Pulmonary veins
Pulmonary veins , right and left, vv. Pulmonales dextrae and sinistrae, carry arterial blood from the lungs; They exit the collar of the lungs, usually two of each lung (although the number of pulmonary veins can reach 3 - 5 or even more). In each pair the upper pulmonary vein is distinguished, v. Pulmonalis superior, and lower pulmonary vein, v. Pulmonalis inferior. All of them, coming out of the lungs' gates, follow in the transverse direction to the left atrium and fall into it in the area of its posterolateral divisions.

The right pulmonary veins are longer than the left and lie downward from the right pulmonary artery and posteriorly from the superior vena cava, the right atrium and the ascending aorta; The left pulmonary veins pass anterior to the descending part of the aorta. Pulmonary veins start with powerful capillary networks of pulmonary acini, the capillaries of which, merging, form larger venous stems (intrasegmentary part, pars intrasegmentalis), directed toward the free or intersegmental surface of the segment and flowing into the intersegmental part, pars intersegmentalis. Both these parts form segmental veins, which lie mainly in connective tissue intersegmental septa, which serves as an accurate guide for segmental resection of the lung.
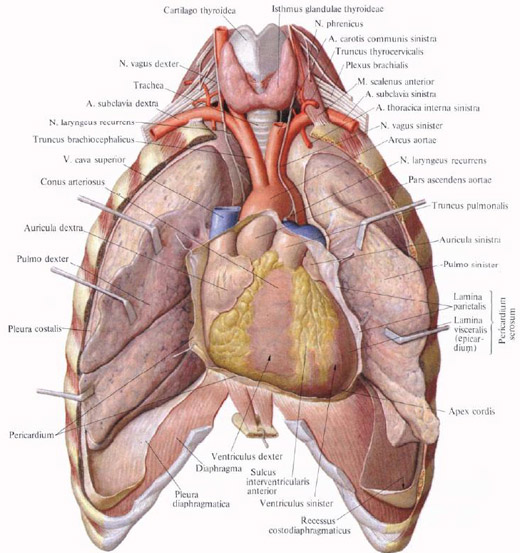
From the right lung, arterial blood flows down the right upper and lower pulmonary veins. The right upper pulmonary vein, v. Pulmonalis superior dextra, is formed by segmental veins of segments of the upper and middle lobes of the lung.
1. The apical branch, r. Apicalis, is a short venous trunk located on the mediastinal surface of the upper lobe; Collects blood from the apex segment. Before entering the right upper pulmonary vein often connects to the posterior segmental branch.
2. Rear branch, r. Posterior, takes blood from the posterior segment. This is the largest vein of segmental veins in the upper lobe. It distinguishes the intrasegmental part, pars intrasegmentalis, and the sub-part, pars infralobaris, which collects blood from the interlobular surface of the lobe in the oblique-slit region.
3. Front branch, r. Anterior, collects blood from the anterior segment of the upper lobe. Sometimes the anterior and posterior branches fall into a common trunk.
4. The branch of the middle lobe, r. Lobi medii, collects blood from the segments of the middle lobe of the right lung. Sometimes this vein, which collects blood from two segments, flows into the right upper pulmonary vein in the form of one trunk, but more often it is formed by two parts; Lateral part, pars lateralis, and medial part, pars medialis, respectively draining lateral and medial segments.
Right lower pulmonary vein, v. Pulmonalis inferior dextra, collects blood from 5 segments of the lower lobe. It has two main tributaries: the upper branch and the common basal vein.
1. The upper branch, r. Superior, lies between the upper and basal segments. It is formed from the main and additional veins, is directed anteriorly and downwards and passes behind the apical segmental bronchus. This is the uppermost branch from the flowing into the right lower pulmonary vein. The main vein in accordance with the bronchus has three inflows: the medial, the superior and the lateral, which are mainly intersegmented, but can lie inside the segment. In the additional vein, blood flows from the upper part of the upper segment to the subalateral part of the posterior segmental vein of the posterior segment of the upper lobe.
2. The common basal vein, r. Basalis communis, is a short trunk, formed as a result of the fusion of the upper and lower basal veins, the main trunks of which are located deep from the anterior surface of the lobe.
1) Upper basal vein, v. Basalis superior, is formed due to the fusion of the largest of the segmental basal veins - anterior basal branch, r. Basalis anterior, and veins that collect blood from the anterior, lateral and medial basal segments.
2) Lower basal vein, v. Basalis inferior, approaches the common basal vein from its lower posterior surface. The main inflow of this vein is the posterior basal branch, which collects blood from the posterior basal segment; It can sometimes approach the upper basal vein.

From the left lung, arterial blood flows down the left upper and lower pulmonary veins, which in rare cases can be opened by one opening in the left atrium.
Left upper pulmonary vein, v. Pulmonalis superior sinistra, collects blood from the upper lobe of the left lung. It is formed by the confluence of the upper, middle and lower tributaries, with the upper inflow draining the apical-posterior segment, the middle and the lower - the ligulate segments.
1. Posterodermal branch, r. Apicoposterior, is formed by the fusion of the apical and posterior segmental veins and represents a trunk providing an outflow from the apex-posterior segment. Vienna lies in the intersegmental gap, and the fusion of its tributaries occurs on the mediastinal surface of the lobe.
2. Front branch, r. Anterior, collects blood from the anterior segment of the upper lobe.
3. The ligament branch, r. Lingularis, is more often formed from two parts: the upper and lower, pars superior et pars inferior, into which the blood flows from the same ligulate segments.
Left lower pulmonary vein, v. Pulmonalis inferior sinistra, is formed by the combination of two tributaries that collect blood from the lower lobe of the left lung.
1. The upper branch, r. Superior, collects blood from the upper segment of the lower lobe.
2. The common basal vein, v. Basalis communis, short, goes inside and up and lies behind the front basal segmental bronchus. It is formed by the upper and lower basal veins.
Upper basal vein, v. Basalis superior, crosses the posterior surface of the cardiac basal segmental bronchus in the transverse direction. The front basal branch flows into it, r. Basalis anterior, draining blood from the anterior and medial basal segments.
Lower basal vein, v. Basalis inferior, flows into the common basal vein. Its tributaries are the segmental branches of the lateral and posterior segments, the number, topography and sizes of these branches varying.
Topography of the bronchi and vessels in the lungs. In the lungs' lungs, the pulmonary artery, the main bronchus and the pulmonary veins on the transition from extrapulmonary (extraorganic) to intrapulmonary part are divided into a number of branches. These branches, grouped together, form the roots of individual lobes of the lungs.
The gates of each lobe, as well as the gates of the lungs, have the form of a depression, the external shape and depth of which are individually variable. The gates of the lungs can be represented as a hemisphere-shaped pit, and the gates of the lobes often resemble the shape of a circle or oval. The gates of individual lobes are part of the gates of the lungs and represent different parts of this hemisphere.
Photos from the preparations, as well as a schematic image of the gates of the lobes of the lungs, are shown in Fig.
In the right lung at the gates of the upper lobe there are 2 - 3 arterial branches, the same number of venous branches and one lobar bronchus. In the gates of the middle lobe, usually two arterial branches, one venous branch and one lobar bronchus. In the gates of the lower lobe, as a rule, two arterial and two venous branches, as well as two lobar bronchi.
In the left lung in the gates of the upper lobe usually 3 to 4 branches of the pulmonary artery, 2 - 3 (often 3) branches of the pulmonary veins and two lobar bronchi. In the lower lobe there are three arterial branches, two - three venous and two lobar bronchi.
The branches of the pulmonary artery are located on the lateral side of the portal of lobes, the branches of the pulmonary veins are closer to the medial margin, the lobar bronchi occupy the middle position. This arrangement of blood vessels and bronchi reflects the features of the layered occurrence of the pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins and lobar bronchus when viewed from the sides of the interlobar sulcus.









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.