Ribs
Ribs , costae, 12 pairs, - narrow, of different length, curved bone plates, symmetrically located along the sides of the thoracic spine .
In each rib distinguish the longer bone portion of the rib, os costale, the short cartilaginous - costal cartilago, cartilago constalis, and the two ends - anterior, facing the sternum, and the posterior, facing the spinal column.
The bony part of the rib has a head, neck and body. The rib head, caput costae, is located on its vertebral end. It has the articular surface of the head of the rib, facies articularis capitis costae. This surface on the II-X ribs is divided by a horizontally running ridge of the head of the rib, crista capitis costae, into the upper, smaller, and lower, larger parts, each of which respectively joins with the costal fossae of two adjacent vertebrae.
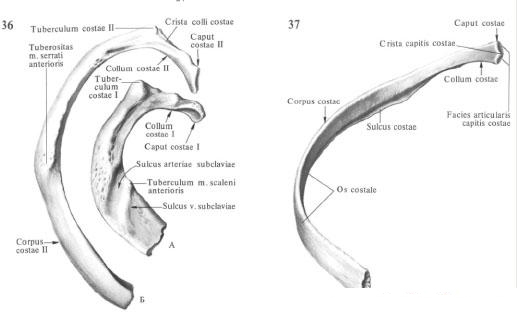
The cervix of the rib, collum costae, - the most narrowed and rounded part of the rib, bears on the upper edge the crest of the neck of the rib, crista colli costae (I and XII do not have ribs of this ridge).
On the border with the body, the 10 upper pairs of ribs on the neck have a small tubercle of the rib, tuberculum costae, on which is located the articular surface of the tubercle of the rib, facies articularis tuberculi costae, articulating with the transverse costal fossa of the corresponding vertebra.
Between the posterior surface of the cervical rib and the anterior surface of the transverse process of the corresponding vertebra, an anterior-transverse aperture is formed, foramen costotransversarium.
The body of the rib , corpus costae, extending from the tubercle to the sternal end of the rib, is the longest section of the osseous part of the rib. At some distance from the tubercle, the body of the rib, strongly curving, forms an angle of the rib, angulus costae. In the first rib, it coincides with the tubercle, and on the other ribs the distance between these formations increases (up to the XI edge); The body of XII does not form an edge.
The entire body of the rib is flattened. This makes it possible to distinguish two surfaces in it: the inner, concave, and outer, convex, and two edges: the upper, the rounded, and the lower, the sharp. On the inner surface along the lower edge there is a furrow of the rib, sulcus costae, where intercostal artery , vein and nerve lie. The edges of the ribs describe a spiral, so the rib is twisted around its long axis.
At the anterior sternal end of the osseous part of the rib there is a pit with a small roughness; To it is attached costal cartilage.
The costal cartilages , cartilagines costales (also 12 pairs), are the continuation of the bone parts of the ribs. From I to II ribs they gradually lengthen and connect directly to the breastbone. Upper 7 pairs of ribs are true ribs, costae verae, lower 5 pairs of ribs are false ribs, costae spuriae, and XI and XII ribs are wavering ribs, costae fluitantes. Cartilages of VIII, IX and X ribs do not fit directly to the sternum, but each of them joins the cartilage of the overlying rib. Cartilages XI and XII ribs (sometimes X) do not reach the sternum and lie free in the muscles of the abdominal wall with their cartilaginous ends.
Some features have two first and two last pairs of ribs. The first rib , costa prima (I), is shorter but wider than the rest, has an almost horizontally arranged upper and lower surface (instead of the outer and inner edges of the other). On the upper surface of the rib, in the anterior part, there is a tubercle of the anterior staircase, tuberculum m. Scaleni anterioris. Outside and behind the tubercle is a shallow furrow of the subclavian artery , sulcus a. Subclaviae, the trace of the same artery lying here, a. Subclavia), behind which there is a small roughness (the place of attachment of the middle staircase , M. scalenus medius). Anteriorly and inwardly from the tubercle there is a weakly expressed groove of the subclavian vein, sulcus v. Subclaviae. The articular surface of the head I of the rib is not divided by the crest; Neck long and thin; The edge angle coincides with the tubercle of the rib.
The second rib , costa secunda (II), has on the outer surface roughness - tuberosity of the anterior cog muscle, tuberositas m. Serrati anterioris (the place of attachment of a tooth of the specified muscle).
The eleventh and twelfth ribs, costa II et costa XII, have articular surfaces of the head not separated by the crest. On the XI edge, the angle, cervix, tubercle and costal furrow are weakly expressed, and on III they are absent.









Comments
When commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.