Tibia
Tibia , tibia, long. It distinguishes between the body and the two epiphyses - the upper and lower. 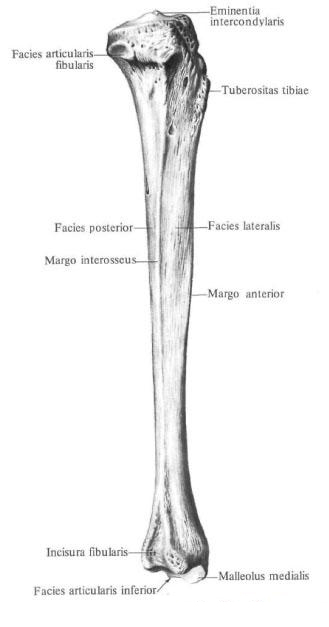
The body of the tibia, corpus tibiae, trihedral shape. It has three edges: anterior, interosseous (external) and medial - and three surfaces: medial, lateral and posterior.
Anterior margin, margo anterior, bones pointed and has the appearance of a crest. In the upper part of the bone, it passes into the tuberosity of the tibia, tuberositas tibiae. The interosseous margin, margo interosseus, is sharpened in the form of a scallop and is directed toward the corresponding edge of the fibula. The medial margin, margo medialis, is rounded. Medial surface, facies medialis. Or anterior, somewhat convex. It, and the front edge of the tibia, bordering it from the front, are well probed through the skin.
Lateral surface, facies lateralis, or anteriorly, slightly concave.
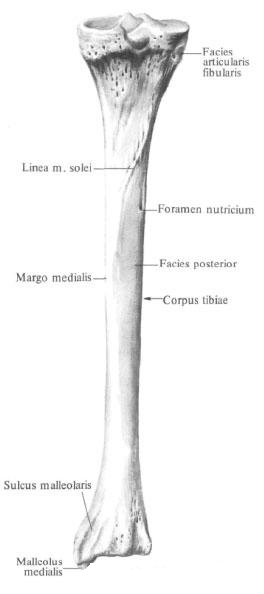
The posterior surface, posterior facies, is flat. It distinguishes the soleus muscle line, linea m. Solei, which extends from the lateral condyle downward and medially. Below it there is a nutrient aperture that leads to the distally directed nutrient channel.
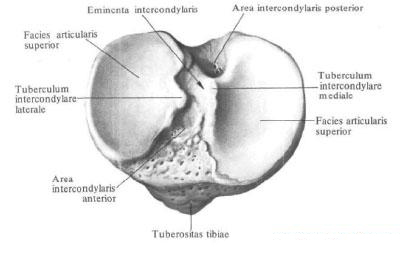
Upper, proximal, tibial epiphysis, epiphysis proximalis tibiae, enlarged. Its lateral divisions are the medial condyle, condylus medialis, and lateral condyle, condylus lateralis. On the outer surface of the lateral condyle is a flat peroneal articular surface, facies articularis fibularis. On the proximal surface of the proximal epiphysis of bone in the middle section there is an intercondylar eminence, eminentia intercondylaris. There are two tubercles in it: an internal medial intercondylar tubercle, a tuberculum intercondylare mediale, posterior to which is the posterior intercondylar field, area intercondylaris posterior, and the outer lateral intercondylar tubercle, tuberculum intercondylare laterale. In front of it is located anterior intercondylar field, area intercondylaris anterior; Both fields serve as the place of attachment of cruciate ligaments of the knee. On the sides of the intercondylar elevation, the upper articular surface, facies articularis superior, carries concave joint surfaces, medial and lateral respectively, to each condyle. The latter are peripherally bounded by the edge of the tibia.
Lower, distal, epiphysis of the tibia, epiphysis distalis tibiae, quadrangular. On the lateral surface of it there is a peroneal incision, incisura fibularis, to which the lower epiphyses of the fibula adhere. An ankle furrow passes through the posterior surface, sulcus malleolaris. Ahead of this furrow, the medial edge of the lower epiphyseal of the tibia goes into the downward directed process - the medial malleolus, malleolus medialis, which is well probed through the skin. The lateral surface of the ankle is occupied by the articular surface of the ankle, facies articularis malleoli. The latter passes to the lower surface of the bone, where it continues into the concave lower articular surface of the tibia, facies articularis inferior tibiae.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.