| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current models of the invention and / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2198462
ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINE
![]()
Name of applicant: Kurkin Pavel
Name of the inventor: Kurkin PV .; Kudryashov VF .; Kurkin VP .; Anzali EA .; Bogomolov GM
The name of the patentee: Kurkin Pavel
Address for correspondence: 462432, Orenburg region, Orsk, st.. Yulin, 6 b, kv.20, P.V.Kurkinu
Starting date of the patent: 2000.08.17
The engine is designed for use in the energy sector. The engine comprises a stationary part - and an inductor rotating part - anchored reinforced shaft and a collector, the armature being in the form of electrical steel sheets and the coil fixed on the core, and the winding ends are connected to the shaft insulated from copper collector plates connected to a voltage source. The inductor segment is made of electrical steel reinforced aluminum based alloys; rotating part is planted on the shaft of the wheels with electromagnets which interact alternately with the inductor. The shaft is mounted vertically on two bearing brackets. The invention provides increased efficiency.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to power engineering and is meant for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy and vice versa.
The closest to the invention is an electromagnetic motor, comprising a housing and / or base of at least one fixed part arranged in the form of an inductor, at least one rotating part, comprising collector means electrobrushes connected to a voltage source, and the PTO (Waldeck AI Electrical machines. A textbook for university students. "Energy", Leningrad branch, 1978, p.27).
The disadvantages of this engine are: a complex manufacturing technology, low efficiency.
The task to be solved by the invention is to simplify the manufacture of engine technology and increase efficiency.
This object is achieved by the fact that the electromagnetic motor comprising a housing and / or base of at least one fixed part arranged in the form of an inductor, at least one rotating part, comprising collector means electrobrushes connected to a voltage source, and a PTO, the inductor is in the form of individual segments of the electrical steel, fixed on the ground, made of an aluminum alloy rotary part is formed as a planted on the wheel shaft with electromagnets mounted with the possibility of alternately interacting with an inductor, a shaft mounted in bearings on two brackets, and the electromagnets are connected to a voltage source through a collector mounted on the shaft.
The shaft may be disposed in the hollow cylinder in the vertical plane, and its bearings - situated in the base of the cylinder and its lids. Wheels provided with three or more electromagnets and rotatably in a vertical plane and to engage its electromagnets with two or more inductors, fixed on the inner surface of the cylinder. The collector is provided with copper plates in an amount equal to the number of electromagnets on all wheels, and the number exceeds the number of inductors electrobrushes established for one wheel, one minus Electrobrushes.
The invention is illustrated by drawings, where
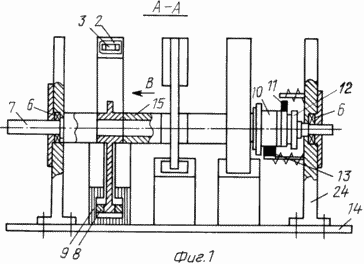 1 schematically illustrates the described electromagnetic motor based on, the cut A-A in Figure 2 |
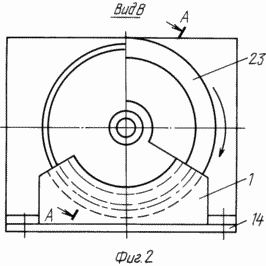 FIG. 2 - view along arrow B in Figure 1 |
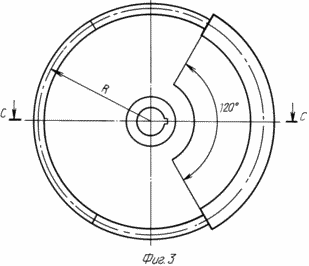 3 - wheel with electromagnets |
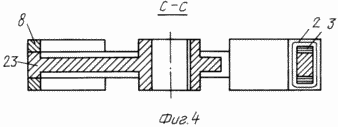 FIG. 4 - sectional view C-C of Figure 3 |
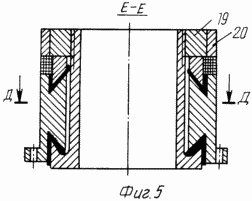 5 - collector, EE section; 6 |
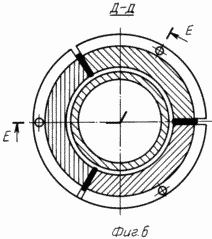 FIG. 6 - A sectional view at D-5 |
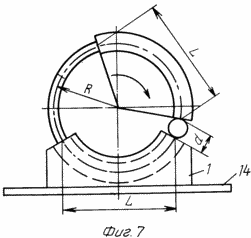 7 - on the basis of an inductor |
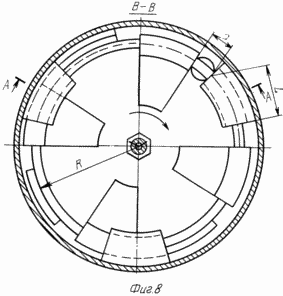 8 - housing with vertically positioned shaft |
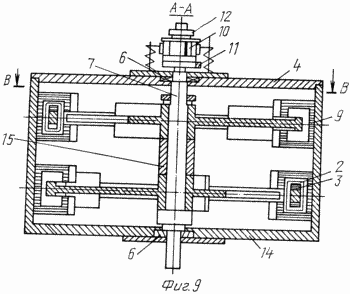 9 - Section B-B in Figure 8 | |
The electromagnetic motor comprises a housing (cylinder) and / or base 14, at least one fixed part arranged in the form of an inductor 9, at least one rotary portion including manifold 10, through electrobrushes 11, 13 connected to the source voltage (conventionally not shown), and the PTO shaft 7.
Inductor 9 is in the form of individual segments of one of the electrical steel, mounted on the base 14 of aluminum alloy rotary part is formed as a planted on the shaft 7 of the wheels 23 to the electromagnets 2, mounted with the possibility of alternately interacting with an inductor (inductors) 9, a shaft mounted in 6 two bearings on brackets 24, and two electromagnets connected to a voltage source via a collector 10 mounted on the shaft 7 (Figure 1).
The shaft may be positioned in the hollow body, the cylinder 14 in a vertical plane and its bearings 6 - arranged in the cylinder base and in the lid 4 (8, 9). Wheels provided with three (or more) 2 and the electromagnets are mounted rotatably in the horizontal plane and to engage its two electromagnets with two or more inductors 9 fixed to the inner surface of the cylinder.
Manifold 10 is provided with copper plates in an amount equal to the number of electromagnets 2 on all four wheels 23, and the number exceeds the number of inductors electrobrushes 9 provided for one wheel, one minus Electrobrushes. There is a balance weight 8 at each wheel 23, the spacers 15, the nuts 12, 19.
1 is an electromagnetic motor. On the shaft 7 is rigidly secured a wheel 23 with three electromagnets 2. The wheel 23 is made of aluminum alloy or titanium. On the rim of the wheel in a sector of 120 degrees naklepyvaetsya sheet electrical steel core 3, and then an insulating layer is applied and the wound wire - an electromagnet 2. On the opposite side of the wheel rim is attached balance weight 8 of the anti-magnetic material. Keyways in the wheels are offset by 120 o. Wheels 23 are planted on the shaft 7 through spacers 15 and then a collector 10 is set and is pressed against the nut 12. Thus, electromagnets wheels offset from each other by 120 o.
The manifold 10 (FIGS. 5, 6) has three copper plate segment 120 o, isolated from each other. Each segment is connected to one end of the electromagnet winding 23. The second wheel 2 electromagnet winding end 2 is connected with the wheel housing 23. The DC voltage supply 10, the collector is made from the source through the electro 11, 13. The copper ring 20 is pressed onto the nut 19 and is connected to it through housing 14.
Based on 14 (fig.1,2,7) three fixed inductor 9, separately for each wheel. Inductor 9 is a cross-sectional letter "C", but with right angles, and along the rim 23 occupies 120 o. As the wheel rotates freely electromagnet housing 23, with a minimum clearance must be included inside the inductor 9 and the disk or spoke wheels must pass freely through the section of the letter "C" of the inductor. When installing the reservoir 10 must take into account the location of the electromagnets 2 relative to inductors 9. If, referring to the drawings, assume that the arrangement of the wheels from left to right (Figure 1), and rotating, as indicated by arrow (1, 7), the brush contact 13 with a copper manifold segment 10, which is connected to the first electromagnet wheels, must occur before the value for the diameter "d" (Figure 7) of the solenoid coil of the solenoid-2 than its end face fit to the end nearest the inductor, and the brush contact 13 with a copper manifold segment 10, an electromagnet which is connected to the second wheel 2 must be interrupted before the first end during rotation equals the second end of the second inducer wheel. This can be achieved by increasing or decreasing the width of the brush 13 and turning around the axis of the inductor 10.
Thus, based on the principle of the electromagnetic motor to retract the solenoid inductor.
By changing the radius "R" wheels or parameters affecting the magnetic moment of the solenoid, solenoid, can change the motor torque and thus affect its output.
FIG. 8 and 9 shows an embodiment of an engine with two wheels mounted on a vertical shaft bearings 6 and 7 at the bottom-the cylinder body 14 and a cover 4. Each wheel 23 has four electromagnets 2 and three inductors 9 which are fixed on the inner walls of the cylinder 14 and spaced circumferentially by 120 o. Wheels 23 mounted one above the other keyed connection. Keyways in the wheels offset from each other and must be on a diametrical line of symmetry of one wheel passing through the center of the electromagnet and the other - through the middle of the gap between the electromagnets. The collector 10 has eight isolated from each other and each odd plates plate is connected to one end of the electromagnet winding upper wheel, and each even plate is connected to one end of the electromagnet coil of the lower wheel. Eight harness wires passed through the axial bore of the shaft, while the wheel hubs - are derived through the radial holes to the electromagnets. The second ends of the winding electromagnets connected with the housing. The DC voltage is supplied through the three electro 13, which relate to the collector plates 10 and are arranged in a circle 120 o against inductors 9. The second pole of the DC voltage is applied across the electro 11, which deals with the copper ring 20 and the collector is connected to the body. A motor works similarly to the above (FIG. 9). Electromagnets during rotation of the wheels must be connected to the source voltage through electro at the time when the electromagnet is closer to the end of the inductor for a distance equal to the average diameter of the coil of the electromagnet-solenoid. At this distance the electromagnetic field begins to interact with the inductor and electromagnet will be involved in the inductor; when the electromagnet is fully seated in the inductor, the contact brush 13, belonging to one of the inductors must be interrupted with a copper plate collector is connected to the electromagnet. This can be achieved by rotating the collector and selecting the width of the brush (the brush). Thus, all the upper and lower electromagnets in one revolution of the wheels will pass through all of the inductors.
The electromagnetic motor makes it possible to achieve significant speeds and with simplification of manufacturing technology provides increased efficiency.
CLAIM
An electromagnetic motor comprising a housing and / or base of at least one fixed part arranged in the form of an inductor, at least one rotating part, comprising collector means electrobrushes connected to a voltage source, and the PTO shaft, characterized in that the inductor is in the form of individual segments of the electrical steel, fixed on the ground, made of an aluminum alloy rotary part is formed as a planted on the wheel shaft with electromagnets mounted with the possibility of alternately interacting with an inductor, a shaft mounted in bearings on the two brackets, and the electromagnets are connected to a voltage source through a collector mounted on the shaft.
An engine according to claim 1, characterized in that the shaft housed in the hollow cylinder in the vertical plane, and its bearings are located in the base of the cylinder and the lid.
An engine according to claim 2, characterized in that the wheels are provided with three or more electromagnets and rotatably in a horizontal plane and to engage its electromagnets with two or more inductors, fixed on the inner surface of the cylinder.
Engine according to any one of claims 1-3, characterized in that the collector is provided with copper plates in an amount equal to the number of electromagnets on all wheels.
Engine according to any one of claims 1-4, characterized in that it is provided with electro in excess of the number of inductor established for one wheel, one minus Electrobrushes.
print version
Publication date 28.12.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.