Director A. Fedotov
Date of commencement of the patent: 2003.11.10
The invention relates to the field of metallurgy of noble metals, in particular to alloys based on palladium of white color, intended for the manufacture of jewelry. An alloy based on palladium of white color containing nickel is proposed, further comprising copper, zinc and indium with the following component ratio, by weight: palladium 85.0-90.0, nickel 5.5-12.0, copper 1 , 5-2.0, zinc 2.0-2.5, indium 1.0-1.5. The technical result is the creation of an alloy based on palladium of white color, close to platinum, possessing optimal physical and mechanical properties and allowing to make jewelry by casting with high precision, stamping, chaining.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to the field of metallurgy of noble metals, in particular to alloys based on palladium, intended for the manufacture of jewelry.
Recently, alloys based on palladium are widely used in jewelry production. Due to its consumer, aesthetic and technological properties and tarnish resistance, palladium is practically inferior to platinum and has even a number of advantages. Depending on the ratio of it in the alloy with other components, you can get the color tone of the jewelry in a wide range. In addition, palladium-based alloys have better workability, for example pressure, have a lower specific gravity compared to platinum and have a significantly lower cost.
Palladium alloys for bijouterie are known (Japanese APs No. 62-279335, 62-279334, C 22 C 5/04, filed on 06.11.87, RG ISM No. 1, issue 48, 1994, P.19) . Alloys contain 50-95% palladium and 5-50% tungsten or molybdenum. To control the color and strength of the alloy, it can contain vanadium, antimony, boron and platinum, which are introduced in an amount of up to 10%.
The disadvantage of the known alloys is that they can be used only for jewelry, The content of a large number of base components does not ensure the corrosion resistance of alloys. These alloy have high hardness and low plasticity.
A palladium alloy for jewelry is known (Japanese AP No. 62-192580, C 22 C 5/04, filed on 03/08/87, op. RI ISM No. 1, issue 48, 1994, p.19 ) . The alloy contains 50-95% palladium and 5-50% chromium. To impart anticorrosive properties and color control to the alloy, up to 10% of silver, tungsten, molybdenum and up to 5% of antimony are introduced into the matrix alloy.
The alloy is supposed to be made for the manufacture of jewelry, however, if the alloy contains additional components from the above series, a white palladium alloy can not be obtained. Silver lowers the corrosion resistance of the alloy due to the presence of sulfur compounds in the atmosphere.
Known is an alloy based on palladium, intended for the jewelry industry (USSR AS No. 811860, C 22 C 5/04, 04.06.79, 1982, issue No. 4).
The palladium-based alloy contains indium and a metal selected from the group consisting of scandium, magnesium and aluminum. The content of indium in the alloy is 22-28%.
The indium content in a palladium alloy of more than 1.5% causes the formation of intermetallides of palladium-indium, which are hard and brittle compounds, which greatly complicates the mechanical processing of jewelry.
The disadvantage of this alloy is low corrosion resistance and low tensile strength, increased hardness and brittleness due to these compounds.
In addition, the components in the composition and their quantity provide only low-quality jewelry.
A palladium-based composition is known (patent of the Russian Federation No. 2132885, C 22 C 5/04, published in Bulletin No. 19, 1999, p.445) containing palladium, nickel and boron in the following ratio, by weight:
- Palladium - 83.4-88.6
- Nickel - 10.0-15.0
- Boron - 1,4-1,6
The disadvantage of the known alloy is the presence in it of a high boron content. The presence of boron increases the strength properties and brittleness of the alloy, which complicates the processing and at the same time the casting properties of the alloy are significantly reduced.
In addition, a disadvantage of this palladium alloy is the impossibility of obtaining a wide range of coloring, in particular, obtaining an alloy of good (cold) white color, close to platinum.
The closest in composition to the claimed is a white palladium-based alloy based on weight, in percentages:
- Palladium 85.0
- Silver - 13,0
- Nickel 2.0
(Interstate Standard GOST 30649-99 "Alloys on the basis of precious metals., Jewelry, Stamps." Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification, Minsk, page 4, published on May 28, 1999)
However, the known alloy has a high melting point and a low plasticity, which increases the complexity of its processing.
In addition, because of the non-optimal ratio of the palladium-nickel components, the alloy has a low coefficient of reflection, i. E. Bad shine, and under certain environmental conditions, jewelry made of this alloy, tend to tarnish.
The task for solving the proposed technical solution is to create a composition of an alloy based on palladium of white color, close to platinum, possessing optimal physical and mechanical properties and allowing to make jewelry by casting with high precision, stamping, chaining, etc.
The technical result of using the invention is the production of high-quality white jewelry with a gloss close to platinum, and corrosion-resistant in time, with improved casting properties, by reducing the melting point and increasing the fluidity of the alloy.
The aim is achieved by adding copper, zinc and indium to the palladium alloy including nickel with the following component ratio, by weight:
- Palladium 85.0-90.0
- Nickel - 5,5-12,0
- Copper - 1,5-2,0
- Zinc - 2.0-2.5
- Indium - 1.0-1.5
The content of palladium in the alloy is determined by the GOST requirement, i.e. In the production of jewelry from the alloy, the latter should correspond to the standard sample.
The presence of nickel in the composition of the claimed range in combination with palladium and zinc significantly reduces the melting point, provides the alloy with a white color and gives shine. In addition, the content of nickel and zinc in the alloy gives it a color tone that is close to that of platinum alloys.
The introduction of up to 1.5% by weight of indium into the composition of the alloy improves the plasticity of the alloy, reduces the melting point, and with a further increase in the indium content, the hardness and brittleness of the alloy increase sharply.
The indium content in the alloy in an amount of 1.0-1.5% by weight is optimal and does not change the color of the alloy. Decrease in indium content less than 1.0% by weight leads to deterioration of casting properties, increases corrosion resistance.
An increase in the nickel content in the alloy of more than 12% by weight reduces its quality as a jewelery alloy.
The content of copper in the claimed amount is optimal for the replacement of palladium in the alloy and provides a high tensile strength.
The presence of zinc reduces the melting temperature of the alloy, increases fluidity.
The alloy based on palladium of the composition according to the invention has high mechanical and consumer properties, fast crystallization, good casting characteristics as compared to the known ones. Due to the decrease in the melting temperature of the alloy, the diffusion processes increase, a uniform distribution of the constituent components occurs. The alloy is suitable for use in the manufacture of products by any methods (OMD, casting, chain-linking both manual and machine).
The inventive alloy was obtained by direct melting of its constituent components, which used palladium with a purity of 99.9%, nickel grade N-00, copper grade M-00, zinc grade Tsn-00, indium grade In-00.
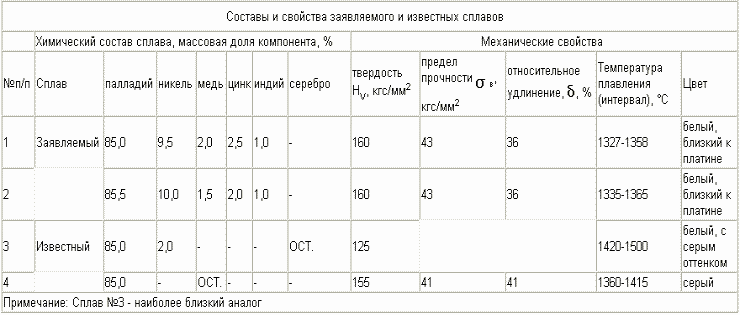
Two charges were prepared with palladium content of 85.0% and 90% (see table). The charge was melted in the Madulan centrifugal casting plant of Gallony (Italy).
The resulting alloy was analyzed and the chemical composition was determined. The mechanical properties were tested on an Instron 3112 unit. The solidus and liquidus temperatures were determined on the samples by differential thermal analysis.
On the finished sections, the color and gloss of the alloys were evaluated.
The compositions of the claimed alloys, their physical and mechanical properties, and the chromaticity indices are shown in the table. As can be seen from the table, the claimed alloy, in comparison with the known alloy due to the optimal combination in the alloy of the components in said quantitative ratio, has improved physicomechanical properties and a more intense white color and shine, corrosion resistance.
CLAIM
An alloy based on palladium of white color, containing nickel, characterized in that it additionally contains copper, zinc and indium with the following ratio of components, mass%:

print version
Date of publication 02.01.2007гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.