Cervical vertebrae
Cervical vertebrae, vertebrae cervicales, number 7, with the exception of the first two, are characterized by small, low bodies, gradually widening towards the last, VII, vertebra. The upper surface of the body is slightly concave from right to left, and the inferior concave from front to back. On the upper surface of the III - VI cervical vertebral bodies noticeably elevate the lateral margins, forming a hook of the body, uncus corporis.
Vertebral foramen, foramen vertebrate, wide, close in shape to triangular.
Articular processes, processus articulares. Relatively short, stand oblique, their articular surfaces flat or slightly convex.
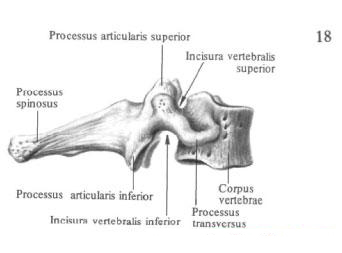
The spinous processes, processus spinosi, from the II to VII vertebra gradually increase in length. Up to the VI vertebra inclusive, they are split at the ends and have a slightly pronounced inclination downwards.
Transverse processes , processus transversi, are short and directed to the sides. A deep furrow of the spinal nerve, sulcus nervi spinalis, passes along the upper surface of each appendage, a trace of the adherence of the cervical nerve. It separates the anterior and posterior tubercles, tuberculum anterius and tuberculum posterius, located at the end of the transverse process. On the 6th cervical vertebra the anterior tubercle is developed. A common carotid artery lies a little way ahead and close to it, a. Carotis communis, which, when bleeding, is pressed against this tubercle; Hence the tubercle and was called the somnolent, tuberculum caroticum. In the cervical vertebrae, the transverse process is formed by two processes. The anterior one is the rudiment of the rib, the posterior is the transverse process proper. Both processes together limit the opening of the transverse process, foramen processus transversi, through which the vertebral artery , vein and the accompanying nerve sympathetic plexus pass, and this hole is also called vertebral arterial.
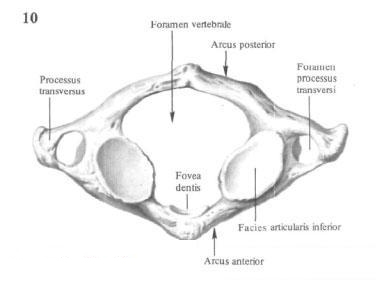

From the general type of the cervical vertebrae, the atlas, atlas, axial vertebra , axis, and the 7th protruding vertebra, vertebra prominens, are distinguished. The first cervical vertebra, atlas, atlas, does not have a body and a spinous process, but is a ring formed from two arcs - anterior and posterior, arcus anterior and arcus posterior, connected by two more developed parts - lateral masses, massae laterales. Each of them has an oval concave upper articular surface on top, a facies articulares superior, a joint site with the occipital bone, and an almost flat lower articular surface, a facies articularis inferior, which joins the second cervical vertebra from below. The anterior arc, arcus anterior, has on its anterior surface anterior tubercle, tuberculum Anterius, on the back - a small articular area - a tooth fossa, fovea dentis, articulating with the tooth of the cervical vertebra.
Posterior arc, arcus posterior, on the spot of the spinous process has a posterior tubercle, posterius tuberculum. On the upper surface of the posterior arch passes the furrow of the vertebral artery, sulcus arteriae vertebralis, which sometimes turns into a canal.
The second (II) cervical vertebra, or axial vertebra, axis, has a tooth, directed upward from the vertebral body. Dens, which ends in apex, apex. Around this tooth, as around the axis, the atlas rotates along with the skull.
On the front surface of the tooth there is anterior articular surface, facies articularis anterior, with which the fossa of the tooth of the atlas is articulated, on the posterior surface - the posterior articular surface, facies articularis posterior, to which the transverse ligament of the atlant, lig. Transversum atlantis. On the transverse processes there are no anterior and posterior tubercles and a furrow of the spinal nerve.
The seventh cervical vertebra, or protruding vertebra, vertebra prominens, is distinguished by a long and undiluted spinous process that is easily probed through the skin, in communication With this vertebra received the name of the speaker. In addition, He has long transverse processes: the transverse openings of his very small, sometimes they may be absent.
On the lower edge of the lateral surface of the body is often located facet, or costal fovea, fovea costalis, - the trail of the joint with the head of the 1st rib .
You will be interested to read this:









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.