| section Home
Production, Amateur Radio amateur Model aircraft, rocket- Useful, entertaining |
Stealth master
Electronics Physics Technologies invention |
space Mystery
Earth Mysteries Secrets of the Ocean Stealth section Map |
|
| Use of material is permitted for reference (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current models of the invention and / back / |
|
INVENTION
Russian Federation Patent RU2088762
PISTON ENGINE ROTARY
![]()
Name of applicant: Yahnis Leonid Isakovich
Name of the inventor: Yahnis Leonid Isakovich
The name of the patentee: Yahnis Leonid Isakovich
Address for correspondence:
Starting date of the patent: 1991.11.19
Use: in mechanical engineering. The inventive rotary piston engine comprises a housing, a rotor rigidly connected to the output shaft, rollers. installed in the bores housing the eccentric rotor rotating ring resting on rollers synchronizer angular rotor velocities and the ring piston group, one element of each of which is pivotally mounted on the ring and the other is connected to the rotor, wherein the rotor made distribution channels for the supply and removal work environment. Elements of piston connected to the rotor, for example cylinders, designed as the rotor of the tangential bores arranged at a predetermined distance from the rotor axis.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to mechanical engineering and can be used in engine in hydraulic and transmissions pnevmoobemnyh vehicles, hydraulic and pneumatic process equipment.
Known radial piston hydraulic motor comprising a body defining a supply channel and discharge the working medium, installed in the rotor housing, formed integrally with the output shaft, the rotary ring, eccentric rotor, resting on rollers mounted in the bores of the housing, piston groups, one of elements pivotally mounted on the ring and the other on the rotor, a gear transmission, a synchronization of the rotor angular velocity and the eccentric ring (SU, 1581852, F 04 B 1/04, 1990).
A disadvantage of the structure under consideration is that the resulting torque on the output shaft power is the difference between the torques on the ring and the rotor, eccentricity value is determined relative to the rotor rings. The disadvantage associated with a radial arrangement of the elements of piston relative to the rotor, and the direction of the force from the impact of the working environment close to 90 o with respect to the main direction of motion (the rotor).
Object of the invention increase the torque force on the output shaft of the engine.
The technical result is achieved in that one element of each of the piston engines groups pivotally mounted on an eccentric ring rests on rollers mounted in the bores of the housing, and the other is connected to the rotor and is for example in the form of tangential bores in the rotor located at a specified distance from the rotor axis.
 |
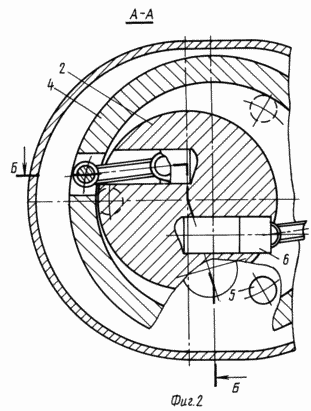 |
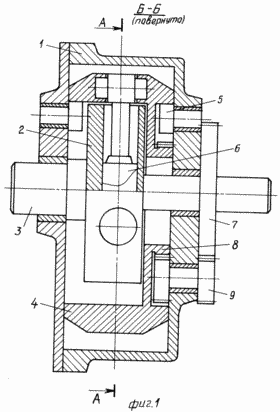
The engine design is illustrated by drawings, where Figure 1 is a rotary piston engine, the cut B-B of Figure 2; FIG. 2 sectional view A-A in Figure 1.
The reciprocating rotary engine comprises a casing 1 in which a rotor 2 is secured to the output shaft 3. The rotor 2 eccentrically installed in the housing ring 4. In the housing on both sides of the ring are made uniformly spaced cylinder bores in which there are support rollers 5, interacting with the inner surface of the rotary ring 4. The rotor 2 at equal distances from the axis are made tangential bore serving as cylinder piston groups. In this case the distribution channels in the rotor for the supply and discharge of the working medium can be performed on the rotating ring 4 is pivotally mounted pistons 6 reciprocating groups. The rotor shaft 3 and the rotary ring gear 4 fixed 7 and 8 with the same number of teeth and the same gear unit mounted on the casing 9, which interacts with gears 7 and 8.
PISTON ROTARY ENGINE RUNNING AS FOLLOWS
Fluid pressure sensed by the pistons, is transmitted through the rotary ring, the housing support rollers. Fluid pressure sensed by cylinders made in the form of tangential bores in the rotor by bores displacement relative to the rotor axis, it is directly converted into a torque force on the rotor shaft. Moreover, the amount of torque proportional mixing of the bore relative to the rotor axis and does not depend on the eccentricity of the rotor relative to the rotary ring. The presence of the gear transmission allows you to synchronize the rotation of the rotor and the rotary ring, unload piston group of radial forces and reduce their contribution.
CLAIM
The reciprocating rotary engine comprising a body mounted in a housing a rotor fixedly connected to the output shaft, rollers mounted in the bores housing the eccentric rotor rotating ring resting on rollers synchronizer angular rotor velocities and the ring piston group, one element of each of which pivotally mounted on the ring and the other is connected to the rotor, wherein the rotor made distribution channels for supply and discharge of the working medium, characterized in that the elements of piston connected to the rotor, for example cylinders, designed as tangential bores in the rotor located at a predetermined distance from the rotor axis.
print version
Publication date 24.12.2006gg




Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.