| Start of section
Production, amateur Radio amateurs Aircraft model, rocket-model Useful, entertaining |
Stealth Master
Electronics Physics Technologies Inventions |
Secrets of the cosmos
Secrets of the Earth Secrets of the Ocean Tricks Map of section |
|
| Use of the site materials is allowed subject to the link (for websites - hyperlinks) | |||
Navigation: => |
Home / Technology market / Current inventions and models / Back / |
|
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2285144
METHOD FOR PRODUCTION AND TRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY OF A WORKING ENVIRONMENT IN MECHANICAL WORK AND DEVICE FOR ITS IMPLEMENTATION
![]()
Applicant's name: Klyucherev Oleg Aleksandrovich (RU); Andreev Evgeniy Ivanovich (RU); Davydenko Roman Alenovich (RU)
The name of the inventor: Klyucherev Oleg Alexandrovich (RU); Andreev Evgeniy Ivanovich (RU); Davydenko Roman Alenovich (RU)
The name of the patent holder: Klyucherev Oleg Aleksandrovich (RU); Andreev Evgeniy Ivanovich (RU); Davydenko Roman Alenovich (RU)
Address for correspondence: 196270, St. Petersburg, Pulkovskoe shosse, 5/1, kv.1, RA Davydenko
Date of commencement of the patent: 2000.10.09
The invention relates to the field of power engineering, namely to power plants, and can be used in engines. The method of obtaining and transforming the energy of the working medium into mechanical work consists in transforming the energy of expansion of a two-component working fluid into useful work. The gaseous component is initially compressed separately from the liquid component, and then the liquid component is injected into the compressed gaseous component, the liquid component being preheated to a temperature equal to or higher than the temperature of the compressed gaseous component. The resulting bicomponent medium is expanded to obtain mechanical energy. The liquid component is injected into the mixing chamber. The gaseous and liquid components are uniformly mixed in the chamber, and then through the formed two-component medium, an electric discharge is produced by a power providing vaporization of the liquid component of the medium and destruction of the working medium molecules to form a plasma, while water is used as a liquid component. The device for obtaining and converting the energy of the working medium into mechanical work includes a compression-expansion machine made in the form of a piston machine. At the top of the cylinder of the piston machine are installed input and output valves to pass the working fluid and a nozzle for supplying the liquid component. And the device comprises an autonomous heat source, a heating and supply system for the liquid component, and a system for processing and feeding the gaseous component. In this case, the device is provided with a mixing chamber of a rounded configuration into which electrodes connected via electrical circuits with an electric power generator are inserted through insulating sleeves. The nozzle for supplying the liquid component is located at the top of the mixing chamber between the electrodes, and the mixing chamber is connected to the upper end of the cylinder by a transition channel.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to power engineering, steam power plants and engines operating on hot gases, as well as devices for processing hot gases by electrically exciting means.
The phenomenon of cold plasma chemistry is known, in which upper electron shells fly from oxygen, nitrogen, argon and other gases, ions and other active particles are formed, with the release of heat due to the partial nuclear decay of atoms. The conditions for the flow of plasma chemistry are determined by a temperature of about 3000 ° C and can be created by electric discharges (Journal Industrial Gazette, No. 9,1999, p . 19) .
A method for increasing the energy of a working medium for performing useful work is known, which includes the processes of suction of the working medium, its compression, transmission through the compressed working medium of an electrically exciting medium (electric arc or laser beam) with increasing energy of the working medium and expansion of this working medium to obtain useful work . To implement this method, the piston machine is provided with a cylinder having an inlet and an outlet valve and electrodes connected to the electric power generator by electric circuits, and a piston reciprocating in the cylinder (UK application No. 2241746, F 02 G 1 / 02. Abstract journal "Inventions of the countries of the world", issue No. 65, No. 5, 1993, p. 22) . However, for ionization and the generation of excess energy in the working medium (air), a sufficiently powerful electric energy generator is needed.
A method is known for converting heat into mechanical work and a power plant for its implementation, comprising the use of the expansion energy of a two-component working fluid, wherein the gaseous component is initially compressed separately from the liquid, and then the liquid component is injected into the compressed gaseous component, the liquid component being preheated to a temperature, Equal to or higher than the temperature of the compressed component, and a plant for implementing this method is known, comprising a compression-expansion machine made in the form of a piston machine, in the upper part of the cylinder of which there are inlet and outlet valves for passing the working fluid and a nozzle for supplying the liquid component, A source of heat, a system for heating and supplying a liquid component, a system for processing and supplying a gaseous component (Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2075599, F 01 K 21/00, Bulletin No. 8 of 20.03.97) . However, to obtain thermal energy, the internal energy of the two-component working medium is not used.
The technical result which can be obtained by implementing the invention on the basis of the proposed method for obtaining and converting the energy of the working medium consists in increasing the efficiency of power plants and engines operating on hot gases, solving the issues of ecological purity of prospective power plants.
In order to achieve this technical result, in the proposed method for obtaining and converting energy of a working medium into mechanical work consisting in converting the expansion energy of a two-component working fluid into a useful work in which the gaseous component is initially compressed separately from the liquid component, then a liquid component is injected into the compressed gaseous component, The liquid component is preheated to a temperature equal to or higher than the temperature of the compressed component, and the resulting bicomponent medium is expanded to obtain mechanical energy, the gaseous and liquid components are uniformly mixed in the mixing chamber, and then through the resulting bicomponent medium, an electric discharge is passed with a power to vaporize the liquid component of the medium And the destruction of the molecules of the working medium with the formation of plasma.
Introduction to the proposed method for obtaining and converting the energy of the working medium to uniform mixing of the gaseous and liquid components and passing through the formed two-component medium of an electric discharge with a power that provides vaporization of the liquid component of the medium and the destruction of the working medium molecules with the formation of plasma allows us to obtain a new property consisting in a combined increase in energy Of the working medium due to vaporization with increasing pressure, and ionization of this medium by means of an electric discharge, which ensures the destruction of the working medium molecules, which leads to the release of heat and an increase in the temperature of the working medium at the beginning of the expansion process.
The proposed method for obtaining and converting the energy of the working medium into mechanical work can be carried out in the device described below.
The device for obtaining and converting energy of the working medium, including a compression-expansion machine made in the form of a piston machine, in the upper part of the cylinder of which there are inlet and outlet valves to pass the working fluid and a nozzle for supplying the liquid component, an independent heat source, a heating system And the supply of the liquid component, the system for processing and supplying the gaseous component, is provided with a mixing chamber of a circular configuration into which electrodes connected via electrical circuits with an electric power generator are inserted through the insulating sleeves, the nozzle for supplying the liquid component is located at the top of the mixing chamber between the electrodes, And the mixing chamber is connected to the upper end of the cylinder by a passageway.
The drawing shows a piston machine of a device that implements the proposed method for obtaining and converting the energy of the working medium into mechanical energy.
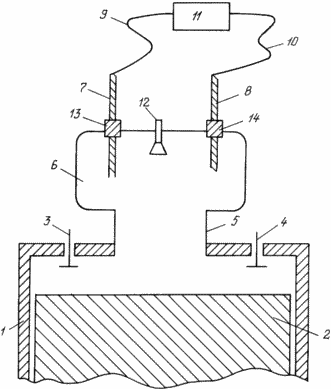 |
The piston machine for converting heat into mechanical work implementing the method of the invention comprises a cylinder 1 inside which the piston 2 is located. The piston cylinder cylinder 1 in the upper end part is provided with an inlet 3 and outlet valve 4 and is connected by a passageway 5 with a special mixing chamber 6 in Which includes electrodes 7 and 8 connected by electric circuits 9 and 10 with the electric power generator 11. Between the electrodes 7 and 8 there is arranged an injector 12 for supplying a compressed liquid component. The electrodes 7 and 8 are mounted in the cylinder 1 by means of sleeves 13 and 14 made of an insulating material. |
The proposed method is carried out in the described piston machine as follows.
When the piston 2 moves down from the BMT through the inlet valve 3 from the environment and the cylinder 1 is sucked in air (the gas part of the working medium). When the HMT reaches the piston 2, the piston 2 begins to move upward towards the TDC, the process of compressing the gas component of the working medium begins, with the compressed gas component through the passageway 5 being mainly concentrated in the special mixing chamber 6. When the piston reaches the 2 TDC in the mixing chamber 5, By pressure through the nozzle 12, a preheated liquid component (for example, water) is injected, which, due to the rounded configuration of the mixing chamber 6, is evenly mixed with the gaseous component. Through the formed two-component medium, an electric discharge is passed between the electrodes 7 and 8 connected by the electric circuits 9 and 10 with the electric power generator 11. The electric discharge leads to an increase in the pressure of the working medium due to the evaporation of the liquid component of the medium and the additional heating of the working medium, Increases the energy of the working environment.
The released heat and pressure of vaporization of the working medium is realized in mechanical work with the expansion of the working medium and the movement of the piston 2 from TDC to NMT. The used working medium is discharged from the cylinder 1 through the exhaust valve 4, when the piston 2 moves from the HMT to the TDC, and then it is restored under natural conditions. Then the cycle of the piston machine is repeated.
For safety of operation, the electrodes 7 and 8 are mounted in the mixing chamber 6 by means of sleeves 13, 14 made of an insulating material.
INFORMATION SOURCES
Magazine "Industrial Herald", №9, 1999, p.19.
Application of the United Kingdom No. 2241746, F 02 G 1/02. The abstract journal "Inventions of the countries of the world", issue No. 65, No. 5, 1993, p.22.
Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2075599, F 01 K 21/00. Bul. №8 from 20.03.97 - the prototype.
CLAIM
A method for obtaining and converting the energy of a working medium into mechanical work, comprising converting the expansion energy of a two-component working fluid into a useful operation, the gaseous component initially being compressed separately from the liquid component, and then injecting the liquid component into the compressed gaseous component, the liquid component being preheated to a temperature, Equal to or higher than the temperature of the compressed gaseous component, and the resulting bicomponent medium is expanded to obtain mechanical energy, characterized in that the injection of the liquid component is carried out into the mixing chamber, the gaseous and liquid components are uniformly mixed in the chamber, and then an electrical discharge is produced through the resulting bicomponent medium, Providing a vaporization of the liquid component of the medium and destruction of the working medium molecules with the formation of plasma, leading to an increase in the energy of the working medium, while water is used as a liquid component.
The device for obtaining and converting the energy of the working medium into a mechanical work including a compression-expansion machine made in the form of a piston machine, in the upper part of the cylinder of which there are inlet and outlet valves for passing the working fluid and a nozzle for supplying the liquid component, an autonomous heat source , A system for heating and supplying a liquid component, a system for treating and supplying a gaseous component, characterized in that it is provided with a mixing chamber of a circular configuration into which electrodes connected by electrical circuits with an electric power generator are inserted through insulating sleeves, the liquid supply nozzle being located In the upper part of the mixing chamber between the electrodes, and the mixing chamber is connected to the upper end part of the cylinder by a transition channel.
print version
Date of publication 24.12.2006гг




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.