Pelvis. Renal segments
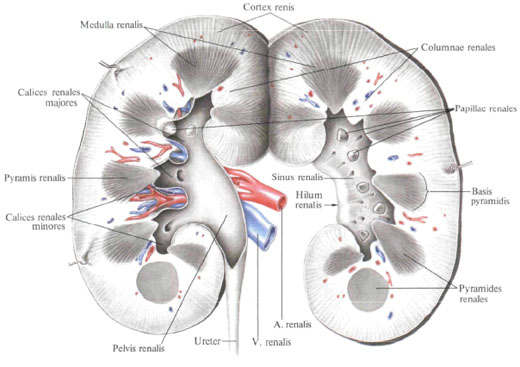
The renal pelvis , pelvis renalis, has a narrowed shape in the anteroposterior direction of the funnel; Its broad part is embedded in the sinus, while the narrowed part protrudes outward in the area of the kidneys' gate and passes into the ureter. The cavities of small and large cups are lined with mucous membrane, which directly passes into the mucous membrane of the pelvis, and the latter - into the mucous membrane of the ureter.
Functionally the most important part of the renal tissue are the epithelial tubules - the urinary renal tubules, tubuli renales. They take part in the formation of the structural and functional unit of the kidney - nephron, nephronum, consisting of the renal corpuscle and the system of the nephron tubules. The renal corpusculum renale consists of a glomerulus of the renal corpuscle, glomerulus corpusculi renalis, and a two-layered glomerulus capsule, capsula glomeruli.
The renal (urinary) canaliculus in the cortical substance of the kidney leaving the capsule is the proximal part of the nephron tubule, pars proximalis tubuli nephroni, passing into the nephron loop, ansa nephroni. The nephron loop lies in the brain substance of the kidney. In it the descending part, pars descendens ansae, and the ascending part, pars ascendens ansae, passing into the distal direct canal of the nephron, pars distalis tubuli nephroni, and then into the collective renal tubules, tubuli renales colligentes, are distinguished. A few collecting tubules flow into the papillary ducts, ductus papillaris. The latter end with papillary holes, foramina papilaria, on the lattice field, area cribrosa, renal papilla, papilla renalis, on top of the renal pyramid, pyramis renalis.
Blood vessels are particularly closely related to the renal tubule system. Branches of the renal artery, a. Renalis, penetrating from the renal sinus, sinus renalis, into the renal substance, are located radially between the pyramids in the form of the interlobar arteries of the kidney, aa. Interlobares renis.
Approaching the boundary of the cortical and cerebral substance, each interlobar artery is divided into two arc arteries, aa. Arcuatae, entering the neighboring parts and located here above the base of the pyramid. They send to the brain substance direct arterioles, arleriolae rectae, and into the cortical substance - interlobular arteries, aa. Interlobulares, terminating in a fibrous capsule with capsular branches. Rr. Capsulares.

From the interlobular arteries, the glomerular arterioles (bringing the blood vessels), arteriola glomerularis afferens (vas afferens), which dissociate into the glomerular capillary network, rete capillare glomerulare, surrounded by a capsule, depart. The capillary network is only arterial (by the type of a wonderful network, rete mirabile), and the glomerular blood capillary, vas haemocapillare glomerulare, emerging from the glomerular network, passes into the outgoing glomerular arteriol (vas efferens), which is already outside the limits of the arteriola glomerularis efferens Capsules. This capillary again breaks up into a network of capillaries, braiding the urinary tubules and giving rise to the venous system.
From the brain substance, the blood collects direct venules, venulae rectae, flowing into the arched veins, vv. Arcuatae. In the cortex, according to the course of the interlobular arteries, there are interlobular veins, vv. Interlobulares. The latter are formed from small vessels of the surface layer of the cortical substance, the so-called stellate veins, vv. Stellatae, and later take the veins from the secondary capillary network, braiding the renal tubules. Interlobular veins are poured into the arched veins. The arc veins of the two adjacent lobes, merging, form the inter-lobe veins, vv. Interlobares, which follow through the kidney poles along with the interlobar arteries. In the circumference of the renal papillae, the interlobar veins emerge from the kidney parenchyma into the renal sinus, where, merging, form a renal vein, v. Renalis, which empties into the inferior vena cava, v. Cava inferior.
In each kidney, the renal segments are distinguished according to the division of the artery, segmenta renalia: the upper segment, segmentum superius, corresponds to the medial margin and partly the anterior surface of the upper end of the kidney; The upper anterior segment, segmentum anterius superius, includes the anterior surface of the upper end, the upper part of the middle part of the kidney, the lateral margin and partially the posterior surface; The lower anterior segment, segmentum anterius inferius, lies, like the upper anterior segment, in front of the renal pelvis, reaching the anterior surface of the kidney in the lower part of its middle part and partly on the posterior surface; The lower segment, segmentum inferius, occupies the lower end of the kidney; Posterior segment, segmentum posterius, lies behind the renal pelvis and corresponds to the posterior surface of the kidney between the upper segment from the top, the lower one from the bottom, the upper and lower anterior segments - laterally.









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.