| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current inventions and models / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2165031
METHOD OF INLAND CLEANING OF EXHAUST GASES OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE
![]()
The applicant's name: Valery Dmitrievich Dudyshev; Zavyalov Stanislav Yurievich
The name of the inventor: Valery Dmitrievich Dudishev; Zavyalov Stanislav Yurievich
The name of the patent owner: Valery Dmitrievich Dudyshev; Zavyalov Stanislav Yurievich
Address for correspondence: 121069, Moscow, Trubnikovsky per. 21, p.2, Zavyalov S.Yu.
Date of commencement of the patent: 1998.08.10
The invention relates to engine building, in particular to motor transport, and can find wide application in modern motor vehicles to reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases. The invention makes it possible to provide an interconnected synthesis of the effects on the air-fuel mixture for intensifying the operation of the ICE . The method for internal cleaning of the exhaust gases of the internal combustion engine by increasing the power and duration of the electrical pulses of ignition of the fuel mixture in the combustion chambers is that simultaneously impoverish the fuel mixture by introducing an adjustable additional air jet into the intake path at an angle to the fuel mixture flow until a minimum toxicity of the exhaust Gas with the preservation of stable operation of the engine in all modes. In carburetor internal combustion engines, an additional air jet from the atmosphere is injected under the throttle valve of the carburettor perpendicularly to the flow of the fuel-air mixture.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to mechanical engineering, specifically to engine building and motor transport, and can find wide application in modern vehicles to reduce the toxicity of its exhaust gases (VG). The invention can be implemented in any internal combustion engine (ICE) with any number of pistons and chambers, as well as rotary and gas turbines, and will help in creating environmentally friendly and economical transport with ICE.
Despite a significant number of developments and patents in this field of technology, motor transport is still far from ecological perfection and contributes up to 70% of the total toxic pollution of the atmosphere of the cities of the planet.
All known inventions in the form of methods and devices for environmental cleaning of VGV DVS can be divided into external (cleaning VG in the exhaust path of ICE ) and internal (directly inside the ICE ). We will make a brief analysis of known inventions and patents on this topic. The greatest application so far is the methods and devices for external cleaning of the VG directly in the exhaust path of the ICE .
Chemical methods and devices for external purification of exhaust gases of combustion engines are known and widely used by flameless catalytic afterburning of toxic components of exhaust gases in the exhaust path of an internal combustion engine on the active surface of a chemical honeycomb catalyst coated with a thin layer of platinum, palladium, rhodium, etc. ( Russian patent No. 2,023,178, N 2023176, Japanese application No. 62-167721 ).
Despite the significant use of such methods and devices for cleaning VG on foreign cars, they have serious and insurmountable shortcomings. Disadvantages of these technical solutions consist in the complexity and cost of their implementation, since for their performance, a system of precise fuel injection of ICE fuel is needed, while practically unapplied in Russia; Relatively low lifetime due to chemical contamination of the surface of the catalyst and the incompetence of such devices; Limited scope, only on cars with gasoline internal combustion engines operating on unleaded petrol because of the inoperability of the chemical honeycomb catalyst in the presence of soot, sulfur, lead, etc. in the SG.
There are known methods and devices for mechanically separating solid and liquid impurities of exhaust gases characteristic of diesel transport by mechanical separation by rotating the exhaust gas flow followed by the accumulation of soot and oil particles in special hoppers with systematic removal ( see, for example, Russian Patent No. 2,023,175 ). Their disadvantage is the complexity of implementation, significant energy costs and high material intensity, since the volume of soot is large because of its low density. Thermal decomposition of soot is uneconomical and leads to an increase in the volume of carbon monoxide.
There are known plasma methods and devices for burning off exhaust gases by passing exhaust gases through a torch of low-temperature plasma ( AS USSR No. 1460368 ). Their disadvantage consists in significant energy consumption, in the consumption of additional fuel, unfavorable temperature conditions of the exhaust pipe when it is overheated by the plasma. In addition, the volume of the oxidant, and hence of the exhaust gases of the internal combustion engine , also increases.
Methods and devices for electrofiltering exhaust gases of internal combustion engines are described ( as in N 117574, No. 1404664 ) by applying an electric field to electrically charged particles (solid and liquid) of exhaust gases with their electrostatic deposition on special electrodes, followed by a systematic removal of the sediment. Their disadvantage is low reliability due to the difficulties in providing reliable electrical insulation of unlike charged electrofilter plates under conditions of soot deposition, soot on the inner surface of the plates and high temperatures.
Combined electrochemical methods and devices for purifying exhaust gases of combustion engines are known , for example, as. N 1188343 , they have all the disadvantages of catalytic afterburning of exhaust gases and electrostatic precipitators for their purification. There are known methods for purifying exhaust gases from soot by electrothermal decomposition ( as in No. 181534 ). However, this method is very energy-consuming and unacceptable for vehicles with low power of the generator. Methods for internal environmental cleaning of VGV IC are known, by improving the quality of fuel-air mixture preparation ( TVS ), for example by mechanical crushing of fuel droplets ( RF patent No. 1772391 ), by improving the evaporation of fuel using porous materials along the gasoline flow path ( RF patent No. 20026645 ) By preheating fuel ( RF patent No. 1784069 ), etc.
The devices for improving the quality of fuel assembly preparation are known, which contain special rotating impellers, evaporator grids on the fuel assembly path, for example, installed in the combustion engine carburettor ( patent of the Russian Federation No. 1772391, patent of the Russian Federation No. 1784069 ). Their disadvantage consists in creating additional aerodynamic resistance in the intake tract of the engine and reducing its power at the previous fuel consumption.
Methods and devices for internal environmental cleaning of VGV IC are known through the internal intensification of the process of ignition of the fuel-air mixture in combustion chambers of combustion engines , for example, by increasing the power of the spark ignition electric spark from a more powerful electronic spark or plasma ignition system ( RF patents Nos. 1835462, 1838664, 2002975 ) - any of these patents may be a prototype. Despite some decrease in carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons in the composition of the VG from their realization (up to 30-40% ), these analogues do not allow to reduce CO and C x H x many times , and the content of nitric oxide can even increase due to the increase in the flame temperature in chambers Combustion engine.
This method-prototype also has disadvantages associated with increasing the power consumption of ICE due to increased electrical load from such an ignition system to the on-board electrical network, an increase in the level of electrical interference, a decrease in the service life of automotive electrospears due to rapid electrocorrosive wear of the central electrode of the candle. All the above analogs and prototype, of course, give a reduction in the toxicity of VGD DVS , however, in connection with the non-optimal ratio of fuel and air in the engine intake, especially at idle, with the throttle closed the carburetor, these methods do not allow for deep environmental cleaning of the SH ICE and, in addition, reduce the degree of stability of the engine, especially in transient modes. In addition, this increases the aerodynamic drag of the intake tract, which leads to a decrease in the engine power.
The task of the proposed method consists in an interconnected synthesis of these two impacts on the fuel assemblies to intensify the operation of the internal combustion engine , since for deep depletion of fuel assemblies, at least at idle speed and a sharp decrease in the toxicity of the VGD engine, while simultaneously increasing the fuel economy, it is necessary simultaneously to dilute the fuel fuel, And simultaneously increase the power and duration of the action of high-voltage ignition pulses to intensify the ignition and stabilize the combustion of fuel assemblies in the combustion chambers of the engine.
The task is achieved due to the fact that in the known method for internal purification of the exhaust gases of the internal combustion engine by increasing the power and duration of the electrical pulses of ignition of the fuel mixture in the combustion chambers, the fuel mixture is simultaneously depleted by introducing an adjustable additional air jet at an angle to the flow of the fuel mixture until a minimum toxicity is achieved Exhaust gases while maintaining the stable operation of the engine in all modes.
The development of the method consists in introducing an additional air jet from the atmosphere into the carburetor internal combustion engine to the throttle valve of the carburettor perpendicular to the flow of the fuel-air mixture.
The development of the method consists in that the adjustment of the additional air jet is carried out at idle speed at the maximum engine speed with the throttle fully closed.
The development of the method consists in simultaneously ionizing and electrostatically spraying fuel and ozonizing the intake air with a strong electric field with a voltage of at least 1 kV / cm .
The development of the method consists in that in engines with injection fuel injection, an additional air jet from the atmosphere is introduced transversely to the flow of the fuel mixture or tangentially to it through calibrated openings in each of the intake manifolds opposite the cutter of the fuel injectors.
The development of the method consists in spraying a water distilled aerosol through a needle-syringe into an additional air jet, while simultaneously treating them with a strong electric field with a strength of not less than 1 kV / cm .
The development of the method consists in regulating the consumption of additional air and water aerosols and the parameters of the electric field, which process the fuel and the additional air-water mixture, depending on the mode of operation of the engine and the quality of its fuel under the condition of minimum toxicity of the exhaust gases.
The implementation of the proposed method for internal environmental cleaning of the VG of a gasoline internal combustion engine is shown using the carburettor internal combustion engine as an example (Fig . The device for carrying out the method is a modernized gasoline engine and consists of an air filter 1, a carburettor 2, a fuel float chamber 3 with a fuel line 4, and a fuel injector 5 electrically insulated from the engine casing 5 connected to the fuel pipe 4, with an additional electrically insulated spacer 6 located under the carburetor 2, comprising a metal spray mesh 7, a revolver mechanical adjuster 8 for supplying additional air with calibrated holes 9 ( 0.3 mm to 4 mm in diameter ) in the center of the intake manifold 10, the combustion chamber of the internal combustion engine 11 , a battery 12 connected to High voltage adjustable voltage converter with an output voltage of 5 to 30 kV , a through electrical insulator 14 through which an electrical potential is supplied to the fuel injector 5, an electric ignition system 15 (shown schematically), thin nozzles 16 for supplying a water aerosol and additional air for the throttle valve of the carburettor 2 .
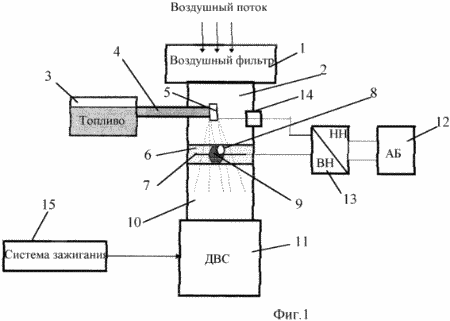
The device works as follows. When the engine is started at idling, an air discharge is created in the intake manifold 10, under the action of which fuel is discharged from the fuel injector 5 in the main air stream passing through the air filter 1. However, in connection with the almost completely closed throttle valve of the carburettor 2 Figure 1.2 is not shown) in this ICE mode, the fuel mixture is usually re-enriched and poorly mixed with air, which leads to increased toxicity of the SH .
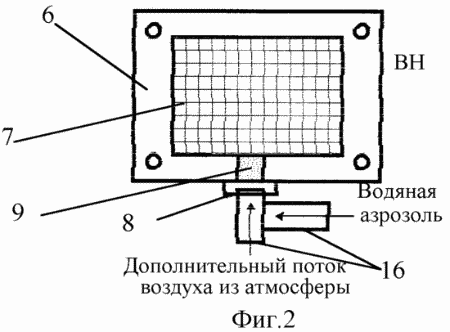
In our case, the additional air flow entering the inlet 10 through the calibrated opening 9 of the air supply regulator 8 perpendicular to the main flow of the fuel mixture impoverishes it and at the same time ensures its better mixing (homogenization), which leads to a more complete combustion of such a mixture, Power ( 1.5-2 times) of electrical ignition pulses from the ignition system 15. An additional effect of cleaning the VG from the realization of this method arises from electrostatic crushing due to mutual repulsion of electrically charged fuel droplets and air ozonization under the influence of an electric field between the fuel injector 5 and grid 7. It is known that ozone is a much stronger oxidant than conventional air, so the ozonization of air in the intake manifold of the internal combustion engine intensifies the process of ignition and combustion of the fuel mixture, which improves the purity of the SH , and the injection of water aerosols through 16 The intake manifold 10 leads to a reduction in the combustion chamber 11 of the temperature of the burning mixture to a level providing the conditions for the minimum formation of toxic nitrogen oxides during its combustion.
The simplest way to configure the device to minimize the toxicity of the VH idling ICE is to regulate the intensity of the additional air flow by changing the hole diameters 9 by turning the regulator drum 8 to fix the maximum engine speed with the fuel consumption constant. Indeed, during the experiments, almost 5% increase in these revolutions was observed with optimum dilution and mixing of the fuel mixture with an additional transverse air flow through the hole 9.
As a result, as demonstrated by bench tests of the method on the internal combustion engine from VAZ 2106 , stable operation of the internal combustion engine is achieved in all modes, when the fuel mixture is depleted by two or more times, and the toxicity of the SH ( CO, C x H x , NO x , etc.) due to More intensive and complete combustion of the fuel mixture in the combustion chambers 11 is reduced by 50-90% .
It is understood that when an excessive amount of air is fed into the intake manifold 10 of the internal combustion engine through a feed controller 8 with a maximum diameter orifice 9, for example 4 mm , an over-fueled fuel mixture is obtained which does not ignite from the ignition system 15. This effect makes it possible to use the proposed method both efficiently Means of protection against car theft, for this purpose it is sufficient to set the maximum passage opening 9 in the engine intake manifold 10 only in the parking area by the regulator 8. Naturally, for normal normal starting of the engine, it is necessary to reduce the cross-section of this hole 9 or even to damp it with a regulator 8.
CLAIM
A method for internal purification of the exhaust gases of an internal combustion engine by increasing the power and duration of the electrical pulses of ignition of the fuel mixture in combustion chambers, characterized in that the fuel mixture is simultaneously depleted by introducing an adjustable additional air jet into the intake path at an angle to the fuel mixture flow, until a minimum toxicity of the exhaust Gas with the preservation of stable operation of the engine in all modes.
The method of claim 1, wherein in the carburettor internal combustion engines, an additional air jet is introduced from the atmosphere to the throttle valve of the carburettor perpendicularly to the fuel-air mixture stream.
The method according to claim 2, characterized in that the adjustment of the additional air jet is carried out at idle speed at the maximum engine speed with the throttle fully closed.
Method according to claims 1 to 3, characterized in that simultaneously ionize and electrostatically spray the fuel and ozonize the intake air with a strong electric field with a strength of at least 1 kV / cm .
The method according to claim 1, characterized in that in engines with injection fuel injection, an additional air jet from the atmosphere is introduced transversely to the flow of the fuel mixture or tangentially to it through calibrated openings in each of the intake manifolds opposite the fuel injector cut.
The method according to claims 1 and 2, characterized in that a water distilled aerosol is sprayed through the needle-syringe into the additional air jet, while simultaneously treating them with a strong electric field with a strength of not less than 1 kV / cm .
A method according to claim 6, characterized in that the flow rate of the additional air and the water spray and the electric field parameters, which process the fuel and the additional air-water mixture, are controlled, depending on the engine operating mode and the quality of its fuel, under the condition of a minimum of toxicity of the exhaust gases.
print version
Date of publication 09.11.2006гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.