The jejunum, ileum. Topography of the small intestine
The mesenteric part of the small intestine is located in the lower abdominal cavity, under the mesentery of the transverse colon. She is Begins at the duodenum-lean curve, to the left of body I (II) Lumbar vertebra. Its lower border is in the right ileal fossa at the level of the body of the IV lumbar vertebra. The diameter of the mesenteric part of the small intestine is 4.8-5.0 cm in the initial part, and 2.7-3.0 cm in the distal part. All this part of the small intestine is located and intraperitoneal, that is, it is covered from all sides by the visceral peritoneum, Except for a narrow band of the attachment site of the mesentery.
The mesenteric part of the small intestine is divided into two parts according to a number of features: the proximal 2/5 of its length is the jejunum , jejunum, the distal 3/5 ileum , ileum there is no sharp border between them.
The loops of the small intestine have a more or less definite position and direction: 6-7 loops of the proximal part (jejunum) are located horizontally and occupy the left upper part of the lower abdominal floor and the umbilical region; 7-8 loops of the distal (ileum) vertical, occupy the hypogastric, right iliac region and cavity of the small pelvis. In the small pelvis, the last loops of the ileum are located before passing to the terminal compartment, as a result of which the latter has a direction from below upwards and to the right (ascending) in the iliac fossa. In addition, the loops of the small intestine are located in two layers.
In the mesenteric part of the small intestine, two edges are distinguished: mesenteric, with the gut fixed to the mesentery, and the opposite free one. In the mesenteric region, vessels and nerves are suitable for the intestinal wall.
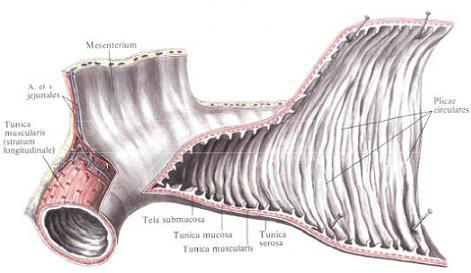
The walls of the mesenteric part of the small intestine consist of three layers: serous, muscular and mucous membranes.
The serous membrane, tunica serosa, surrounds the gut on the outside on three sides, leaving only a narrow strip on the mesenteric margin free, where the two mesentery leaves go to the side of the intestine and spread out on either side of it.
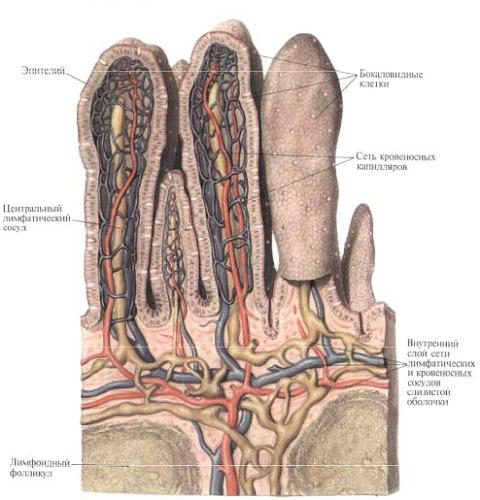
With the underlying muscle membrane, the serous membrane is connected by means of a subserous base, tela subserosa . Mucosal base, tela submucosa. The mucous membrane forms circular folds, plicae circulares, has intestinal villi, villi intestinales, and crypts in which the intestinal gland ducts, glandulae intestinales, and lymphatic follicles, folliculi lymphatici, are opened, ie all those formations that (with the exception of duodenal Glands) are inherent in the mucosa of the duodenum. The difference in the structure of these formations is as follows: in the mesenteric part of the small intestine the number of circular folds is less than in the duodenum, and from the jejunum to the ileum their number gradually decreases, and in the terminal part they are almost absent. The total number of folds in the small intestine ranges from 500 to 1200. In the same sequence (from the beginning to the end of the small intestine), the height of the folds also decreases.
Vorsels in the mesenteric part of the small intestine are thinner and somewhat shorter than in the duodenum. The number of them decreases in the distal direction; In the jejunum their number reaches 30-40, in the ileum -18-30 per 1 mm 2 ; The length and thickness of them also decrease.
The location of the ileum in the blind is the ileocecal opening, ostium ileoceale, it is bordered by a funnel-shaped flap with convexity towards the lumen of the cecum - the ileocecal valve, valva ileocecalis (valva ilealis).
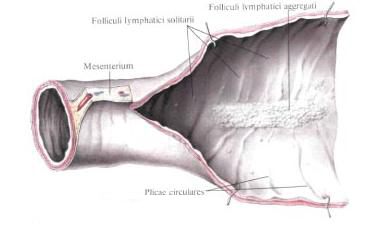
In the submucosa, tela submucosa, mesenteric part of the small intestine, single lymphatic follicles, folliculi lymphatici solitarii, reaching the surface of the mucosa; Their value is equal to the millet grain, the number reaches 200. In addition, in this section of the small intestine the lymphatic follicles collected in groups - group lymphatic follicles, folliculi lymphatici aggregati - are located. They are located on the opposite mesentery margin, have a length of 2-10 cm, a width of 1-3 cm; Their number in the small intestine reaches 30-40.
Topography of the mesenteric part of the small intestine.
The mesenteric part of the small intestine occupies a central position in the lower floor of the abdominal cavity, located below the mesentery of the transverse colon. On the right, from above and from the left, the loops of the small intestine are bordered by the ascending (right), transverse (top), descending (left) colon. From the front, the loops of the small intestine are covered, like an apron, with a large omentum descending from the large curvature of the stomach and the lower edge of the transverse colon and separating them from the anterior abdominal wall. The posterior surface of the small intestine is attached to the parietal peritoneum, which covers the lower part of the duodenum, the pancreas head, the lower end of the right kidney, the right ureter, the right major lumbar muscle, to the right of the mesentery root, and to the left of the mesentery root - the lower end of the left kidney, the left ureter, Lumbar muscle, abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava and common ileal vessels. On the left and below to the loops of the small intestine is a sigmoid colon with its mesentery.
In the cavity of the small pelvis, the loops of the small intestine are located in front - to the bladder, from behind - to the rectum, and in the womb - to the uterus and its appendages.
The terminal part of the ileum crosses the right large lumbar muscle and right common ileal vessels.
Innervation: duodenum - plexus gastrici, hepaticus, mesentericus superior and branch n. Vagus; Mesenteric part of the small intestine - plexus coeliacus, mesentericus superior. In the thickness of the intestinal wall there is an extensive intestinal plexus (plexus entericus) associated with plexus mesentericus superior, it combines: plexus submucosus, plexus myentericus (between the circular and longitudinal muscle layers), plexus subserosus.
Blood supply: duodenum - aa. Pancreatoduodenales superior, anterior and posterior (from a. gastroduodenalis) and a. Pancreatoduodenalis inferior (from a. Mesenterica superior); Mesenteric part - aa. Intestinales (from a. Mesenterica superior). Venous blood from the same veins goes to v. Portae. Lymphatic vessels carry lymph to the nodi lymphatici pancreatoduodenales superiores, colici (from the duodenum), mesenterici, ileocolici.









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.