Feet bones
The bones of the foot in the region of the tarsus, tarsus, are represented by the following bones: talus, heel, navicular, three wedge-shaped bones: medial, intermediate and lateral, and cuboid. The composition of the metatarsus, metatarsus, includes 5 metatarsal bones. Phalanges, phalanges, toes are called the same as the phalanges of the fingers.
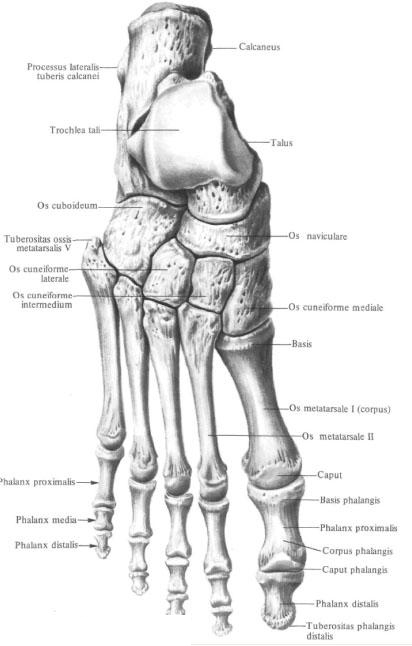
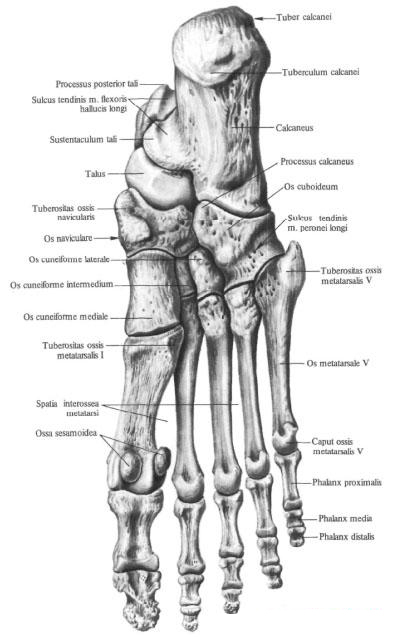
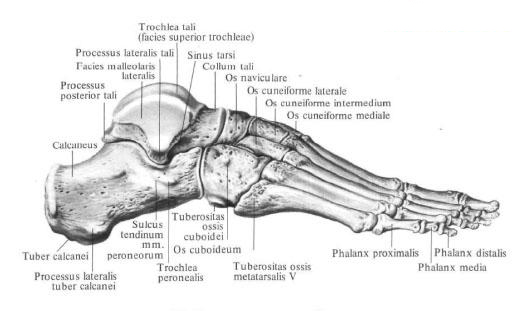
The bones of the tarsus , ossa tarsi, are arranged in two rows: the proximal is the talus and calcaneus, the distal one is the scaphoid, cuboid, and three wedge-shaped bones. The bones of the tarsus articulate with the bones of the lower leg; The distal row of tarsal bones is articulated with the bones of the metatarsus.
Talus bone , talus, is the only bone in the foot that joins the bones of the lower leg. The rear of her department is the body of the talus, corpus tali. Ahead the body passes into the narrowed part of the bone - the collar of the talus, collum tali; The latter connects the body with the forward directed head of the talus, caput tali. The talus bone from the top and sides of the fork embrace the bones of the shins. Between the bones of the shank and the talus bone an ankle joint is formed, articulatio talocruralis. Correspondingly, the articular surfaces are: the upper surface of the talus, facies superior ossis tali, shaped like a block - the talus block, trochlea tali, and lateral, lateral and medial, ankle surfaces, facies malleolaris lateralis et facies malleolaris medialis. The upper surface of the block is convex in the sagittal direction and concave in the transverse.
Lateral and medial ankle surfaces flat. The lateral ankle surface extends to the upper surface of the lateral process of the talus, processus lateralis tali. The posterior surface of the body of the talus is from the top down the intersection of the tendon fissure of the long flexor of the thumb of the foot of the sulcus tendinis m. Flexoris hallucis longi. The furrow divides the posterior edge of the bone into two tubercles: a larger medial tubercle, tuberculum mediale, and a smaller lateral tubercle, tuberculum laterale. Both tubercles, separated by a furrow, form the posterior process of the talus, processus posterior tali. The lateral tubercle of the posterior process of the talus
Bones sometimes, in case of its independent ossification, is a separate triangular bone, os trigonum.
On the lower surface of the body in the posterolateral region there is a concave posterior calcaneus articular surface, facies articularis calcanea posterior. The anterior medial divisions of this surface are limited to the lateral forward and lateral groove of the talus, sulcus tali. Anterior and outward from this furrow is the middle calcaneus articular surface, facies articularis calcanea media. Ahead of it lies the anterior calcaneus articular surface, facies articularis calcanea anterior.
Through the articular surfaces, the lower part of the talus bone joins with the heel bone. At the front of the head of the talus is a spherical-shaped navicular joint surface, facies articularis navicularis, through which it joins with the scaphoid bone.
Calcaneus calcaneus, located down and behind the talus. The posterior part of it is formed by a pronounced tubercle of the calcaneus, tuber calcanei. The lower parts of the hillock from the lateral and medial sides pass into the lateral process of the calcaneus calcaneus, processus lateralis tuberis calcanei, and into the medial process of the calcaneus calcaneus, processus medialis tuberis calcanei. On the lower surface of the hillock there is a calcaneal tubercle, tuberculum calcanei, located at the anterior end of the attachment line of the long plantar ligament, lig. Plantare longum.
On the anterior surface of the calcaneus there is a saddle-shaped cuboid articular surface, facies articularis cuboidea, for articulation with a cuboid bone.
In the anterior part of the medial surface of the calcaneus is a short and thick process - the support of the talus, sustentaculum tali. The furrow of the tendon of the long flexor of the big toe passes along the lower surface of this process, sulcus tendinis m. Flexoris hallucis longi.
On the lateral surface of the calcaneus, in the anterior part, there is a small peroneal block, trochlea fibularis, behind which there is a furrow of the tendon of the long fibular muscle, sulcus tendinis m. Peronei (fibularis) longi.
On the upper surface of the bone, in the middle section, there is an extensive posterior talus articular surface, facies articularis talaris posterior. In front of her lies the groove of the calcaneus, sulcus calcanei, which passes behind and in the lateral. Anterior to the furrow, along the medial edge of the bone, two articular surfaces are distinguished: the middle talus articular surface, facies articularis talaris media, and in front of it - the front talus articular surface, facies articularis talaris anterior, corresponding to the same-named surfaces on the talus. When the talus bone is applied to the heel front sections, the grooves of the talus and the grooves of the calcaneus bone form a depression - the sinus sinus, sinus tarsi, which is probed as a slight depression.
The navicular bone , os naviculare, flattened in front and behind, lies in the region of the inner edge of the foot. On the posterior surface of the bone there is a concave articular surface, through which it articulates with the articular surface of the head of the talus. The upper surface of the bone is convex. The anterior surface of the bone carries an articular surface for articulation with three wedge-shaped bones. The borders defining the junction of the scaphoid bone with each wedge-shaped bone are small scallops.
On the lateral surface of the bone there is a small articular surface - the junction with the cuboid bone. The lower surface of the scaphoid bone is concave. In the medial part of it there is a tuberosity of the scaphoid bone, tuberositas ossis navicularis.
The wedge-shaped bones , ossa cuneiformia, in the number of three, are located in front of the scaphoid bone. There are medial, intermediate and lateral wedge-shaped bones. The intermediate sphenoid bone is shorter than the rest, so the anterior, distal, surfaces of these bones are not on the same level. They have articular surfaces for articulation with the corresponding metatarsal bones,
The base of the wedge (the broader part of the bone) in the medial wedge bone is turned downward, and at the intermediate and lateral bone it is upward.
The posterior surfaces of the sphenoid bones have joint articulations for articulation with the scaphoid bone.
The medial wedge bone, os cuneiforme mediale, carries on its concave lateral surface two articular surfaces for articulation with an intermediate wedge bone, os cuneiforme intermedium, and II metatarsal bone.
The intermediate sphenoid bone, os cuneiforme intermedium, has articular surfaces: on the medial surface - for articulation with the medial wedge bone, os cuneiforme mediale, on the lateral side - for articulation with the lateral wedge bone, os cuneiforme laterale.
The lateral wedge bone, os cuneiforme laterale, also has two articular surfaces: on the medial side for articulation with the intermediate wedge bone, os cuneiforme intermedium, and the base of the metatarsale II II, and from the lateral - with the cuboid bone, os cuboideum.
Cuboid bone , os cuboideum, is located outside of the lateral cuneate bone, in front of the calcaneus and behind the base of the IV and V metatarsal bones.
The upper surface of the bone is rough, on the medial surface there are joint articulations for articulation with the lateral wedge bone, os cuneiforme laterale, and the scaphoid bone, os naviculare. On the lateral edge of the bone there is a tuberous tuberosity of the cuboid bone, tuberositas ossis cuboidei. A furrow of the tendon of the long peroneal muscle begins sideways, sulcus tendinis m. Peronei longi, which passes to the lower surface of the bone and crosses it obliquely from behind and outside, anterior and inside, respectively, the tendon of the same muscle.
The posterior surface of the bone has a saddle-shaped articular surface for
Articulations with the same articular surface of the calcaneus. The protuberance of the lower medial cube region bordering the edge of this articular surface was called the calcaneus processus calcaneus. It provides support for the anterior end of the calcaneus.
The front surface of the cuboid bone has a joint-scaled joint surface for articulation with the IV and V metatarsal, os metatarsale IV et os metatarsale V.
Plusset bones
The metatarsalia ossa metatarsalia consists of five (IV) thin long bones located in front of the tarsus. In each metatarsal bone distinguish the body, corpus, and two epiphyses: proximal - base, basis, and distal - head, caput.
The bones are counted from the medial edge of the foot (from the thumb to the little finger). Of 5 metatarsal bones, I bone is shorter, but thicker than the rest, II bone is the longest. The bodies of metatarsal bones are triangular. The upper, dorsal surface of the body is somewhat convex, the other two are lower (plantar) surfaces, converge below, forming a pointed scallop.
The bases of metatarsal bones represent the most massive part of them. They have the form of a wedge, which is directed upwards in its extended part in I-IV metatarsal bones, and in V metatarsal bone - in the medial side. The lateral surfaces of the bases have articular areas, through which the adjacent metatarsal arches are joined together.
The posterior surfaces of the bases have articular surfaces for articulation with tarsal bones. On the lower surface of the base I of the metatarsal bone there is the tuberosity I of the metatarsal bone, tuberositas ossis metatarsalis primi. Have
V metatarsal bone in the lateral part of the base also has tuberosity
V of the metatarsal bone, tuberositas ossis metatarsalis quinti, which is well probed. The anterior ends, or heads, of metatarsal bones are compressed laterally. The peripheral part of the heads has spherical articular surfaces, articulating with phalanges of the fingers. On the lower surface of the head I of the metatarsal bone, on the sides, there are two small smooth platforms, adjacent to the sesamoid bones, ossa sesamoidea, the big toe. The head of the metatarsal bone is palpable.
In addition to these sesamoid bones in the area of the metatarsophalangeal articulation of the thumb, there is one sesamoid bone in the interphalangeal articulation of the same finger, as well as unstable sesamoid bones in the thickness of the tendon of the long fibular muscle, in the region of the plantar surface of the cuboid bone.
Between the bones of the metatarsi, there are 4 interosseous spaces, spatia interossea metatarsi, which are filled with interosseous muscles.
Finger bones (phalanxes)
The bones of the fingers, ossa digitorum, are represented by phalanges, phalanges. In shape, number and relationship, they correspond to the phalanges of the fingers of the hand. In each phalanx, the body is distinguished, corpus phalangis, and two epiphyses: posterior, proximal, epiphysis - base of phalanx, basis of phalangis, and anterior, distal, epiphysis - phalanx head, caput phalangis. The surfaces of the proximal and middle phalanx heads, phalanx proximalis and phalanx medialis, are block-shaped.
At the distal end of each distal phalanx, phalanx distalis, is located the tubercle of the distal phalanx, tuberositas phalangis distalis.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.