Radius. Structure of the radius
Radial bone , radius, is located outward and slightly anterior to the ulna . It distinguishes between the body and the two epiphyses - the upper and lower. 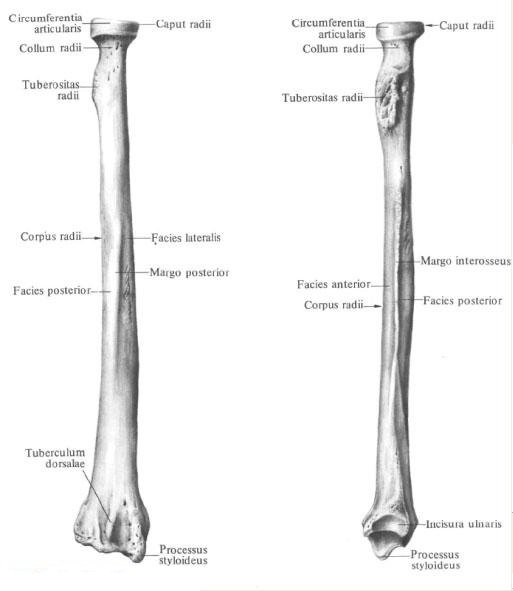
The structure of the radius.
The body of the radius , corpus radii, triangular shape. It has three edges: anterior, posterior and interosseous (medial) - and three surfaces: anterior, posterior and lateral.
Anterior margin, margo anterior, and posterior margin, margo posterior, rounded.
The inner, or medial, edge of the bone is pointed, directed toward the ulna and called the interocean edge, margo interosseus.
The front surface, facies anterior, is somewhat concave. On it is a nutritional hole, foramen nutricium, which begins proximally directed nutrient channel, canalis nutricius.
Posterior surface, facies posterior, smooth, separated from lateral surface, facies lateralis, posterior margin.
The upper, or proximal, epiphysis, epiphysis proximalis, at the border with the body carries a well developed tuberosity of the radial bone, tuberositas radii, directed to the medial side. Above the tuberosity there is a uniformly narrowed section of the bone - the cervix of the radius, collum radii. Above the neck is a cylindrical shape of the head of the radius, caput radii. The upper surface of the head is concave, it has an articular fovea, fovea articularis. The lateral part of the head carries an articular surface for articulation with a radial incision of the ulna and is called the articular circumference of the radius, circumferentia articularis radii (partially probed through the skin).
The lower, or distal, epiphysis, epiphysis distalis, is thickened and expanded in the frontal plane. From it departs the styloid process of the radius, processus styloideus radii, which is well probed through the skin. On the inner surface of the lower end of the radius there is an ulnar incision, incisura ulnaris, bearing the articular surface for articulation with the articular semicircle of the ulna head. On the posterior surface of the distal epiphysis, closer to the styloid process, there is a dorsal tubercle, tuberculum dorsale, lying between the tendons of m. Extensoris policis longi and m. Extensoris carpi radialis brevis.
The anterior surface of the lower epiphysis of the radius is smooth, on the posterior there are small scallops separating the grooves in which tendons of muscles lie.
The bottom surface is concave in the transverse and anteroposterior directions. It is the place of articulation with the bones of the wrist and is called the carpal articular surface, facies articularis carpea. It has a small scallop that goes in the anteroposterior direction and divides this surface into two parts, corresponding to the two bones of the wrist, which joins the radius in the radiocarpal joint.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.