Glands of the mouth
The glands of the mouth , glandulae oris, secrete saliva, saliva, therefore they are called salivary glands, glandulae salivariae. They are divided into large salivary glands, glandulae salivariae majores, and small salivary glands, glandulae salivariae minores. Three glands, which are quite large paired organs, combine into a group of large salivary glands:
- Parotid gland , glandula parotidea;
- The submandibular gland , glandula submandibularis;
- Hyoid gland , glandula sublingualis.
Large salivary glands.
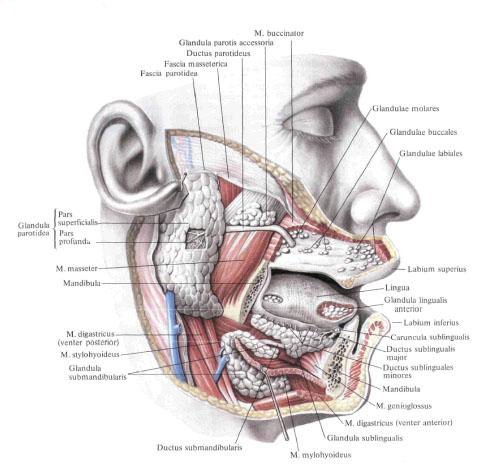
Parotid gland.
Parotid glandula, glandula parotidea, is structurally complex alveolar gland. It has the form of an irregular triangle, located on the outer surface of the branch of the lower jaw and the posterior edge of the masticatory muscle . The lower part of the gland can come into contact with the submandibular gland, glandula submandibularis, separating from it by fascia. In the depth of the gland adjoins the styloid process, the tyillo- and styloclinic muscles, as well as the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein. The gland is surrounded by the fascia of the parotid gland, fascia parotidea, which sends out the appendages between the lobules of the gland.
There are superficial and deep parts of the parotid gland.
The superficial part, pars superficialis, corresponds to that part of the gland that is located on the masticatory muscle .
The deep part, pars profunda, lies in the recess behind the branch of the lower jaw .
The excretory duct of the parotid gland is parotid duct, ductus parotideus, exits at the upper part of the anterior edge of the gland and runs almost horizontally, parallel to the zygomatic arch , along the external surface of the masticatory muscle ; Reaching the front of its edge, passes through the fatty body of the cheek, perforates the buccal muscle and opens on the threshold of the mouth at the level of the upper second molar, where on the mucous membrane of the cheek there is a papilla parotid duct of the parotid. In the course of the parotid duct there is a variable in size additional parotid gland, glandula parotis accessoria. Through the parotid gland are the external carotid artery and its branches, the submandibular vein and the trunks of the facial nerve.
Innervation: rr. Parotidei n. Auriculotemporalis (n. Mandibularis); Secretory fibers from ganglion oticum; Sympathetic nerves accompanying a. Temporalis superficialis.
Blood supply: rr. Parotidei aa. Temporales superficialis et maxillaris. Venous blood flows out by v. Retromandibularis. The lymph flows off into the nodi lymphatici submandibulares.
The submandibular gland.
The submandibular gland, glandula submandibularis, is structurally related to complex alveolar glands. It is located in the submandibular triangle in the fascial vagina, formed by the surface plate of the cervical fascia.
The upper surface of the gland adjoins the maxillofacial muscle and, circling its posterior edge, lies on the upper surface of the muscle, where it contacts the posterolateral surface of the hyoid gland. Behind the iron reaches the capsule of the parotid gland and the medial pterygoid muscle . The terminal duct of the submandibular jaw - submandibular duct, ductus submandibularis, runs along the inner surface of the hyoid gland anteriorly and upward and opens on the hyoid papilla, caruncula sublingualis.
Innervation: chorda tympani (from n. Facialis) through ganglion submandibulare and sympathetic nerves accompanying a. Facialis.
Blood supply: rr. Glandulares (a. Facialis), and also from a. Lingualis and a. Mentalis. Venous blood flows out by v. Facialis. Lymphatic vessels flow into the nodi lymphatici submandibulares.
The hyoid gland.
The hyoid gland, glandula sublingualis, is structurally related to complex mixed alveolar-tubular glands. It is located directly under the mucosa of the bottom of the mouth, at m. Mylohyoideus , lying outside of m. Geniohyoideus, m. Genioglossus and m. Hyoglossus. The anterior end of the gland adjoins the inner surface of the body of the lower jaw, and the posterior end to the submaxillary gland. Numerous short ducts of the gland - small hyoid ducts, ductus sublingualis minores, open along the hyoid fold. In addition to these small ducts, sometimes there is a large hyoid duct, ductus sublingualis major. It passes along the inner surface of the gland and, either alone or connected to the duct of the submandibular gland, opens in the hyoid papilla.
Innervation: chorda tympani (from n. Facialis) through ganglion submandibulare and sympathetic nerves accompanying a. Facialis .
Blood supply: aa. Sublingualis, submentalis (a. Facialis). Venous blood flows out by v. Sublingualis. The lymph flows off into the nodi lymphatici submandibulares and submentales.
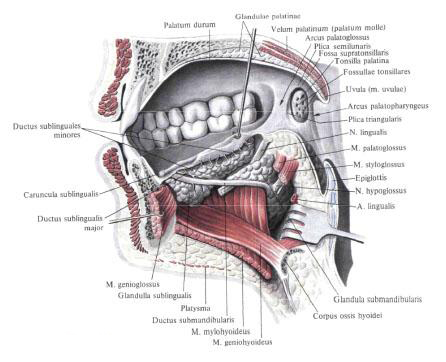
Small salivary glands.
Small salivary glands, glandulae salivariae minores, are mucous, serous and mixed. They lie alone and in groups, and their names are based on a topographic feature. Distinguish: labial glands, glandulae labiales, buccal glands, glandulae buccales, molar glands, glandulae molares, palatine glands, glandulae palatinae, and lingual glands, glandulae linguales.
These glands are considered in more detail when describing individual organs and walls of the oral cavity.
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.