The fallopian tubes
Fallopian tube, tuba uterina (salpinx), a paired organ, is located almost horizontally on both sides of the uterine fundus, in the free (upper) edge of the wide uterus tale. Pipes are cylindrical channels (tubes), one (lateral) end of which opens into the cavity of the peritoneum, the other (medial) into the uterine cavity. The length of a pipe in an adult woman averages 10-12 cm, and a width of 0.4-0.6 cm. The right and left tubes have an unequal length.
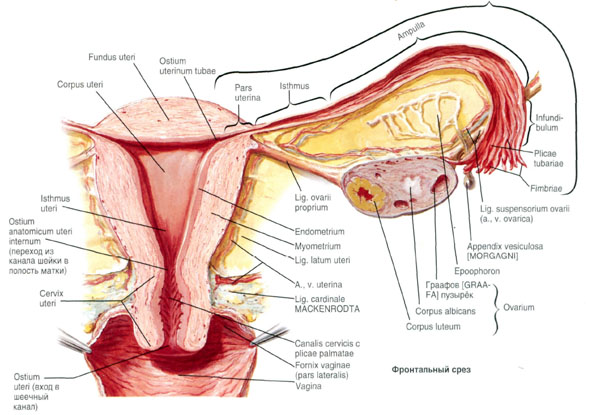
The following divisions of the fallopian tube are distinguished: funnel of the fallopian tube, infundibulum tubae uterinae, expansion - ampulla of the fallopian tube, ampulla tubae uterinae, isthmus tubae uterinae, and uterine part, pars uterina.
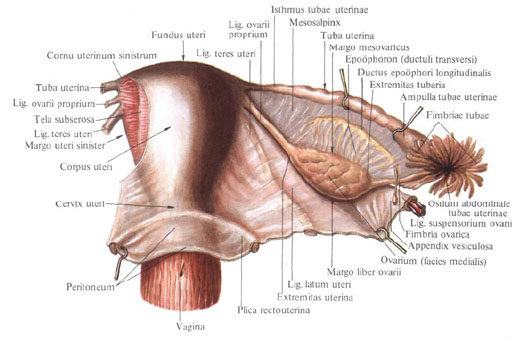
The outer end is the funnel of the uterine tube, the infundibulum tubae uterinae, has the abdominal opening of the uterine tube, the ostium abdominale tubae uterinae, bordered by a large number of spiky outgrowths - a pipe fimbriae, fimbriae tubae. Each fringe has small cuttings along its edge. The longest of them is the ovarian fimbria, fimbria ovarica, follows the outer edge of the mesentery of the tube and is a kind of trough that goes to the tube end of the ovary where it is attached. Sometimes on the free abdominal end of the tube there is a small vesicle appendage that hangs freely on the long leg.
The abdominal opening of the tube has a diameter of up to 2 mm: through this opening the peritoneal cavity through the uterine tube , uterus and vagina communicates with the external environment. Lateral, enlarged part - ampulla of the uterine tube, ampulla tubae uterinae, is the longest part of it, has a curved shape; Its lumen is wider than in other parts, the thickness is up to 8 mm.
The medial, more straight and narrow part of the fallopian tube - its isthmus, isthmus tubae uterinae, approaches the corner of the uterus at the border between its bottom and body. This is the thinnest part of the tube, its lumen is very narrow, the thickness is about 3 mm. It continues into the portion of the tube that is in the wall of the uterus - into the uterine part, pars uterina. This part opens into the uterine cavity by the uterine opening of the tube, ostium uterinum tubae, up to 1 mm in diameter.
The fallopian tube is covered from the sides and from above by the serosa, tunica serosa, which forms the lateral surfaces of the broad ligament of the uterus. That part of the fallopian tube, which is directed into the lumen of the broad ligament, is free from the peritoneum. Here, the front and back sheets of the broad ligament are joined, forming a ligament between the tube to the ovary's own ligament - the so-called mesentery of the fallopian tube, mesosalpinx.
Under the serous membrane is a loose connective tissue - subserous base, tela subserosa.
Deeper lies the muscular membrane, tunica muscularis. It consists of smooth muscle fibers arranged in three layers: a more thin outer longitudinal layer (subperitoneal); Middle, thicker circular layer and inner longitudinal layer (submucosa). The fibers of the last layer are best expressed in the region of the isthmus and the uterine part of the tube. The muscular membrane of the uterine tube is more developed in the medial part and at the uterine end and gradually becomes thinner towards the distal (ovarian).
The muscular membrane surrounds the innermost layer of the wall of the uterine tube - the mucosa, the tunica mucosa, a characteristic feature of which are the longitudinally located tubular folds, plicae tubariae. The folds of the ampulla of the uterine tube are well expressed, they are high and form secondary and tertiary folds: the isthmus folds are less developed, they are lower and have no secondary folds; Finally, in the interstitial (intrauterine) section the folds are the lowest and weakly expressed.
At the edges of the fringe, the mucous membrane of the uterine tube borders on the peritoneum. The mucous membrane is covered with a single-layer prismatic and ciliate epithelium; Cilia flicker towards the end of the tube. Part of the cells of the epithelium is devoid of cilia, these cells are secretory.
The section of the isthmus of the uterine tube from the uterus goes at right angles and almost horizontally; The ampulla of the uterine tube is located in an arc around the lateral surface of the ovary (a bend is formed here); The end section of the tube, passing along the medial surface of the ovary, reaches the level of the horizontal part of the isthmus.
Innervation: plexus ovaricus, plexus uterovaginalis.
Blood supply: r. Tubarius (a. Uterina), branches from a. Ovarica to the funnel of the uterine tube. Venous blood flows along the veins of the same name in v. Ovarica and plexus venosus uterinus. Lymphatic vessels divert lymph to nodi lymphatici lumbales and nodi iliaci interni.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.