Sulphides: Cobaltine
 Diagnostic card.
Diagnostic card.
Crystals of cobaltite on chalcopyrite, Tunaberg, Sweden
Co As S
Cubic amount of cubic zirconia
Hardness
Specific weight 6,3
Cleavage is perfect
Crack irregular
Color silvery white, gray-black
Color in powder grayish black
Glitter metal
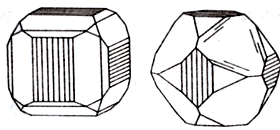
Cobaltine (cobalt shine), - cobalt sulfide and arsenic. Glitter is metallic. Opaque. Colors: silver-white, pinkish. The line is gray to black. The fracture is conchoidal, uneven. It's fragile. Cleavage is perfect. It is formed mainly in skarns, less often in hydrothermal veins.
Crystals (cubic syngony) often in the form of pentagonal dodecahedrons, also dense solid aggregates or disseminated ores. Deposits: in the Ore Mountains (Germany), in Germany, England, Norway, the CIS (Transcaucasia), Canada, Morocco.
 It crystallizes in the form of individuals, which are usually cubes, octahedra and pitoithedra, sometimes a combination of the two latter forms. The facets of crystals are usually shaded, similar to pyrite.
It crystallizes in the form of individuals, which are usually cubes, octahedra and pitoithedra, sometimes a combination of the two latter forms. The facets of crystals are usually shaded, similar to pyrite.
Cobaltin still occurs more often in the form of massive accumulations, dense or granular addition. Has perfect cleavage, fragility. The color of the mineral varies from silvery white with violet gleams to black and gray. Opaque, has a metallic sheen of varying intensity. There are species heavier and harder.
Diagnostic signs.
It dissolves in nitric acid; Fairly easily melts, forming a weakly magnetic ball.
Origin.
Cobaltin is a typical mineral of hydrothermal genesis. It occurs mainly in veins and veins among granites and pegmatites.
Deposits and applications.
In the United States, this mineral is found in Colorado, Idaho and California. The most significant deposits in Canada (Cobalt in Ontario) and Mexico (the Sonora deposit). Fine crystals come from Sweden, Great Britain, Norway, Germany, Russia, Morocco, India and Australia. Cobaltin is present in nature in large quantities and is of great economic importance as cobalt ore. This element is used in many industries for steel production.
ADR 4.1

Highly flammable solids , self-reactive substances and solid desensitized explosives
Risk of fire. Flammable or combustible substances can ignite from sparks or flames. May contain self-reactive substances capable of exothermic decomposition in the case of heating, contact with other substances (such as: acids, heavy metal compounds or amines), friction or impact.
This can lead to the emission of harmful or flammable gases or vapor or spontaneous combustion. Containers can explode when heated (over-dangerous - practically do not burn).
Risk of explosion of desensitized explosives after loss of desensitizer
Seven vertical red stripes on a white background, equal in number, ADR number, black flame
ADR 6.1
Toxic substances (poison)
Risk of poisoning by inhalation, in contact with skin or if swallowed. Dangerous to aquatic environment or sewer system
Use a mask for emergency leaving the vehicle
White diamond, ADR number, black skull and crossbones
| The name of a cargo that is particularly dangerous for transportation | room
UN |
Class
ADR |
| COBALT RUBBER DEPOSITED | 1318 | 4.1 |
| COBALT NAPHTHENATES - POWDER | 2001 | 4.1 |
- Ghetchellit - "New Almaden blend" - arsenide and antimony sulfide (modern sulfosol)
- Antimony is a toxic metal (semimetal) , widely used in metallurgy, medicine and engineering
- Zirconium - a rare and undiscovered metal and the most dangerous precious stone in oxide and salt
- Gold - yellow dangerous and poisonous metal of modern accurate digital and cable technologies
- Sulfur is a golden-yellow toxic substance and a sign of active volcanic activity
- Cadmium is an undisputed toxic silvery metal unknown to a wide range of people
- Lead - a toxic gray imitator of metallic silver and toxic metal blende
- Arsenic is a classic poison of medieval and modern poisoners and medicine in medicine
Poisonous and radioactive dangerous stones and minerals
** - poisonous stones and minerals (mandatory check in the chemical laboratory + explicit indication of toxicity)
** - radioactive stones and minerals (mandatory check on the standard dosimeter + ban on open sales in case of radioactivity exceeding 24 milli / g / h + additional measures of population protection)
Catalog of minerals and semi-precious stones of the world by groups
** - poisonous stones and minerals
** - radioactive stones and minerals


Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.