Muscles of the urogenital diaphragm
Muscles of urogenital diaphragm.
1. Deep transverse perineal muscle , m. Transversus perinei profundus, steam, narrow, small; Begins on the sciatic hillocks, behind the place of attachment of the sciatic-cavernous muscle, and is directed to the median line, where it joins the same muscle of the opposite side.
Function: participates in contraction of the membranous part of the urethra.
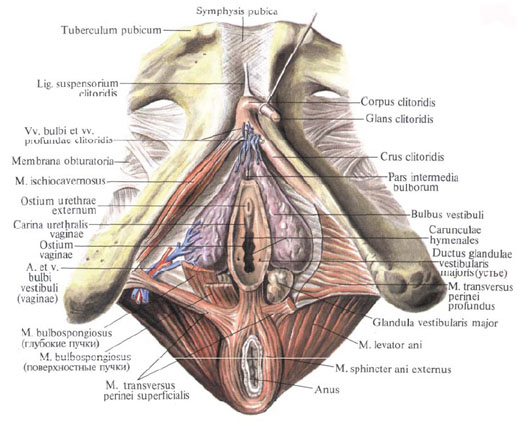
2. Uterine sphincter , m. Sphincter urethrae, - paired muscle, lies anterior to the previous one. It distinguishes peripherally located bundles that are directed to the branches of the pubic bones and to the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, and the deeper central, circular, surrounding membranous part of the urethra. In addition, in men the muscle is connected to the prostate gland , in women - to the vagina .
In addition to the striated muscle beams, there is a small part of the smooth fibers in the muscle.
Function: compresses the urethra, as well as bulbourethral glands in men and large glands of the vestibule in women.
Innervation and blood supply are the same as in the muscles of the pelvic diaphragm.
3. Superficial perineal transverse muscle, m. Transversus perinei superficialis, unstable, sometimes absent on one or both sides. It is located at the posterior edge of the genitourinary diaphragm, it is a thin muscular stripe running across the perineum.
The lateral end of the muscle is attached to the ischium bone, the medial end is crossed along the median line with the same muscle of the opposite side, partially intertwined in the bulbous-spongy muscle, in part - into the external sphincter of the anus.
Function: is involved in strengthening the genitourinary diaphragm and fixing the legs of the penis.

4. The ischium-cavernous muscle, m. Ischiocavernosus, steam, looks like a narrow muscle band. It begins with a narrow tendon from the inner surface of the ischial hillock, bypasses the pedicle of the cavernous body of the penis (clitoris) from the inside outwards and is lost in its belly coat on the back side. Sometimes it connects on the back of the penis with the same muscle of the opposite side, forming a semblance of a loop at its root. Its posterior end is located at the beginning of the superficial perineal transverse muscle.
Function: presses the superficial veins of the penis, which causes stagnation of blood in the cavernous bodies and promotes lifting of the penis during erection; In women its effect is insignificant.
5. Bulb-spongy muscle, m. Bulbospongiosus, paired, in men covers the lower and lateral convex surfaces of the bulb of the penis to the junction of the cavernous bodies. Behind her, muscle tufts reach the outer sphincter of the anus.
In the muscle, three layers are distinguished: the surface layer originates from the fibrous plate located along the midline of the gallbladder shell of the bulb of the penis. The second layer starts from a transversely extending fibrous lamina formed by the posterior edge of the perineal fascia. The third layer, the deepest, covers the posterior part of the bulb of the penis.
Ahead of the muscle ends in the fascia at the rear of the penis; Behind the muscle is connected to the superficial perineal transverse muscle, with the anterior end of the external anal sphincter.
The junction of bulbous-spongy, superficial transverse muscles and the external sphincter of the anus with the middle of the posterior edge of the urogenital diaphragm is the so-called tendon center of the perineum, centrum tendineum perinei; Here most of the muscles of the surface and deep layers of the perineum converge.
The bulbous-spongy muscle in women is surrounded by the opening of the vagina. Going around it from the sides, the muscle is sent anteriorly and attached to the alveolar shell of the clitoris, on its upper and lateral surfaces; The posterior parts of this muscle are weaved into the tendinous center of the perineum. Part of the deep beams of this muscle, in addition to the vaginal opening, surrounds the external opening of the urethra and is called the urethrovaginal sphincter, m. Sphincter uretrovaginalis. Due to its position, the muscle narrows the entrance to the vagina and therefore in women it is the compressor of the entrance to the vagina.
Function: squeezes the bulb and cavernous bodies of the penis and together with them bulbourethral glands and deep dorsal vein of the penis. In women, the entrance to the vagina, the bulb of the vestibule and the large gland of the vestibule are compressed.
Innervation and blood supply as in the muscles of the pelvic diaphragm.









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.