| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current inventions and models / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2130684
VAMAS-MOVERNER
![]()
The applicant's name: Egorov-Kuzmin Alexander Stepanovich; Chaykina Valentina Mikhailovna
The name of the inventor: Egorov-Kuzmin Alexander Stepanovich; Chaykina Valentina Mikhailovna
The name of the patentee: Egorov-Kuzmin Alexander Stepanovich; Chaykina Valentina Mikhailovna
Address for correspondence: 129626, Moscow, Prospect Mira 112-262, Chaykina V.M.
Date of commencement of the patent: 1997.05.20
Usage: to communicate direct traction and movement in any given direction to various electrified transport objects, such as a tram, trolley, electric locomotive, battery car, leading cars of electric trains, subway, surface and submarine vessels, and and aircraft. The propeller consists of an armature with a working winding of a loop or wave type of an inductor, with an alternating magnetic polarity of the poles. The anchor and inductor are made flat and mechanically firmly connected to each other and to the traction object. When a direct current flows through the working winding of a VAMAS propulsor, a resultant Ampère force is produced in it, pulling the winding, and with it a thrust object in the chosen direction. At the same time there is no need for power motors with their associated gearboxes, but also with the propellers or propellers driven by them into rotation. Wheel pairs of the corresponding traction objects are deprived of the traction function, remaining only a means of support, rolling and the direction of movement of the traction object. This is the technical result.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to electrical engineering and can be used in electrified vehicles.
The most close to the proposal for technical essence and purpose is a propulsion device consisting of a series of double solenoids with a current uniformly distributed over the ring, in the working gaps of which there is installed a streamlined conductor in the form of a ring ( see Journal of Technique of Youth No. 3, 1933, 6-7, Fig. 2 3 /.
The principle of operation of the claimed propulsor, as well as the known one, is based on the use of the Ampere force F A = B · l · I , which arises in a conductor l with a current I located in a homogeneous magnetic field with induction B so that the axis of the conductor is perpendicular to the field lines. The direction of the force F A is determined by the rule of the left hand. In this case, a physical vacuum is used as a propulsion medium, which is in the state of a magnetic field.
 |
 |
 |
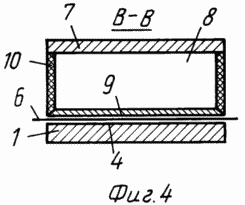 |
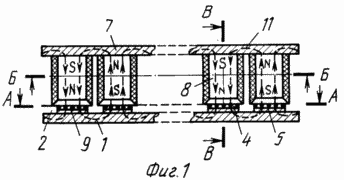
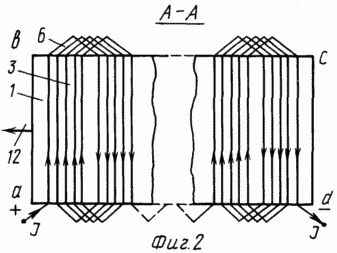
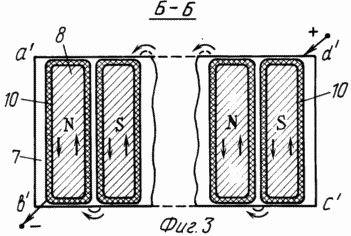
The invention is explained in the drawings, in which FIG. 1 schematically represents a view of the propulsor in a section. FIG. 2 is a section along AA showing a working / anchor / winding. In Fig. 3 is a section along B-B, showing the cross section of the inductor. In Fig. 4 is a section along the B-B, specifying the shape and dimensions of the poles and the VAMAS propulsion device as a whole.
Anchor 1 is made in the form of a ferromagnetic rectangular plate a'b'c'd . The working / anchoring / winding is assembled on its smooth protrusions 2.
Straight lines of length l active conductors 3 are parallel to each other and are assembled into equal groups located in the zones of poles. The winding is shown as a single-layer, made of conductors of circular cross-section. However, it can consist of several layers, and can be made of a conductor of square or rectangular cross-section.
The active conductors 3 of the working winding are connected in series and in this case form a loop winding. From the positive terminal, the current, sequentially bypassing all conductors of the winding, comes to a minus terminal. The winding is supplied from contacts, for example, sliding over the wires of the contact network.
The group of active conductors in the N- polarity magnetic field is denoted by 4, the group of active conductors in the S- polarity magnetic field is denoted by 5, the frontal parts of the working winding are denoted by 6.
The yoke 7 of the inductor is made in the form of a ferromagnetic plate a'b'c'd ' , similar to an anchor plate.
To the yoke 7 of the inductor, the poles 8 are connected to the tips 9 and to the excitation winding 10, which ensures the alternating magnetic polarity of the poles. Position 11 shows the outline of the magnetic lines of force.
The vector 12 denotes the resulting thrust force developed by the VAMAS propulsor when a DC current passes through its working winding.
The vector 12 lies in the plane of the working winding, perpendicular to the centers of the active conductors, and to the magnetic field lines of the poles penetrating the conductors.
Between the protrusions of the anchor plate there are / not shown in the drawings / spacers separating the groups of conductors in order to prevent their displacement by Ampere forces. The end parts ab and dc of the anchor plate are connected by ferromagnetic strips, respectively, with a'b' and c'd ' yoke 7 of the inductor to improve the conditions of the magnetic lines of force at the end poles.
In the drawings, these bars are not shown. Not shown and a metal casing covering the entire VAMAS-propulsion to shield it from the surface electric field of the Earth, which can exclude the possibility of the operation of the VAMAS propulsor .
The VAMAS propulsor can be combined with any of the modern electrified means of translational motion, excluding the electric motor from them, the gearbox associated with it and its coupling with the driving wheel pair, which is the case in ground and underground transportation facilities. In the cases of above-water and underwater objects, along with the electric motor, propellers, their shafts and openings in the underwater part of the ship's hull, through which the shafts pass, are excluded.
CLAIM
A propeller comprising an inductor consisting of a yoke attached to it poles with tips and an excitation winding, and an armless armature with a working winding, characterized in that the yoke of the reducer and the armature have the form of rectangular ferromagnetic plates mechanically interconnected so that the active conductors of the armature winding Are concentrated by parallel groups pinned to the armature in the areas of the inductor poles, the excitation winding of which creates the alternating magnetic polarity of its poles, providing, when the DC winding is supplied to the excitation winding and to the DC winding, the resulting traction force lying in the working winding plane perpendicular to the centers of active conductors of the working winding And to the power lines of the magnetic field of the inductor poles penetrating it, and the propeller as a whole is covered by a metal casing and fastened to the frame or body of the traction object.
print version
Date of publication 11/28/2006




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.