Sulphates: Celestine
 Diagnostic card.
Diagnostic card.
In the photo: tabloid crystals of celestine. Below: the normal shape of the mineral in the form of strongly elongated crystals.
Sr SO 4 (strontium sulfate)
Singonia monoclinic
Hardness 2
Specific weight 2,3-2,4
Cleavage is perfect
Crack irregular
Color is colorless, diverse
Color in powder white
Glitter from glass to pearly
Celestine is strontium sulfate. The hardness is 3-3.5. The density is 3.9-4.0. Glitter pearl to glass. Transparent to translucent. It is colorless or white, but often the differences are colored in light grayish-blue color. The line is white. The fracture is uneven. It's fragile. Cleavage is perfect. Stains the flame red. It is formed in cracks and drusen cavities. Crystals (rhombic syngony) are rich in facets. There are columnar, tabular, and there are also granular aggregates. Places of distribution: North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany), Jena (Germany), Salzburg (Austria), Sicily (Italy), England, Mexico, CIS.
 It is represented by elongated-prismatic or (much less frequently) tabular crystals with coloring from colorless and milky-white to blue and brown-yellow. Usually, celestite forms aggregates with radially or in parallel crystals or massive clusters of dense or concretionary structure. Often forms pseudomorphs in calcite. Not too hard and heavy, celestite has perfect cleavage, parallel to the base of the crystals. Most often it is transparent, has a glass and pearlescent shine. Very dangerous.
It is represented by elongated-prismatic or (much less frequently) tabular crystals with coloring from colorless and milky-white to blue and brown-yellow. Usually, celestite forms aggregates with radially or in parallel crystals or massive clusters of dense or concretionary structure. Often forms pseudomorphs in calcite. Not too hard and heavy, celestite has perfect cleavage, parallel to the base of the crystals. Most often it is transparent, has a glass and pearlescent shine. Very dangerous.
Diagnostic signs.
Celestine can sometimes be confused with other sulfates, for example barite, whose specific gravity, however, is much larger. For testing, you can conduct a simple chemical test - take the mineral powder on the tip of the platinum needle and place it in the flame of the gas burner. It will turn into a carmine-red color due to the presence of strontium.
Origin.
Celestine can have hydrothermal origin. But for him the sedimentary evaporite genesis is more typical. Together with it, sulfur, aragonite and a complex of typical evaporite minerals are deposited.
Place of Birth.
Blue crystals are found in the basalts of Montecchio Maggiore (Vicenza province) and in the pegmatites of Madagascar. In the regions of Sicily and Romagna (Italy) in rocks containing gypsum and sulfur, celestite is usually white. Near the city of Jena (Germany), it is found in veins of a fibrous structure of blue color. Fields suitable for industrial development are in England, Russia and Tunisia. Very large crystals, grayish-white and almost opaque, up to 75 cm long and weighing up to 2 kg are found in the United States. Fine specimens, although small in size, are found in Italian deposits. In Enne and Agrigento (Sicily, Italy) and in Perthara (Marche region), magnificent groups (druses) of celestite crystals were found for the most part practically white (very light !!) in association with sulfur and gypsum.
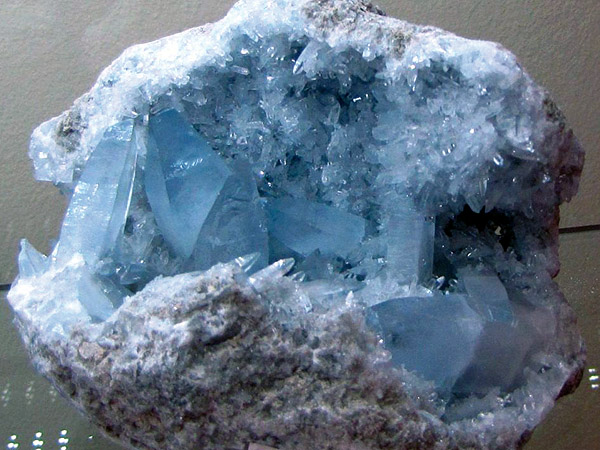


Celestine is strontium sulfate in the Druze (more dangerous). Madagascar. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
 Physical features of celestite.
Physical features of celestite.
This mineral can contain radioactive components , especially the stones of intense blue color (the norm of natural radiation is 17-24 millicorentgen / hour). The increased level of radiation radiation from stones and minerals is the level of radiation from 29-32 milli-radentgen / hour and above. On the right is a sign of a potential radiation hazard (Ukraine, K.305). Transportation of large volumes of celestine without a sign of radiation hazard - the image of "radioactive" (Ukr.) On the right - is strictly forbidden - this is a dangerous ore for strontium !!
Radioactive stones and minerals with prolonged wearing and uncontrolled application inside can cause radiation damage to the thyroid gland and cause its changes (including cancer). Similar damage can be caused by the prolonged wearing of dangerous minerals directly on the chest or in the pockets of men's trousers. Because of the high background of radiation, these men who are dangerous for health choose men who lead a hermitic way of life - and this harm their health and environment (they lead an unhealthy lifestyle) - celestine can "remove" unwanted competitors, including the church (especially long reception Celestine inside instead of table salt - in closed monasteries, sects and institutions such as "magic").
Celestines are not worn! In any case, for safety and environmental reasons, it is not recommended to carry poisonous and radioactive stones and minerals constantly and keep large samples of such minerals in the apartment or office (the house and apartment are not a mineralogical museum with an allowable radiation level from 32 to 120 milli / Above for special expositions and mineralogical special protection of state institutions, where this is permitted in the presence of warning signs and special applications of employees of these specialized institutions). Celebrities are categorically forbidden to pregnant women and especially small children, who uncontrollably often pull in their mouths interesting objects (in particular, interesting in appearance celestine and their intergrowths).
Radiation from a point source and a small object decreases in proportion to the square of the distance to this object. Moving 2 meters from a dangerous object, you will reduce the level of learning from this object by 4 times. Going 10 meters, you reduce the radiation level of this object by 100 times. If the object has a point source of radiation of 2000 milli / g / h with a natural background of ambient radiation of 19 milli / g / hour (total 2000 + 19 = 2019 milli / g), moving away from the dangerous object by 10 meters, you will secure yourself to a radiation level of 20 milli / From the object and 19 milli / g / hour from the environment (total total radiation level from the object and the environment will be 20 + 19 = 39 milli / g).
Dangerous is the direct contact with the body and the wearing on the body of point and diffuse poisonous and radioactive sources and components - especially water-soluble and hydrothermal origin (about 50% of radiation is absorbed by contact with the outer surface of the body and about 100% of the radiation - when ingested radioactive Or an infected object). The most dangerous is the direct ingestion of toxic and radioactive components, stones and minerals, including in the grated form and especially soluble in the liquid. All unauthorized injections of poisonous and especially radioactive preparations are strictly prohibited. These are unseasonable and very dangerous for life and health stones and minerals !!
Application.
Celestine is the main ore for strontium, which is used in pyrotechnics and the production of tracer bullets (special facility, do not inhale the smoke - strontium stains the flame in carmine-red color ). Strontium is also used in nuclear power engineering, in production of special lacquers, etc. It is not recommended to store it in home collections.
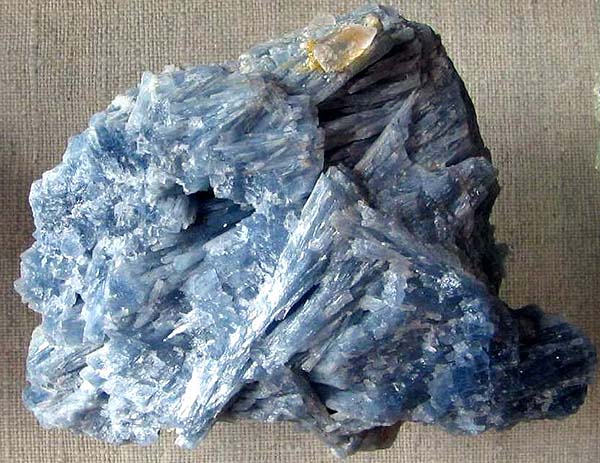

Celestine. Lucky tube, Yakutia. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.


Celestine. Sakoani r-k, Madagascar. A ghost of bluish celestite crystals (Madagascar). Photo: © В.И. Dvoryadkin.
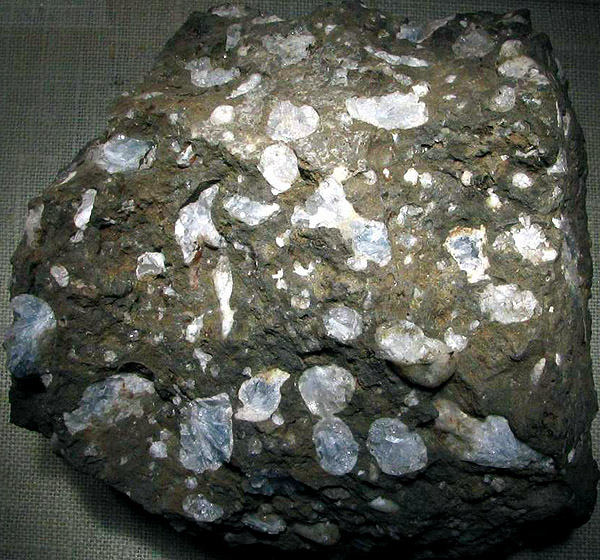


Celestine (blue, in voids in the basalt). Montecchio Maggiore, Vicenza, Italy. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
Strontium - an element, the exchange of which is associated with the exchange of calcium. In the body it is in amounts up to 3-4 mg per day and prevents the development of caries and osteoporosis. Strontium, supplied with food, is relatively poorly absorbed by the body (about 5-10%). Absorption of strontium occurs in the duodenum and ileum (pancreatic cancer and spleen cancer). Absorbed in the body of strontium is excreted in the urine (kidney cancer) and, to a lesser extent, with bile (liver cancer). In the stool is unabsorbed strontium (colon cancer).
In the human body weighing 70 kg is about 320 mg of strontium, and its main amount (up to 99%) is deposited in the bones. Relatively high concentrations of strontium - in the lymph nodes (0.30 ± 0.08 μg / g), causes cancer of the lymph nodes, in the lungs (0.20 ± 0.02), ovaries (0.14 ± 0.06), liver And kidneys (0.1 ± 0.03). In the blood, 0.02 ± 0.002 μg / ml of strontium was found. A lot of strontium is a weak vital activity of the organism (stimulus).
Strontium is able to accumulate in the body. The average strontium content in the body is 0.002%. The main manifestations of excess strontium: rachitis-like diseases (curvature of bones under the body's own weight), "level" disease; Pulmonary fibrosis. To remove strontium from the body use preparations of magnesium, calcium, dietary fiber, sodium sulfate and barium sulfate. Celestine - cartilaginous pseudomorphs in corpses.
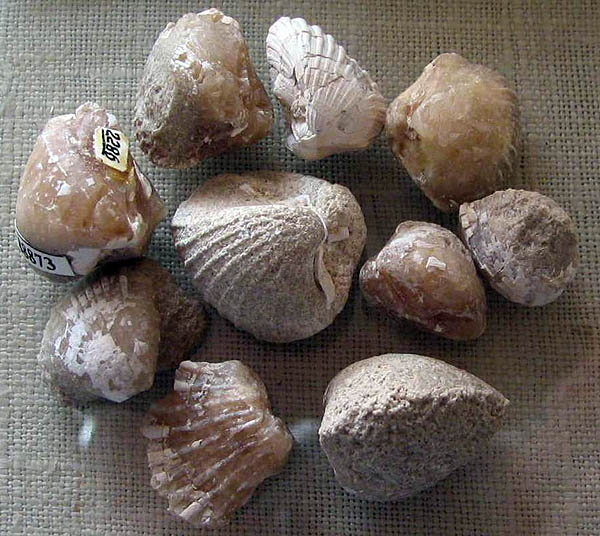

Celestine on the shells (pseudomorphs). Mangyshlak, Kazakhstan. Middle Asia. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
Substitution of 99.3% of the cartilage component of the shell of the mollusc (celestite inside the shell, not pyritization)
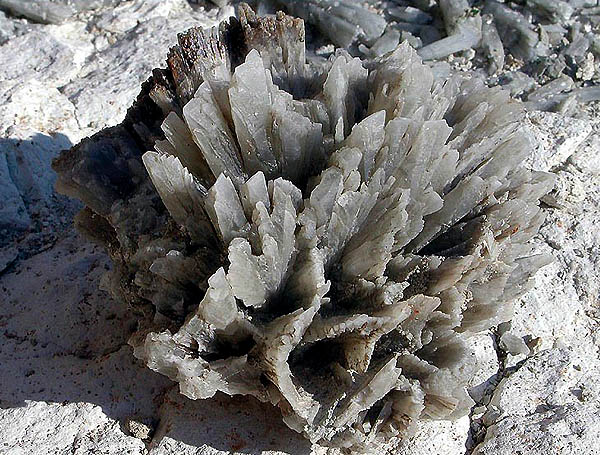

Pseudomorphs of celestine (strontium sulfide). Mangyshlak, Kazakhstan. Middle Asia. Photo: © V. Ponomarenko.
Possible pseudomorphosis of celestine by cartilaginous fish and organic scales (near - the water caldera of the volcano)


Celestine (left, looks like a staurolite). Ungazia, Mangyshlak, Kazakhstan, the CIS. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
Celestine, gypsum. Shurab, Isfara district, Sev. Tajikistan, the CIS. 5х4 cm. Central Asia.
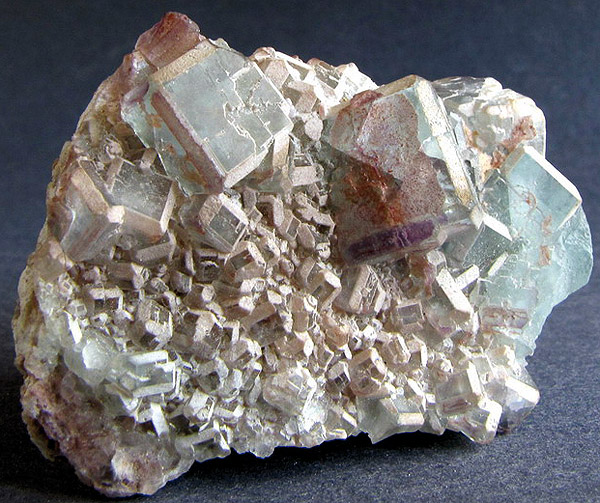

Fluorite. Near Tyrone, New Mexico, USA. Crystals up to 1.5 cm. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
The sample is extremely similar to celestite and aquamarine, it is fluorite - calcium fluoride
Calcium, which is part of the bone tissue, is close in properties to strontium, so strontium ions can replace calcium in the bones. In this case, there are cases of both synergism and antagonism of strontium. Vitamin D, lactose, amino acids lysine and arginine improve the absorption (assimilation) of strontium. Vegetable food, rich in dietary fiber, as well as sodium sulfate and barium sulfate, can reduce the absorption of strontium.
"Level disease" (strontium rickets) occurs due to the displacement of calcium ions by strontium ions from bone tissue or the entry into the body of strontium in place of calcium. Accumulation in the body of strontium leads to damage to the body, but the development of dystrophic changes in the osteoarticular system is typical during the growth and development of the organism, in adolescence (symmetrical deforming osteoporosis is formed due to inhibition of bone growth in the zones of metaphyseal cartilage, there is no growth zone of the cartilaginous bone component ). Poisoning with strontium.
Strontium actively provokes the development of lingual and connective tissue (bones, ligaments, joints, abdominal tissues). Consumption of a diet with a reduced content of strontium leads to growth inhibition, damage, excessive calcification of bones and teeth (increased fragility, insufficient development of cartilaginous tissue and skin), increased dental caries and brittle nails (teeth and nails break, brittle hair, split at the ends) . Eat - the bone marrow (inside the beef and pork horse bone, goliazhka) and pork legs (jelly, jelly), pork brawn.
Dangerous for the organism is the radioactive isotope of strontium 90Sr, which, when ingested in bone tissue, can affect the bone marrow and disrupt the hematopoiesis (instead of provoking the growth of the femur, it destroys the bone marrow inside the bone, the sign is the hip fracture). They eat - bone meal, bones.
Food sources of strontium: leguminous plants (beans, peas, soybeans, beans, etc.) are rich in strontium, cereals (buckwheat, oats, millet, soft wheat, hard wheat, wild rice, rye) and plants that form root crops and tubers (ginger, Potatoes, beets, carrots, etc.), fruit: apricots, quince, pineapple, grapes, pears, kiwi; Dried fruits: raisins, dried apricots, dates; Nuts and seeds: peanuts, cashews, macadamia, Brazilian nuts, pistachios, hazelnuts; Greens of arugula, celery greens, dill; Seaweed: kelp (sea kale); Bones and cartilage.
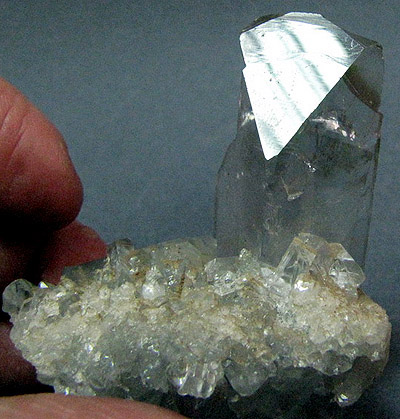

Celestine. Sakoani, Madagascar. Crystal 7 cm. Photo: © А.А. Evseev.
It looks like glass, fluorite, amethyst and aquamarine and other stones
ADR 7


Radioactive materials ( radiation , Ukraine)
Risk of absorption of external and internal radiation exposure
Limit impact time, radiation burns, radiation exposure of photographic and cinematographic materials
Yellow upper half of rhombus, white - lower, equal, ADR number, black sign of radiation, inscription
ADR 6.1
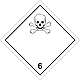
Toxic substances (poison)
Risk of poisoning by inhalation, in contact with skin or if swallowed. Dangerous to aquatic environment or sewer system
Use a mask for emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, ADR number, black skull and crossbones
ADR 5.1
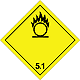
Substances that are oxidized
Risk of violent reaction, ignition or explosion if exposed to flammable or flammable substances
Do not allow the formation of a mixture of cargo with flammable or combustible substances (eg sawdust)
Yellow diamond, ADR number, black flame above the circle
ADR 4.3


Substances that emit flammable gases in contact with water
Risk of fire and explosion if exposed to water.
The cargo, which crumbled, must be covered and kept dry
Blue and blue diamond, ADR number, black or white flame
ADR 9

Other dangerous substances and articles
Risk of burns. Risk of fire. Risk of explosion.
Dangerous to aquatic environment or sewer system
Seven vertical black stripes on white background - top, white - lower half of diamond, ADR number
| The name of a cargo that is particularly dangerous for transportation | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| Strontium nitric acid STRONTIUM NITRATE | 1507 | 5.1. |
| STRONG ARSENIT | 1691 | 6.1. |
| Strontium carbonate. Not subject to the Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods | - | - |
| STRONG NITRATE | 1507 | 5.1. |
| Strontium nitrate, an aqueous solution that does not oxidize | 9 | |
| STRONG PEROXIDE (peroxide) | 1509 | 5.1. |
| STRONG PERCHLORAT | 1508 | 5.1. |
| STRONTIUM PHOSPHIDE | 2013 | 4.3 |
| STRONTIUM CHLORATES | 1506 | 5.1. |
- Ghetchellit - "New Almaden blend" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulfosol)
- Antimony is a toxic metal (semimetal) , widely used in metallurgy, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and undiscovered metal and the most dangerous precious stone in oxide and salt
- Gold - yellow dangerous and poisonous metal of modern accurate digital and cable technologies
- Sulfur is a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of active volcanic activity
- Cadmium is an undisputed toxic silvery metal unknown to a wide range of people
- Lead - a toxic gray imitator of metallic silver and toxic metal blende
- Arsenic is a classic poison of medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity)
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in case of radioactivity exceeding 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection)
Catalog of minerals and semi-precious stones of the world by groups
** - poisonous stones and minerals
** - radioactive stones and minerals


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.