| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current models of the invention and / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2249701
Internal combustion engine shakes rotary pistons
![]()
Name of applicant: Lipnevenko Valentin A. (UA); Lukyanov Margarita Valentinovna (UA)
Name of the inventor: Lipnevenko Valentin A. (UA); Lukyanov Margarita Valentinovna (UA)
The name of the patentee: Lipnevenko Valentin A. (UA); Lukyanov Margarita Valentinovna (UA)
Address for correspondence: 91050, Lugansk, st. Training, 4a, JSC "Institute" Spetsavtomatika "VA Lipnevenko
Starting date of the patent: 2003.07.21
The invention relates to mechanical engineering, namely to engines with oscillating working elements. The technical result is to increase the efficiency of the engine. The invention consists in the fact that the engine includes a housing 1 formed in the annular working chamber therein two vortex chambers 39 and 40 made in the partition walls 9, 10. On the input shaft 8 mounted oscillating rotary piston 7 of magnetically hard material having hub 30 with blades 28, 29 forming two working with partitions 33, 34 and two injectors 35, 36 of the cavity. drive rotor-piston mechanism includes a crank mechanism. According to the invention the body 1 of the engine is arranged diametrically oppositely located grooves 51, 52 are T-shaped, inside which are placed the rods 53, 54 of the electrical steel with the windings 55, 56 in contact with the inner surface embracing their plate 57 of the electrical steel C-shaped form. The partitions 9, 10 are radial grooves 43, 44 having access to the swirl chamber 39, 40. The center electrodes 45, 46 candles strengthened in the partitions 9, 10 and entered into the swirl chamber 39, 40. This will provide a simple means of expanding the functional capabilities , increasing engine efficiency and increase engine reliability in operation.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to mechanical engineering, in particular engine building, namely to engines with oscillating working elements.
Known rotary internal combustion engine comprising a housing having an annular working chamber coaxial output shafts mounted with the blades forming the annular chamber four working and injection / outside / cavity, the output shaft and drive mechanism of the blades mounted on the drive shafts kinematically connecting them the output shaft and including a pinion mounted rigidly on the housing coaxially with the working shafts, crank assemblies provided with gears, pinions and sliders mounted mutually-opposed and kinematically connected to the output shaft, the gears are engaged with the fixed gear fixed on the housing, and slides in the slots are cross installed on drive shafts. To improve the reliability of the rotary engine output shaft and a drive mechanism provided with pinions, meshing, the gear drive mechanism has an inner spokes on drive shafts mounted toothed sectors meshing with which there are bevel gears mounted on the spokes and connected rigidly with torsion springs, the working rollers are provided angular velocity stabilization mechanism comprising two rocker arms interconnected by springs and provided with rollers, and the profiled cam mounted pivotably on the machine housing and provided with a handle to rotate. / See. A.s.SSSR №1442683 "The rotary internal combustion engine", IPC 7 F 02 B 53/00, 12/07/88, the /
A disadvantage of this engine is the complexity of its design, the drive mechanism caused by the presence of the blades, the two crank mechanisms and the mechanism for stabilizing the angular velocity.
Execution and working of injection cavities and auxiliary working blades rotating blades require different speeds of the mechanisms of the system and hence require additional power consumption, which reduces the efficiency / efficiency / motor.
The lack of effective exhaust purging process results in a lower quality of the incoming fuel mixture due to mixing it with the exhaust gas residues.
These shortcomings partly eliminated in the "two-stroke internal combustion engine with oscillating rotor-piston" comprising a cylindrical, closed on both sides of the cover 4, casing 5 1 / Carter / forming an annular working chamber, which is set in the middle of the input shaft 3 /fig.1 / oscillating rotor-piston 6, in the hub is a recess 17, segmental baffle 7 attached to the housing 1 by bolts 10, 11, the alternator / ignition device / 43, and channels for feeding the fuel mixture 18 and for discharging the exhaust gases 19, which are closed and opened blade 22 oscillating-piston rotor. On the shaft 3 is attached a crank /fig.3/ 23 / lever / connecting rod 25 which is connected by a crank 26 mounted on the output shaft 27. In housing 1 near the partition segment 7 is a spark plug 16, and between the piston 6 and set seals 12, 13, 14, 15. / See. German patent №3811760 "The two-stroke internal combustion engine with oscillating rotor-piston," IPC 7 F 02 B 53/00, F 01 C 9/00, 01.06.89 g / .
A disadvantage of this engine is that it has a rotor-piston with a single blade, which is divided by a partition with an annular working chamber into two cavities, one injector and one working. This leads to the fact that the return of the piston-rotor BDC / NMT / BTDC / TDC / additional power required for rotating the output shaft, reducing engine efficiency.
When the swing piston-rotor imbalance due to its frictional forces arise, causing wear of the shaft bearings, housing, rotor vane-piston engine and a reduction in operation reliability.
The presence of the alternator side of the body increases the motor size and the complexity of its construction.
Known and "Internal combustion engine with oscillating rotor-piston" which is the closest analogue-prototype of the claimed invention. For a prototype accepted by an internal combustion engine, comprising a cylindrical housing 7 /fig.1 2 / s channels to cool and set in it nozzles 21 /fig.1 - variant of the diesel engine / or two spark plugs 22 /fig.2 - engine option " Otto "/. The main body of the engine 7 /fig.2/ provided for supplying a combustible mixture inlet duct 25 and to exhaust an exhaust outlet duct 26. Inside the housing 7 on the working shaft 10 mounted oscillating rotary piston 8 / anchor / two blades and fixed rigidly with the inside of his hand in front of the nozzles 21 /fig.1/ and in the place of installation of spark plugs 22 /fig.2/ partitions 27 / transitions /. Rotor-piston 8 and the partition 27 divide the annular working chamber defined by the housing 7 by four variable-volume cavity size, two of which discharge chamber 23 and two working cavities 24. To the overflow fuel mixture in the working chamber 24 in the hub of the oscillating-piston rotor 8 a recess 9 /fig.1, 2 /. The rigid partitions 27 are swirl chamber 20 /fig.1 - a variant of the diesel engine /, which will arrive in a combustible mixture of the working cavity will be compressed and with a strong twist to thicken due to the rotating movement of the oscillating-piston rotor 8. Inside the rotor-piston 8 and the output shaft of the engine 11 for lubrication and cooling channels 18 formed /fig.1, 2, 3 /. For lubrication of the pump through the holes 29. The spring are coil springs ceramic seal rings 17 and 16 are located on the rotor blades 8-piston and the partitions 27. At the crank shaft 10 and the crank shaft 12 is a rod / bar / /fig.3 13, 4 / converting the rocking movement of the shaft 10 into rotational movement of the shaft 12 on which the pinion 15 /fig.5/ meshed with the pinion 14 is fitted on the shaft 11 which is movably disposed within the hollow shaft 10 fixedly mounted thereon a rotor-piston 8. All of the above constitutes a drive mechanism for the blades. When starting the engine, for example, the starter shaft 11 is rotated /fig.3 4 / which transmits rotation through gears 14, 15, crank shaft 12, and it is through the connecting rod 13 and crank shaft 10 transmits oscillating motion to the rotor-piston 8, whereby internal combustion engine / ICE / starts. After starting the engine intake fuel mixture occurs in the working cavity 24 /fig.1/ which occurs as a result of compression and ignition of the combustible mixture of gases formed by the action of the swing piston-rotor 8. From 8 rotor-piston oscillates crank shaft 10 is passed, which passes movement of the connecting rod 13, resulting in the rotation of the crank shaft 12. on the shaft 12 through the gear 15 and gear 14 is transferred to the rotation shaft 11. in order to balance the crank shaft 12, it is set opposed to 19, and 11 mounted on the shaft-flywheel gear 14. / See. German application №3725277, IPC 7 F 01 C 9/00, F 02 B 53/00, 09.02.89 g /
A disadvantage is the complicated construction of the engine drive mechanism blades if it contains a system of shafts and gears, which reduces the reliability of the engine during operation.
The design of the motor housing does not allow its use as an alternator to generate discharge between the electrodes of the spark plugs, and the need for further engine driven generator. This leads to the complexity of the design, the engine and reduce its reliability in operation.
No communication swirls chambers with recesses in the hub of the rotor-piston does not allow entry of compressed fuel-air mixture injection into cavities swirl chamber and eliminate the formation therein of CO exhaust gas residues, which reduces engine efficiency.
Lack eye observation does not allow visual control of the quality and composition of the combustible mixture combustion in the working chamber, which reduces the reliability of the engine during operation.
blades drive design does not allow him to change the compression ratio of the combustible mixture in the working cavity of the engine, thereby eliminating the operation of the engine at various grades of fuel, which does not allow to expand the range of fuel used and reduces the functional capabilities of the engine.
The design and location of the spark plugs of the electrodes outside the chamber requires a further twist of the distributor of ignition with the breaker and its drive to provide only one category for the ignition of the combustible mixture. This leads to structural complexity, reduced reliability in operation of the engine in the carburetor embodiment.
The claimed technical solution is aimed at simplifying the design of the engine in order to facilitate its production, expanding the opportunities for the application of the engine for different nomenclature fuel and improving its performance.
The technical result of the use of the invention is to reduce the number of electrical devices to drive in the expanding functionality by changing the compression ratio of the combustible mixture in the engine operating cavities, increasing the efficiency of the engine by removing the exhaust gas residues from the camera twists and engine working cavities and improving the reliability of the engine when operation by increasing the number of bits of the spark plugs.
The invention consists in that in an internal combustion engine with oscillating rotor-piston, comprising a housing having formed therein an annular working chamber, bounded on the end faces end caps, which are arranged rigidly fixed to the housing walls with cameras swirls, and the input shaft is installed the rotary piston having a hub with overflow recesses for the combustible mixture and at least two blades defining two working with baffles and discharge cavity connected to the housing of the spark plug, the fuel mixture inlet window and the exhaust placed on the input shaft and rotore- piston lubricant cooling channels, and the mechanism drive-piston rotor mounted on two parallel shafts and comprising a crank mechanism, the motor housing is formed with diametrically oppositely disposed grooves of T-shaped, inside which are placed rods with coils in contact with the inner surface covering of plate C-shape having a hollow in the middle portion of the spark plug, in which the rods are made channels for their cooling and winding, the channels of the supply and removal of the plate, and in partitions, radial grooves having access to the swirl chamber, in front of which are located viewing window formed on one of the side covers the housing, wherein a crank mechanism for driving the rotor-piston installed on the output shaft, a groove in which is movably disposed along the axis of the finger of the crank, and the spark plugs are made with the central electrodes strengthened in the septa housing, and electrodes introduced into the swirl chamber opposite electrodes which are disposed on opposite sides of one of the blades, the piston rotor perpendicular to its lateral surfaces with a gap "a" between the outer diameter of the threaded ends of these electrodes and the central electrode spark ignition at a height H determined from the expression
H = h + h 1 = h + L · tg ![]() where
where
h - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to the lateral surface of the blade; h 1 - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to a threaded end of the electrode; L - the distance from the vertical axis of the rotor-piston to the screw axis of the electrode; ![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston spark advance before TDC or BDC / upper or lower dead point /.
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston spark advance before TDC or BDC / upper or lower dead point /.
Rotor-piston engine is made of hard magnetic material having a radial magnetization direction relative to its axis of oscillation, a housing cover and the input shaft - a non-magnetic material and housing parts, plates and rods - electrical steel. The groove in the piston-crank drive mechanism for the rotor is made oval in shape, and its length l is chosen from the condition of the piston rotation-angle rotor at ![]() and it is determined from the expression
and it is determined from the expression
![]()
where S - the path traversed by the rotor-piston when turning at an angle ![]() Defined chord; R - the radius of the crank installation on the output shaft; d pal.kr. - The diameter of the crank pin;
Defined chord; R - the radius of the crank installation on the output shaft; d pal.kr. - The diameter of the crank pin; ![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank.
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank.
To provide adequate clearance "a" between the central screw and the spark plug electrodes mounted adjusting rings, which are arranged between the housing and the spark plugs.
Running casing diametrically oppositely disposed grooves of T-shaped, inside which are placed rods with coils in contact with the inner surface embracing their plate C-shape having a hollow in the middle portion of the spark plug or injector in rods channels for cooling them and windings that are connected with channels for supplying and removing the plate and the execution cores and the electrical steel plate allows the housing interacting with the rotor-piston, made of a hard magnetic material as the alternator cooling its winding, which simplifies engine design by additional generator driven exceptions and ensures its reliability in operation.
Performing in the partitions of the radial slots having access to the camera swirls, allows entry of the combustible mixture from the injection cavity of the working chamber in the camera swirls and out in the working space of the working chamber with the exhaust gases, to thrust them completely in the outlet box, and filling them with the regular portion of the combustible mixture that eliminates the formation of CO exhaust gas residues in the swirl chambers and working spaces, and increases engine efficiency.
Running on one of the side covers of the housing viewing window located in front of the cameras swirl allows without special devices to produce a visual control of the amount of bits on the spark plugs, the quality of the composition and the combustion of the combustible mixture for the color of its flash that when using flexible optical fibers with the diaphragm is used for the direction indicators alarm or other vehicle, which increases the reliability of engine operation and simplifies the design of the vehicle.
Performance of the crank drive-piston rotor mechanism mounted on the output shaft groove oval, which is movable along the axis of crankpin allows to change the radius of the installation of the crank respectively through a connecting rod and crank of the input shaft to change the path S, traversed by the rotor -porshnem when turning at an angle ![]() Defined by a chord, and a compression ratio of the combustible mixture in the engine operating cavities. l The length of the groove is chosen from the condition of the piston-rotation of the rotor at an angle
Defined by a chord, and a compression ratio of the combustible mixture in the engine operating cavities. l The length of the groove is chosen from the condition of the piston-rotation of the rotor at an angle ![]() and it is determined from the expression
and it is determined from the expression
![]()
where S - the path traversed by the rotor-piston when turning at an angle ![]() Defined chord; R - the radius of the crank installation on the output shaft; d pal.kr. - The diameter of the crank pin;
Defined chord; R - the radius of the crank installation on the output shaft; d pal.kr. - The diameter of the crank pin; ![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank. This allows you to extend the functionality of the engine and to ensure operation of the engine at different fuel grades.
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank. This allows you to extend the functionality of the engine and to ensure operation of the engine at different fuel grades.
Performing the spark plug electrodes with a central, strengthening them in the partitions body through adjusting ring with electrodes introduced into the chamber opposite the swirl of threaded electrodes enables multiple ignition of the fuel mixture in the chambers swirls, reduce the level of carbon monoxide in the exhaust gases and enhance engine efficiency. In addition, at a suitable pressure and compression can replace the spark plugs on the fuel injector to be converted into diesel variant that enhances the functionality of the engine performance.
Set screw electrodes on opposite sides of one of the rotor blades, the piston perpendicular to its lateral surfaces with a gap "a" between the outer diameter of the threaded ends of these central electrodes and spark plug electrodes at a height H determined from the expression
H = h + h 1 = h + L · tg ![]() .
.
where h - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to the lateral surface of the blade; h 1 - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to a threaded end of the electrode; L - the distance from the vertical axis of the rotor-piston to the screw axis of the electrode; ![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston spark advance before TDC or BDC / upper or lower dead point /, provides a number of bits equal to the number of threads of electrodes with the piston-rotation of the rotor at an angle
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston spark advance before TDC or BDC / upper or lower dead point /, provides a number of bits equal to the number of threads of electrodes with the piston-rotation of the rotor at an angle ![]() . Such increase of the spark plug discharges can improve the reliability and working mixture ignition engine during operation.
. Such increase of the spark plug discharges can improve the reliability and working mixture ignition engine during operation.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
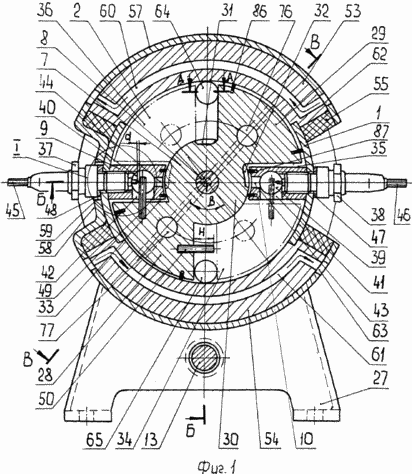
Figure 1 shows a general view of the engine, the transverse incision
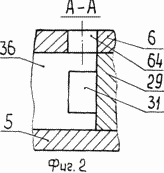
2 - section A-A in Figure 1
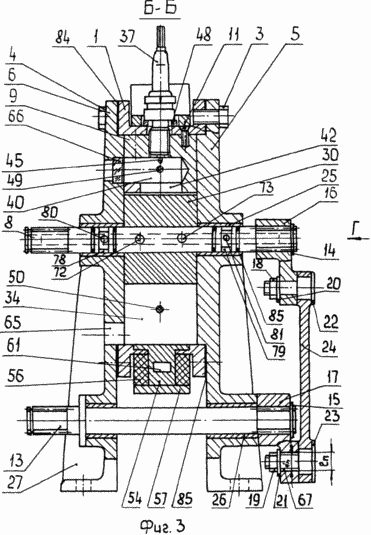 3 - a longitudinal section B-B in Figure 1 |
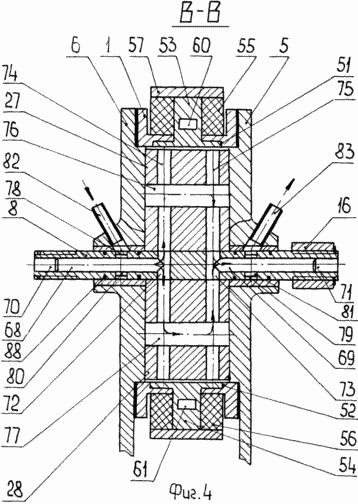 4 - a longitudinal section B-B in Figure 1 |
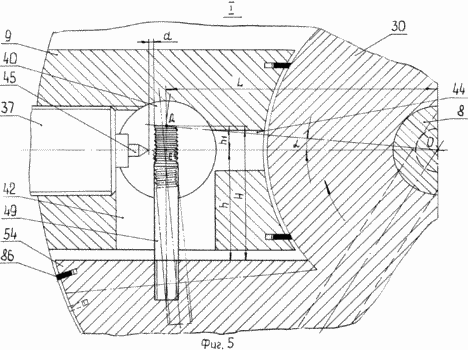
5 - assembly T in Figure 1 on an enlarged scale
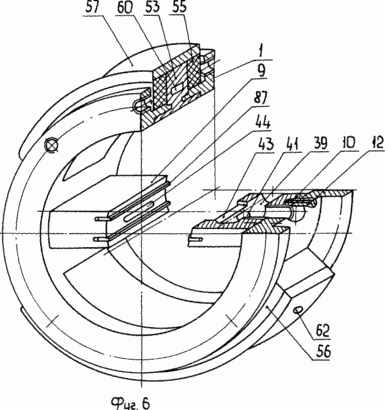
6 - the motor housing in perspective
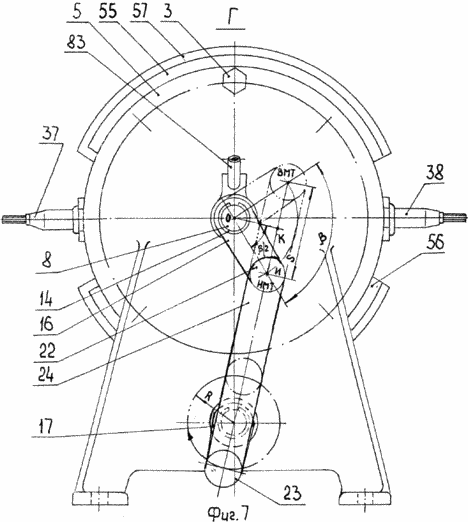
7 - D view Figure 3 - action diagram of a crank mechanism
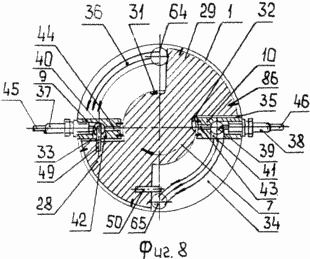 8 - position rotor blades-piston when turning on ygol |
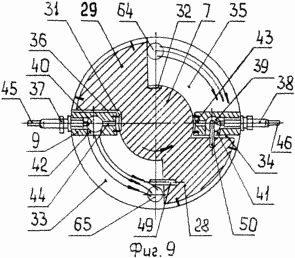 9 - the position of the piston-blade rotor as it rotates through the angle |
Internal combustion engine with oscillating rotor-piston comprises a body /fig.1 1, 3, 4, 6 / with the annular working chamber 2 formed therein, bounded on the ends attached thereto by means of bolts 3, 4, side covers 5, 6, rocker rotary piston 7 mounted in the chamber at the input spline shaft 8 partitions 9, 10 are attached by bolts 11, 12 to the inner cylindrical surface of the housing and drive mechanism, the piston rotor which comprises two shafts - the oscillating input spline shaft 8 and the rotary output splined shaft 13, which is splined to the right fixed spring washers 14, 15, cranks 16, 17, which are fixed with nuts 18 and washers 19, 20, 21, fingers 22, 23 through which the cranks are pivotally connected to a connecting rod 24.
8 and 13, Shafts /fig.3/ have slots on both sides and mounted in slide bearings 25, 26 housed in holes caps 5, 6 are at the bottom provided with legs 27 for supporting the engine mount. Splined end of the output shaft 13 and the input shaft 8 on the left side is used to transmit user and oscillating rotational movements. Rotor-piston /fig.1 7, 8, 9 / is in the form of two blades 28, 29 with the hub 30, which is formed on the recess 31, 32 for the overflow of the combustible mixture. The working chamber 2 blades 28, 29 and the partitions 9, 10 is divided into two working 33, 34 and two injectors 35, 36 with a variable volume cavity size and contains a spark plug 37, injector 38, or variant of diesel / not shown /. Partitions 9, 10 have a chamber swirls 39, 40 with openings 41, 42 for the exit of the compressed fuel-air mixture, and they are made radial grooves 43, 44 that connect the chambers swirls with the recesses 31, 32 of the hub 30 of the rotor-piston 7 to enter the combustible mixture of injection cavities 35 and 36.
Spark plugs 37, 38 /fig.1 5 / formed with the central electrodes 45 and 46 are set through the adjustment ring 47, holes 48 in walls 9, 10 with the placement of electrodes in vortex chambers 39, 40 opposite the threaded electrodes 49, 50 for spark ignition. Adjustment ring 47, 48 which serve simultaneously seal disposed between the housing 1 and the spark plugs 37, 38.
Threaded electrodes 49, 50 are mounted on opposite sides of the blade 28 of the piston rotor 7 perpendicular to its lateral surfaces with a gap "a" between the outer diameter of the threaded ends of these electrodes and the central electrodes 45, 46 of the spark plugs 37, 38 at a height H determined from the expression
H = h + h 1 = h + L · tg ![]() .
.
where h - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to the lateral surface of the blade; h 1 - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to a threaded end of the electrode; L - the distance from the vertical axis of the rotor-piston to the screw axis of the electrode; ![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston ignition timing before TDC or BDC. The size of the gap "a" is regulated by the rings 47, 48. The value of h 1 = L · tg is determined from the triangle OGE /fig.5/, the angle value
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston ignition timing before TDC or BDC. The size of the gap "a" is regulated by the rings 47, 48. The value of h 1 = L · tg is determined from the triangle OGE /fig.5/, the angle value ![]() 5 ° -7 °, and the clearance "a" of 0.5-0.8 mm according to the data received and to adjust the vehicle control. /Cm. "The device, VAZ-2105 car service, VAZ-2104, VAZ-2107 and other authors V.A.Vershigora. Moscow," Patriot ", 1990, p.17 /.
5 ° -7 °, and the clearance "a" of 0.5-0.8 mm according to the data received and to adjust the vehicle control. /Cm. "The device, VAZ-2105 car service, VAZ-2104, VAZ-2107 and other authors V.A.Vershigora. Moscow," Patriot ", 1990, p.17 /.
Cylindrical housing /fig.1 1, 4, 6 / is arranged diametrically oppositely located grooves 51, 52 are T-shaped, which are placed rods 53, 54 arranged on them with coils 55, 56 in contact with the inner surface of the plate mounted on them 57 C-shaped with a cavity 58 with an opening 59 at a middle portion of the spark 37 which plays the role of the magnetic circuit. To cool the windings 55, 56 in the rods 53, 54 are channels 60, 61 and 57 in the plate 62 two channels 63 and two channels for the supply and discharge of coolant.
Rotor-piston 7 is made of a hard magnetic material having a radial magnetization direction relative to its axis of oscillation, the housing 1, the cover 5, 6 and the input shaft 8 from a non-magnetic material and housing parts - a plate 57 and rods 53, 54 - of electrical steel.
Such a body structure 1 and-piston rotor 7a and the material from which they are made, allows their use as a stator and the rotor of the alternator, generating its own electricity to create electrical discharge between the electrodes 45, 46 and 49, 50, providing work an internal combustion engine.
The side cover 6 of the housing 1 holds the window 64 for supplying the fuel mixture and a window 65 for the exhaust gas exhaust, and two viewing windows and 66 of heat-resistant glass, placed in front of the cameras twists 39, 40.
The crank drive 17 /fig.3/ rotor-piston mechanism 7 is oval groove 67 in which is movably disposed along the axis of the finger 23 allows to provide a range of swing of the rotor-piston 7 and, correspondingly varying the compression ratio of the combustible mixture in the vortex chambers 39, 40 depending on its length. The length l of the groove is selected from a rotor-rotation conditions of the piston 7 at an angle ![]() and it is determined from the expression
and it is determined from the expression
![]()
where S - the path traversed by the rotor-piston when turning at an angle ![]() Defined chord; d pal.kr. - The diameter of the crank pin; R - the radius of the crank installation on the output shaft;
Defined chord; d pal.kr. - The diameter of the crank pin; R - the radius of the crank installation on the output shaft; ![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank. Value
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank. Value ![]() determined from the triangle DEC /fig.7/, the angle value
determined from the triangle DEC /fig.7/, the angle value ![]() 90 ° -100 ° and the radius R of the crank made according to the degree of compression in its scale, ad pal.kr. paven groove width.
90 ° -100 ° and the radius R of the crank made according to the degree of compression in its scale, ad pal.kr. paven groove width.
Therefore, for use in the engine of different fuel grades is necessary to change in the compression ratio of the combustible mixture in the chambers twists 39, 40, which is achieved by changing the angle of rotation of the oscillating-piston rotor 7 before TDC or BDC and the radius R installation crank 17 on the output shaft 13 by moving his fingertip 23 in the groove 67.
Location of the spark plugs 37 in the openings 38 of partitions 9, 10 and their connection electrodes 45, 46 with the swirl chambers 39, 40 allows them to replace the fuel injection nozzle and converted into diesel variant.
For cooling and lubrication of the piston-rotor 7 /fig.4/ oil pump / not shown / in the input shaft 8 from both sides met longitudinal channels 68, 69 with installed plugs 70, 71, connected to the holes 72, 73 with through radial channels 74, 75 made in the rotor-piston 7 which is communicated between the elongated holes 76, 77. The input shaft 8 on the installation site in slide bearings 25 are annular grooves 78, 79 with radial holes 80, 81, providing communication with the nozzles 82, 83 mounted in the covers 5, 6.
To ensure the tightness of the engine body 1 /fig.1, 3, 4 / is connected to the lid 5, 6 through a gasket 84, 85, and 28 on the blades 29 of the rotor-piston 7 and the partitions 9, 10 are spring-loaded plates 86, 87 and input shaft 8 - O-rings 88.
The engine runs on two-stroke cycle follows. When starting the motor shaft 13 of the starter reported rotational movement which is converted in the drive mechanism and rocking transmitted to input shaft 8 and the rotor-piston 7 to rotate through an angle ![]() / Start system is not shown /.
/ Start system is not shown /.
When the rotor-piston motion 7 /fig.8/ clockwise from TDC to BDC is compressed combustible mixture in the working chamber 33 and swirl chamber 40 with the discharge chamber 36 in discharge occurs, the carburetor 64 and the window / not shown / it enters the fuel mixture in the discharge chamber 35 compresses the combustible mixture, and then through the recess 32 in the hub 30 of the piston rotor 7 and the radial groove 43, it enters the swirl chamber 39, carrying out purging exhaust gases through the aperture 41 into the working cavity 34 and a window 65 and filling the cavity with a fresh charge of combustible mixture.
Ignition of the combustible mixture in the swirl chamber 40 occurs at the moment of coincidence of the central electrode 45 of the spark plug 37 with the first coil electrode 49 thread by turning the rotor-piston 7 on the initial angle ![]() ignition timing. The number of bits is equal to the number of threads of the electrode 49 coinciding with the central electrode 45 by turning-on the piston rotor angle
ignition timing. The number of bits is equal to the number of threads of the electrode 49 coinciding with the central electrode 45 by turning-on the piston rotor angle ![]() .
.
When the rotor-piston motion 7 /fig.1 6 / it interacts with the rods 53, 54 and plate 57 to form in the windings 55, 56 of alternating electric current to the coil through the high-voltage / not illustrated / are used to create an electrical discharge between the electrodes 45, 46 and 49, 50 and the needs of the vehicle.
After ignition of the fuel in the working chamber 33 /fig.8/ rotary piston 7 performs /fig.9/ counterclockwise motion from BDC to TDC, wherein the combustible mixture is compressed in the working chamber 34 and swirl chamber 39 and a discharge cavity 35 occurs vacuum, and through the window 64 from the carburetor into it enters the fuel mixture in the discharge chamber 36 compresses the combustible mixture, and then through the recess 31 in the hub 30 of the piston rotor 7 and the radial groove 44, it enters the chamber swirls 40, carrying venting exhaust gases through the aperture 42 into the working cavity 33 and the window 65 and filling the cavity with a fresh charge of combustible mixture.
Ignition of the combustible mixture in the swirl chamber 39 occurs at the moment of coincidence of the central electrode 46 of the spark plug 38 with the first coil electrode thread 50 by rotating the rotor-piston 7 at an angle ![]() . When the engine cooling /fig.1/ body 1, the rods 53, 54, windings 55, 56 and the plate 57 flows through coolant channels 62, 63 into the channels 60, 61.
. When the engine cooling /fig.1/ body 1, the rods 53, 54, windings 55, 56 and the plate 57 flows through coolant channels 62, 63 into the channels 60, 61.
For cooling and lubrication of the rotor-piston 7 /fig.4/ coolant enters the nozzle 82 through the holes 80 into the longitudinal channel 68 and the input shaft 8 through the through hole 72 in the radial passage 74, then through the slots 76, 77 in the groove channel 75 and through opening 73 into the longitudinal bore 69 of the shaft 8 and then through the hole 81 in the tube 83.
When the engine rebuilding to different brand of fuel and generate permutation fixing with the nuts 19 /fig.3, 7 /, finger 23 in the groove 67 of the crank 17 on the scale / not shown / located on this crank. Digital calibration of the scale corresponds to the degree of compression used fuel grades.
The proposed internal combustion engine with oscillating-piston rotor is easy to manufacture and use, and it can be used with different nomenclature and diesel fuels embodiment. In addition, the motor is reliable in operation, can increase the efficiency and provide better performance.
CLAIM
1. Internal combustion engine with oscillating rotor-piston, comprising a housing having formed therein an annular working chamber bounded by the ends with side covers, in which there are rigidly secured to the housing walls with swirl chambers, and installed on the input shaft of the rotary piston having a hub with overflow recesses for the combustible mixture and at least two blades defining two working with baffles and discharge cavity connected to the housing of the spark plug, the fuel mixture inlet window and the exhaust placed on the input shaft and the rotor-piston, lubricant cooling channels, and the mechanism drive-piston rotor mounted on two parallel shafts and comprising a crank mechanism, wherein the motor housing is formed with diametrically oppositely disposed grooves of T-shaped, inside which are placed rods with coils in contact with the inner surface covering of plate C-shape having a hollow in the middle portion of the spark plug, in which the rods are made channels for their cooling and winding, the channels of the supply and removal of the plate, and baffles - radial grooves having access to the swirl chamber , opposite which there are inspection holes formed on one of the side housing covers, while in the crank drive-piston rotor mechanism mounted on the output shaft, a groove in which is movably disposed along the axis of the crank pin, the spark ignition is performed with central electrodes are reinforced in the septa housing and electrodes introduced into the swirl chamber opposite threaded electrodes, which are mounted on opposite sides of one of the blades, the piston rotor perpendicular to its lateral surfaces with a gap "a" between the outer diameter of the threaded ends of these electrodes and the central electrode of the spark plugs at a height H determined from the expression
H = h + h 1 = h + L · tg ![]() .
.
where h - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to the lateral surface of the blade;
h 1 - height of the horizontal piston-rotor axis to a threaded end of the electrode;
L - the distance from the vertical axis of the rotor-piston to the screw axis of the electrode;
![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston ignition timing before TDC or BDC.
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston ignition timing before TDC or BDC.
2. The engine of claim 1, characterized in that the rotary piston is made of a hard magnetic material having a radial magnetization direction relative to its axis of oscillation, a housing cover and the input shaft of a non-magnetic material and housing parts, and a plate of electrical steel rods .
3. The engine of claim 1, wherein the groove in the piston-crank drive mechanism for the rotor is made oval in shape and its length l is chosen from the condition of the piston rotation-angle rotor at ![]() and it is determined from the expression
and it is determined from the expression
![]()
where S - the path traversed by the rotor-piston when turning at an angle ![]() Defined chord;
Defined chord;
R - the radius of the crank installation on the output shaft;
pal.kr d - diameter of the crank pin;
![]() - Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank.
- Angle of rotation of the rotor-piston when moving the finger in the groove of the crank.
4. An engine according to claim 1, characterized in that to provide the required clearance "a" between the central screw and the spark plug electrodes mounted adjusting ring between the housing and the spark plugs.
print version
Publication date 28.12.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.