Sulfides: Bismutinit (Vismutin, bismuth luster)
 Diagnostic Card.
Diagnostic Card.
Bi 2 S 3 (bismuth sulfide)
Crystal system orthorhombic
Hardness 2
Specific gravity 6.8
Cleavage is perfect
Fracture irregular, splintery
Color tin gray
Color powder lead-gray
shine metal
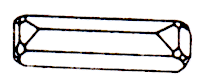
Vismutin (bismuth luster), bismuth sulfide. The strong metallic luster, opaque. Colour white with lead-gray tint, sometimes mottled discolouration. Dash gray. Fracture conchoidal. Fragile. Cleavage very perfect. It occurs in hydrothermal deposits. Crystals (orthorhombic system) are rare - columnar, needle. Units radiant, stalked, dense, grainy. The most important ore of bismuth. Distribution Area: the Ore Mountains, Saxony (Germany), Sweden, Bolivia, CIS.
 Mineral orthorhombic system, forms crystals elongated, columnar shape. Along the vertical face of the prism is observed perfect cleavage; their covers dense hatching. The most common mineral forms dense granular or fibrous aggregates. Bismutinit opaque, mineral color tin-gray metallic luster. The products have change or rosy or yellowish color. The powder color - lead-gray. The crystals are flexible.
Mineral orthorhombic system, forms crystals elongated, columnar shape. Along the vertical face of the prism is observed perfect cleavage; their covers dense hatching. The most common mineral forms dense granular or fibrous aggregates. Bismutinit opaque, mineral color tin-gray metallic luster. The products have change or rosy or yellowish color. The powder color - lead-gray. The crystals are flexible.
Bismuth (Bi) 81,2%, sulfur (S) 18,8%, mostly with minor impurities of lead, copper, iron, arsenic, antimony, tellurium. Form crystals. Columnar crystals; crystal faces usually covered by a thin vertical hatching. The crystal structure. Similar to the structure of stibnite. Class symmetry. Rombo-bipyramidal - mmm. Cleavage. Perfect for a prism (010). Aggregates. Radiant education, solid granular massive clusters.
Diagnostic features.
Bismutinit very similar to antimony and outwardly indistinguishable from it. Easily melts on charcoal, leaving a lemon-yellow coating of bismuth oxide in the reducing flame melts in bismuth wren. Behavior in acids. Readily soluble in nitric acid.
Origin.
Bismutinit has hydrothermal origin. A common association with stibnite, which is formed at a somewhat lower temperature.
Deposits and application.
Clusters that have commercial interest, established in Bolivia, Peru. UK (Cornwall), and Australia. Good crystals were discovered in the United States (California and Dakota), in Mexico and Canada. This mineral is used to extract bismuth (content - 81.2% by weight).



Bismuth. Porretta, Italy (left) and the Southern Urals (Russia, CIS) - bismuth and bismuthinite. Photo: © AA Evseev.
Bismuth belongs to moderately toxic to the human body ultramicroelements. It affects the formation of "tanning pigment" ( "Gorman Negro") - melanin - and participates in ossification processes. Hazards are chronic intake of bismuth in amounts of 1-1.5 grams per day. In humans it falls bismuth with food, water and air. Suction bismuth released to the gastrointestinal tract, and minor amounts of 5%. Is found in blood in the form of compounds with the proteins, it penetrates into erythrocytes.
Much more probable intake of bismuth with drugs when taking them into or through the skin (when applied topically). bismuth salts are used in medicine are insoluble in water are used in the form of colloidal solutions and have high toxicity. However, with prolonged or vigorous reception preparations containing bismuth, there may be complications. One of the main manifestations - the so-called "bismuth fringe" - an inflammation that occurs due to the deposition of bismuth sulphide at the edges of the gums. Possible violations on the part of the urinary tract.
Between organs and tissues bismuth is distributed evenly. bismuth accumulation can be observed in the liver, kidney (1 ug / g), spleen and bone and brain (Psychiatry). Bismuth having passed through the gastrointestinal tract, it is released in the form of bismuth sulfide, staining the feces in a dark color. Resorbed bismuth is excreted in the urine. Bismuth belongs to the category of heavy metals, it is moderately toxic element.
Bismuth induces the synthesis of low molecular weight proteins, is involved in the ossification process forms intracellular inclusion in renal tubular epithelium is genotoxic and mutagenic properties. Intoxication occurs after prolonged exposure of the body of bismuth salts in high doses. There are cases of iatrogenic, professional and household poisonings.
The main manifestations of excess of bismuth: loss of memory, insomnia, symptoms of damage to the nervous system (sensitivity disorder, neck stiffness), weakness, cardiac arrhythmia, the occurrence of a dark border around the gums (acts as cinnabar - mercury sulphide), pigmentation ( "melanism") mucous gum shell and mouth; stomatitis, pharyngitis, difficulty in swallowing; excessive salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea; toxic hepatitis with fatty degeneration and cirrhosis; albuminuria, the cylinders in the urine, "Bismuth" dermatitis, loss of appetite, fatigue, weight loss.
Subgallate bismuth when applied to the skin and mucous membranes causes seal colloids (silica gel, silica) extracellular fluid, mucus, exudate and forms a protective film that protects the end of the sensory nerve irritation, and which is able to reduce the pain and prevent the development of edema. Bismuth subnitrate as ointments and powders is used as a protective and anti-inflammatory agent for dermatitis, eczema, skin ulcers and erosions. When inside designation bismuth salts form on the surface of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract film - chelate to a protein substrate, which helps to reduce inflammation, peptic ulcers healing and decrease the number of recurrences. Bismuth preparations have antibacterial activity (like silver).
ADR 5.1
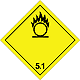
Substances which are oxidized
Risk of vigorous reaction, ignition and explosion in contact with combustible or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, the number of ADR, a black flame over a circle
| Name of especially dangerous during transportation of cargo | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| Bismuth (III) nitrate | 1477 | 5.1 |
- Gatchell - "New Almadén snag" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulphosalts)
- Antimony - toxic metal (semi-metal) are widely used in industry, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and non- metal and dangerous jewel in the oxide and salts
- Gold - yellow dangerous and toxic metal -date and accurate digital cable technology
- Sulphur - a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of volcanic activity
- Cadmium - a toxic uncirculated unknown wide range of people silvery metal
- Lead - a poisonous gray simulator silver metal and toxic metal snag
- Arsenic - poison classic medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Toxic and hazardous radioactive rocks and minerals
** - Poisonous stones and minerals (obligatory check in chemical laboratory + clear indication of toxicity)
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals (obligatory check on a regular dosimeter + ban on the open sale of radioactivity in the event of more than 24 mR / hour + additional measures to protect the population)
Catalog minerals and gems in groups of the world
** - Poisonous stones and minerals
** - Radioactive rocks and minerals


Comments
Commenting, keep in mind that the content and the tone of your messages can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to his interlocutors, even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in terms of freedom of speech and anonymity offered by the Internet, is changing not only virtual, but real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam control.