Bluetooth (FAQ and hacking)

* What is Bluetooth?
* How does Bluetooth work?
* Is it possible to have a frequency conflict between Bluetooth devices and others using wireless radio communication?
* Is Bluetooth technology certified in Russia?
* Why do many call Bluetooth "blue tooth"?
* What are Bluetooth-devices?
* How can I use Bluetooth?
* At what distance can a Bluetooth connection be made?
* What is the power consumption and data transfer speed via Blutooth connection?
* Is it possible to protect the data transmitted via Bluetooth, and how does it work?
* Who can access my Bluetooth device while the wireless feature is active?
* How to set up Bluetooth devices for interaction? * What is the "pairing" of Bluetooth devices?
* I am constantly asked for a password when I am communicating with two Bluetooth-enabled devices. Is it possible to automate the process of their identification?
* I made all the settings for Bluetooth, but the devices can not communicate. How can this problem be solved?
* Who makes Bluetooth chips?
* Should we expect integration of Bluetooth technology with personal computers?
* Are there any competitors for Bluetooth?
* How much does Bluetooth manufacture cost and when will the technology be available to an ordinary user?
* What are the prospects for the development of technology?
Technical part:
What is Bluetooth?
Globally, Bluetooth is a wireless data transmission technology for any device with its support: mobile phones, PDAs, laptops, desktop computers, printers, digital devices and even home appliances. The material embodiment of Bluetooth is a small chip, which is a high-frequency short-range transceiver operating in the ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) frequency range 2.4465-2.4835 GHz. The range is designed for the operation of medical devices, household appliances, cordless phones, wireless LANs of the IEEE standard. To use it, you do not need a license.
How does Bluetooth work?
Bluetooth operates as a multi-point radio channel, controlled by a multilevel protocol, like GSM cellular communications. Bluetooth is able to "bypass" obstacles (walls including), so connected devices can be out of line of sight. The connection can occur not only on a point-to-point basis (two devices), but also on the point-to-point principle (several devices work with several others). In addition to having a Bluetooth chip in various devices, certain software is required to operate the system. The technology uses small short-range transceivers, either directly embedded in the device, or connected via a free port or expansion slot (USB, CF, SD / MMC, MS, PCMCIA). The technology uses FHSS - frequency hopping (1600 jumps per second) with spreading. In operation, the transmitter switches from one operating frequency to another by a pseudo-random algorithm to avoid conflicts with other devices. Full-duplex transmission uses time-division duplex (TDD). It supports isochronous and asynchronous data transfer, and provides easy integration with TCP / IP. Time Slots are deployed for synchronous packets, each of which is transmitted at its radio frequency. Each device has a unique 48-bit network address that is compatible with the IEEE 802.11x standard.
Is it possible for a Bluetooth device to have a frequency conflict with others using wireless radio?
The frequency range of Bluetooth work coincides with the operating range of most modern wireless systems in industry, scientific and medical institutions, and everyday life. In the event of a so-called "frequency conflict", serious interference may occur between Bluetooth and other wireless systems in this range. To solve this problem, the intermittent principle of Bluetooth was implemented. That is, during its operation, the frequency of the radio transmitter constantly changes from one to the other (1600 jumps per second). This allows you to free the frequencies you need to other devices and avoid conflicts.
Is Bluetooth certified in Russia?
At the time of writing this material, Bluetooth in Russia has not yet been officially certified. Many countries of the world have already been convinced of its safety and usefulness, but in the Russian Federation they are traditionally afraid of everything new. As far as the process of licensing technology is still delayed, it is not yet known. It is quite obvious that until this happens, the large companies that manufacture Bluetooth equipment will not deliver it to the country, which naturally hinders the spread and cheapening of technology in Russia. At the moment, only those devices that have Bluetooth support as a secondary function (cell phones, printers, etc.) are officially supplied. Devices that are primarily designed to carry out Bluetooth-communication (Bluetooth-adapters, etc.) are still present in the market illegally.
But if this issue can be resolved positively in the near future, then, for example, in France this will not happen soon. The fact is that there the 2.4 GHz band, used by Bluetooth, is occupied by the military, who, as is usually the case, do not make concessions. True, a small part of the ISM-band (2.4465-2.4835 GHz) still remains free. For France, apparently, will be developed special Bluetooth-devices that are incompatible with the devices produced for the rest of the world.
Why do many people call Bluetooth "blue tooth"?
The fact is that the literal translation of Bluetooth from English is a "blue tooth". However, the name of the technology arose not accidentally, and it was not invented by the dentist. In fact, it is inextricably linked with history. Long ago, Bluetooth'om called Danish Christian king, who lived in the 900's and ruled during the raids of the Vikings in Western Europe. King Harald Blue Tooth (Harald Bluetooth) went down in history as a collector of Scandinavian lands. In particular, he is attributed to the union of Denmark and Norway. Apparently, the inventors of Bluetooth technology, aware of historical issues, decided that, by analogy with the history of the king of the land unifier, it was intended to unify the world of mobile electronics.
What are Bluetooth-devices?
To date, Bluetooth-devices are the following: wireless handsfree or headset, cell phones, PDAs, adapters and Bluetooth modules, printers, car control systems, handwriting recognition pens, household appliances. In the future, their number and varieties will grow rapidly.
How can I use Bluetooth?
Already today we can cite a lot of examples of successful use of Bluetooth. To date, the most common example is the transfer of various kinds of data between devices at a short distance. For example, all the same phone conversation via a wireless earpiece or Internet connection from a mobile computer without using any cable connections. In this case, the phone acts as a remote telephone or modem, which can lie, say, in the pocket of a suitcase or suitcase, without occupying the user's hands. Or the access point to the corporate network in the office may be out of sight in another room, but the equipment can still work with the deleted data just as if its user's computer was connected to the local network via a cable.
How far can a Bluetooth connection be made?
Initially, the technology was conceived for a rather narrow application in communication equipment and assumed the possibility of communication at a distance of up to 10 meters. Today some companies already offer Bluetooth chips that can communicate at a distance of up to 100 meters. Since Bluetooth radio technology "is not afraid" of obstacles, so connected devices can be out of line of sight. The connection is automatic, as soon as Bluetooth-devices are within reach, not only with one device, but also with several (if they are within reach).
What is the power consumption and data transfer speed via Blutooth connection?
According to the established standard, the power consumption of Bluetooth devices should not exceed 10 mW (0.1 W). The data transfer rate provided by the standard is about 720 Kbps in asymmetric mode and 420 Kbps in full-duplex mode. Transmit three voice channels, but not a video signal.
Is it possible to protect the data transmitted by
Bluetooth, and how does it work?
Yes. First, a standard authentication procedure is required to communicate with any Bluetooth-enabled device. Each device has a unique 48-bit network address that is compatible with the IEEE 802.11x standard. At these addresses, the devices identify each other. To access from any Bluetooth device to another, active and within reach, two-way password verification is required. Only after this, interaction can be realized. Secondly, the software can be used to encrypt data transmitted between any devices that support a compatible algorithm.
Who can access my Bluetooth device while the wireless feature is active?
It all depends on the mode of operation of your device. As a rule, the software of Bluetooth-devices has a wide range of settings, which makes it easy to change its behavior in relation to the communication partners. You can enable / disable the visibility of your device for other users. For example, by creating a list of periodically used devices, you can make sure that your device is unavailable for any others. In this case, all attempts to access your device from the "outsiders" will be blocked, since they are not in the pre-formed list of communication partners. Configuring the interaction of Bluetooth-devices requires some experience and understanding of their interaction scheme. To avoid unauthorized access to your device's data, it is necessary to perform all necessary settings in terms of interaction with the network environment.
How to set up Bluetooth devices for interaction? What is the "pairing" of Bluetooth devices?
First, Bluetooth is activated on at least two devices that need to be made to work together. They should be located within reach of each other (for mobile devices 8-10 m).
Then one of them searches for available devices, and an environment list is generated. Each Bluetooth device has its own unique 48-bit network address, similar to the MAC address of the network adapter in a typical PC, which identifies the devices.
The identification process itself is further carried out. Suppose that when searching in a network environment, the network address of a mobile phone is found. It is stored in the memory of the device that was searching. Then you decide to "pair" both devices for interaction and activate the corresponding entry about the cell phone on the device that you were looking for. As a result, your device tries to access your mobile phone and passes it your unique network address. He, in turn, enters this address in his list of network environments, but before you open access to its resources, the phone will ask for a digital password. After entering it on the phone, a similar request will appear on the device that requested the session. If the passwords match on both devices, the interaction will be established. The second and third stages are called the "pairing" process of Bluetooth-devices.
General issues:
"Click to show the spoiler - click again to hide ..."
Q: What is BlueChalking / BlueJacking?
A: BlueChalking is a way to get to know and communicate with people, use the services of networks (game over the network, access to file servers, the Internet) using devices equipped with a wireless Bluetooth interface. They are equipped with many modern mobile phones, PDAs, laptops.
Also - the symbols used by the Blochaker.
BlueJacking is practically the same as BlueChalking, only the soup showers usually send anonymous messages in order to have fun. Their interest is to observe the reaction of the people who received their messages.
Q: I want to start right now, what do I need to do?
A: To start, turn on Bluetooth on your device (see the instruction and technical section FAQ), set there "visibility for others", and give your device a meaningful name (many use their network nicknames). Now you have become a full member of the community. You can use the search to identify the devices that are nearby or wait until they find you.
Q: Where can I get the software for BlueChalking (Jacking)?
A: In the simplest case, software is not needed. Create a new contact in the address book, write a message in the name field (or any other) and send it via Bluetooth (for instructions on how to do this, see the manual for your device).
If you want additional opportunities, then there are special programs. For example, BuZZone (http://www.buzzone.net/) for Pocket PC, Mobiluck (http://www.mobiluck.com/) for Symbian Series 60 smartphones (Nokia 3650, 3660, 6600, 7650, etc .)
Q: I managed to find some device, what should I do next?
A: See the question Where can I get the software for BlueChalking (Jacking)? Or you can try sending a picture.
Q: "Neighbors" I found, but that's only they have some strange figures instead of names or a phone model, why?
A: This situation usually occurs if the device owner does not know about the amazing opportunities that are available to him. These people need to be treated with special attention, because they are potential members of the so far few BlueChalkers. Incorrect numbers is the unique address of the Bluetooth module. On it, if desired, you can determine the manufacturer of the module (here - http://standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.shtml) .
* I have a password constantly being requested when I communicate with two Bluetooth-enabled devices. Is it possible to automate the process of their identification?
Can. The Bluetooth-device software has a wide range of settings that regulates their interaction with communication partners. There are a lot of settings, and they can differ from device to device. Among the common functions, there is usually the possibility of automatic identification of devices after they have been "paired". In this case, no passwords will be re-requested, since the necessary authentication information is stored in the device memory after the primary authentication.
* I made all the settings for Bluetooth, but the devices can not communicate. How can this problem be solved?
Check if the Bluetooth function is activated on the second device with which you are connecting.
Make sure that the devices are within range of each other (for mobile devices this distance is 8-10 meters, which can decrease somewhat when the batteries are depleted).
Please double-check all settings carefully. If one of the devices has a data encryption function, the second one must also support it.
If the automatic password saving feature is enabled, disable it on both devices, perform the identification process again.
Delete the old information from the list of partners for communication, re-search for active equipment and again "pair" the desired devices.
Check the availability of software updates on the websites of the developers of the devices used. While software often causes incompatibility problems for some functions on devices from different manufacturers.
* Who makes Bluetooth chips?
The development of Bluetooth-devices can be used by any company. Bluetooth-filling is developed directly by the manufacturer of the equipment or purchased from other companies. Ericsson was the first company to create a device that actually works with Bluetooth technology. In early 1998, several giants of the computer and telecommunications market, such as Ericsson, 3COM, Nokia, Intel, IBM, Toshiba, merged to create a wireless connection technology between mobile devices and peripheral equipment. Shortly thereafter, a special working group SIG (Special Interest Group) was represented. Very quickly, it joined such companies as Motorola, Dell, Compaq, Xircom and many others. A Bluetooth forum was created, which includes about two thousand companies (http://www.bluetooth.com/). The mass output of technology to the open market has already begun, and we can personally see this for ourselves. Bluetooth technology is not in vain called one of the most promising and rapidly developing, because it is convenient, easy to use and relatively cheap.
* Should we expect integration of Bluetooth technology with personal computers?
Yes, certainly. Recently, Bluetooth technology has been paying increasing attention, and this should facilitate its adoption in a variety of devices. While the price of Bluetooth devices is quite high, and many developers are slow to implement it, which slows the mass distribution of technology. To date, even Microsoft corporation announced about Bluetooth support, which promises to soon release the necessary software updates for the operation of such devices under Windows XP. Some companies already provide for the possibility of installing internal Bluetooth modules when buying, for example, laptops.
* Are there any competitors for Bluetooth?
At the initial development stage, the "blue tooth" was not considered a competitor for technologies such as IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b and HomeRF. It, like them, works in the 2.44 GHz band, but this project was oriented to more formal specifications, less global and narrower in its purpose. Rather, the main competitor to Bluetooth at the first stage of development was IrDA - today the most widely used technology of wireless connection of computers and external devices. It converts information into infrared radiation and transmits from one device to another. However, along with the advantages, IR communication has significant drawbacks: work on the point-to-point principle (only two devices at the same time), the equipment must be in line of sight, the range of infrared transceivers is usually not more than a few meters. And Bluetooth acts as a multipoint radio channel (several devices at the same time), it does not have to be very close to them (up to 8-10 m and more) for full connection of all components, there may be physical barriers between them.
New, especially "long-range" Bluetooth equipment is now considered as a competitor to IEEE 802.11x, HomeRF, ie, as a technology for building local networks. Due to the fact that one of the most important parameters of the "blue tooth" was to be the low cost of communication devices, as well as the miniaturization of chips, the technology is becoming more attractive for a variety of applications. In the near future, Bluetooth can become the de facto standard for wireless communications, replacing other, more expensive and less mobile standards. The most significant competition for Bluetooth will be the specifications of wireless LANs IEEE 802.11x.
* How much does Bluetooth manufacture cost and when will the technology be available to an ordinary user?
Analysts believe that the optimal price of a set of components to support Bluetooth: a processor, a radio transmitter, an antenna and a flash memory - is $ 5. Now manufacturers of various equipment embed these elements costing $ 10-15, and this is a significant difference. For comparison, infrared port costs companies only $ 1 per set. It turns out that as soon as the production volumes of Bluetooth components increase, and the prices for them decrease, the technology will become super popular. The solution to the problem can be a complex version of a Bluetooth device on a single chip, which will significantly reduce its cost, which is already being implemented by some manufacturers
Bluetooth components.
* What are the prospects for the development of technology?
They are Bluetooth huge. It is expected that this technology will be compatible with so many protocols and systems. Low cost, high degree of protection, convenience and ease of use are very significant advantages of the standard. Using the frequency of 2.4 GHz does not require licensing, and the distribution of other licenses for working with Bluetooth is for a nominal fee. In addition to general availability, this technology promises to become common, as in the near future the world industrial community will adopt technology as a global standard. This unity is due to the fact that it is much easier and cheaper to supply all devices with standard chips, rather than developing computers for different interface cards. The cheapness of network adapters will allow them to be embedded literally in all communications, household appliances, computers and other office equipment.
The facilities for users who promise the introduction of technology are extremely tempting and will certainly be very popular. Say, when you come to the office, your pocket computer immediately automatically synchronizes with the desktop PC, new contacts are transferred to your mobile phone. The technology will allow to unite any electronic devices, down to refrigerators, washing machines, microwave ovens and door locks. Just imagine how your refrigerator sends information to your mobile phone that it has run out of certain types of products, and that, in turn, replenishes the list of necessary purchases on your PDA.
A: BlueChalking is a way to get to know and communicate with people, use the services of networks (game over the network, access to file servers, the Internet) using devices equipped with a wireless Bluetooth interface. They are equipped with many modern mobile phones, PDAs, laptops.
Also - the symbols used by the Blochaker.
BlueJacking is practically the same as BlueChalking, only the soup showers usually send anonymous messages in order to have fun. Their interest is to observe the reaction of the people who received their messages.
Q: I want to start right now, what do I need to do?
A: To start, turn on Bluetooth on your device (see the instruction and technical section FAQ), set there "visibility for others", and give your device a meaningful name (many use their network nicknames). Now you have become a full member of the community. You can use the search to identify the devices that are nearby or wait until they find you.
Q: Where can I get the software for BlueChalking (Jacking)?
A: In the simplest case, software is not needed. Create a new contact in the address book, write a message in the name field (or any other) and send it via Bluetooth (for instructions on how to do this, see the manual for your device).
If you want additional opportunities, then there are special programs. For example, BuZZone (http://www.buzzone.net/) for Pocket PC, Mobiluck (http://www.mobiluck.com/) for Symbian Series 60 smartphones (Nokia 3650, 3660, 6600, 7650, etc .)
Q: I managed to find some device, what should I do next?
A: See the question Where can I get the software for BlueChalking (Jacking)? Or you can try sending a picture.
Q: "Neighbors" I found, but that's only they have some strange figures instead of names or a phone model, why?
A: This situation usually occurs if the device owner does not know about the amazing opportunities that are available to him. These people need to be treated with special attention, because they are potential members of the so far few BlueChalkers. Incorrect numbers is the unique address of the Bluetooth module. On it, if desired, you can determine the manufacturer of the module (here - http://standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.shtml) .
* I have a password constantly being requested when I communicate with two Bluetooth-enabled devices. Is it possible to automate the process of their identification?
Can. The Bluetooth-device software has a wide range of settings that regulates their interaction with communication partners. There are a lot of settings, and they can differ from device to device. Among the common functions, there is usually the possibility of automatic identification of devices after they have been "paired". In this case, no passwords will be re-requested, since the necessary authentication information is stored in the device memory after the primary authentication.
* I made all the settings for Bluetooth, but the devices can not communicate. How can this problem be solved?
Check if the Bluetooth function is activated on the second device with which you are connecting.
Make sure that the devices are within range of each other (for mobile devices this distance is 8-10 meters, which can decrease somewhat when the batteries are depleted).
Please double-check all settings carefully. If one of the devices has a data encryption function, the second one must also support it.
If the automatic password saving feature is enabled, disable it on both devices, perform the identification process again.
Delete the old information from the list of partners for communication, re-search for active equipment and again "pair" the desired devices.
Check the availability of software updates on the websites of the developers of the devices used. While software often causes incompatibility problems for some functions on devices from different manufacturers.
* Who makes Bluetooth chips?
The development of Bluetooth-devices can be used by any company. Bluetooth-filling is developed directly by the manufacturer of the equipment or purchased from other companies. Ericsson was the first company to create a device that actually works with Bluetooth technology. In early 1998, several giants of the computer and telecommunications market, such as Ericsson, 3COM, Nokia, Intel, IBM, Toshiba, merged to create a wireless connection technology between mobile devices and peripheral equipment. Shortly thereafter, a special working group SIG (Special Interest Group) was represented. Very quickly, it joined such companies as Motorola, Dell, Compaq, Xircom and many others. A Bluetooth forum was created, which includes about two thousand companies (http://www.bluetooth.com/). The mass output of technology to the open market has already begun, and we can personally see this for ourselves. Bluetooth technology is not in vain called one of the most promising and rapidly developing, because it is convenient, easy to use and relatively cheap.
* Should we expect integration of Bluetooth technology with personal computers?
Yes, certainly. Recently, Bluetooth technology has been paying increasing attention, and this should facilitate its adoption in a variety of devices. While the price of Bluetooth devices is quite high, and many developers are slow to implement it, which slows the mass distribution of technology. To date, even Microsoft corporation announced about Bluetooth support, which promises to soon release the necessary software updates for the operation of such devices under Windows XP. Some companies already provide for the possibility of installing internal Bluetooth modules when buying, for example, laptops.
* Are there any competitors for Bluetooth?
At the initial development stage, the "blue tooth" was not considered a competitor for technologies such as IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b and HomeRF. It, like them, works in the 2.44 GHz band, but this project was oriented to more formal specifications, less global and narrower in its purpose. Rather, the main competitor to Bluetooth at the first stage of development was IrDA - today the most widely used technology of wireless connection of computers and external devices. It converts information into infrared radiation and transmits from one device to another. However, along with the advantages, IR communication has significant drawbacks: work on the point-to-point principle (only two devices at the same time), the equipment must be in line of sight, the range of infrared transceivers is usually not more than a few meters. And Bluetooth acts as a multipoint radio channel (several devices at the same time), it does not have to be very close to them (up to 8-10 m and more) for full connection of all components, there may be physical barriers between them.
New, especially "long-range" Bluetooth equipment is now considered as a competitor to IEEE 802.11x, HomeRF, ie, as a technology for building local networks. Due to the fact that one of the most important parameters of the "blue tooth" was to be the low cost of communication devices, as well as the miniaturization of chips, the technology is becoming more attractive for a variety of applications. In the near future, Bluetooth can become the de facto standard for wireless communications, replacing other, more expensive and less mobile standards. The most significant competition for Bluetooth will be the specifications of wireless LANs IEEE 802.11x.
* How much does Bluetooth manufacture cost and when will the technology be available to an ordinary user?
Analysts believe that the optimal price of a set of components to support Bluetooth: a processor, a radio transmitter, an antenna and a flash memory - is $ 5. Now manufacturers of various equipment embed these elements costing $ 10-15, and this is a significant difference. For comparison, infrared port costs companies only $ 1 per set. It turns out that as soon as the production volumes of Bluetooth components increase, and the prices for them decrease, the technology will become super popular. The solution to the problem can be a complex version of a Bluetooth device on a single chip, which will significantly reduce its cost, which is already being implemented by some manufacturers
Bluetooth components.
* What are the prospects for the development of technology?
They are Bluetooth huge. It is expected that this technology will be compatible with so many protocols and systems. Low cost, high degree of protection, convenience and ease of use are very significant advantages of the standard. Using the frequency of 2.4 GHz does not require licensing, and the distribution of other licenses for working with Bluetooth is for a nominal fee. In addition to general availability, this technology promises to become common, as in the near future the world industrial community will adopt technology as a global standard. This unity is due to the fact that it is much easier and cheaper to supply all devices with standard chips, rather than developing computers for different interface cards. The cheapness of network adapters will allow them to be embedded literally in all communications, household appliances, computers and other office equipment.
The facilities for users who promise the introduction of technology are extremely tempting and will certainly be very popular. Say, when you come to the office, your pocket computer immediately automatically synchronizes with the desktop PC, new contacts are transferred to your mobile phone. The technology will allow to unite any electronic devices, down to refrigerators, washing machines, microwave ovens and door locks. Just imagine how your refrigerator sends information to your mobile phone that it has run out of certain types of products, and that, in turn, replenishes the list of necessary purchases on your PDA.
Software for hacking:
"Click to show the spoiler - click again to hide ..."
For starters, who are interested, a small list of AT commands for mobile can be found here: http://gatling.ikk.sztaki.hu/~kissg/gsm/at+c.html
Super Bluetooth Hack (* .jar)
When your smartphone is connected to another phone via bluetooth, you can:
- read his messages
- read his contacts
- change profile
- listen to his rington
- listen to his songs (in his phone)
- turn off his phone, etc.
Http://forum.0day.kiev.ua/index.php?showto...mp;hl=bluetooth
Bluesweep
Bluetooth scanner to identify nearby wireless devices, connections between them, running services and identifying potential vulnerabilities. Works on XP with a mandatory second service pack. Details (in particular, a list of supported Bluetooth adapters) and links for download can be found on the manufacturer's website .
Bluediving
Utilities for pen test wireless networks. A software package that allows you to test bluetooth devices for Bluebug, BlueSnarf, BlueSnarf ++, BlueSmack and perform penetration tests. Works with the BlueZ stack. Download / watch here
Blooover
The most famous utility for hacking cellular, Blooover. In addition to the attack, BlueBug includes the implementation of the HeloMoto attack, BlueSnarf and the ability to send malformed objects via OBEX.
Used on phones supporting J2ME (with support for MIDP 2.0 and JSR-82 (Bluetooth API)). Developers site with links to download ( jar & sis )
Russified versions of bluetooth:
Blooover1 (* .jar)
Blooover2 (* .jar)
BSS (Bluetooth Stack Smasher)
Fuzzer frames that allow Denial of Service attacks in a wireless environment. Download, see the example of use here .
BTScanner
Utility for detailed information retrieval from a bluetooth device (blueprinting). Uses bluecove library. The program page is here . The version for XP to download here , for the Nixes here .
GreenPlaque
Multi-dongle Bluetooth Discovery Scanner download this site .
Bluetooth phone book dumping tool
Creates a backup copy of phonebook via bluetooth. Tested on Nokia 6310i, Ericsson T610 and T68i .. Source codes can be viewed here .
Bluesniff
Proof of concept code for a bluetooth wardriving utility. Download / watch .
BlueScanner
Interesting tool for PC. Simply put scanner of toothy devices for PC. Downloading .
BlueSpam (* .prc for PALM)
BlueSpam is an application for Palm OS , which allows to send files to all found bluetooth devices, if they support OBEX. This happiness can be downloaded here .
CIHwBT
CIHwBT is a Bluetooth Security Framework for Windows Mobile 2005. Currently, it only supports some bluetooth exploits and tools like BlueSnarf, BlueJack, and some DoS attacks. It is intended to work with any pocketpc with Microsoft Bluetooth Stack. The idea is an interesting program. Watch .
Here are the sources of a fast enough scanner.
BlueZ
The Bluetooth protocol stack for Linux is developed in Qualcomm and is included in the Linux kernel since version 2.4.18, but it is necessary to install this package of libraries and utilities. To bluetooth hack'u refers to the fact that the main attacks are implemented by standard means.
This package includes the following utilities:
Hcitool - a Bluetooth scanner (with a command line interface), allows you to detect all devices that are in the open mode. The man page for hcitool can be found here.
L2ping - Bluetooth version of the "ping" command
L2test - utility for testing devices
Hcidump - batch sniffer, bluetooth-version of the utility tcpdump
Also contains daemons - hcid, hciemud and configuration utility hciconfig. Downloading .
BlueJacker
The program uses the Palm OS . Sends text messages via Bluetooth to the specified devices. In general, something like BlueSpam.
Sway
BtCrawler is a simple bluetooth scanner for Windows Mobile devices . It searches for bluetooth devices within range and can perform service requests. The user can also make service requests to his device for self-diagnosis of equipment.
There is support for bluejacking and bluesnarfing.
Requirements:
- MS Bluetooth Stack (WIDCOMM / Broadcom is not supported).
- Windows Mobile 5, PPC2003, PPC2003SE, Smartphone 2003, Smartphone 2003SE and Smartphone with WM5.
Download: http://elvis000.ifolder.ru/4411968
Offsite: http://www.silentservices.de/btCrawler.html
Super Bluetooth Hack New 2008
This is a new version of the program Super Bluetooth Hack for conventional mobile phones and based on Symbian .
If you do not know what Super Bluetooth Hack is, then it's a program, with the help of which you can control another's mobile phone at a distance (10-15 meters)
BT INFO v1.08 ( * .jar )
The program is connected via bluetooth. On the other phone you need to give permission.
BT File Manager ( * .jar )
A program that allows you to view and change the file system via Bluetooth, and also copy files to your phone. The interface in Russian is quite simple and convenient. Requires confirmation but when you are asked, you need to exchange data.
"There is no pale yellow as the picture is transferred."
Http://tracers.ru/upload/656975
A set of some programs from the magazine "Hacker"
TERMINAL, access to mobile resources via BT (Windows Mobile)
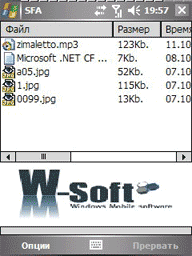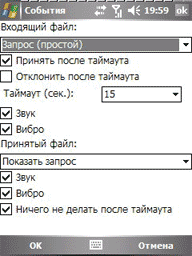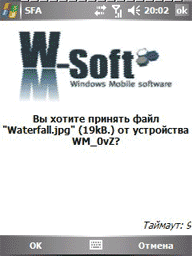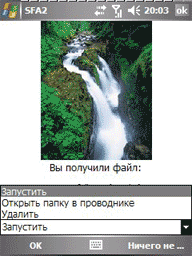
At the moment the program has 6 possible modes of operation: OBEX FTP, AT, IrMC, sending files, sending messages, receiving files.
The OBEX FTP mode allows you to access the target phone file system. You can download, send, delete files, create files. It is important to note that the implementation of OBEX is different in each phone, so not all the declared features will work.
The AT mode allows you to send commands to the target phone. This mode provides virtually unlimited possibilities for managing the target phone
You can easily find in Iternet the information you are interested in AT commands.
Also in AT mode you can get a phone book and a text message for the target phone. Because All phones respond differently to a phone book / sms request, there is no guarantee that this will work, I can not give you.
The IrMC mode allows you to access the phone book and the target phone calendar through the synchronization service. All received data is stored in the VCARD format (.vcf).
Unfortunately I do not have enough information about this format, so its conversion to html is only partial. Encodings are supported: UTF7, UTF8 and Quoted-Printable encoding method.
At the moment, the fields should be defined normally: name, phone number, phone number type, e-mail, group membership.
Since version 0.9.7, the BlueBug attack has appeared in IrMC mode. It only works on phones of the time Sony-Ericsson T610!
The file transfer mode allows you to send several files to the target phone at once. Sending occurs in the same way as if you were sending through a file manager.
But there is one nice thing: sending files is pretty fast. For example, sending a file to Nokia N80 goes twice as fast as through Smart Explorer (measured with a stopwatch).
The messaging mode allows you to send a text message to the selected phone.
The file retrieval mode is an Obex Object Push server. Now you can receive files on BT directly to the USB flash drive! The files are saved in the folder selected in the settings (either \ My Documents \ Terminal or \ Storage Card \ My Documents \ Terminal).
The method used differs from the method used in the moBlue and Sniper programs. In them, the files were first received in RAM memory, from where they were copied to the destination. In the Terminal, the file is immediately addressed to the final location.
The program is free for all Russian-speaking users and is distributed on the principle of DonateWare, i.e. You can thank the author for his work.
The program requires a Bluetooth stack from Microsoft and the .NET Compact Framework 2.0
Off. site
(Do not be afraid of the messages about the price, immediately go to the Russian version, everything is free there)
download:
Http://www.wm-soft.com/rus_products/terminal
.NET Compact Framework 2.0 CAB for 2003. (5.4 MB)
Some AT commands (rename to .txt)
Super Bluetooth Hack (* .jar)
When your smartphone is connected to another phone via bluetooth, you can:
- read his messages
- read his contacts
- change profile
- listen to his rington
- listen to his songs (in his phone)
- turn off his phone, etc.
Http://forum.0day.kiev.ua/index.php?showto...mp;hl=bluetooth
Bluesweep
Bluetooth scanner to identify nearby wireless devices, connections between them, running services and identifying potential vulnerabilities. Works on XP with a mandatory second service pack. Details (in particular, a list of supported Bluetooth adapters) and links for download can be found on the manufacturer's website .
Bluediving
Utilities for pen test wireless networks. A software package that allows you to test bluetooth devices for Bluebug, BlueSnarf, BlueSnarf ++, BlueSmack and perform penetration tests. Works with the BlueZ stack. Download / watch here
Blooover
The most famous utility for hacking cellular, Blooover. In addition to the attack, BlueBug includes the implementation of the HeloMoto attack, BlueSnarf and the ability to send malformed objects via OBEX.
Used on phones supporting J2ME (with support for MIDP 2.0 and JSR-82 (Bluetooth API)). Developers site with links to download ( jar & sis )
Russified versions of bluetooth:
Blooover1 (* .jar)
Blooover2 (* .jar)
BSS (Bluetooth Stack Smasher)
Fuzzer frames that allow Denial of Service attacks in a wireless environment. Download, see the example of use here .
BTScanner
Utility for detailed information retrieval from a bluetooth device (blueprinting). Uses bluecove library. The program page is here . The version for XP to download here , for the Nixes here .
GreenPlaque
Multi-dongle Bluetooth Discovery Scanner download this site .
Bluetooth phone book dumping tool
Creates a backup copy of phonebook via bluetooth. Tested on Nokia 6310i, Ericsson T610 and T68i .. Source codes can be viewed here .
Bluesniff
Proof of concept code for a bluetooth wardriving utility. Download / watch .
BlueScanner
Interesting tool for PC. Simply put scanner of toothy devices for PC. Downloading .
BlueSpam (* .prc for PALM)
BlueSpam is an application for Palm OS , which allows to send files to all found bluetooth devices, if they support OBEX. This happiness can be downloaded here .
CIHwBT
CIHwBT is a Bluetooth Security Framework for Windows Mobile 2005. Currently, it only supports some bluetooth exploits and tools like BlueSnarf, BlueJack, and some DoS attacks. It is intended to work with any pocketpc with Microsoft Bluetooth Stack. The idea is an interesting program. Watch .
Here are the sources of a fast enough scanner.
BlueZ
The Bluetooth protocol stack for Linux is developed in Qualcomm and is included in the Linux kernel since version 2.4.18, but it is necessary to install this package of libraries and utilities. To bluetooth hack'u refers to the fact that the main attacks are implemented by standard means.
This package includes the following utilities:
Hcitool - a Bluetooth scanner (with a command line interface), allows you to detect all devices that are in the open mode. The man page for hcitool can be found here.
L2ping - Bluetooth version of the "ping" command
L2test - utility for testing devices
Hcidump - batch sniffer, bluetooth-version of the utility tcpdump
Also contains daemons - hcid, hciemud and configuration utility hciconfig. Downloading .
BlueJacker
The program uses the Palm OS . Sends text messages via Bluetooth to the specified devices. In general, something like BlueSpam.
Sway
BtCrawler is a simple bluetooth scanner for Windows Mobile devices . It searches for bluetooth devices within range and can perform service requests. The user can also make service requests to his device for self-diagnosis of equipment.
There is support for bluejacking and bluesnarfing.
Requirements:
- MS Bluetooth Stack (WIDCOMM / Broadcom is not supported).
- Windows Mobile 5, PPC2003, PPC2003SE, Smartphone 2003, Smartphone 2003SE and Smartphone with WM5.
Download: http://elvis000.ifolder.ru/4411968
Offsite: http://www.silentservices.de/btCrawler.html
Super Bluetooth Hack New 2008
This is a new version of the program Super Bluetooth Hack for conventional mobile phones and based on Symbian .
If you do not know what Super Bluetooth Hack is, then it's a program, with the help of which you can control another's mobile phone at a distance (10-15 meters)
"Click to show the spoiler - click again to hide ..."
What can I do?
1) Read SMS
2) Turn off the telenfon
3) Turn on the music
4) Select modes (normal, no sound ...)
5) Block the phone
Installation:
1) Download on the computer.
2) fill in the mobile
3) Run the installer (what you downloaded, by the way you need JAVA)
4) He will install it and you will be able to run the program
5) Select languages and climb in the settings
6) Click Connection
7) Click search devices
8) Select the "victim"
9) AND MANAGEMENT !!!
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Why does the white screen appear when I click to connect?
Answer: So this is an anamal zone, in short, the bluetooth does not work well there, or you have problems with JAVA (unlikely), just reboot and everything seems to go away.
2) Why when I connect to the "victim" to it comes messages like "User * your name * wants to access this phone, allow it?"
Answer: this means that the phone of the "victim" has something like a protection to avoid this, try to make it so that the victim added you to the contact list on bluetooth, this should bypass the protection. Incidentally, on some phones, there is no such protection, and you immediately get access. In the archive there are two programs for regular phones and for Symbian phones.
In the archive also BTInfo
| DeposiFiles |
| RapidShare |
1) Read SMS
2) Turn off the telenfon
3) Turn on the music
4) Select modes (normal, no sound ...)
5) Block the phone
Installation:
1) Download on the computer.
2) fill in the mobile
3) Run the installer (what you downloaded, by the way you need JAVA)
4) He will install it and you will be able to run the program
5) Select languages and climb in the settings
6) Click Connection
7) Click search devices
8) Select the "victim"
9) AND MANAGEMENT !!!
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Why does the white screen appear when I click to connect?
Answer: So this is an anamal zone, in short, the bluetooth does not work well there, or you have problems with JAVA (unlikely), just reboot and everything seems to go away.
2) Why when I connect to the "victim" to it comes messages like "User * your name * wants to access this phone, allow it?"
Answer: this means that the phone of the "victim" has something like a protection to avoid this, try to make it so that the victim added you to the contact list on bluetooth, this should bypass the protection. Incidentally, on some phones, there is no such protection, and you immediately get access. In the archive there are two programs for regular phones and for Symbian phones.
In the archive also BTInfo
| DeposiFiles |
| RapidShare |
BT INFO v1.08 ( * .jar )
The program is connected via bluetooth. On the other phone you need to give permission.
"Click to show the spoiler - click again to hide ..."
Allows you to:
-read sms
Written book
-to call from his phone
-to control buttons
-Play on / off
-view the application
-and many other things
Honed for Sony Ericsson, so Sony Ericsson is the best administrator. On other phones, half of the functions do not work.
Download from the site
Bluetooth Hack is made of this program
-read sms
Written book
-to call from his phone
-to control buttons
-Play on / off
-view the application
-and many other things
Honed for Sony Ericsson, so Sony Ericsson is the best administrator. On other phones, half of the functions do not work.
Download from the site
Bluetooth Hack is made of this program
BT File Manager ( * .jar )
A program that allows you to view and change the file system via Bluetooth, and also copy files to your phone. The interface in Russian is quite simple and convenient. Requires confirmation but when you are asked, you need to exchange data.
"There is no pale yellow as the picture is transferred."
Http://tracers.ru/upload/656975
A set of some programs from the magazine "Hacker"
"Click to show the spoiler - click again to hide ..."
Bluedos
An attacker demonstrating a connection attack. When compiling, you must specify
-l bluetooth, because the corresponding socket-family is used.
Carwhisperer.
Utility of the famous reserver Joshua Wright. Everything described in the article you can create
It is with her help that.
The same in the archive:
BlueProximity 1.2.4
Bluetooth Remote Control 3.0
Connect btdos
LockItNow! 1.2
Redfang 2.5
Description of the protocol vulnerability (in English)
Http://slil.ru/25717392
An attacker demonstrating a connection attack. When compiling, you must specify
-l bluetooth, because the corresponding socket-family is used.
Carwhisperer.
Utility of the famous reserver Joshua Wright. Everything described in the article you can create
It is with her help that.
The same in the archive:
BlueProximity 1.2.4
Bluetooth Remote Control 3.0
Connect btdos
LockItNow! 1.2
Redfang 2.5
Description of the protocol vulnerability (in English)
Http://slil.ru/25717392
TERMINAL, access to mobile resources via BT (Windows Mobile)
"Click to show the spoiler - click again to hide ..."

At the moment the program has 6 possible modes of operation: OBEX FTP, AT, IrMC, sending files, sending messages, receiving files.
The OBEX FTP mode allows you to access the target phone file system. You can download, send, delete files, create files. It is important to note that the implementation of OBEX is different in each phone, so not all the declared features will work.
The AT mode allows you to send commands to the target phone. This mode provides virtually unlimited possibilities for managing the target phone
You can easily find in Iternet the information you are interested in AT commands.
Also in AT mode you can get a phone book and a text message for the target phone. Because All phones respond differently to a phone book / sms request, there is no guarantee that this will work, I can not give you.
The IrMC mode allows you to access the phone book and the target phone calendar through the synchronization service. All received data is stored in the VCARD format (.vcf).
Unfortunately I do not have enough information about this format, so its conversion to html is only partial. Encodings are supported: UTF7, UTF8 and Quoted-Printable encoding method.
At the moment, the fields should be defined normally: name, phone number, phone number type, e-mail, group membership.
Since version 0.9.7, the BlueBug attack has appeared in IrMC mode. It only works on phones of the time Sony-Ericsson T610!
The file transfer mode allows you to send several files to the target phone at once. Sending occurs in the same way as if you were sending through a file manager.
But there is one nice thing: sending files is pretty fast. For example, sending a file to Nokia N80 goes twice as fast as through Smart Explorer (measured with a stopwatch).
The messaging mode allows you to send a text message to the selected phone.
The file retrieval mode is an Obex Object Push server. Now you can receive files on BT directly to the USB flash drive! The files are saved in the folder selected in the settings (either \ My Documents \ Terminal or \ Storage Card \ My Documents \ Terminal).
The method used differs from the method used in the moBlue and Sniper programs. In them, the files were first received in RAM memory, from where they were copied to the destination. In the Terminal, the file is immediately addressed to the final location.
The program is free for all Russian-speaking users and is distributed on the principle of DonateWare, i.e. You can thank the author for his work.
The program requires a Bluetooth stack from Microsoft and the .NET Compact Framework 2.0
Off. site
(Do not be afraid of the messages about the price, immediately go to the Russian version, everything is free there)
download:
Http://www.wm-soft.com/rus_products/terminal
.NET Compact Framework 2.0 CAB for 2003. (5.4 MB)
Some AT commands (rename to .txt)




Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.