Scapula
Scapula , scapula, is a flat bone. It is located between the muscles of the back at the level of II to VIII ribs. The blade has a triangular shape and accordingly it distinguishes three edges: the upper, medial and lateral, and three corners: the upper, the lower and the lateral.
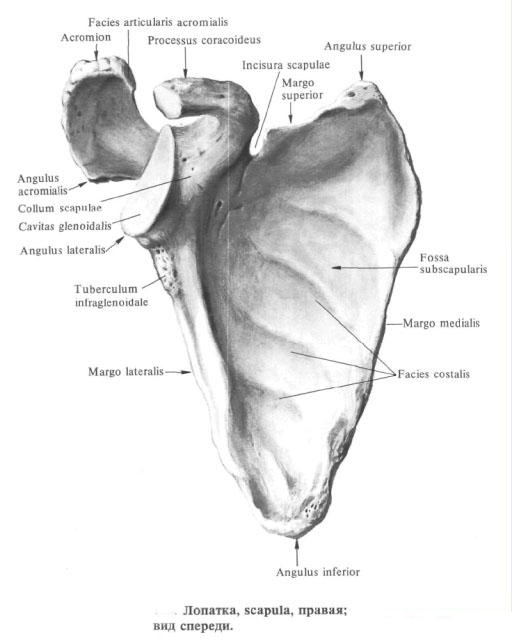
The upper edge of the scapula, margo superior scapulae, is thinned; in its outer part there is scrap of scapula, incisura scapulae: above it, on the unmatched bone, the upper transverse ligament of the scapula is stretched, lig. Transversum scapulae superius, forming together with this notch a hole through which the suprathiopathic nerve passes, n. Suprascapularis.
The outer parts of the upper edge of the scapula pass into the coracoid process, processus coracoideus. Initially, the process is directed upwards, then bends forward and somewhat outward.
Medial edge of scapula, margo medialis scapulae. It faces the spinal column and is well probed through the skin.
The lateral margin of the scapula , margo lateralis scapulae, is thickened, directed towards the axillary cavity.
The upper corner, angulus superior, rounded, turned upward and medially.
Lower angle, angulus inferior, roughened, thickened and facing downward.
The lateral angle, angulus lateralis, is thickened. On its outer surface is a flattened joint cavity, cavitas glenoidalis, from which the articular surface of the head of the humerus articulates. From the rest of the scapula, the lateral angle is separated by a slight narrowing-the neck of the scapula, the collum scapulae.
In the cervical region, above the upper edge of the articular cavity, there is an articular tubercle, tuberculum supraglenoidale, and below the articular cavity is the subarticular tubercle, tuberculum infraglenoidale (traces of the beginning of the muscles).
The costal surface (front), facies costalis (anterior), concave, is called subscapular fossa, fossa subscapularis. It is filled with a subscapularis muscle, m. Subscapularis.
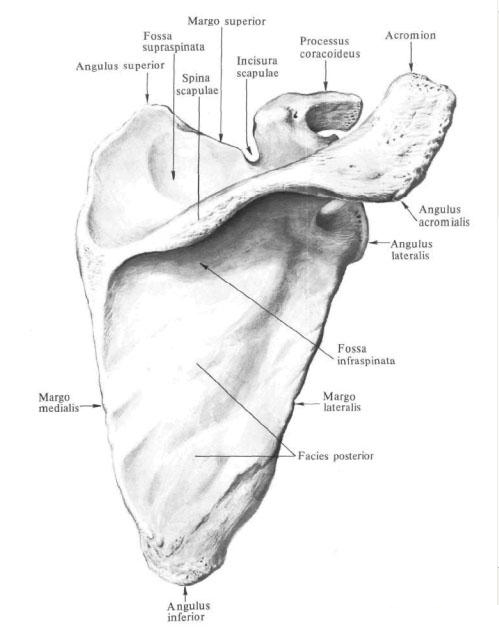
The posterior surface of the facies posterior, divided by a spine of the scapula, spina scapulae, is divided into two parts: one of them, the smaller one, is located above the awn and is called the supraspinatus, the fossa supraspinata, the other large, occupies the rest of the posterior surface of the scapula - it is the subacute fossa. Fossa infraspinata; In these pits, the muscles of the same name begin.
Spine blade, spina scapulae, is a well-developed crest that crosses the posterior surface of the scapula from its medial margin towards the lateral angle.
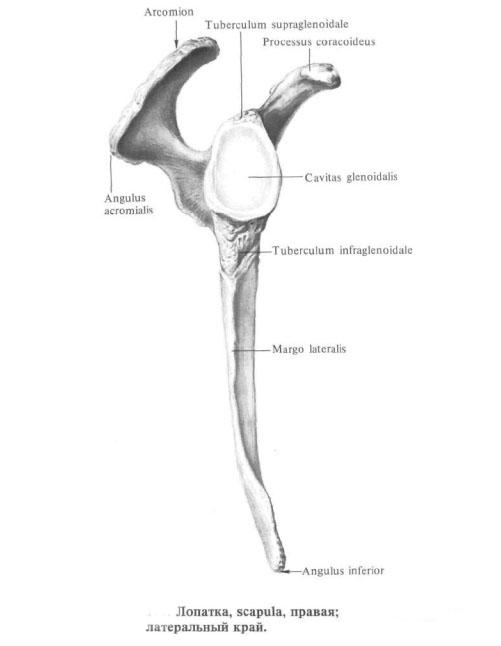
The lateral part of the shoulder blade develops more strongly and, forming the angle of the acromion, angulus acromialis, passes into the procession - acromion, acromion, which is directed to the outside and slightly forward and carries on its anterior margin the articular acromialis articular surface for articulation with the clavicle.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.