External iliac artery
External iliac artery , a. Iliaca externa, steam room. Moving away from a. Iliaca communis with a large trunk, it, resting retroperitoneally, is guided along the medial edge of the large lumbar muscle forward and downward and passes under the inguinal ligament in the vascular lacuna, where it lies lateral to the vein of the same name. Upon reaching the thigh, the artery directly extends into the femoral artery, a. Femoralis.
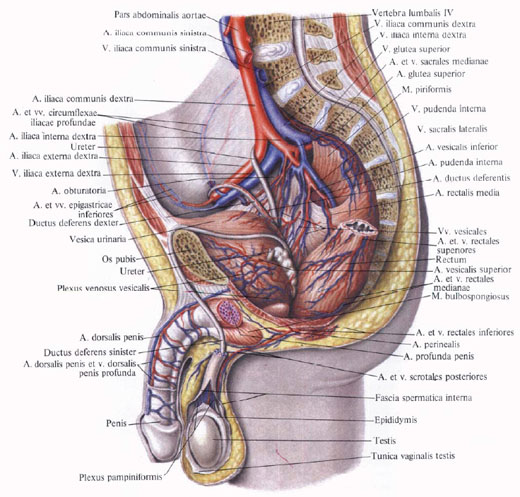
The external iliac artery gives off a number of branches.
1. The lower epigastric artery, a. Epigastrica inferior, leaves a thin stem from the anterior surface of the external iliac artery before it enters the vascular lacuna and is directed upward and medially along the posterior surface of the anterior abdominal wall between the peritoneum and the transverse fascia.
The artery first goes along the back wall of the inguinal canal; Rising above, penetrates into the vagina of the rectus abdominis muscle, where it passes between the muscle and the back wall of its vagina, gives branches to them and at the level of the umbilical ring splits into a series of branches anastomosing with a. Epigastrica superior (a branch of thoracica interna).
In its turn, the lower epigastric artery anastomizes with the terminal branches of the lower 4 - 5 posterior intercostal and lumbar arteries, also penetrating into the vagina of the rectus abdominis muscle. From her branch leaves:
A) pubic branch, r. Pubicus, - a small artery leaves at the very beginning of the lower epigastric artery, follows the posterior surface of the pubic bone to the pubic symphysis, giving up the obturator branch, r. Obturatorius, and an additional occlusive artery, a. Obturatoria accessoria. Anastomoses with the same branch of the opposite side and the pubic branch from the occlusion artery, a. Obturatoria. The pubic branch blood supply the lower sections of the rectus and pyramidal muscles of the abdomen;
B) a cremasteric artery, a. Cremasterica (the artery of the round ligament of the uterus in women), thinner than the previous one, leaves somewhat higher than the pubic branch and, passing through the inner inguinal ring into the inguinal canal, joins the spermatic cord, descending into the scrotum with it. Blood supply to the muscle that lifts the testicle, and all the testicle shells, anastomosing with a. Testicularis (branch of aortae abdominalis), external genital arteries, aa. Pudendae externae (branches of a. Femoralis), and with the artery of the vas deferens, a. Ductus deferentis (branch of a. Iliaca interna). In women, this artery goes together with the round ligament of the uterus to the large labia.
2. Deep artery surrounding the iliac bone, a. Circumflexa iliaca profunda, starts from the lateral wall of the external iliac artery and, following the outside and up along the inguinal ligament, reaches the superior anterior iliac awn where the ascending branch rests, r. Ascendens, blood supply to the skin and muscles of the lower lateral portion of the anterior abdominal wall. Further along the iliac crest, giving branches to the muscles of the anterolateral wall of the abdomen. The artery lies between the iliac and transverse fascia. The terminal branches anastomose with the iliac branch of the ilio-lumbar artery, r. Iliacus a. Iliolumbalis.









Comments
Commenting on, remember that the content and tone of your message can hurt the feelings of real people, show respect and tolerance to your interlocutors even if you do not share their opinion, your behavior in the conditions of freedom of expression and anonymity provided by the Internet, changes Not only virtual, but also the real world. All comments are hidden from the index, spam is controlled.